【嵌入式系统】20计科3-4班 第1讲 文件IO操作测试
【嵌入式系统】20计科3-4班 第2讲第4讲进程控制与线程测试
【嵌入式系统】20计科3-4班 第3讲进程通信测试
【嵌入式系统】20计科3-4班 第5-6讲内核和BootLoader开发测试
【嵌入式系统】20计科3-4班 第7讲驱动程序开发测试
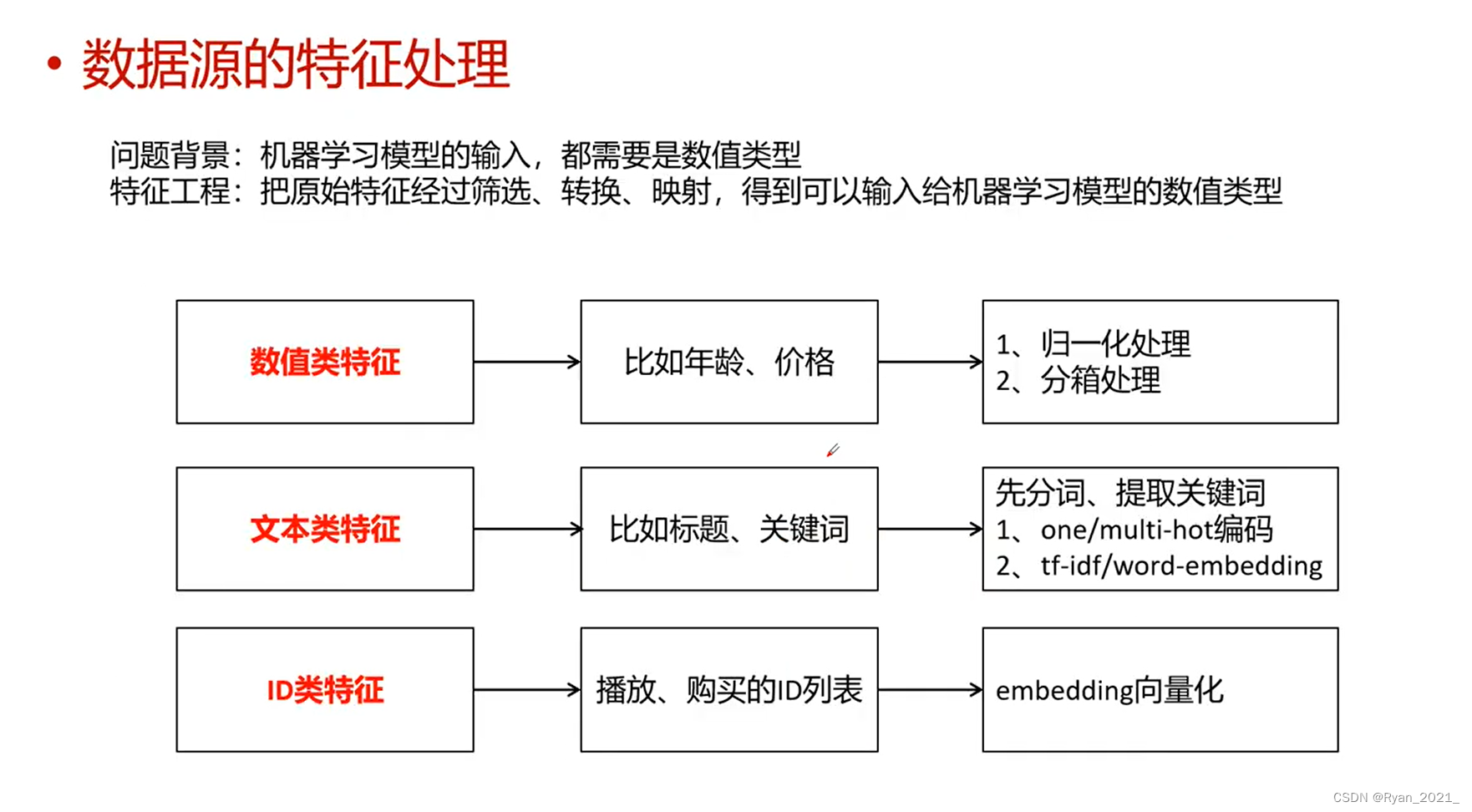
大题
1
编写一个C语言程序,利用文件I/O编程的系统调用函数实现:
在当前目录下创建一个文件"hello.txt",在文件中写入 “hello, software weekly”,
再从文件中读取其中的weekly并显示在屏幕上
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
char buf[1024];
int fd = creat("hello.txt", S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("创建文件失败\n");
exit(1);
}
write(fd, "hello, software weekly", 22);
close(fd);
fd = open("hello.txt", O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("打开文件失败\n");
exit(1);
}
lseek(fd, -6, SEEK_END); // 将文件指针移动到"weekly"的起始位置
int n = read(fd, buf, 6); // 读取"weekly"
if (n == -1)
{
printf("读取文件失败\n");
exit(1);
}
buf[n] = '\0'; // 将读取到的字符串末尾加上结束符
printf("%s\n", buf);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
2.
用fork创建子进程, 要求在子进程中分别输出字符"A~F",在父进程中输出数字“1~5”
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main() {
pid_t pid;
int i;
pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) { // 子进程
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
printf("%c\n", 'A' + i);
}
} else if (pid > 0) { // 父进程
for (i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
printf("%d\n", i);
}
wait(NULL); // 等待子进程结束
} else { // fork出错
printf("Failed to fork\n");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
3.
创建无名管道实现父进程将字符串"123456"传给子进程
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 6
int main() {
int pipefd[2]; // 无名管道的文件描述符数组
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; // 缓冲区
pid_t pid;
int nbytes;
if (pipe(pipefd) == -1) { // 创建管道失败
perror("pipe");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
pid = fork();
if (pid > 0) { // 父进程
close(pipefd[0]); // 关闭读端
write(pipefd[1], "123456", BUFFER_SIZE); // 写入数据
close(pipefd[1]); // 关闭写端
} else if (pid == 0) { // 子进程
close(pipefd[1]); // 关闭写端
nbytes = read(pipefd[0], buffer, BUFFER_SIZE); // 读取数据
printf("Received string: %s\n", buffer);
close(pipefd[0]); // 关闭读端
} else { // fork出错
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return 0;
}
4
创建新线程,在创建的新线程中实现求1~10的累加和,并要求从新线程中返回后主线程才终止
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void* sum(void* arg) { // 新线程函数
int i, sum = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum += i;
}
printf("Sum: %d\n", sum);
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_t tid; // 新线程的线程ID
int ret;
ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, sum, NULL); // 创建新线程
if (ret != 0) { // 创建新线程失败
printf("Failed to create thread.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ret = pthread_join(tid, NULL); // 等待新线程结束
if (ret != 0) { // 等待新线程失败
printf("Failed to join thread.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return 0;
}
5
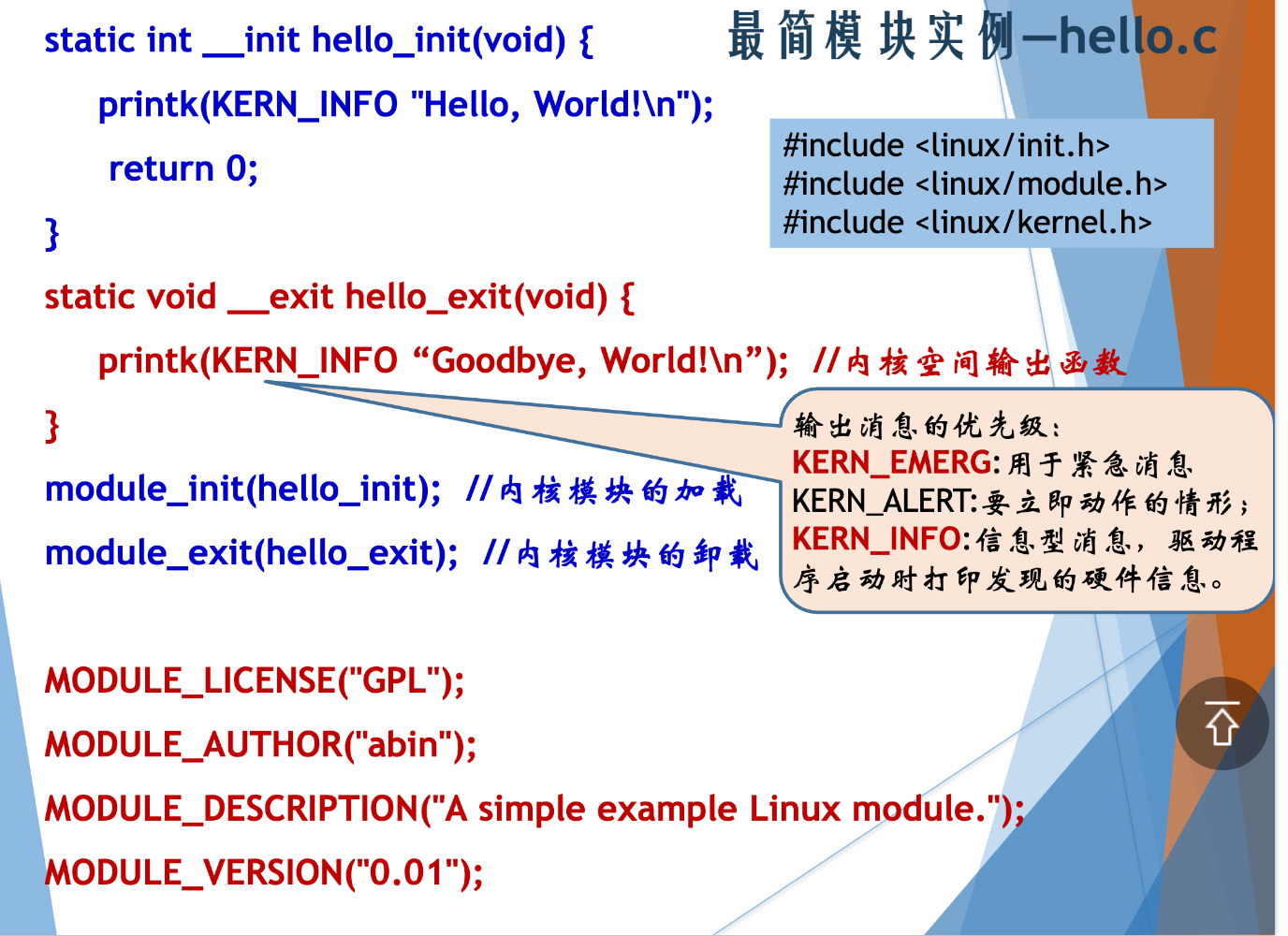
(1)设计一个简单的内核模块,要求模块加载时再内核日志中显示“hello”,在卸载模块时内核日志中显示“bye”
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
static int __init hello_init(void) {
printk(KERN_INFO "hello\n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit hello_exit(void) {
printk(KERN_INFO "bye\n");
}
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
(2)编写相应的Makefile文件
obj-m += hello.o
all:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) clean
(3)写出加载内核模块的命令和卸载内核模块的命令。
sudo insmod hello.ko // 加载
sudo rmmod hello // 卸载
第五章
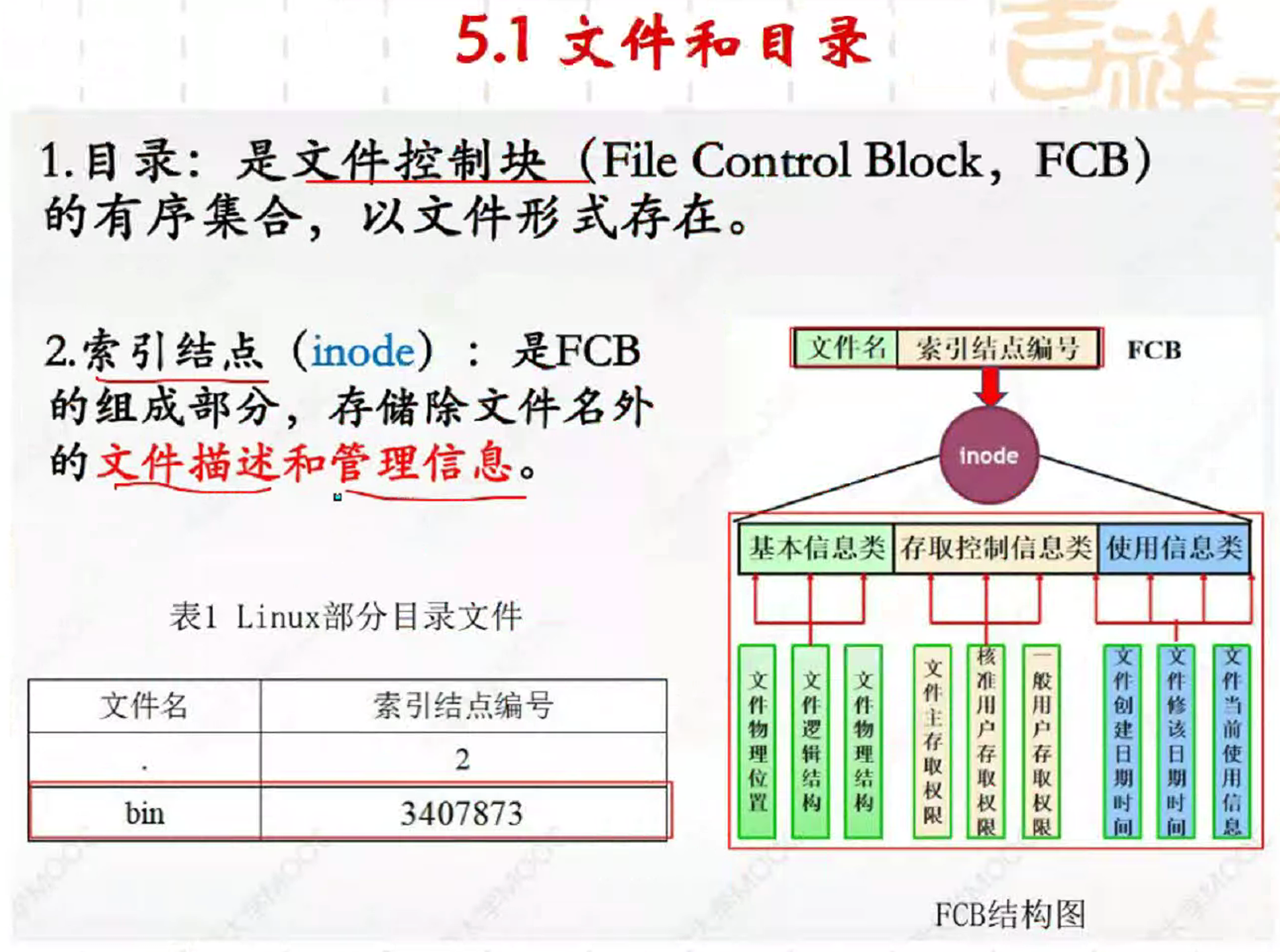
1. 目录操作
stat() 非常重要!
最重要的是函数怎么用,参数都是啥意思

