文章目录
- Pytorch数据类型Tensor张量操作
- 一.创建张量的方式
- 1.创建无初始化张量
- 2.创建随机张量
- 3.创建初值为指定数值的张量
- 4.从数据创建张量
- 5.生成等差数列张量
- 二.改变张量形状
- 三.索引
- 四.维度变换
- 1.维度增加unsqueeze
- 2.维度扩展expand
- 3.维度减少squeeze
- 4.维度扩展repeat
- 五.维度交换
- 1.简单的二维转置函数t:
- 2.交换任意两个维度transpose
- 3.重新排列原来的维度顺序permute
- 六.张量合并
- 1.cat操作
- 2.stack操作
- 七.张量的分割
- 1.split操作
- 2.chunk操作
Pytorch数据类型Tensor张量操作
本文只简单介绍pytorch中的对于张量的各种操作,主要列举介绍其大致用法和简单demo。后续更为详细的介绍会进行补充…
一.创建张量的方式
1.创建无初始化张量
- torch.empty(3, 4) 创建未初始化内存的张量
2.创建随机张量
- x = torch.rand(3, 4) 服从0~1间均匀分布
- x = torch.randn(3, 4) 服从(0,1)的正态分布
- x = torch.rand_like(y) 以rand方式随机创建一个和y形状相同的张量
- x = torch.randint(1, 10, [3, 3]) 创建元素介于[1,10)的形状为(3,3)的随机张量
3.创建初值为指定数值的张量
- x = torch.zeros(3, 4) 生成形状为(3,4)的初值全为0的张量
- x = torch.full([3, 4], 6) 生成形状为(3,4)的初值全为6的张量
- x = torch.eye(5, 5) 生成形状为(5,5)的单位阵
4.从数据创建张量
-
x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]) 接收数据
-
torch.Tensor(3, 4) 接收tensor的维度
5.生成等差数列张量
- x = torch.arange(0, 10) 生成[0,10)公差为1的等差数列张量
- x = torch.arange(0, 10, 3) 生成[0,10)公差为3的等差数列张量
二.改变张量形状
view()与reshape()方法功能用法完全一致
通过传入改变后每一个维度的大小来重塑张量的形状:
x = x.view(2, 3)
x = x.reshape(2, 3)
view和reshape操作的示例:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
b = a.reshape(2, 4)
c = a.view(2, 4)
print(b)
print(c)

三.索引
y = x.index_select(0, torch.tensor([0, 2]))
第一个参数表示选择的维度,第二个参数以tensor的形式传入,选择该维度中的指定索引index
x = torch.tensor([
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9, 10, 11, 12],
])
y = x.index_select(0, torch.tensor([0, 2]))
print(y)
y = x.index_select(1, torch.tensor([1, 2]))
print(y)

根据掩码获得打平后的指定索引张量:
mask = x.ge(5)
y = torch.masked_select(x, mask)
通过比较运算获得一个mask索引,然后将mask索引传入masked_select方法来获得打平后的新张量,具体示例如下:
x = torch.tensor([
[1, 2, 0, 2],
[3, 6, 1, 9],
[-1, 7, -8, 1],
])
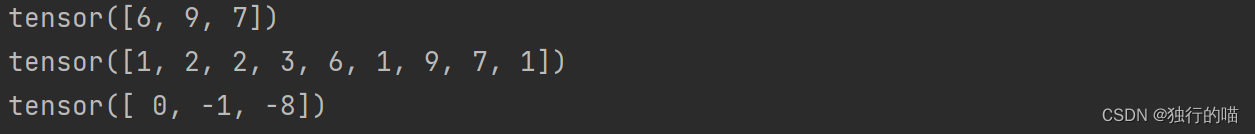
mask = x.ge(5)
y = torch.masked_select(x, mask)
