目录
1-菜单路由权限分析
2-菜单权限实现
2.1-路由拆分
2.2-动态计算当前用户的权限
3-按钮权限实现
1-菜单路由权限分析
目前我们系统中有:login(登录页面)、404(404一级路由)、任意路由、首页(/home)、数据大屏、权限管理(三个子路由)商品管理模块(四个子路由)。我们现在需要实现不同角色有不同的权限,所以我们需要对路由进行拆分。
静态(常量)路由:大家都可以拥有的路由。比如我们的 login、首页、数据大屏、404;
异步路由:不同的身份有的有这个路由、对于我们系统就是权限管理(三个子路由)商品管理模块(四个子路由)。
任意路由:就是除了上面两个路由之外的路由,我们定义重定向404。
2-菜单权限实现
2.1-路由拆分
我们按照上面的逻辑将路由进行拆分。文件src\router\router.ts拆分后如下:
//对外暴露配置路由(常量路由):全部用户都可以访问到的路由
export const constantRoute = [
{
//登录
path: '/login',
component: () => import('@/views/login/index.vue'),
name: 'login',
meta: {
title: '登录', //菜单标题
hidden: true, //代表路由标题在菜单中是否隐藏 true:隐藏 false:不隐藏
icon: 'Promotion', //菜单文字左侧的图标,支持element-plus全部图标
},
},
{
//登录成功以后展示数据的路由
path: '/',
component: () => import('@/layout/index.vue'),
name: 'layout',
meta: {
title: '',
hidden: false,
icon: '',
},
redirect: '/home',
children: [
{
path: '/home',
component: () => import('@/views/home/index.vue'),
meta: {
title: '首页',
hidden: false,
icon: 'HomeFilled',
},
},
],
},
{
//404
path: '/404',
component: () => import('@/views/404/index.vue'),
name: '404',
meta: {
title: '404',
hidden: true,
icon: 'DocumentDelete',
},
},
{
path: '/screen',
component: () => import('@/views/screen/index.vue'),
name: 'Screen',
meta: {
hidden: false,
title: '数据大屏',
icon: 'Platform',
},
},
]
//异步路由
export const asnycRoute = [
{
path: '/acl',
component: () => import('@/layout/index.vue'),
name: 'Acl',
meta: {
title: '权限管理',
icon: 'Lock',
},
redirect: '/acl/user',
children: [
{
path: '/acl/user',
component: () => import('@/views/acl/user/index.vue'),
name: 'User',
meta: {
title: '用户管理',
icon: 'User',
},
},
{
path: '/acl/role',
component: () => import('@/views/acl/role/index.vue'),
name: 'Role',
meta: {
title: '角色管理',
icon: 'UserFilled',
},
},
{
path: '/acl/permission',
component: () => import('@/views/acl/permission/index.vue'),
name: 'Permission',
meta: {
title: '菜单管理',
icon: 'Monitor',
},
},
],
},
{
path: '/product',
component: () => import('@/layout/index.vue'),
name: 'Product',
meta: {
title: '商品管理',
icon: 'Goods',
},
redirect: '/product/trademark',
children: [
{
path: '/product/trademark',
component: () => import('@/views/product/trademark/index.vue'),
name: 'Trademark',
meta: {
title: '品牌管理',
icon: 'ShoppingCartFull',
},
},
{
path: '/product/attr',
component: () => import('@/views/product/attr/index.vue'),
name: 'Attr',
meta: {
title: '属性管理',
icon: 'ChromeFilled',
},
},
{
path: '/product/spu',
component: () => import('@/views/product/spu/index.vue'),
name: 'Spu',
meta: {
title: 'SPU管理',
icon: 'Calendar',
},
},
{
path: '/product/sku',
component: () => import('@/views/product/sku/index.vue'),
name: 'Sku',
meta: {
title: 'SKU管理',
icon: 'Orange',
},
},
],
},
]
//任意路由
export const anyRoute = {
//任意路由
path: '/:pathMatch(.*)*',
redirect: '/404',
name: 'Any',
meta: {
title: '任意路由',
hidden: true,
icon: 'DataLine',
},
}
2.2-动态计算当前用户的权限
当我们登录账号后,我们获取用户信息接口会返回当前用户拥有的菜单和按钮权限,我们需要对服务端返回的菜单和按钮权限进行处理,得到当前用户的菜单和按钮权限数据。
ps:
1:每次我们计算异步路由的时候,我们需要对router配置的异步路由进行一次深度拷贝;
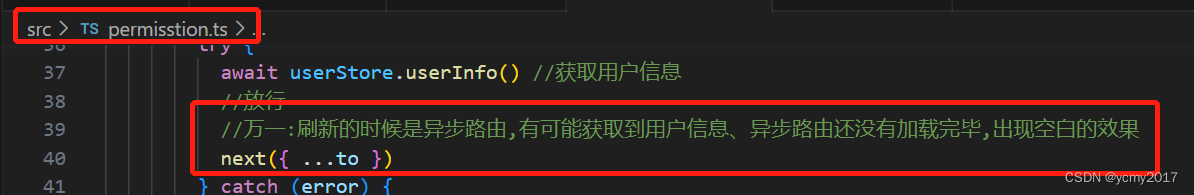
2:当我们直接访问异步路由的时候,刷新,页面出现空白,我们发现页面的dom没有加载完成,我们需要在守卫那边,等待加载完成,再渲染页面。