选择题有可能出填空题

描述了目录的两个结构体





(可能简答题,让你编写一个c语言程序:xxx,并且创建完之后打印信息)
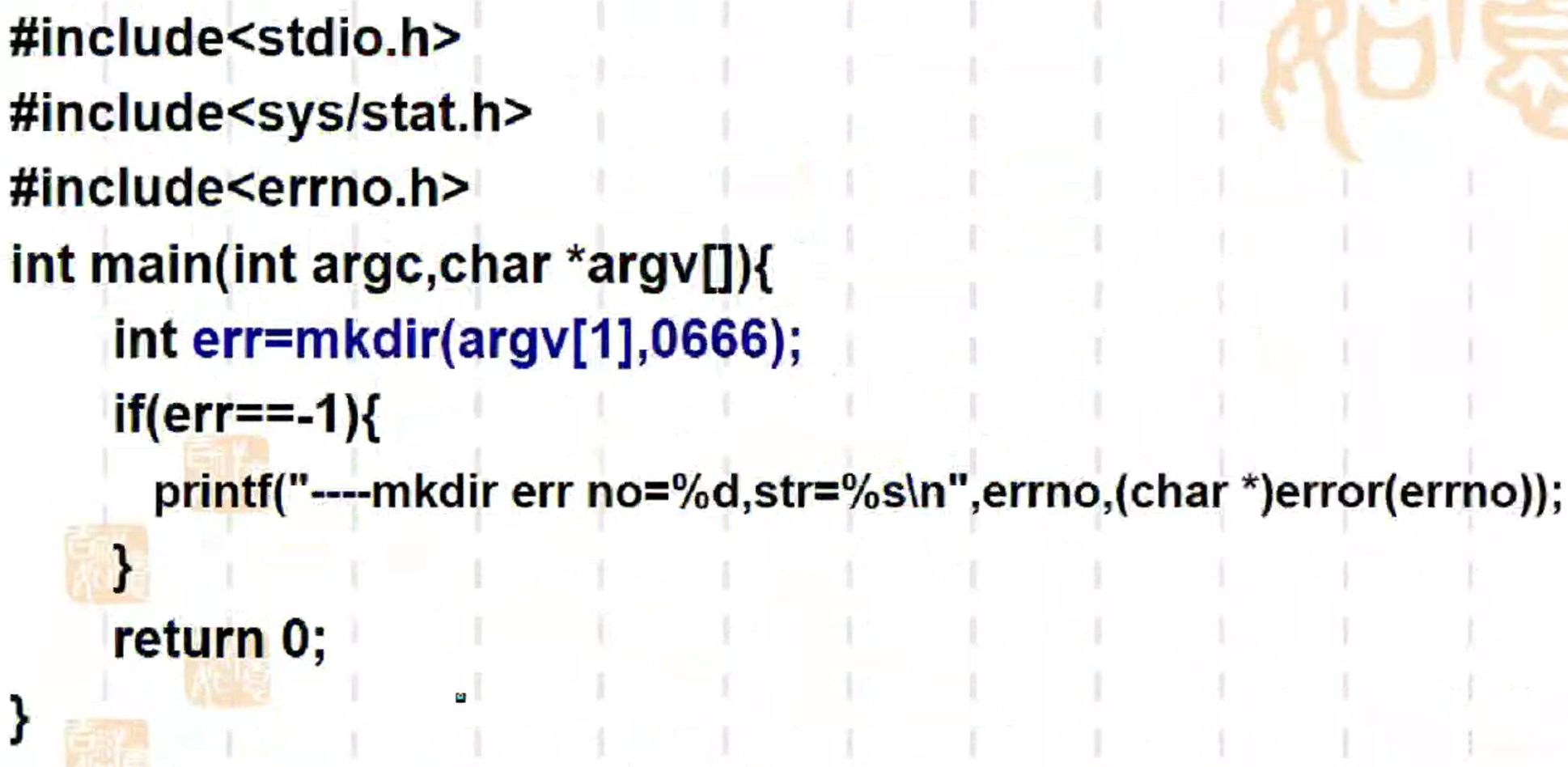

getcwd用法:

两个例子可能合并成一个简答题!



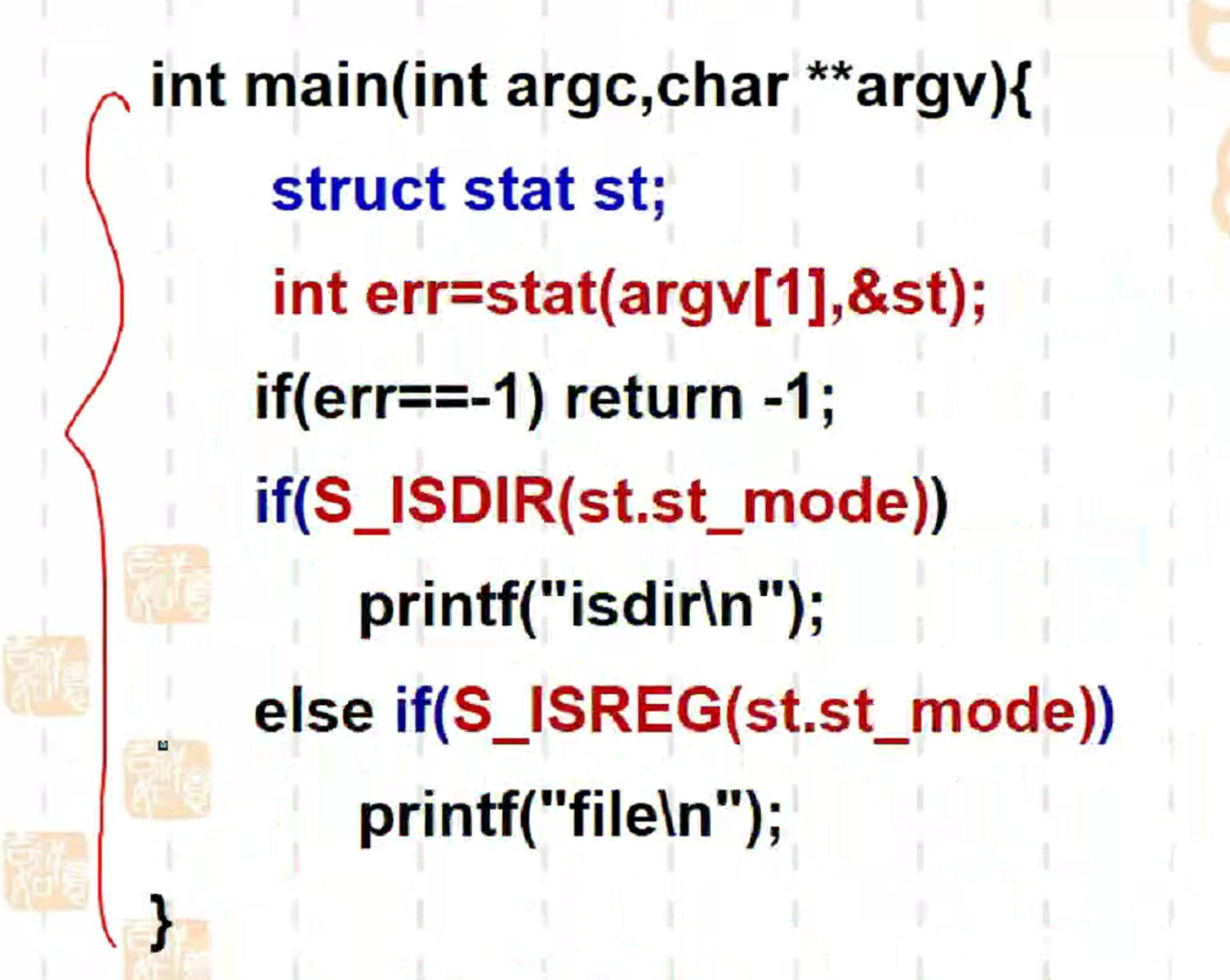
读当前目录下xxx文件的状态,并判断
要能解释出来啥意思,也要知道每一个函数的含义
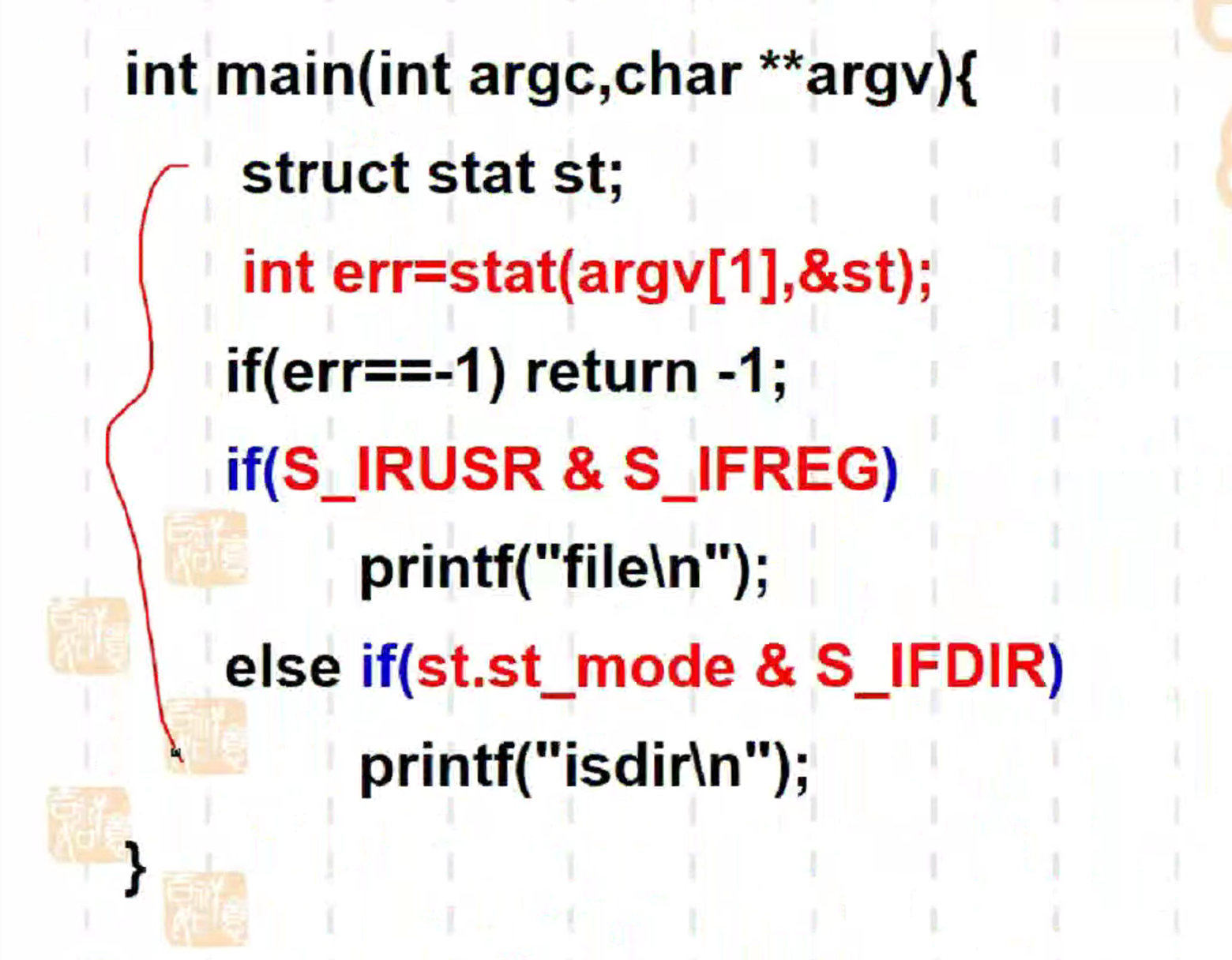

实现ls

像这个练习题,可能就会变一下:



不仅要能写、还要能读懂、解释

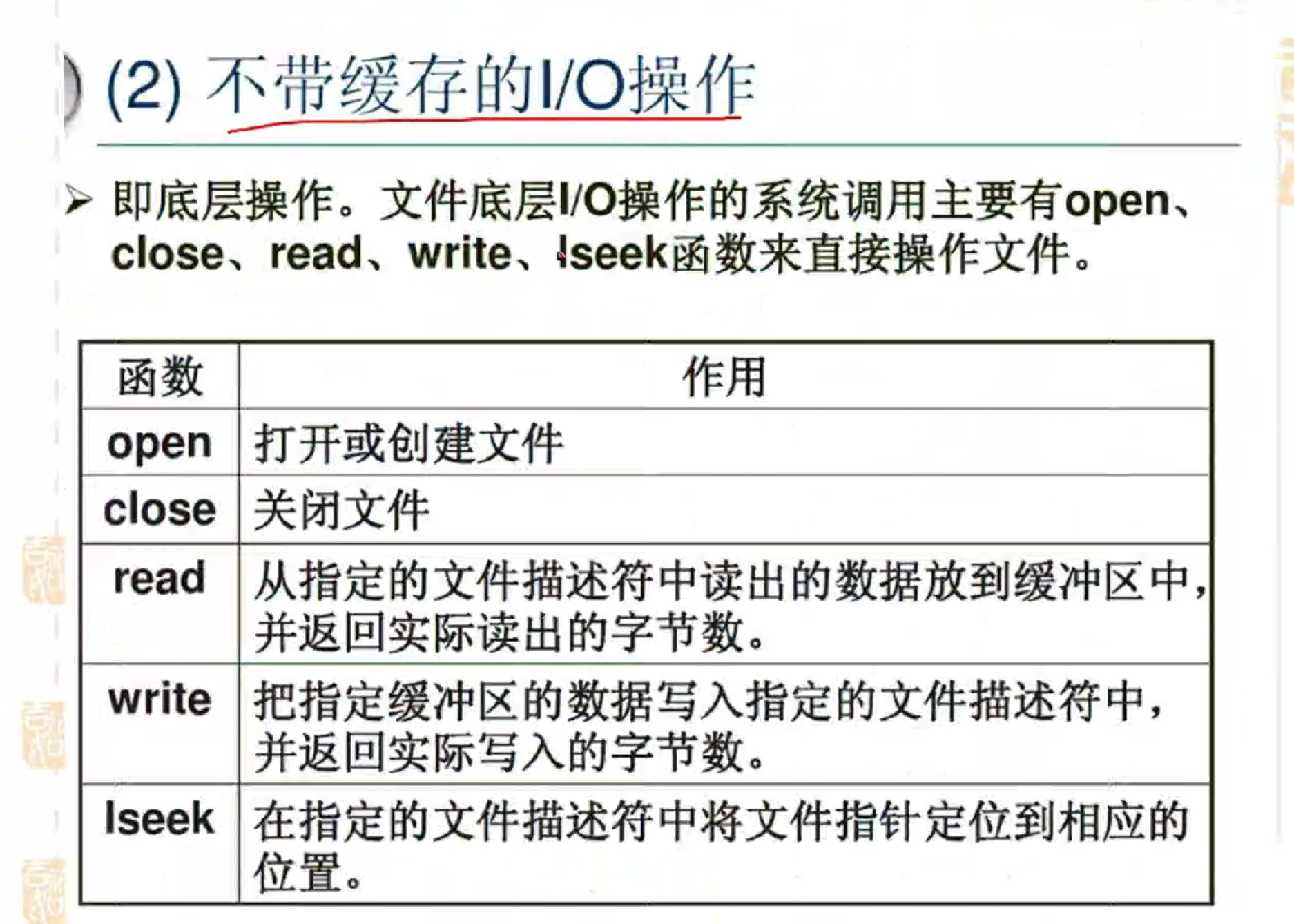
2. 文件操作
基本概念从测试题里看,我就不说了
creat 你可以不用看

有两个参数的还有三个参数的
大题的话,要看有open,然后还要读/写/先写后读这种例子
(这里缺一个open的例子)
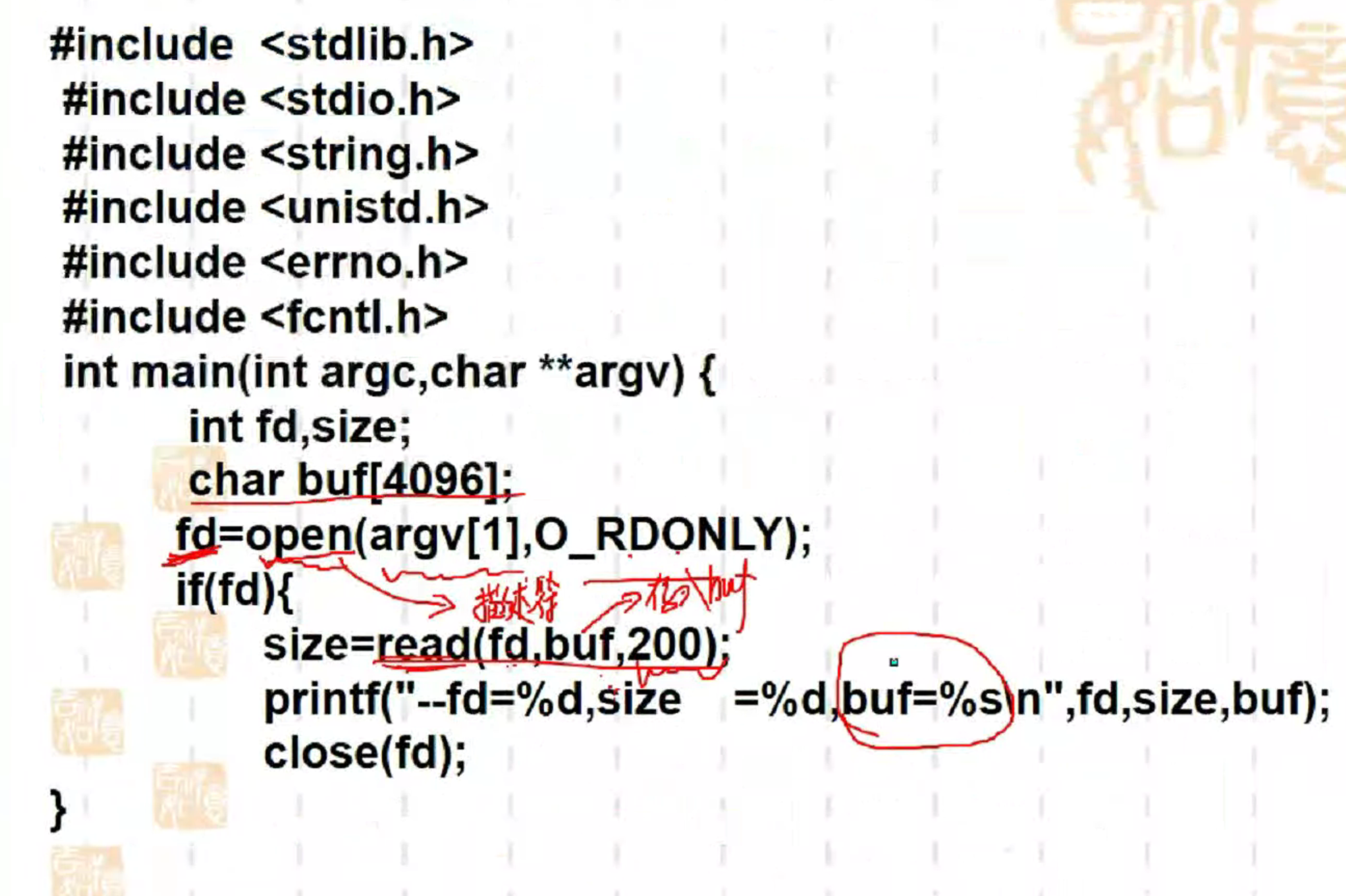


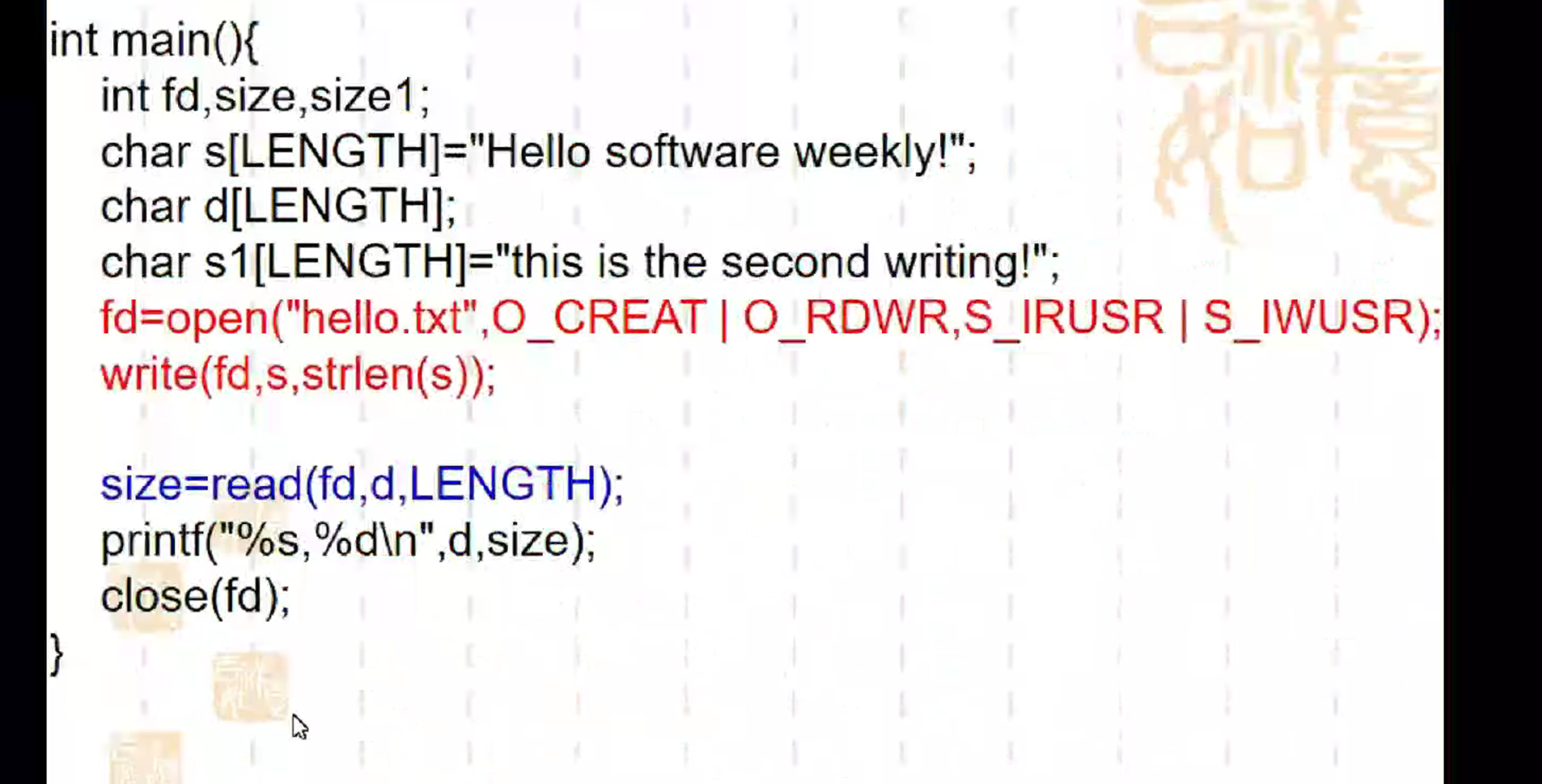
这里不能写完直接读,直接读会从文件末尾读,是读不到你写的东西的






让你从这个字符串里的第6个字符开始读起
让你改下面的基础上,让你单独把 software读出来
这样下面的 printf要输出 software

3. 设备控制



带缓冲前面加f,但是是c语言的库函数了
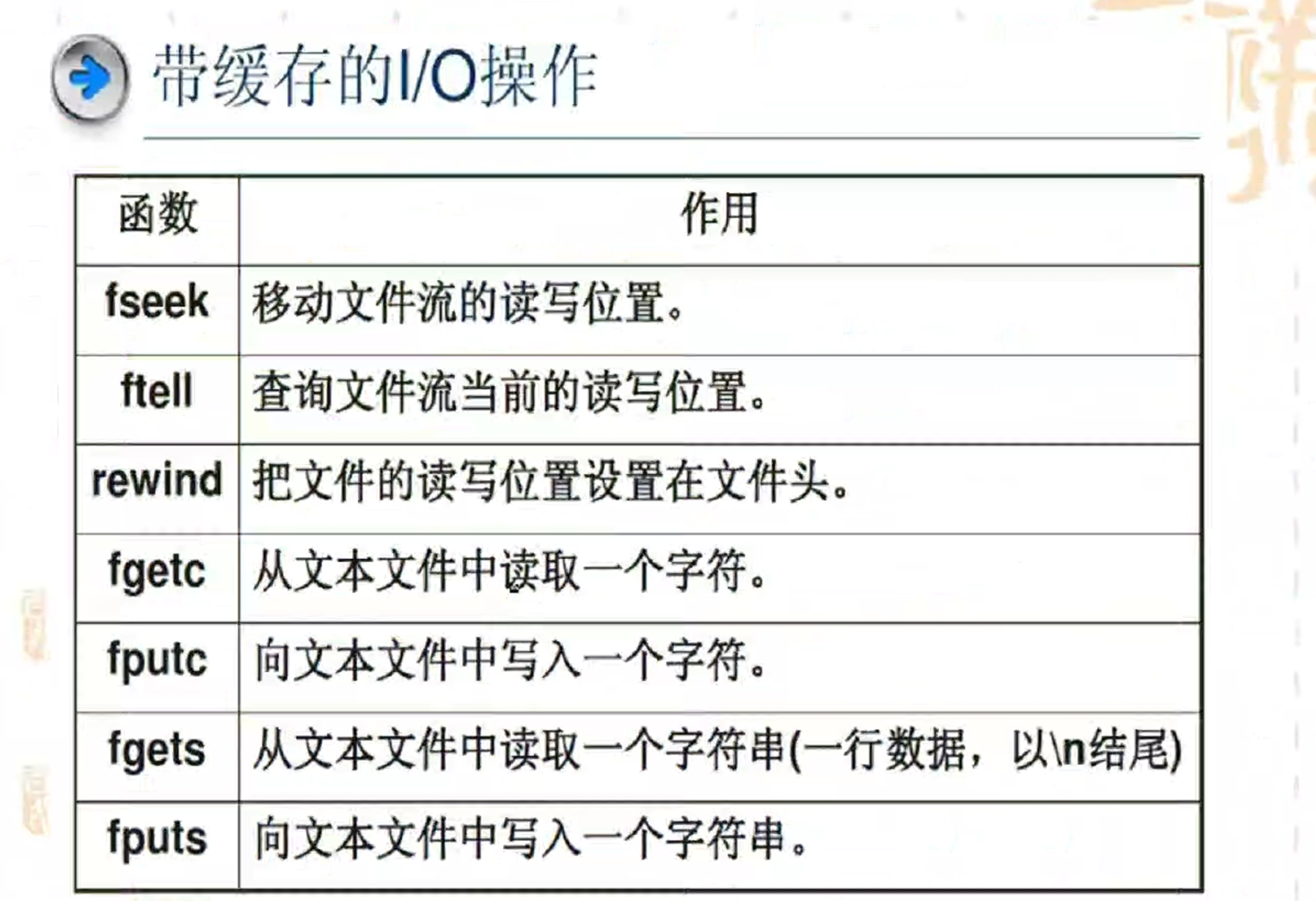

格式就和read()不太一样了

总结:其实就是讲了怎么调用函数,复习函数、实参的类型、数量、意义
学了哪些函数,功能是什么
第六章 进程控制
基本概念,重点是矜持编程

fork比较重要

返回两次!!



问:什么情况下输出某某某语句?



问你:这是执行啥操作呢?

执行那种可执行程序,或者命令


带p的可以写相对路径


这个程序最后怎么用
主要介绍的:fork system exec
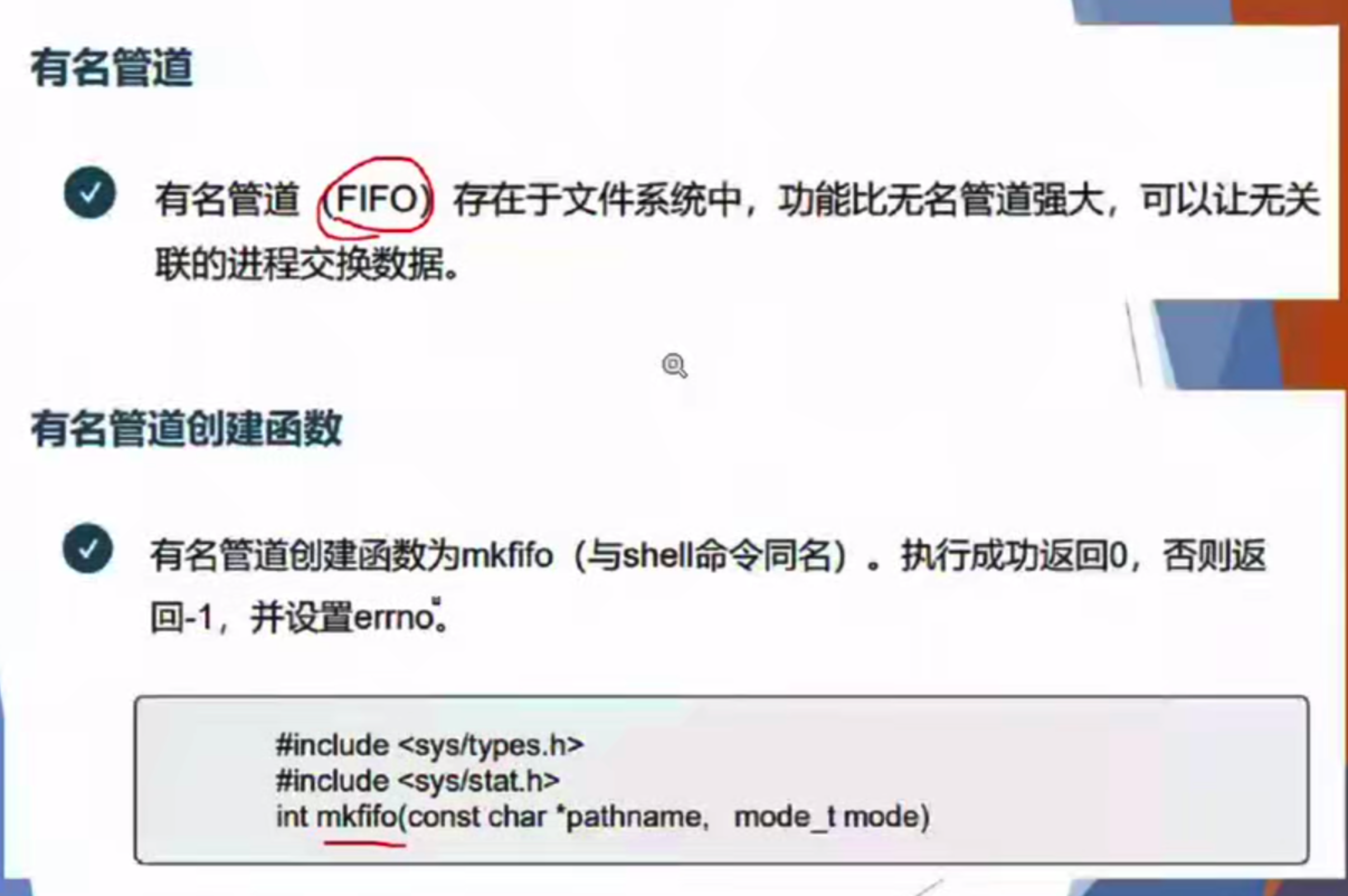
第七章 进程通信(重点)
基本概念

判断题和选择题⬇️


参数是一个数组 int filedes[2]:无名管道的一个“读”还有一个“写”
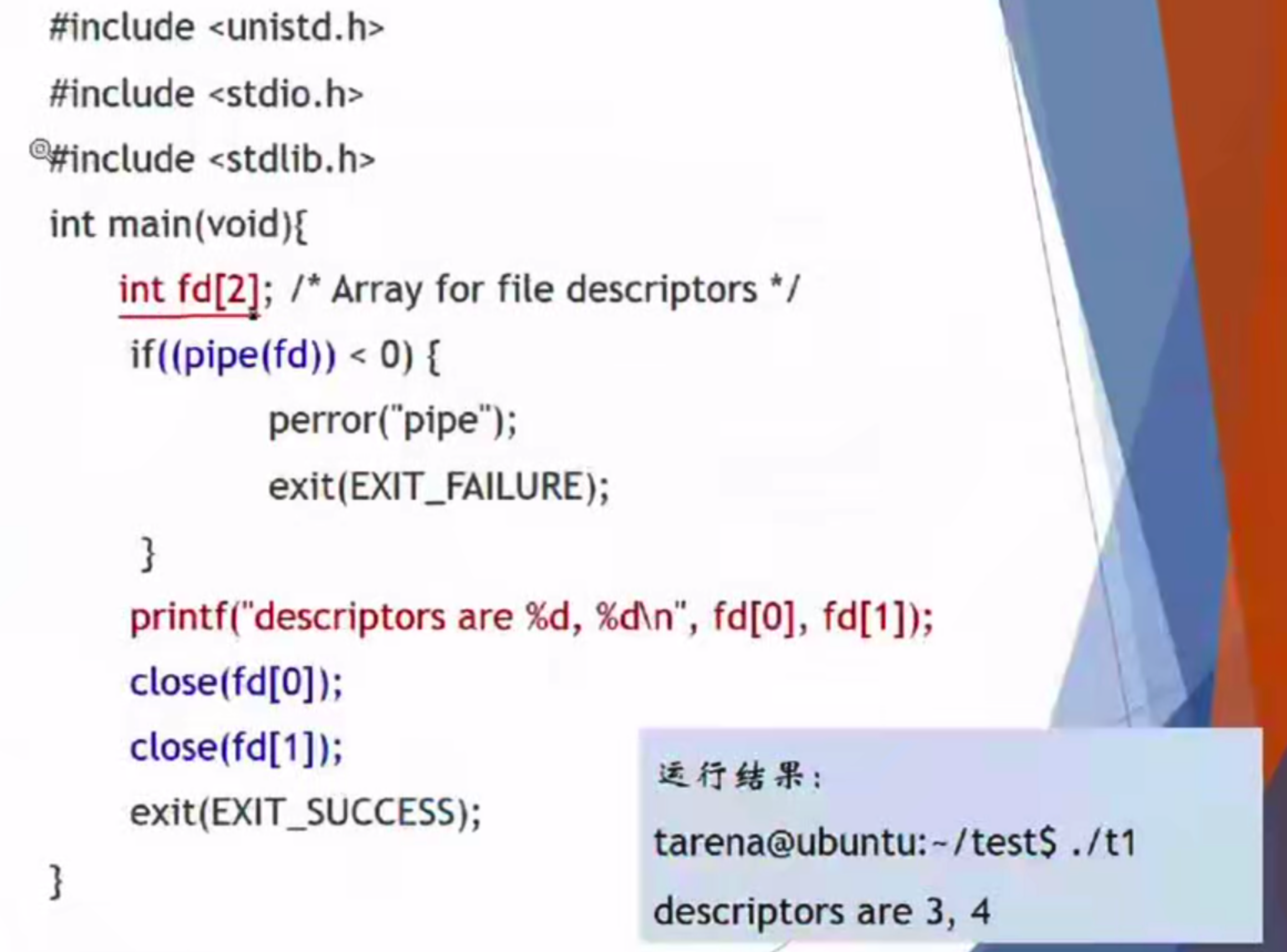
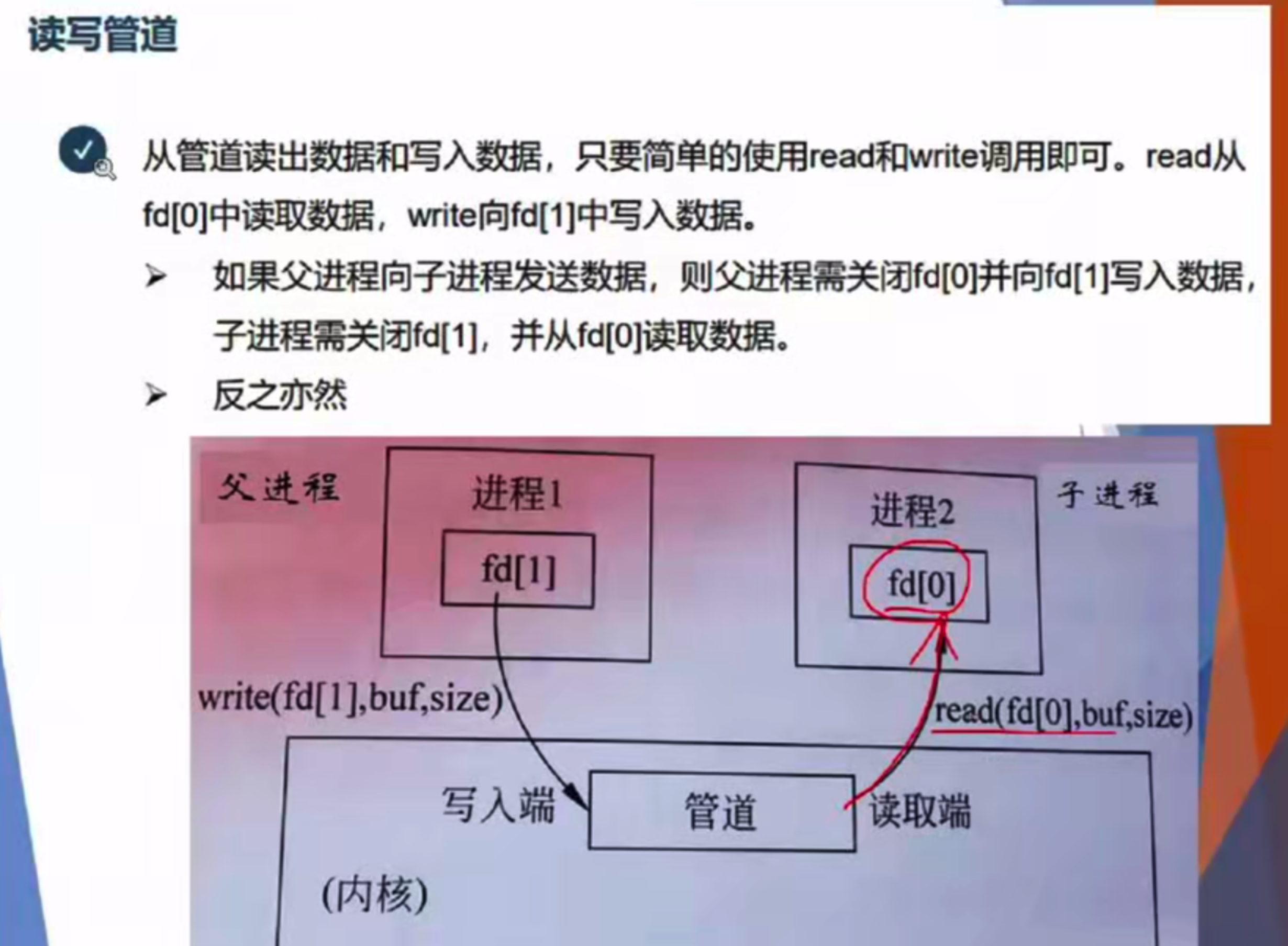
父进程一定要是写进程,子进程一定是读进程。
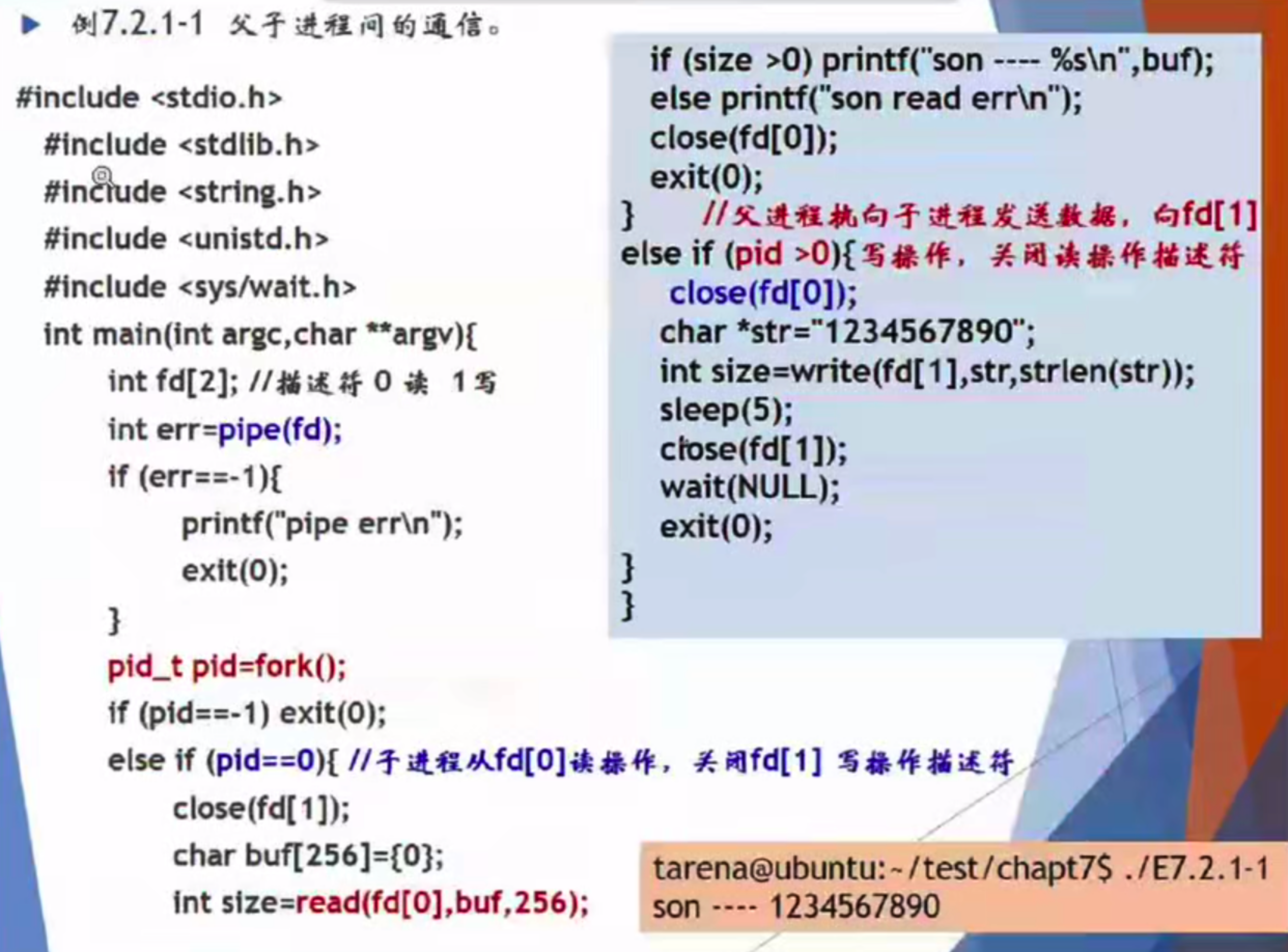
关键的pipe, read, wait 很重要,关键字一定要写。



















要会定义一个 消息的格式(结构体)(简答题、应用题)
创建一个消息队列,权限是0666,但是那个1234一定要强制类型转换!
msgrcv 还有 msgctl



some_data是个啥?而这个消息是一个结构体
strcpy的意思?:要把buf的值赋值给
strncmp的含义?





system("ipcs -m"); shell命令,查看我们所有的共享内存的。


这里的 shm_addr 通常是空的(代表系统自动选择)
还有 shmflg 权限一般都是空





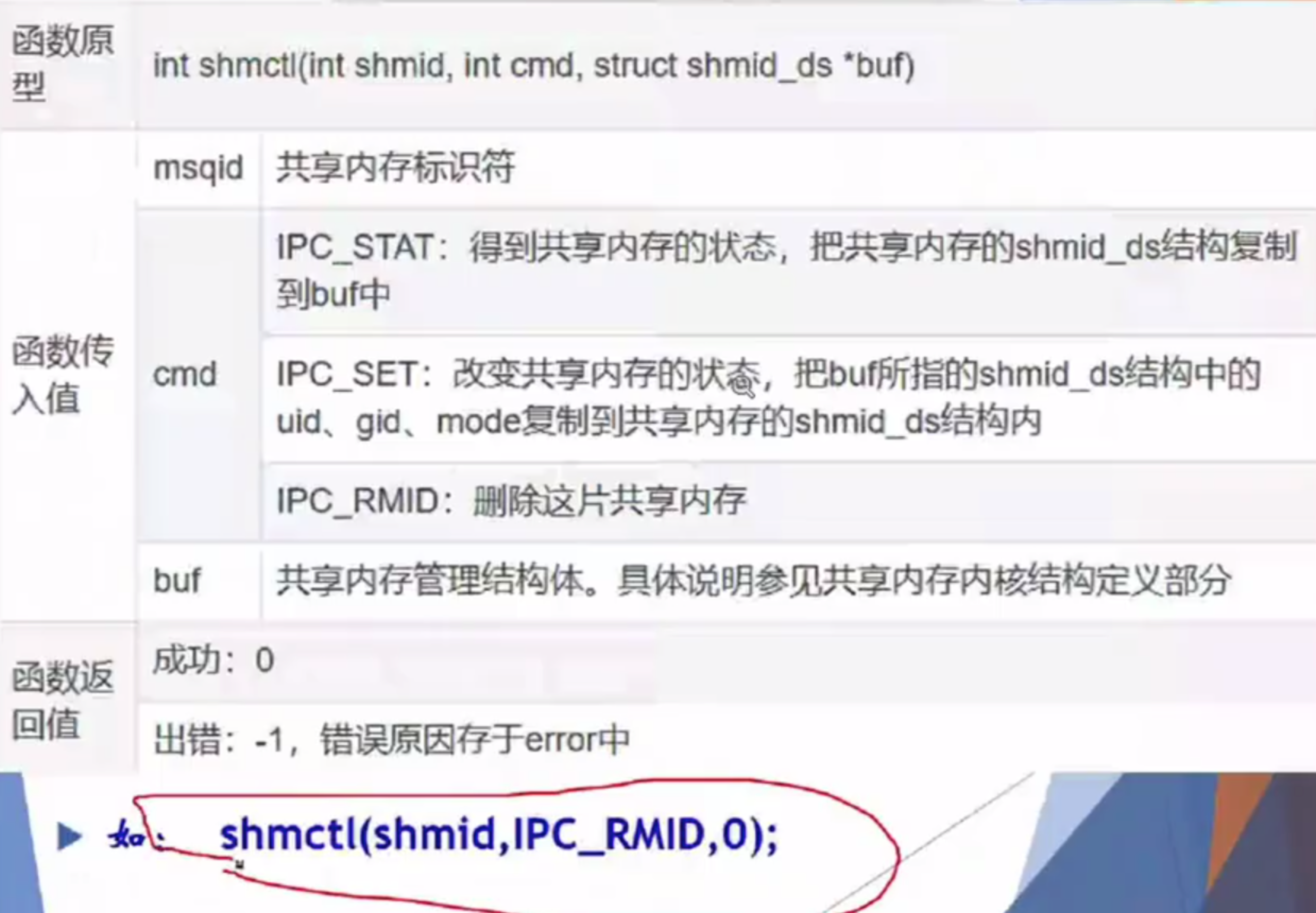
删除共享内存
第八章 线程





重要:pthread_join()的作用






第十章 内核
可能出简答题、填空题:
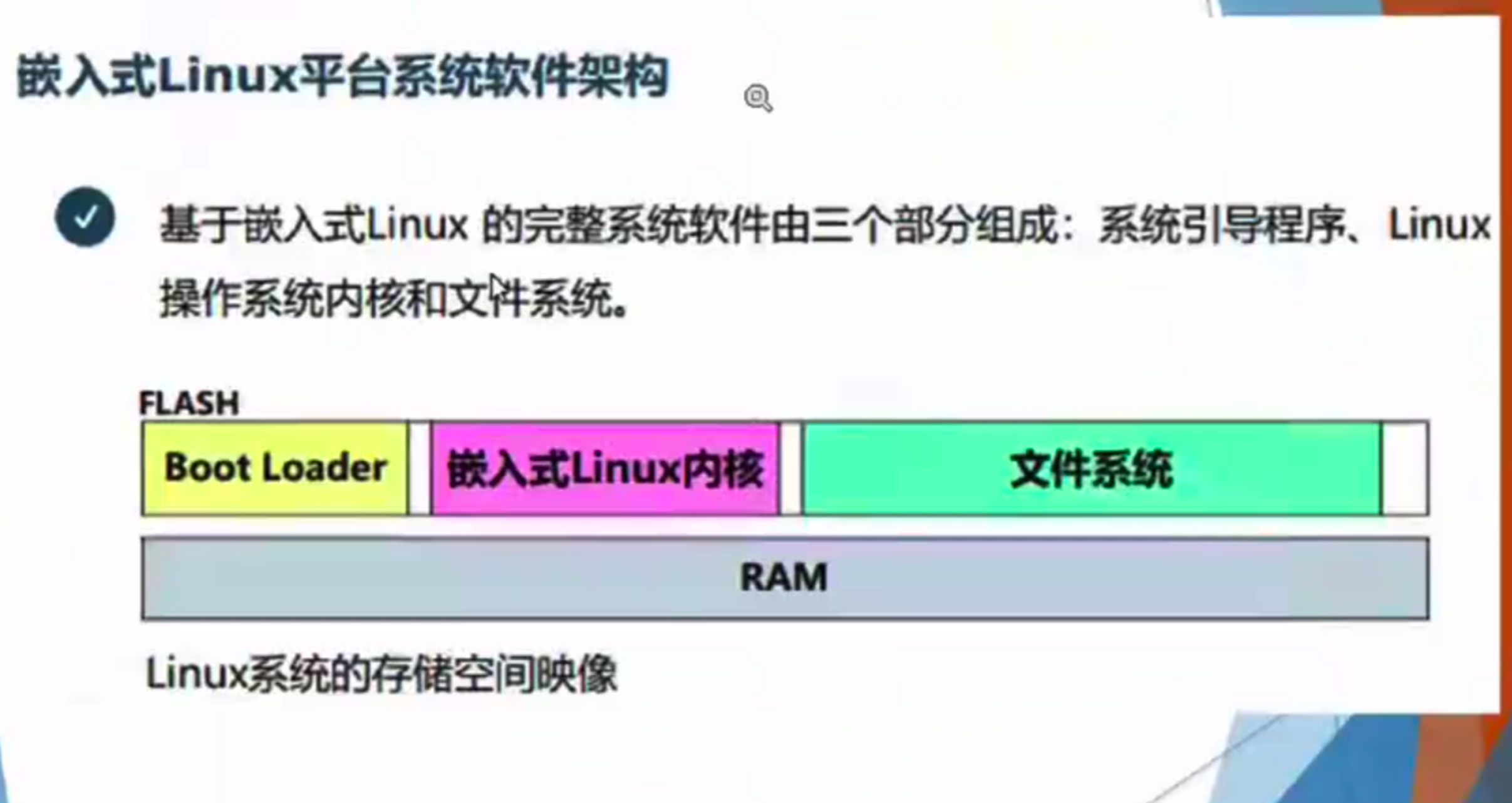

- arm-linux-gcc,在宿主机编译
- 在目标机上运行
三个构成:



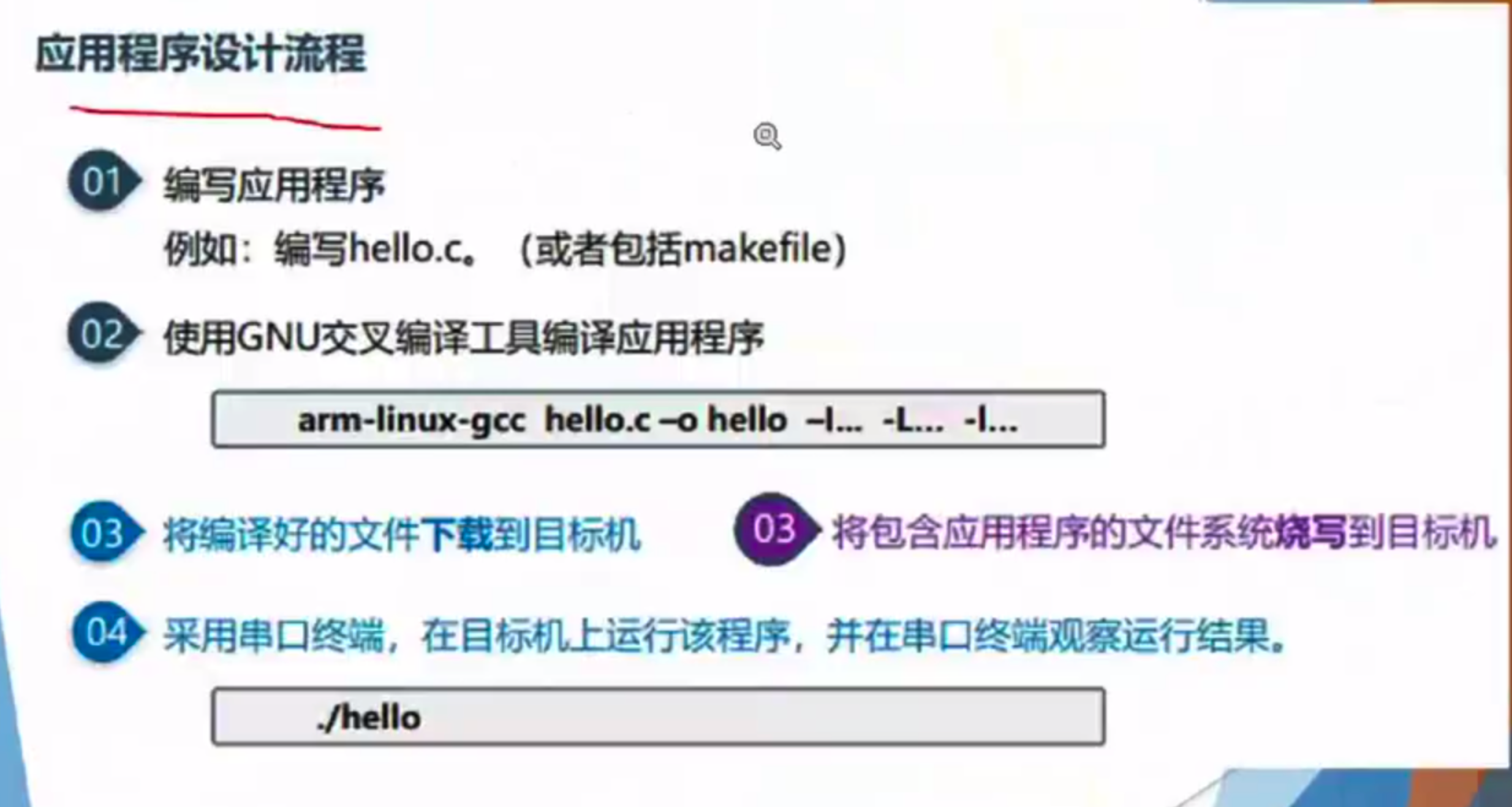

填空题、判断题:⬇️,容易出
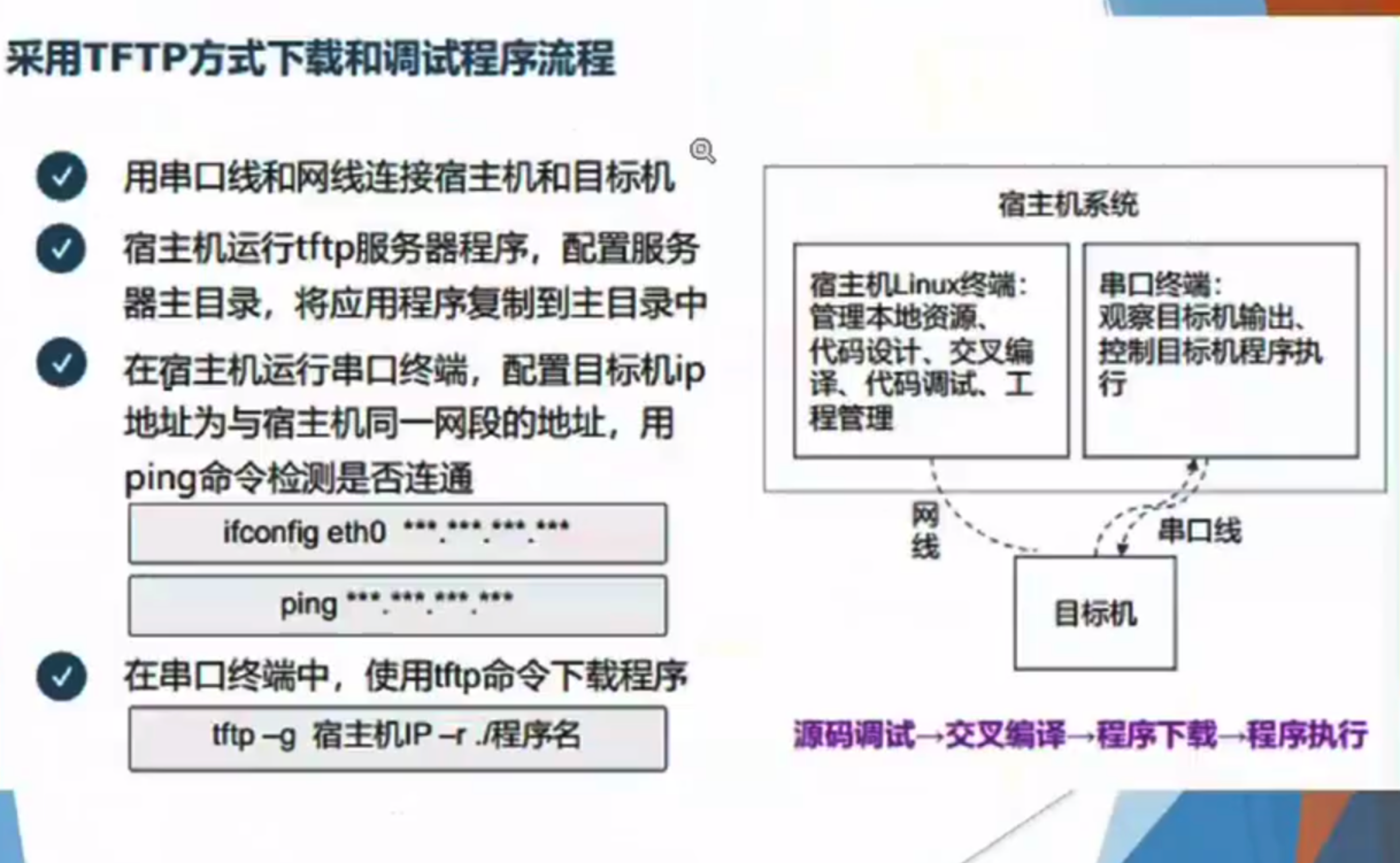

串口线:目标机的ip地址、
网线:下载、挂载

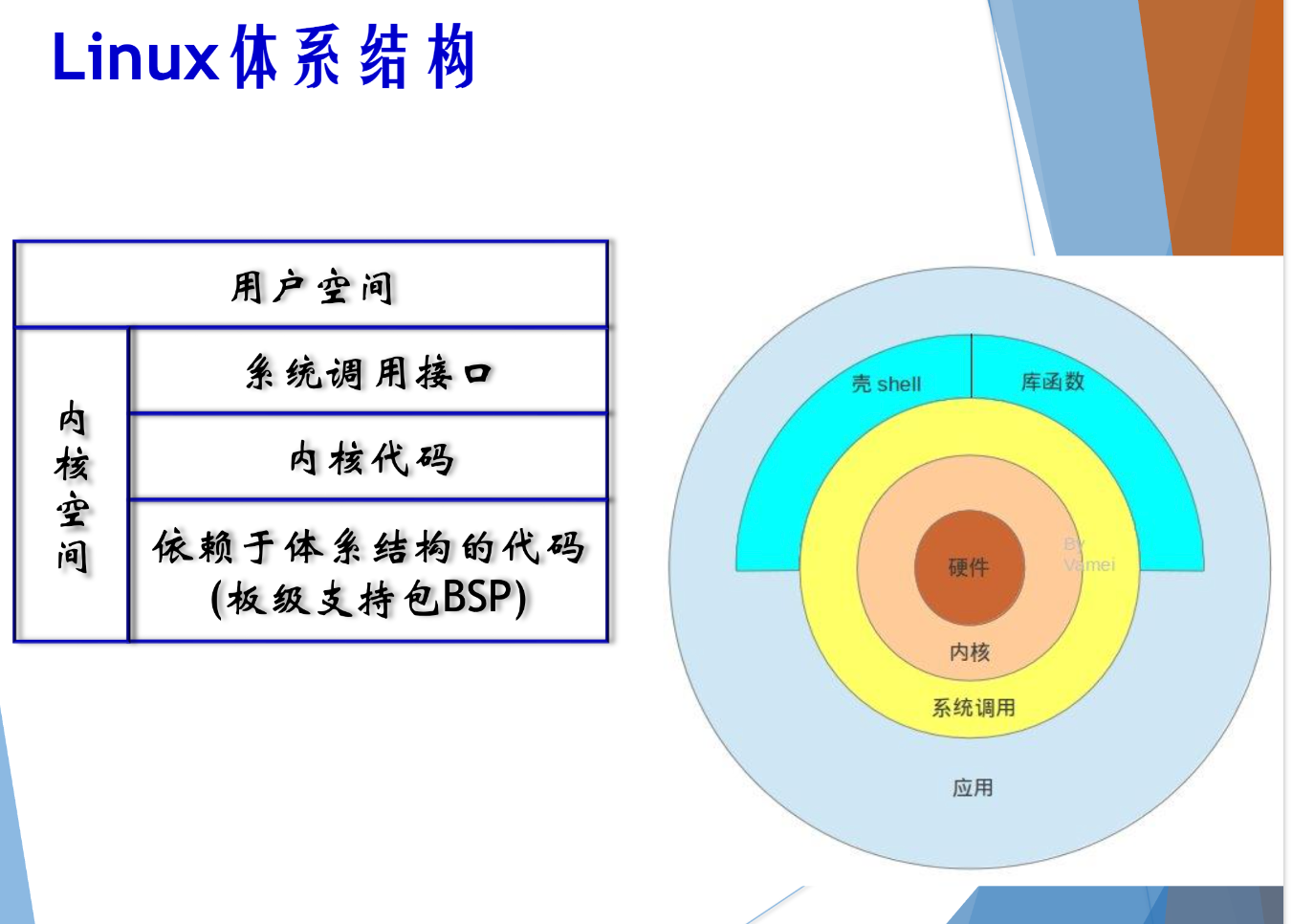
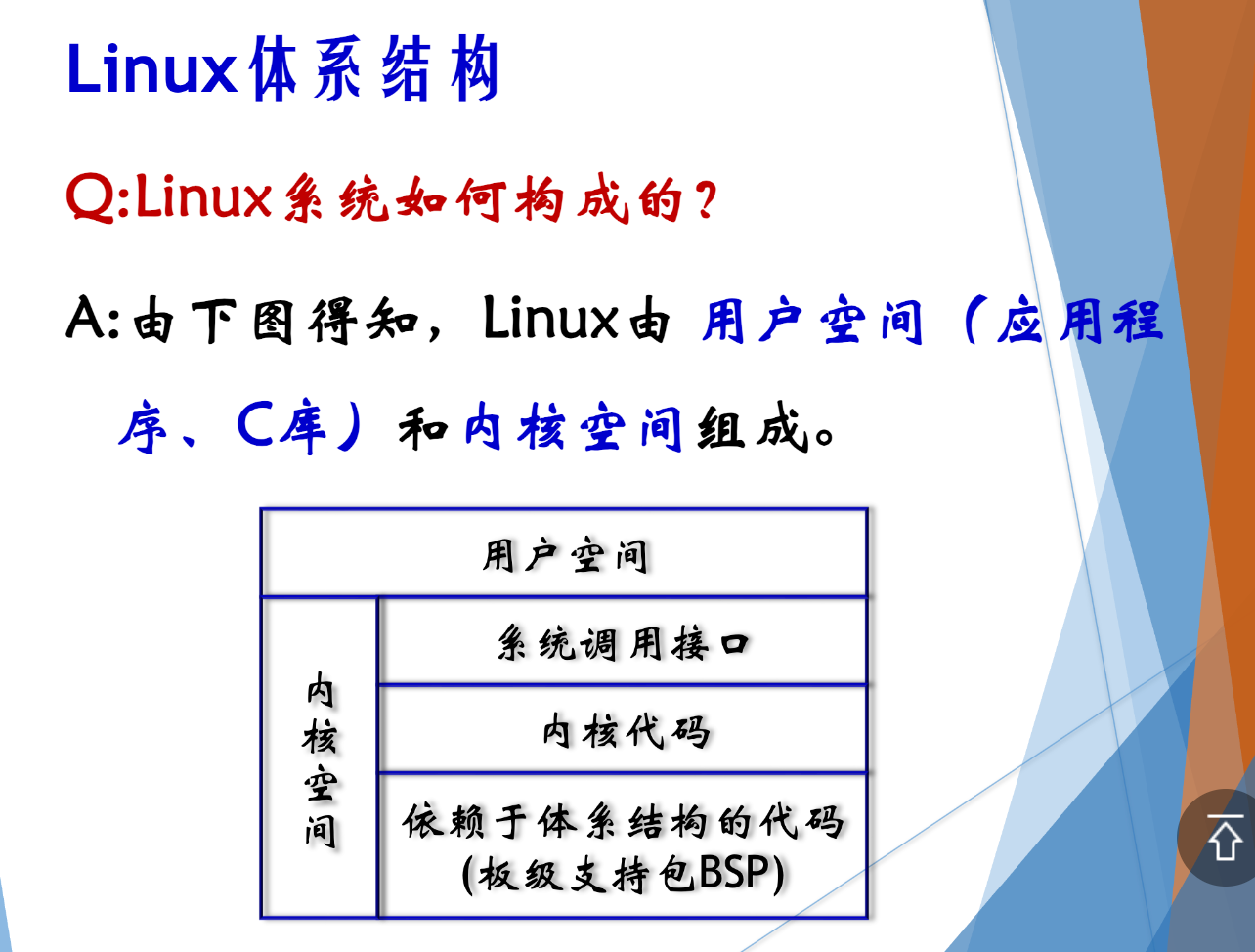