print(y)
mask = x.gt(0)
y = torch.masked_select(x, mask)
print(y)
mask = x.lt(1)
y = torch.masked_select(x, mask)
print(y)
四.维度变换
1.维度增加unsqueeze
unsqueeze操作可以让张量在指定非负维度前插入新的维度,在负维度后插入新的维度,传入参数n表示指定的维度,即n若大于等于0则在n前插入新的维度,若n小于0则在n后插入新的维度:
x.unsqueeze(n)
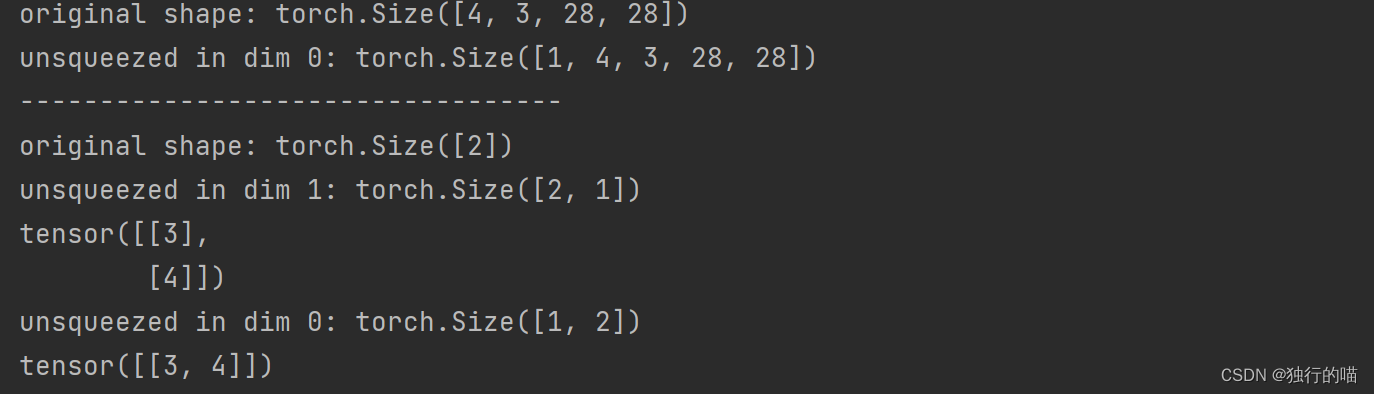
假设原张量x的shape为(4,3,28,28),使用x.unsqueeze(0) 在0维度前插入新的维度后,张量的shape变为(1,4,3,28,28)。原张量y的shape为(2),使用y.unsqueeze(1)在维度1前插入新的维度后,张量的shape变为(2,1)。代码示例如下:
x = torch.randint(1, 10, [4, 3, 28, 28])
print(f"original shape: {x.shape}")
x = x.unsqueeze(0)
print(f"unsqueezed in dim 0: {x.shape}")
print("----------------------------------")
y = torch.tensor([3, 4])
print(f"original shape: {y.shape}")
m = y.unsqueeze(1)
print(f"unsqueezed in dim 1: {m.shape}\n{m}")
n = y.unsqueeze(0)
print(f"unsqueezed in dim 0: {n.shape}\n{n}")
运行结果:
2.维度扩展expand
x.expand(a, b, c, d) 操作将原来维度扩展为(a,b ,c ,d),传入n个参数a,b,c,d…表示维度扩展后的形状,其中当传入的维度上的参数为-1时表示该维度保持不变。
