背景:
一个东西的执行有多个入参和出参, 一个东西的出参又可以是别的东西的入参, 因此执行的依赖关系.
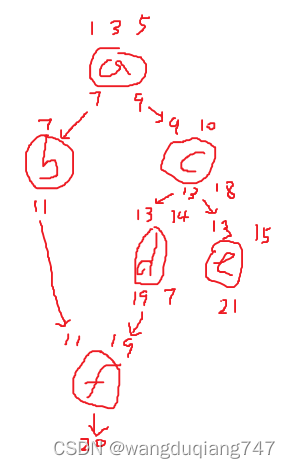
草图里a b c d e f为三个东西, 上面的数字是入参,下面的数字是出参
当前已知这6个东西, 和他们的入参出参
求他们的运行顺序.
要求同样执行顺序的东西可以并行执行.
代码如下:
import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class TestAOV {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LogManager.getLogger(TestAOV.class);
@Test
public void test() {
LOGGER.info("zzzzzzzzzz");
Entity a = new Entity();
a.input = new int[]{1, 3, 5};
a.output = new int[]{7, 9};
a.name = "a";
Entity b = new Entity();
b.input = new int[]{7};
b.output = new int[]{11};
b.name = "b";
Entity c = new Entity();
c.input = new int[]{9, 10};
c.output = new int[]{13, 18};
c.name = "c";
Entity d = new Entity();
d.input = new int[]{13, 14};
d.output = new int[]{19, 7};
d.name = "d";
Entity e = new Entity();
e.input = new int[]{13, 15};
e.output = new int[]{21};
e.name = "e";
Entity f = new Entity();
f.input = new int[]{11, 19};
f.output = new int[]{20};
f.name = "f";
//如果一个entity的输入不是任何entity的输出,第一顺位 放入大集合. //不需要mid-in mid-out//代码里选外部参数,再参数池的顺序找值.
//大集合的结果参数加输入参数够 .第二顺位, 放大集合
//同理一直到所有entity都排序好
LinkedList<Entity> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(a);
list.add(b);
list.add(c);
list.add(d);
list.add(e);
list.add(f);
LinkedList<LinkedList> result = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> necessaryInput = new LinkedList<>();
// for (Entity entity: list){
// necessaryInput =
// }
// 所有的input的集合减去output的集合 //代码不写了直接赋值
necessaryInput.add(1);
necessaryInput.add(3);
necessaryInput.add(5);
necessaryInput.add(10);
necessaryInput.add(18);
necessaryInput.add(14);
necessaryInput.add(15);
LinkedList<Integer> poolParams = new LinkedList<>();
for (Entity entityX : list) {
LinkedList<Entity> entities = new LinkedList<>();
for (Entity entityY : list) {
//if (entityY.input 是 ( necessaryInput 并 poolParams )的子集 ){
if (is子集(entityY.input, necessaryInput, poolParams) && !在结果里(entityY, result)) {
entities.add(entityY);
}
}
//如果有,放入结果
if (entities.size() != 0) {
//entities 的output都放进poolParams;
for (Entity es :
entities) {
poolParams.addAll(makeList(es.output));
}
result.add(entities);
}
}
//LOGGER.info(result);
for (LinkedList<Entity> aa : result
) {
LOGGER.info("-------------------------");
for (Entity zzz : aa) {
LOGGER.info(zzz.name);
}
}
}
public static LinkedList<Integer> makeList(int[] a) {
LinkedList<Integer> x = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
x.add(a[i]);
}
return x;
}
// a是(b并c)的子集
public static boolean is子集(int[] a, LinkedList<Integer> b, LinkedList<Integer> c) {
LinkedList<Integer> d = new LinkedList<>();
d.addAll(b);
d.addAll(c);
//TODO 去重
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
if (d.contains(a[i])) {
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// a在 result里
public static boolean 在结果里(Entity a, LinkedList<LinkedList> result) {
for (LinkedList<Entity> aa : result
) {
if (aa.contains(a))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
class Entity {
int[] input;
int[] output;
String name;
}
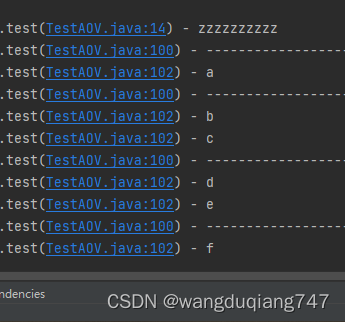
执行结果: