注解:和XML配置文件一样,注解本身并不能执行,注解本身仅仅只是做一个标记,具体的功能是框架检测到注解标记的位置,然后针对这个位置按照注解标记的功能来执行具体操作。
本质上:所以一切的操作都是java代码来完成的,XML和注解只是告诉框架中的代码如何执行。
扫描:Spring为了知道程序员在哪些地方标记了什么注解,就需要通过扫描的方式,来进行检测,然后根据注解进行后续操作。
注解和扫描:
我们创建一个新项目,导入依赖如下所示:
<!--基于Maven依赖传递性,导入spring-context依赖即可导入当前所需所有jar包--> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.3.1</version> </dependency> <!--junit测试--> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>标记组件的常用注解: @Component:将类标识为普通组件 @Controller:将类标识为控制层组件 @Service:将类标识为业务层组件 @Repository:将类标识为持久层组件对于Spring使用IOC容器管理这些组件来说没有区别
我们在相对应的不同层的实现类添加注解之后我们来进行扫描:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--扫描组件--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.rgf"></context:component-scan> </beans>我们通常采用这种方式,除此之外,我们还会通过:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rgf.UserConller,com.rgf.UserService"></context:component-scan>以逗号进行分割。
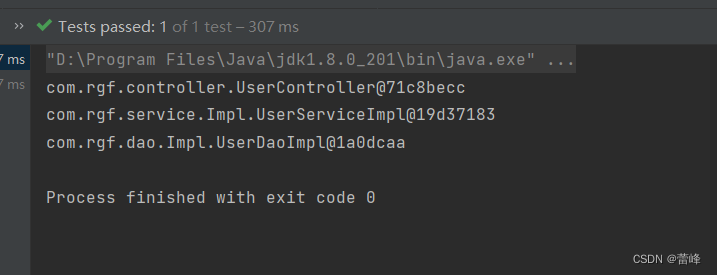
我们进行测试如下所示:
package com.rgf.spring.test; import com.rgf.controller.UserController; import com.rgf.dao.UserDao; import com.rgf.service.UserService; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class IOCByAnnotationTest { /** * 标记组件的常用注解: * @Component:将类标识为普通组件 * @Controller:将类标识为控制层组件 * @Service:将类标识为业务层组件 * @Repository:将类标识为持久层组件 */ @Test public void test(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc-annotation.xml"); UserController userController = ioc.getBean(UserController.class); System.out.println(userController); UserService userService = ioc.getBean(UserService.class); System.out.println(userService); UserDao userDao = ioc.getBean(UserDao.class); System.out.println(userDao); } }运行之后如下所示:
扫描组件:
SpringMVC扫描的是controller层,控制层的组件,Spring扫描的是除controller层之外的其他组件。
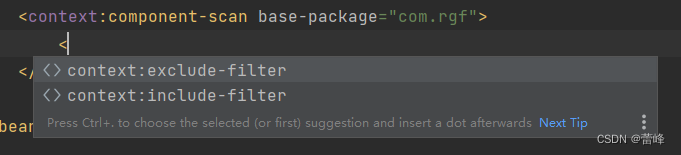
<context:include-filter />包含对某些组件的扫描,(只扫描谁) <context:exclude-filter />排除扫描,排除我们对某些组件的扫描(不扫描谁)

annotation:根据注解的类型进行排除
assignable:根据类的类型进行排除
我们进行排除的时候,在控制层的注解上点击右键: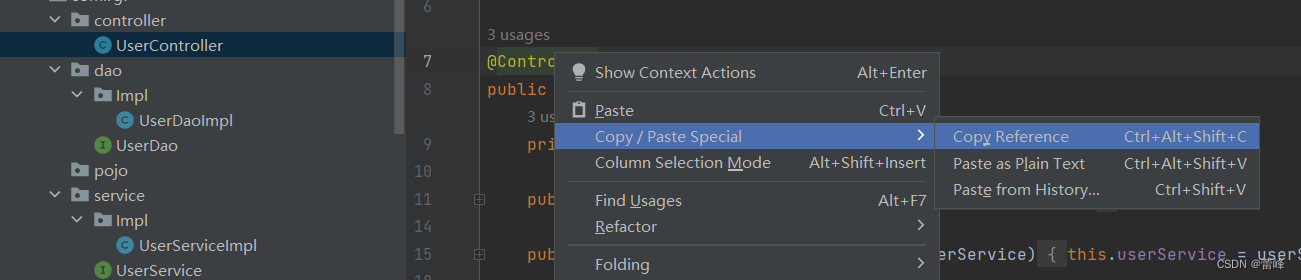
在IOC组件里面进行如下记述:
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>即不再扫描控制层了。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--扫描组件-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rgf">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
</beans>我们继续进行测试之后如下所示:
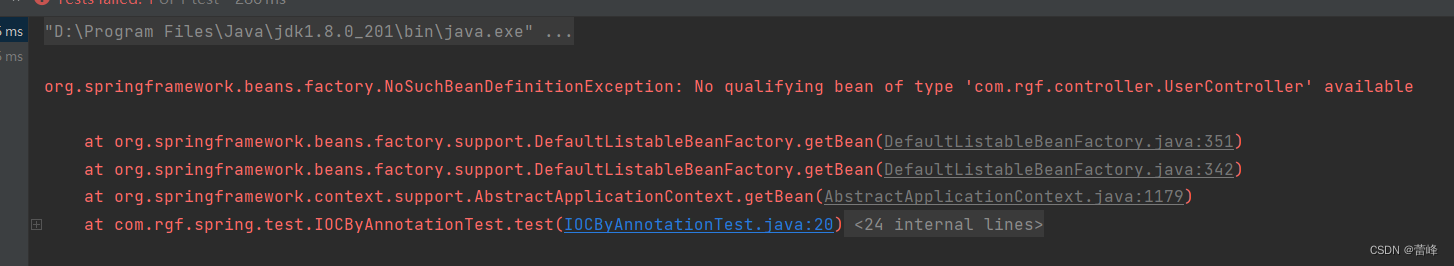
我们发现没有扫描上controller层。
我们继续查看:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--扫描组件-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rgf">
<context:include-filter type="assignable" expression="com.rgf.controller.UserController"/>
</context:component-scan>
</beans>我们的bean修改为如下所示:
<context:exclude-filter type="assignable" expression="com.rgf.controller.UserController"/>仍然为获取不到。
我们进行查看包含的另一个标签:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--扫描组件-->
<!--
context:exclude-filter:排除扫描
type:排除扫描的方式
type="annotation|assignable"
annotation:根据注解的类型进行排除,expression需要设置排除的注解的全类名
assignable:根据类的类型进行排除,expression需要设置排除的类的全类名
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rgf" >
<!--<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>-->
<!-- <context:exclude-filter type="assignable" expression="com.rgf.controller.UserController"/>-->
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
</beans>我们运行之后发现如下所示:
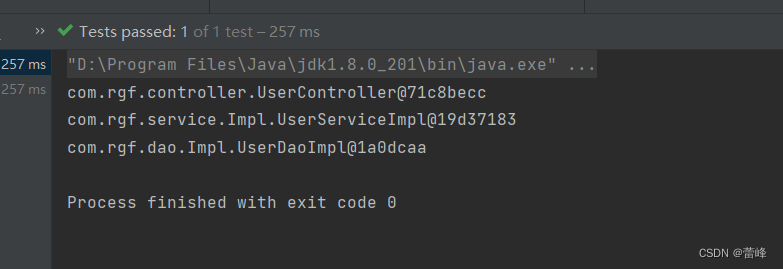
结果显示并不是只出现一个,这是因为有如下标签,use-default-filters(使用默认的过滤规则),默认的规则为包下的所有类都要进行扫描
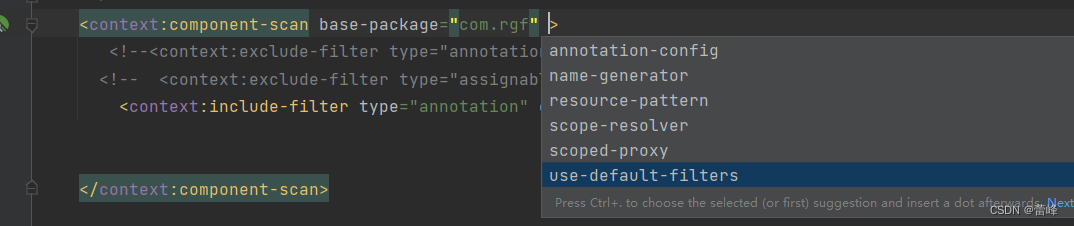
我们将该标签设置为true,同时进行扫描我们需要的组件,如下所示:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rgf" use-default-filters="false">
<!--<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>-->
<!-- <context:exclude-filter type="assignable" expression="com.rgf.controller.UserController"/>-->
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>我们运行之后如下所示: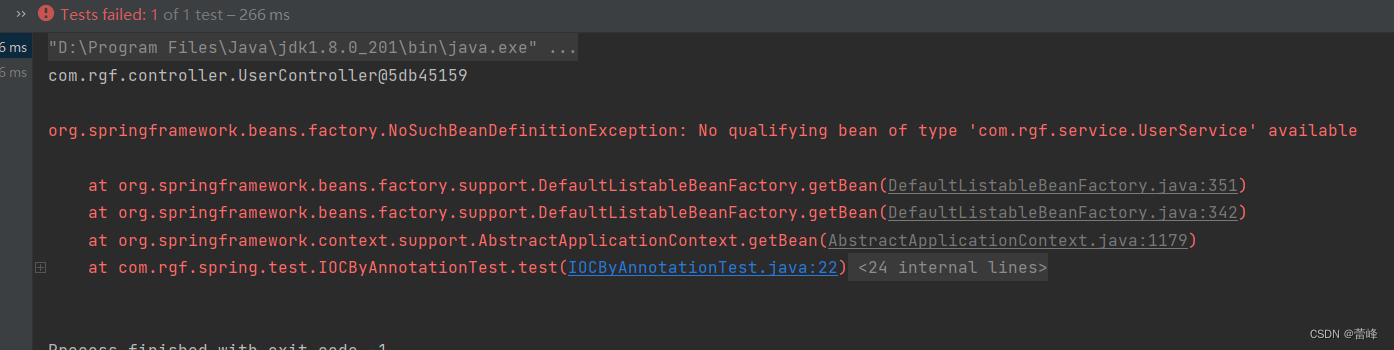
我们发现我们所需要的组件成功扫描出来了。
我们进行总结如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--扫描组件-->
<!--
context:exclude-filter:排除扫描
type:排除扫描的方式
type="annotation|assignable"
annotation:根据注解的类型进行排除,expression需要设置排除的注解的全类名
assignable:根据类的类型进行排除,expression需要设置排除的类的全类名
context:include-filter:包含扫描
注意:需要在context:component-scan标签中设置use-default-filters="false"
use-default-filters="true"(默认的),所设置的包下的所有类都需要扫描,此时可以使用排除扫描
use-default-filters="false",所设置的包下的所有类都不需要扫描,此时可以使用包含扫描。
可以设置多个排除和多个包含,但不能同时设置排除和包含,
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rgf" use-default-filters="false">
<!--<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>-->
<!-- <context:exclude-filter type="assignable" expression="com.rgf.controller.UserController"/>-->
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
</beans>我们通过注解+扫描所配置的bean的id的方式进行解决:我们进行测试如下所示:
package com.rgf.spring.test;
import com.rgf.controller.UserController;
import com.rgf.dao.UserDao;
import com.rgf.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class IOCByAnnotationTest {
/**
* 标记组件的常用注解:
* @Component:将类标识为普通组件
* @Controller:将类标识为控制层组件
* @Service:将类标识为业务层组件
* @Repository:将类标识为持久层组件
*
* 通过注解+扫描所配置的bean的id,默认值为类的小驼峰,即类名的首字母为小写的结果
*/
@Test
public void test(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc-annotation.xml");
UserController userController = ioc.getBean("userController",UserController.class);
System.out.println(userController);
UserService userService = ioc.getBean("userServiceImpl",UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService);
UserDao userDao = ioc.getBean("userDaoImpl",UserDao.class);
System.out.println(userDao);
}
}
我们运行之后如下所示:
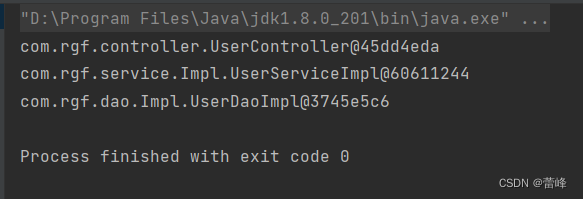
我们可以通过在所扫描的类里面的注解部分进行如下设置:
package com.rgf.controller;
import com.rgf.service.Impl.UserServiceImpl;
import com.rgf.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller("controller")
public class UserController {
private UserService userService;
public UserService getUserService() {
return userService;
}
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
public void saveUser(){
userService.saveUser();
}
}
此时的注解部分的设置就是为当前我们配置的bean所设置的自定义的id,为当前注解+扫描配置的bean设置的自定义的id.
此时我们继续测试之后如下所示:
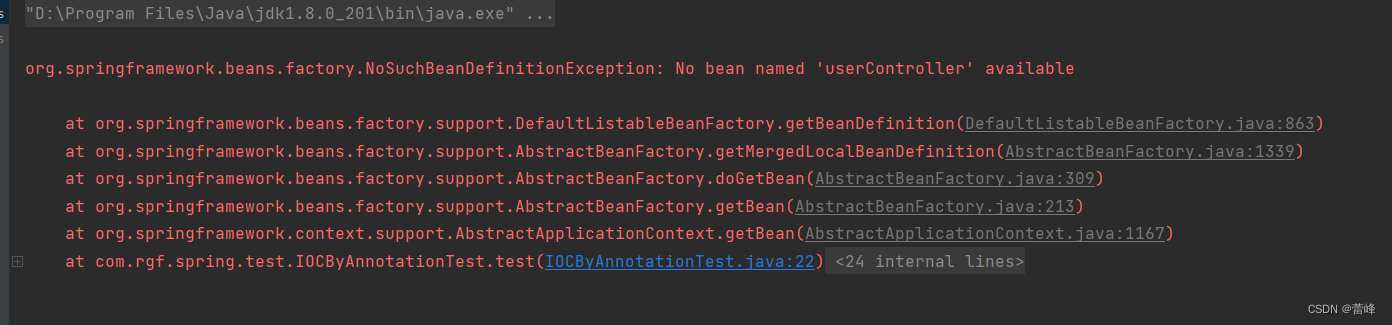
我们发现进行报错了,我们修改如下所示:
package com.rgf.spring.test;
import com.rgf.controller.UserController;
import com.rgf.dao.UserDao;
import com.rgf.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class IOCByAnnotationTest {
/**
* 标记组件的常用注解:
* @Component:将类标识为普通组件
* @Controller:将类标识为控制层组件
* @Service:将类标识为业务层组件
* @Repository:将类标识为持久层组件
*
* 通过注解+扫描所配置的bean的id,默认值为类的小驼峰,即类名的首字母为小写的结果
*/
@Test
public void test(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc-annotation.xml");
UserController userController = ioc.getBean("controller",UserController.class);
System.out.println(userController);
UserService userService = ioc.getBean("userServiceImpl",UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService);
UserDao userDao = ioc.getBean("userDaoImpl",UserDao.class);
System.out.println(userDao);
}
}
继续运行之后如下所示:
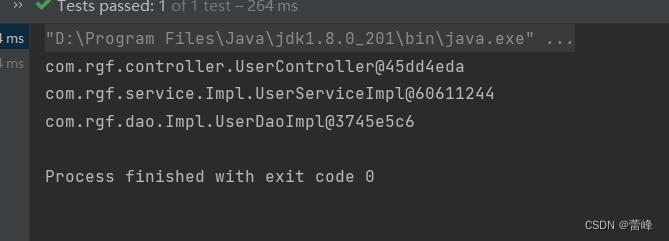
我们基本是通过类型来获取,但是很少会通过id来获取,除非一些特殊情况。
package com.rgf.spring.test;
import com.rgf.controller.UserController;
import com.rgf.dao.UserDao;
import com.rgf.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class IOCByAnnotationTest {
/**
* 标记组件的常用注解:
* @Component:将类标识为普通组件
* @Controller:将类标识为控制层组件
* @Service:将类标识为业务层组件
* @Repository:将类标识为持久层组件
*
* 通过注解+扫描所配置的bean的id,默认值为类的小驼峰,即类名的首字母为小写的结果
* 可以通过标识组件的注解的value属性值设置bean的自定义的id
*/
@Test
public void test(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc-annotation.xml");
UserController userController = ioc.getBean("controller",UserController.class);
System.out.println(userController);
UserService userService = ioc.getBean("userServiceImpl",UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService);
UserDao userDao = ioc.getBean("userDaoImpl",UserDao.class);
System.out.println(userDao);
}
}
基于注解的自动装配:
我们进行创建该方法如下所示:‘
controller层:
package com.rgf.controller;
import com.rgf.service.Impl.UserServiceImpl;
import com.rgf.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
//@Controller("controller")
@Controller("controller")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
public void saveUser(){
userService.saveUser();
}
}
service层:
package com.rgf.service;
public interface UserService {
/**
* 保存用户信息
*/
void saveUser();
}
package com.rgf.service.Impl;
import com.rgf.dao.UserDao;
import com.rgf.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
public void saveUser() {
userDao.saveUser();
}
}
dao层如下所示:
package com.rgf.dao;
public interface UserDao {
/**
* 保存用户信息
*/
void saveUser();
}
package com.rgf.dao.Impl;
import com.rgf.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public void saveUser() {
System.out.println("保存成功");
}
}
我们进行测试如下所示:
package com.rgf.spring.test;
import com.rgf.controller.UserController;
import com.rgf.dao.UserDao;
import com.rgf.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class IOCByAnnotationTest {
/**
* 标记组件的常用注解:
* @Component:将类标识为普通组件
* @Controller:将类标识为控制层组件
* @Service:将类标识为业务层组件
* @Repository:将类标识为持久层组件
*
* 通过注解+扫描所配置的bean的id,默认值为类的小驼峰,即类名的首字母为小写的结果
* 可以通过标识组件的注解的value属性值设置bean的自定义的id
*/
@Test
public void test(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc-annotation.xml");
UserController controller = ioc.getBean("controller", UserController.class);
controller.saveUser();
}
}
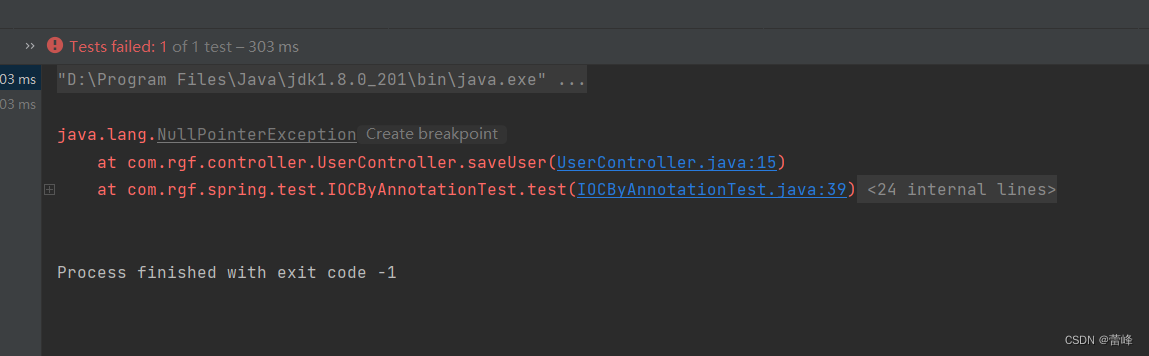
运行之后如下所示:

我们总结如下所示:
@Autowired:实现自动装配功能的注解
* 1.@Autowired注解能够标识的位置
* a>标识在成员变量上,此时不需要设置成员变量的set方法
* b>标识在set方法上
* c>为当前成员变量赋值的有参构造上2.@Autowired注解的原理
* a>默认通过byType的方式,在IOC容器中通过类型匹配某个bean为属性赋值
我们直接运行如下所示:
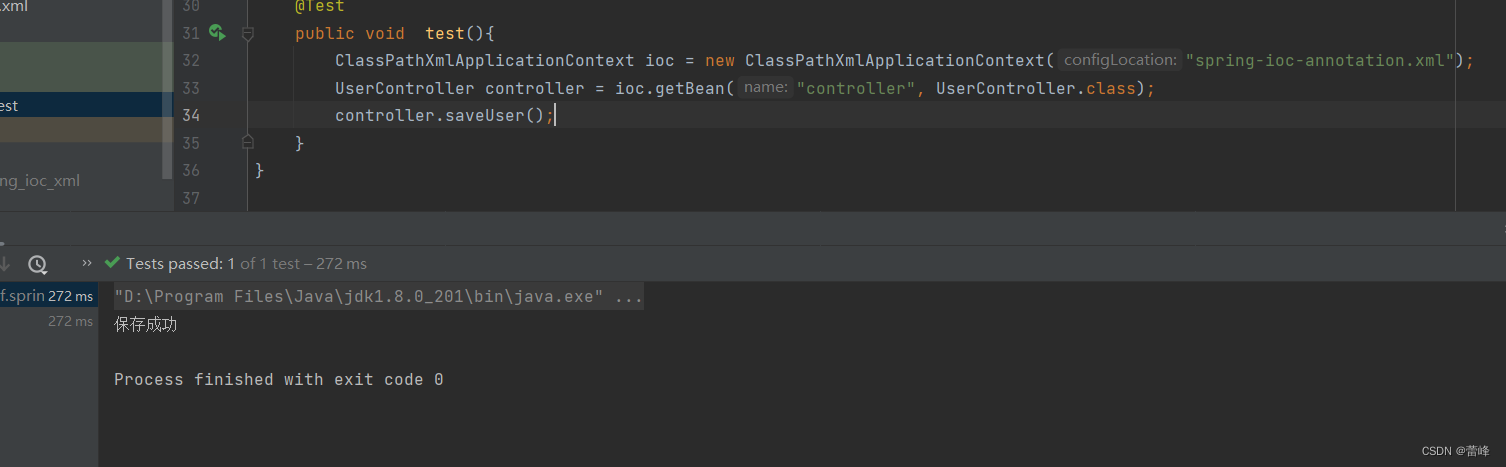
b>若有多个类型匹配的bean,此时会自动转换为byName的方式实现自动装配的效果
* 即将要赋值的属性的属性名来作为bean的id匹配某个bean为属性赋值
package com.rgf.controller;
import com.rgf.service.Impl.UserServiceImpl;
import com.rgf.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
//@Controller("controller")
@Controller("controller")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
public void saveUser(){
userService.saveUser();
}
}
将属性值userService如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--扫描组件-->
<!--
context:exclude-filter:排除扫描
type:排除扫描的方式
type="annotation|assignable"
annotation:根据注解的类型进行排除,expression需要设置排除的注解的全类名
assignable:根据类的类型进行排除,expression需要设置排除的类的全类名
context:include-filter:包含扫描
注意:需要在context:component-scan标签中设置use-default-filters="false"
use-default-filters="true"(默认的),所设置的包下的所有类都需要扫描,此时可以使用排除扫描
use-default-filters="false",所设置的包下的所有类都不需要扫描,此时可以使用包含扫描。
可以设置多个排除和多个包含,但不能同时设置排除和包含,
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rgf" >
</context:component-scan>