x.expand(a, b, c, d)
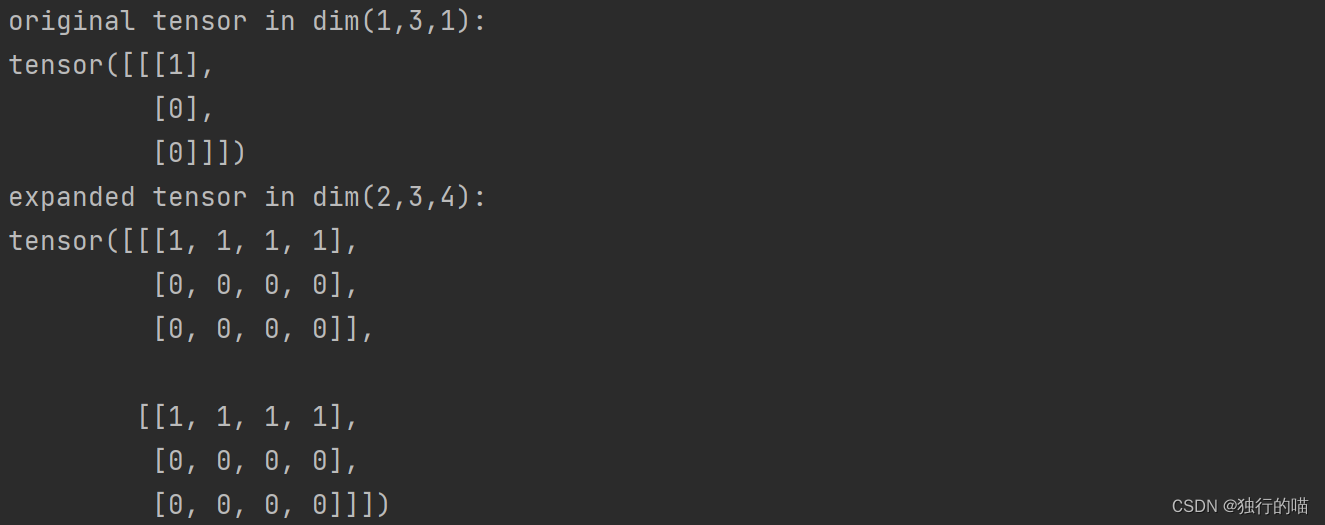
使用expand只能扩张原来大小为1的维度,该维度扩张为n后的张量将在该维度上将数据复制n次,将原shape为(1,3,1)的张量扩展为shape为(2,3,4)的张量:
x = torch.randint(0, 2, [1, 3, 1])
y = x.expand(2, 3, 4)
print(f"original tensor in dim(1,3,1):\n{x}")
print(f"expanded tensor in dim(2,3,4):\n{y}")
运行结果:
3.维度减少squeeze
x.squeeze()操作可以压缩张量的维度,当不传入任何参数时,squeeze()操作压缩所有可以压缩的维度,当传入指定参数时,参数可以是负数,将压缩张量的指定维度。
x.squeeze()
x.squeeze(n)
x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
y = x.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(0)
print(f"original shape : {y.shape}")
print(f"squeezed in all dim: {y.squeeze().shape}")
print(f"squeezed in dim 0: {y.squeeze(0).shape}")
print(f"squeezed in dim 1: {y.squeeze(1).shape}")
运行结果:

4.维度扩展repeat
x.repeat(a,b,c,d) 在原来维度上分别拷贝a,b,c,d次
x.repeat(a, b, c, d)
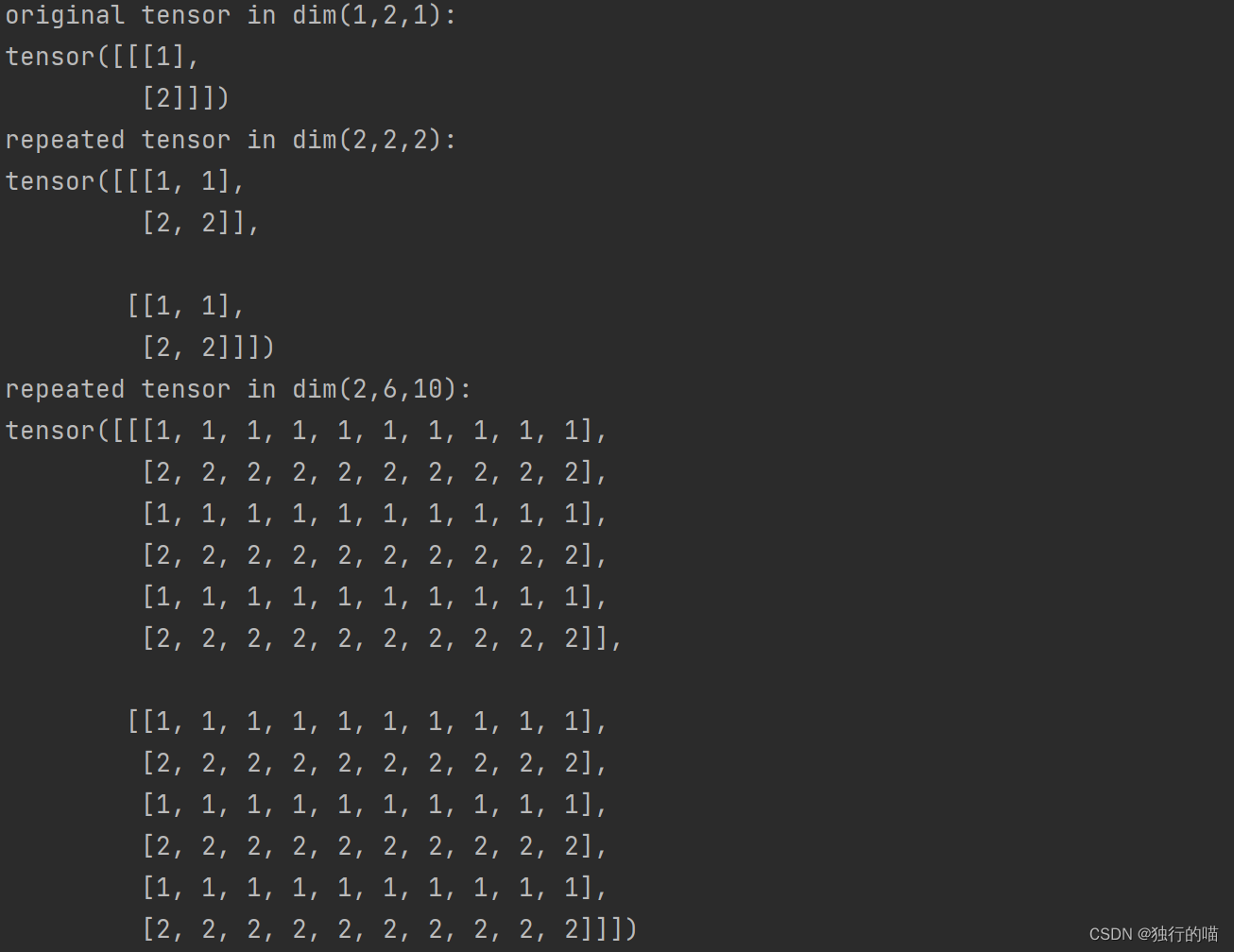
原张量x的shape为(1,2,1),通过执行repeat(2,1,2)操作后shape变为(2,2,2),再通过repeat(1,3,5)操作后shape变为(2,6,10):
x = torch.tensor([1, 2]).reshape(1, 2, 1)
y = x.repeat(2, 1, 2)
z = y.repeat(1, 3, 5)
print(f"original tensor in dim(1,2,1): \n{x}")
print(f"repeated tensor in dim(2,2,2): \n{y}")
print(f"repeated tensor in dim(2,6,10): \n{z}")
五.维度交换
1.简单的二维转置函数t:
x.t()
2.交换任意两个维度transpose
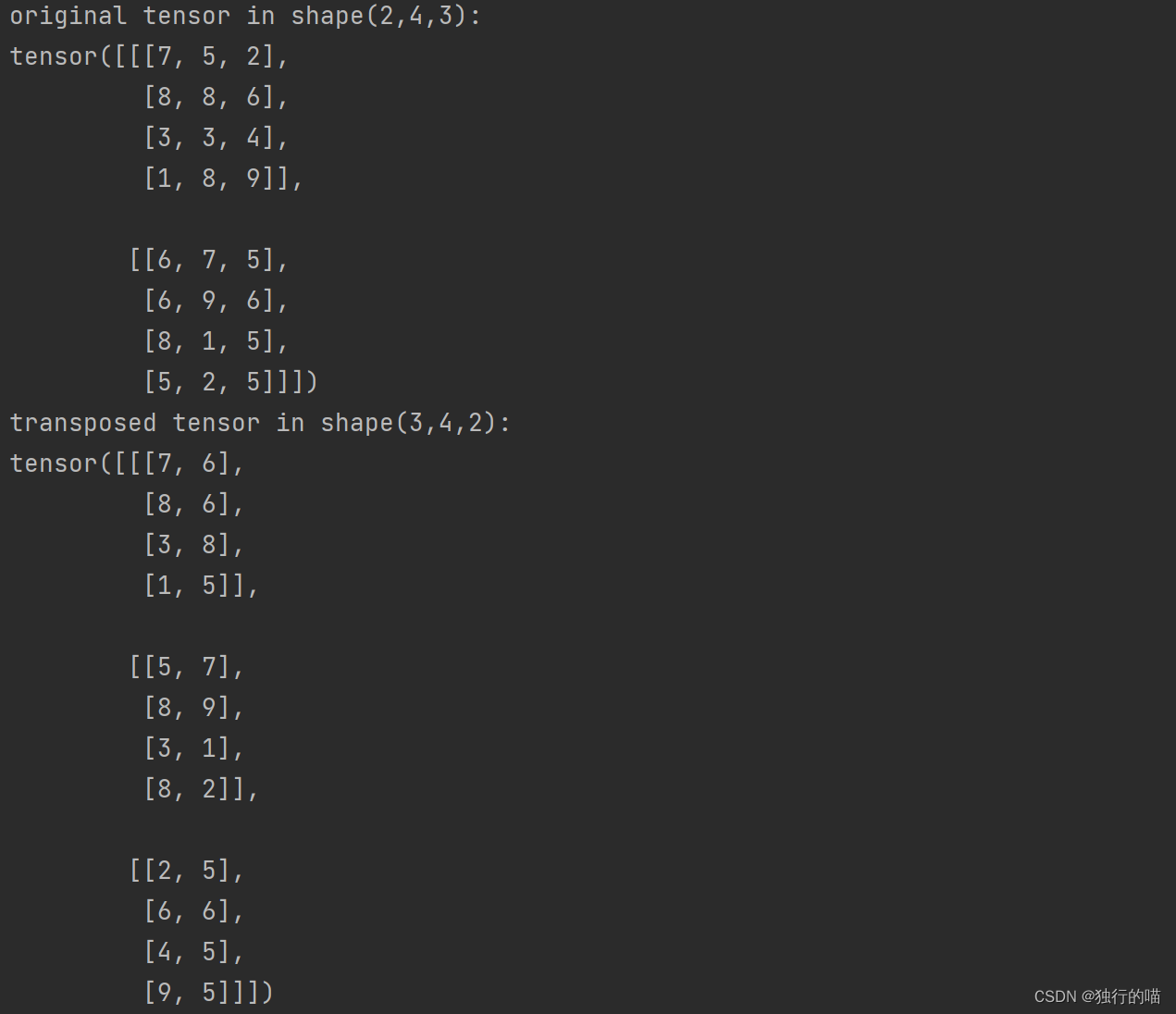
x = torch.randint(1, 10, [2, 4, 3])
y = x.transpose(0, 2)
print(f"original tensor in shape(2,4,3):\n{x}")
print(f"transposed tensor in shape(3,4,2):\n{y}")
3.重新排列原来的维度顺序permute
permute操作用于重新排列维度顺序,传入的参数代表维度的索引,即dim a,dim b…
x.permute(a, b, c, d)
x.permute(1,2,0)的意义是将原来的1维度放到0维度的位置,将原来的2维度放到1维度的位置,将原来的0维度放到2维度的位置,以此重新排列维度顺序:
x = torch.tensor([
[
[1, 2, 3, 1],
[4, 5, 3, 6],
[1, 1, 0, 1]
],
[
[7, 8, 9, 1],
[0, 2, 0, 3],
[6, 5, 1, 8],
]
])
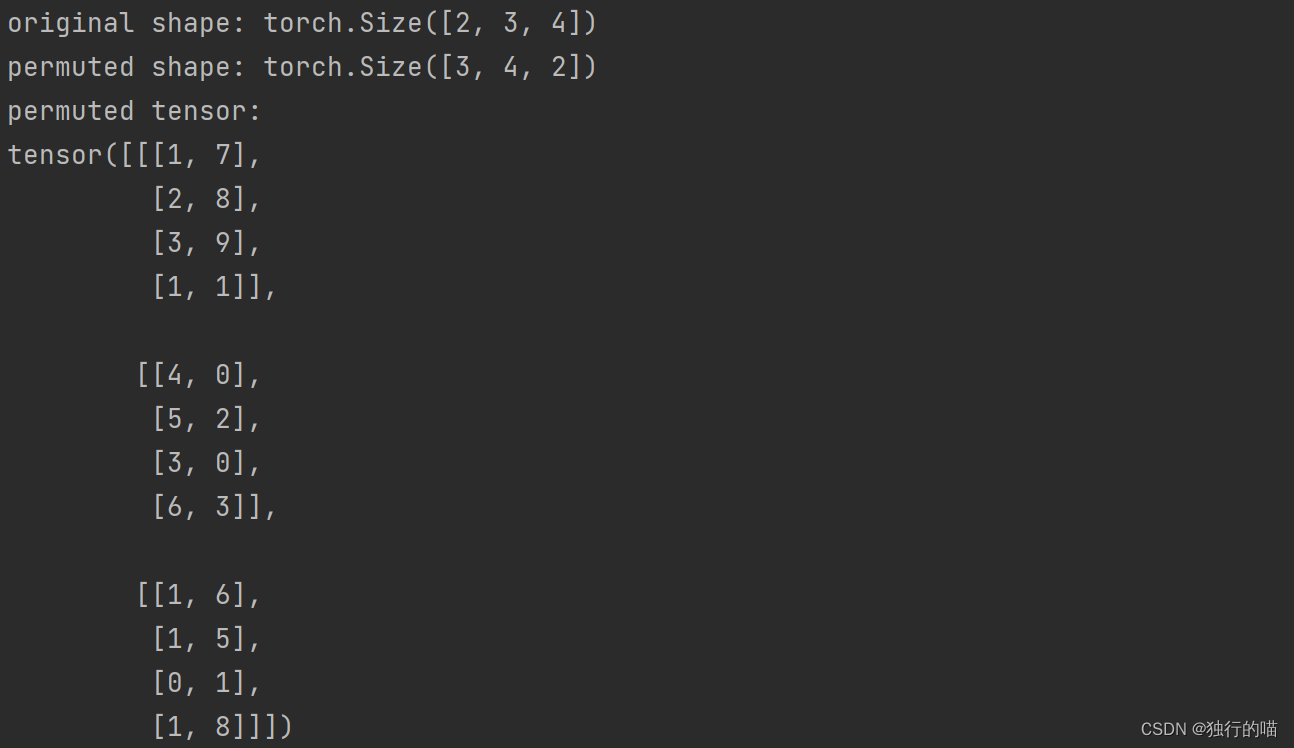
y = x.permute(1, 2, 0)
print(f"original shape: {x.shape}")
print(f"permuted shape: {y.shape}")
print(f"permuted tensor:\n{y}")
六.张量合并
1.cat操作
代码示例:
torch.cat([a,b], dim=0)
cat()函数中首先传入一个列表[a, b, c…]表示要合并的张量集合,然后传入一个维度dim=n,表示将这些张量在维度n上进行合并操作。
注意concat操作合并的维度上两个张量的维度大小可以不同,但是其余维度上必须具有相同的大小,例如(3,4,5)可以和(2,4,5)在0维度上concat合并为(5,4,5)。但是不能在1维度上合并,因为0维度上两个张量的维度大小不同,分别为3和2。
a = torch.tensor([
[
[1, 0, 1],
[9, 1, 2],
[3, 3, 1]
],
[
[0, 0, 1],
[2, 5, 1],
[3, 3, 2]
],
[
[4, 1, 10],
[0, 2, 1],
[1, 1, 1]
]
], dtype=int)
b = torch.tensor([
[
[0, 0, 2],
[1, 10, 2],
[2, 3, 0]
],
[
[0, 4, 1],
[2, 0, 1],
[1, 3, 6]
],
[
[0, 1, 4],
[1, 2, 1],
[1, 4, 1]
]
], dtype=int)
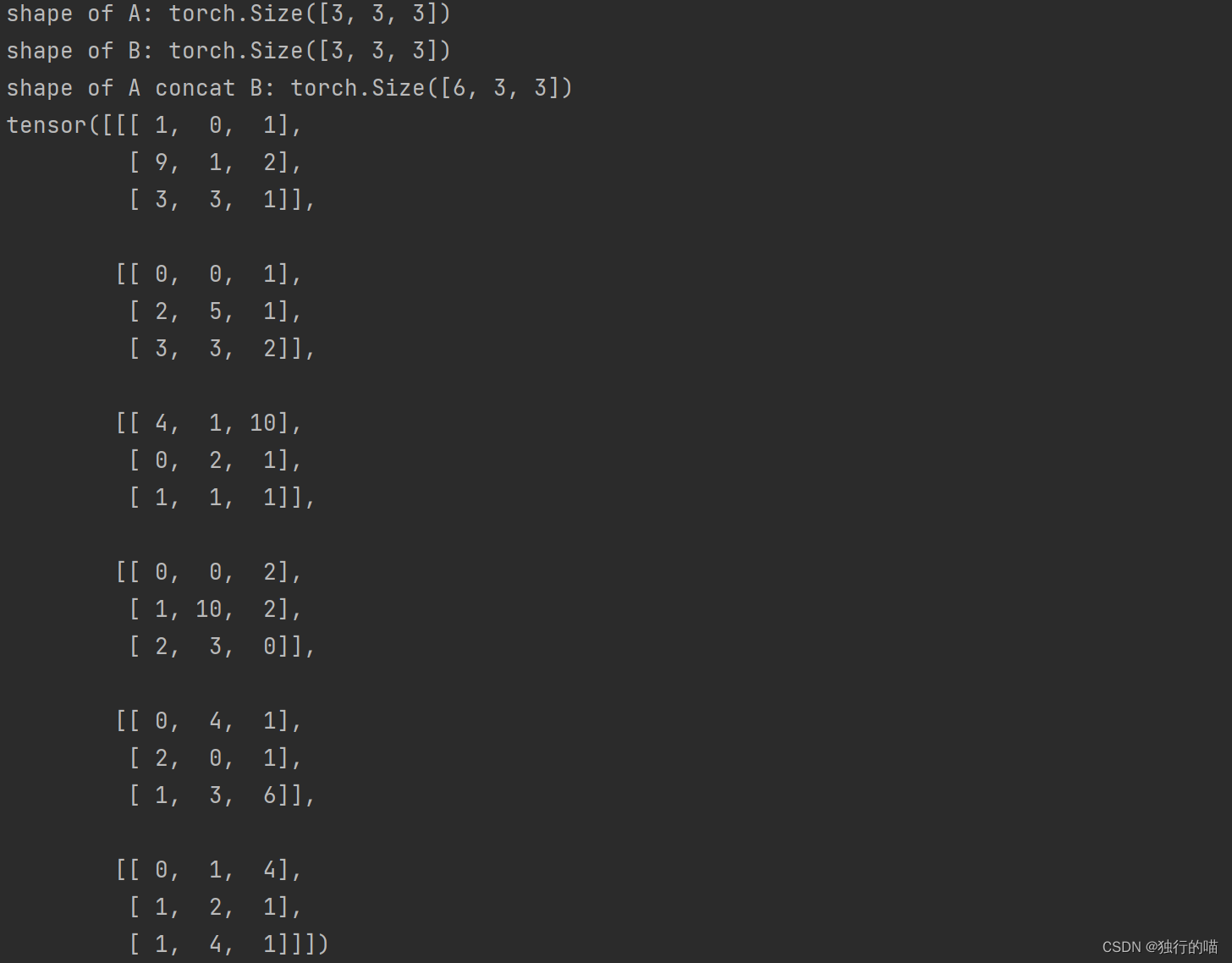
c = torch.cat([a, b], dim=0)
print(f"shape of A: {a.shape}")
print(f"shape of B: {b.shape}")
print(f"shape of A concat B: {c.shape}")
print(c)
运行结果:
2.stack操作
stack操作在合并维度处创建一个新的维度。
代码示例:
torch.stack([a, b], dim=0)
tensorA = torch.tensor([
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]
])
tensorB = torch.tensor([
[7, 8, 9],
[3, 2, 1]
])
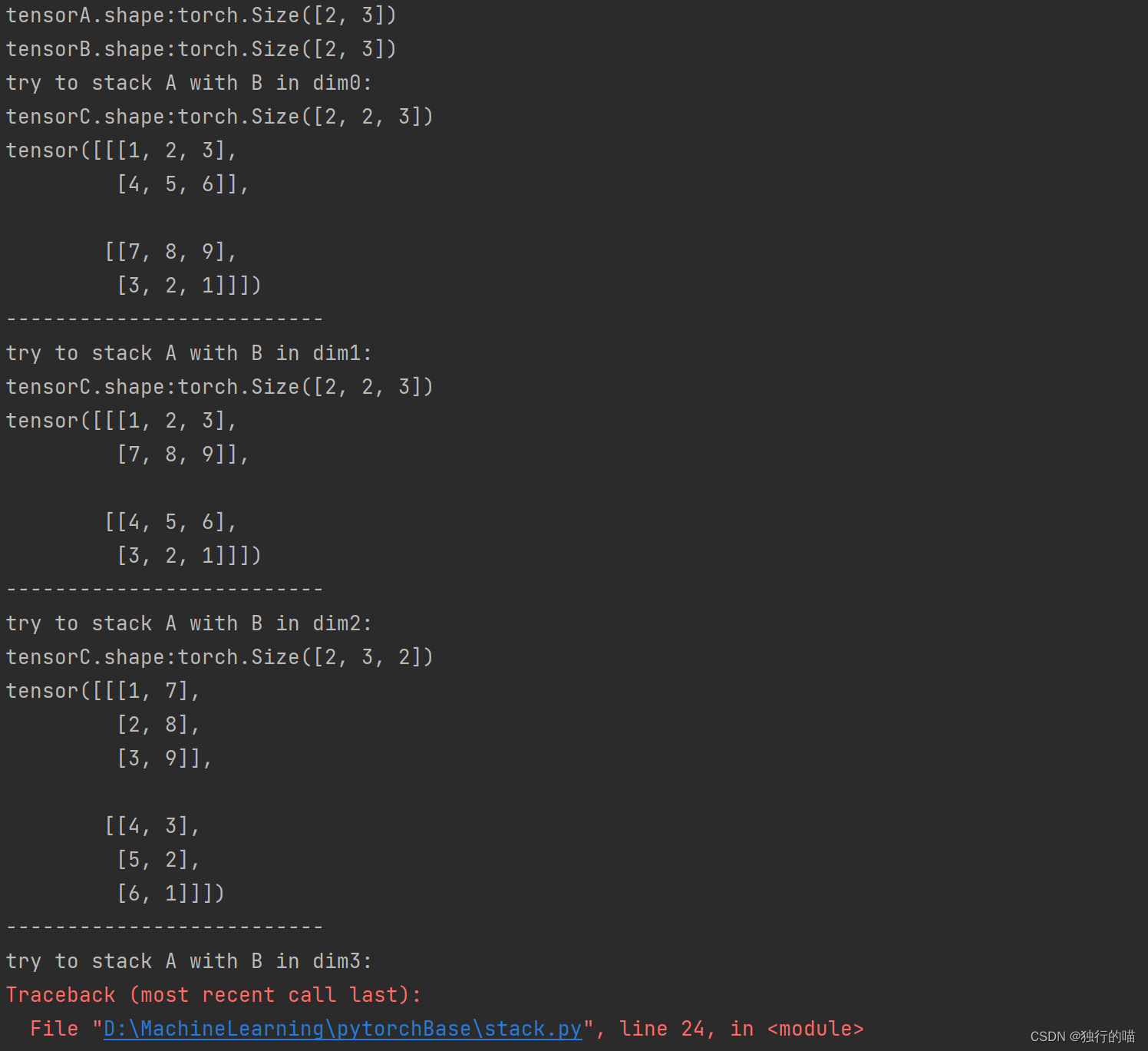
print(f"tensorA.shape:{tensorA.shape}")
print(f"tensorB.shape:{tensorB.shape}")
print("try to stack A with B in dim0:")
tensorC = torch.stack([tensorA, tensorB], dim=0)
print(f"tensorC.shape:{tensorC.shape}\n{tensorC}\n--------------------------")
print("try to stack A with B in dim1:")
tensorC = torch.stack([tensorA, tensorB], dim=1)
print(f"tensorC.shape:{tensorC.shape}\n{tensorC}\n--------------------------")
print("try to stack A with B in dim2:")
tensorC = torch.stack([tensorA, tensorB], dim=2)
print(f"tensorC.shape:{tensorC.shape}\n{tensorC}\n--------------------------")
print("try to stack A with B in dim3:")
tensorC = torch.stack([tensorA, tensorB], dim=3)
print(f"tensorC.shape:{tensorC.shape}")
print(tensorC)
运行结果:
七.张量的分割