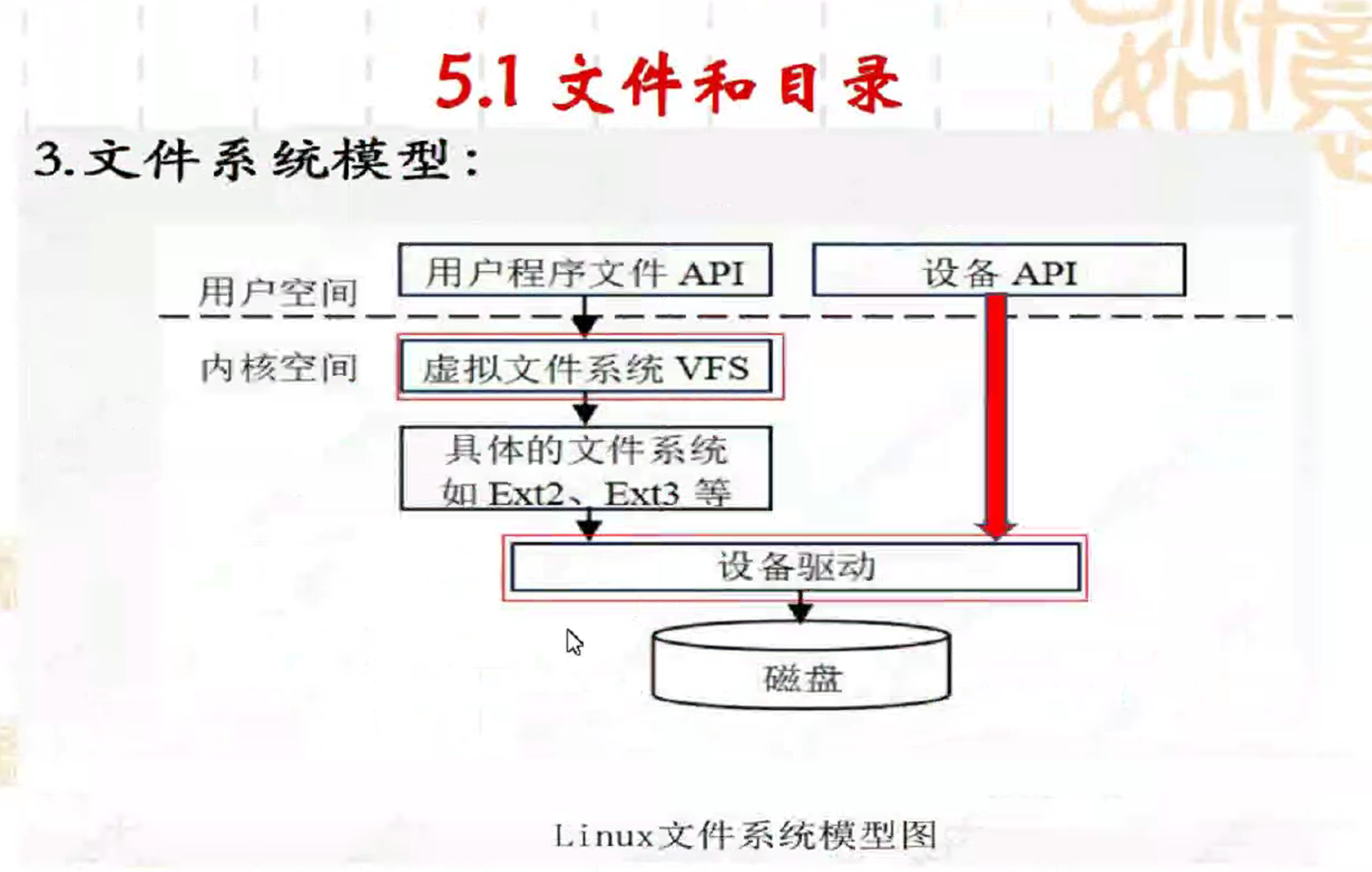
虚拟文件系统几层?
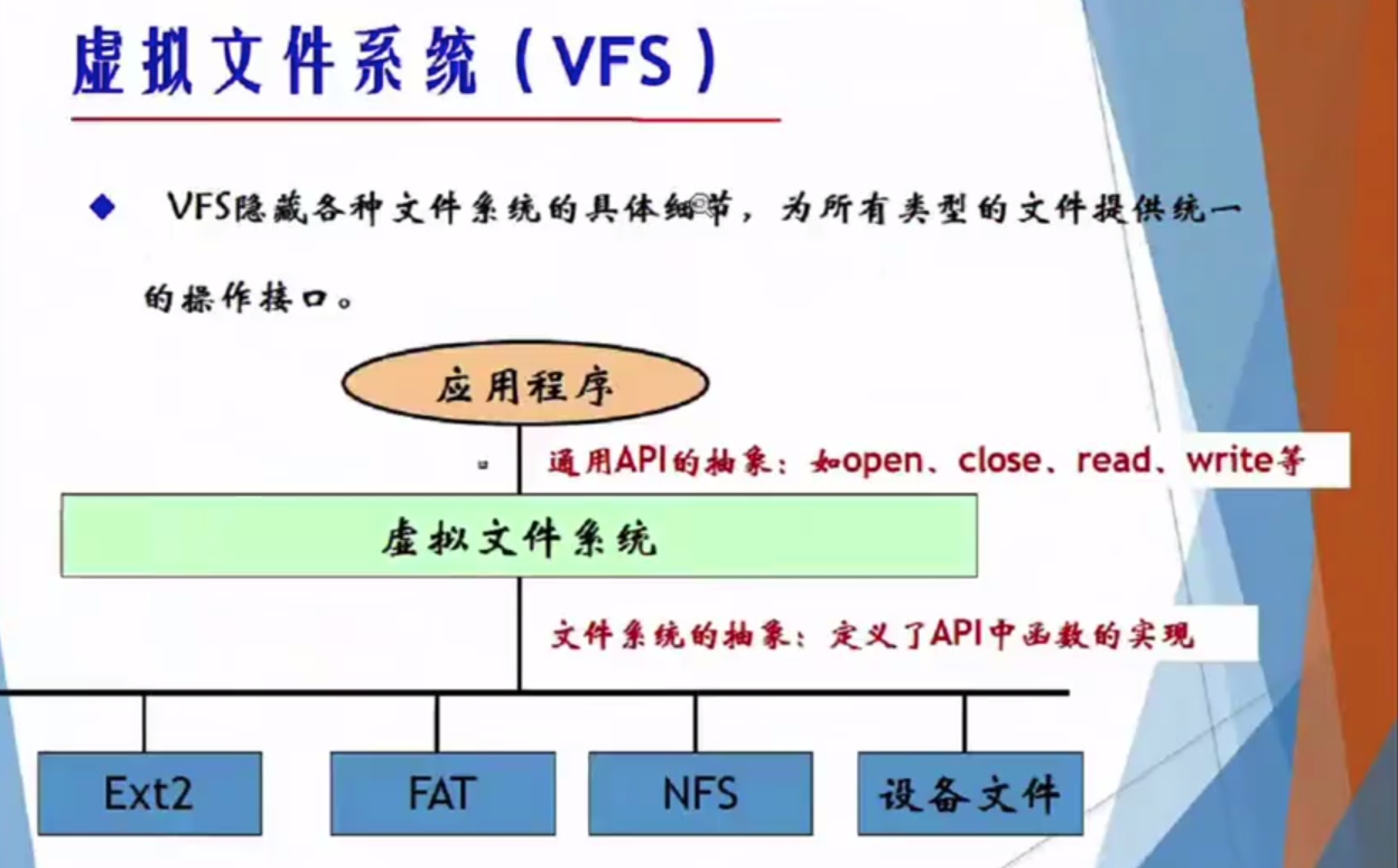
常用命令

Linux内核模块,有可能让大家写一个内核模块,然后加载上去。
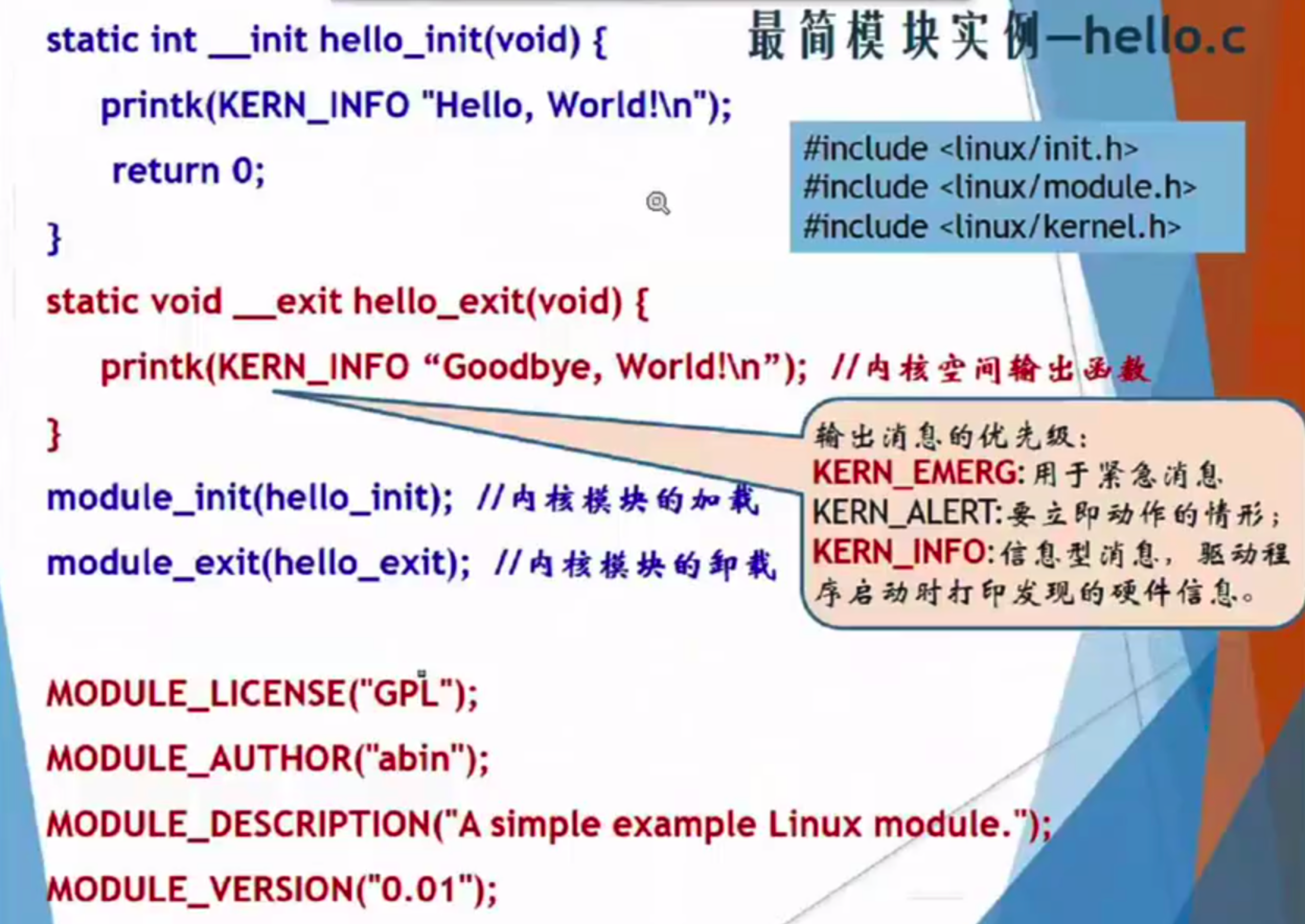
10分的大题,让大家写内核模块



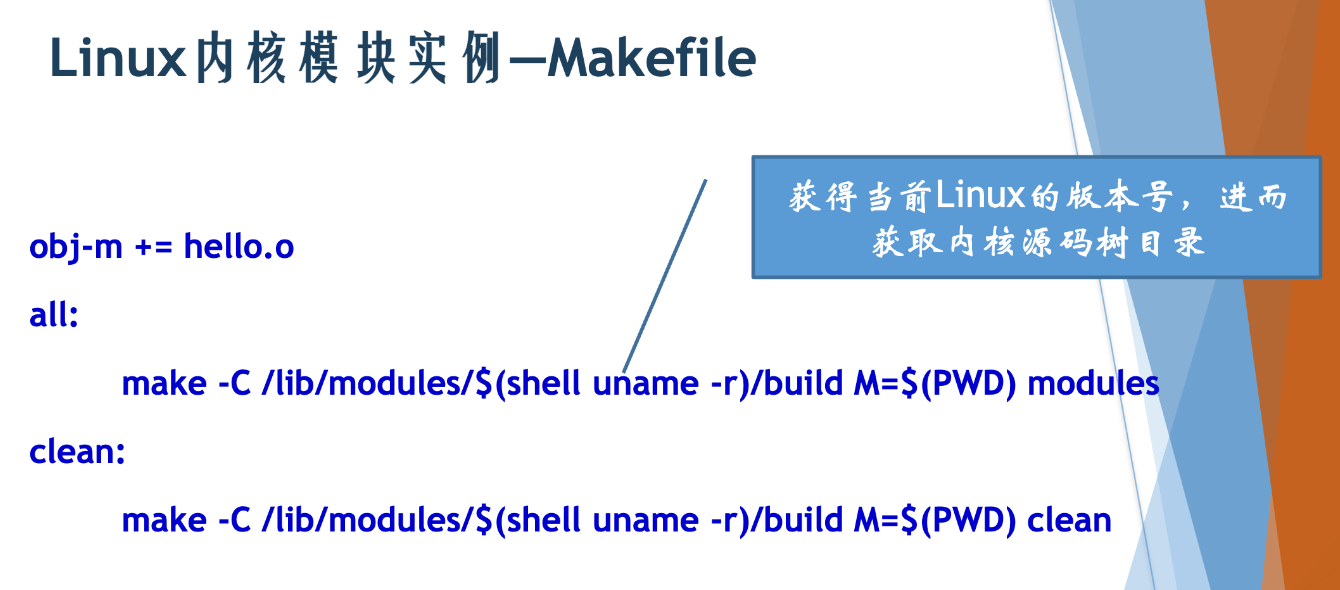

驱动开发