<bean id="userService" class="com.rgf.service.Impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.rgf.dao.Impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>我们运行之后如下所示:
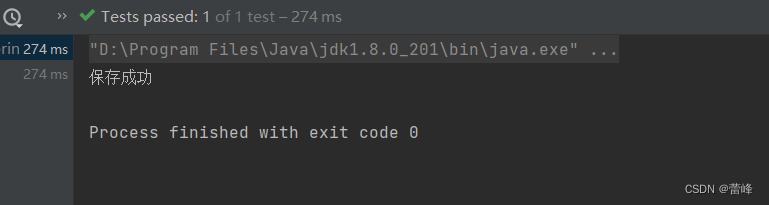
c>若byType和byName的方式都无法实现自动装配,即IOC容器中有多个类型匹配的bean,且这些bean的id和要赋值的属性的属性名都不一致
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rgf" >
</context:component-scan>
<bean id="Service" class="com.rgf.service.Impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="Dao" class="com.rgf.dao.Impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>我们继续进行测试如下所示:
我们发现直接进行报错:
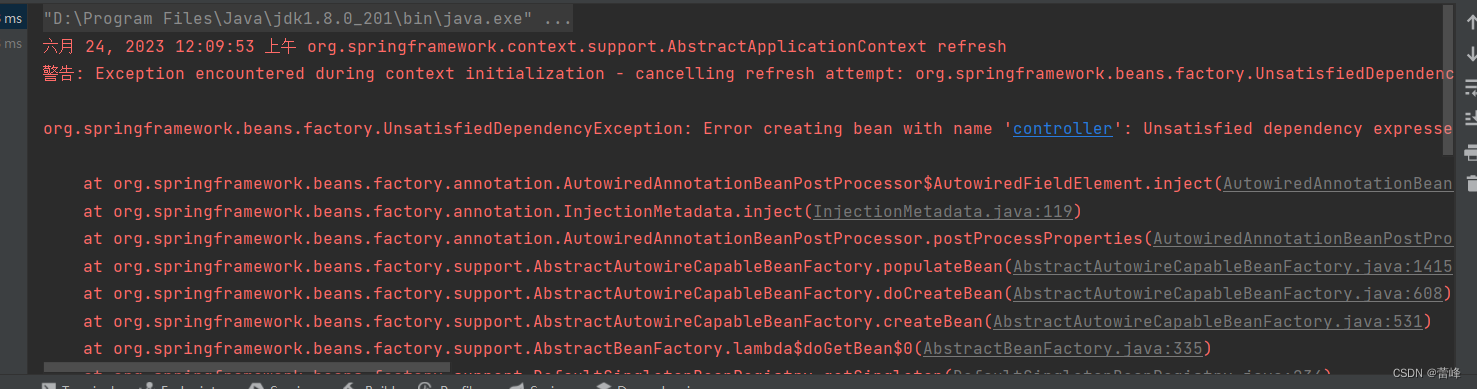
d>此时可以在要赋值的属性上,添加一个注解@Qualifier
我们在controller层里面进行写如下所示:
package com.rgf.controller;
import com.rgf.service.Impl.UserServiceImpl;
import com.rgf.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
//@Controller("controller")
@Controller("controller")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("userServiceImpl")
private UserService userService;
public void saveUser(){
userService.saveUser();
}
}
我们在service层里面进行书写如下所示:
package com.rgf.service.Impl;
import com.rgf.dao.UserDao;
import com.rgf.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("userDaoImpl")
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
public void saveUser() {
userDao.saveUser();
}
}
我们运行之后如下所示:
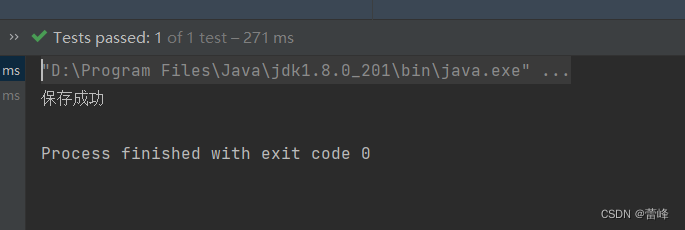
此种情况为出现如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rgf" >
</context:component-scan>
<bean id="Service" class="com.rgf.service.Impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="Dao" class="com.rgf.dao.Impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>当我们出现如下情况时:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rgf" >