1.split操作
split操作是对张量在指定维度上将张量进行分割,可以按给定长度等分,也可以通过列表传入分割方法。下面两种分割方式结果是相同的,第一种方式是将张量x在维度0上按照每一份长度为1进行等分;第二种方式是按照长度[1, 1, 1]的模式将张量x分成三份。
a, b, c = x.split(1, dim=0)
a, b, c = x.split([1, 1, 1], dim=0)
x = torch.tensor([
[
[1, 2, 1, 3],
[0, 1, 2, 1],
[9, 8, 1, 2]
],
[
[1, 2, 1, 2],
[4, 2, 4, 4],
[1, 0, 0, 0]
],
[
[3, 3, 3, 1],
[1, 0, 2, 3],
[5, 1, 2, 5]
]
])
print(x.shape)
a, b, c = x.split(1, dim=0)
print(f"a.shape:{a.shape}\nb.shape:{b.shape}\nc.shape:{c.shape}")
print("------------------------------------")
a, b = x.split([1, 2], dim=0)
print(f"a.shape:{a.shape}\nb.shape:{b.shape}")

2.chunk操作
chunk操作是对张量的某一维度按数量进行分割,首先传入第一个参数代表要分割成的份数,第二个参数指定了在哪一个维度上分割,下面的API样例代表将张量在维度0上分割为3个张:
a, b, c = x.chunk(3, dim=0)
对上例split中的张量x用chunk做分割的示例如下:
a, b, c = x.chunk(3, dim=1)
print(a.shape)
print(b.shape)
print(c.shape)
print("---------------------")
a, b = x.chunk(2, dim=2)
print(a.shape)
print(b.shape)