//用于过滤当前用户需要展示的异步路由
function filterAsyncRoute(asnycRoute: any, routes: any) {
return asnycRoute.filter((item: any) => {
if (routes.includes(item.name)) {
if (item.children && item.children.length > 0) {
item.children = filterAsyncRoute(item.children, routes)
}
return true
}
})
}
3-按钮权限实现
在获取用户信息接口,接口会返回当前用户拥有的按钮的权限,我们在用户仓库中存储当前用户的按钮权限。然后定义一个全局指令,在按钮的地方使用该指令,来控制按钮的显示和隐藏。

指令文件src\directive\has.ts里面核心逻辑如下:
import pinia from '@/store'
import useUserStore from '@/store/modules/user'
const userStore = useUserStore(pinia)
export const isHasButton = (app: any) => {
//获取对应的用户仓库
//全局自定义指令:实现按钮的权限
app.directive('has', {
//代表使用这个全局自定义指令的DOM|组件挂载完毕的时候会执行一次
mounted(el: any, options: any) {
//自定义指令右侧的数值:如果在用户信息buttons数组当中没有
//从DOM树上干掉
if (!userStore.buttons.includes(options.value)) {
el.parentNode.removeChild(el)
}
},
})
}在入口文件main.ts中需要注册

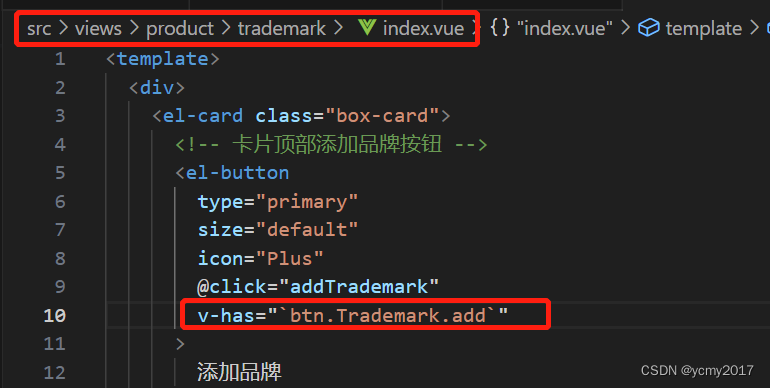
我们在项目中有按钮权限的地方直接使用该指令就可以显示当前按钮的隐藏和显示。比如我们在品牌管理模块的添加品牌v-has="`btn.Trademark.add`"中使用。