</context:component-scan>
</beans>我们继续进行测试之后如下所示:
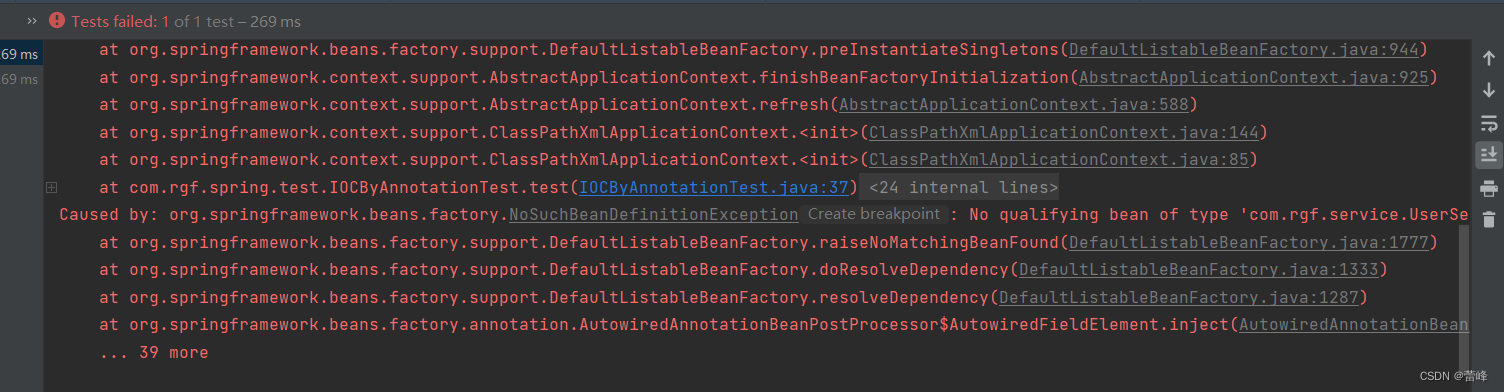

此时报错为NoSuchBeanDefinitionException
我们将注解默认进行修改,如下所示:
我们总结如下所示:
package com.rgf.spring.test;
import com.rgf.controller.UserController;
import com.rgf.dao.UserDao;
import com.rgf.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class IOCByAnnotationTest {
/**
* 标记组件的常用注解:
* @Component:将类标识为普通组件
* @Controller:将类标识为控制层组件
* @Service:将类标识为业务层组件
* @Repository:将类标识为持久层组件
*
* 通过注解+扫描所配置的bean的id,默认值为类的小驼峰,即类名的首字母为小写的结果
* 可以通过标识组件的注解的value属性值设置bean的自定义的id
*
* @Autowired:实现自动装配功能的注解
* 1.@Autowired注解能够标识的位置
* a>标识在成员变量上,此时不需要设置成员变量的set方法
* b>标识在set方法上
* c>为当前成员变量赋值的有参构造上
* 2.@Autowired注解的原理
* a>默认通过byType的方式,在IOC容器中通过类型匹配某个bean为属性赋值
* b>若有多个类型匹配的bean,此时会自动转换为byName的方式实现自动装配的效果
* 即将要赋值的属性的属性名来作为bean的id匹配某个bean为属性赋值
* c>若byType和byName的方式都无法实现自动装配,即IOC容器中有多个类型匹配的bean,
* 且这些bean的id和要赋值的属性的属性名都不一致,此时抛异常:NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException
* d>此时可以在要赋值的属性上,添加一个注解@Qualifier
* 通过该注解的value属性值,指定某个bean的id,将这个bean为属性赋值
* 注意:若IOC容器中没有任何一个类型匹配的bean,此时抛出异常:NoSuchBeanDefinitionException
* 在@Autowired注解中有个属性required,默认值为true,要求必须完成自动装配,可以将required设置为false,
* 此时能装配则装配,无法装配则使用属性的默认值
*/
@Test
public void test(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc-annotation.xml");
UserController controller = ioc.getBean("controller", UserController.class);
controller.saveUser();
}
}