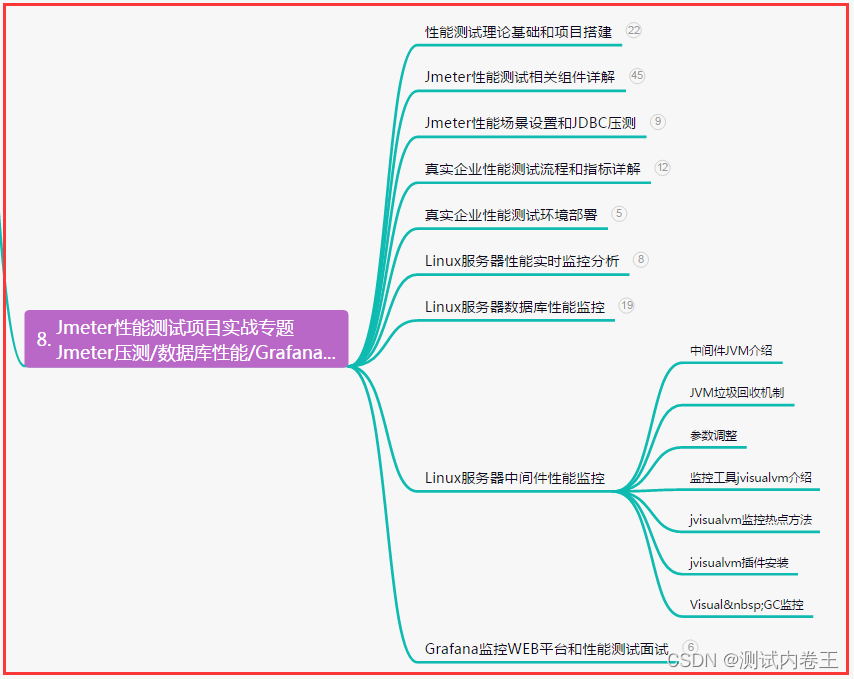
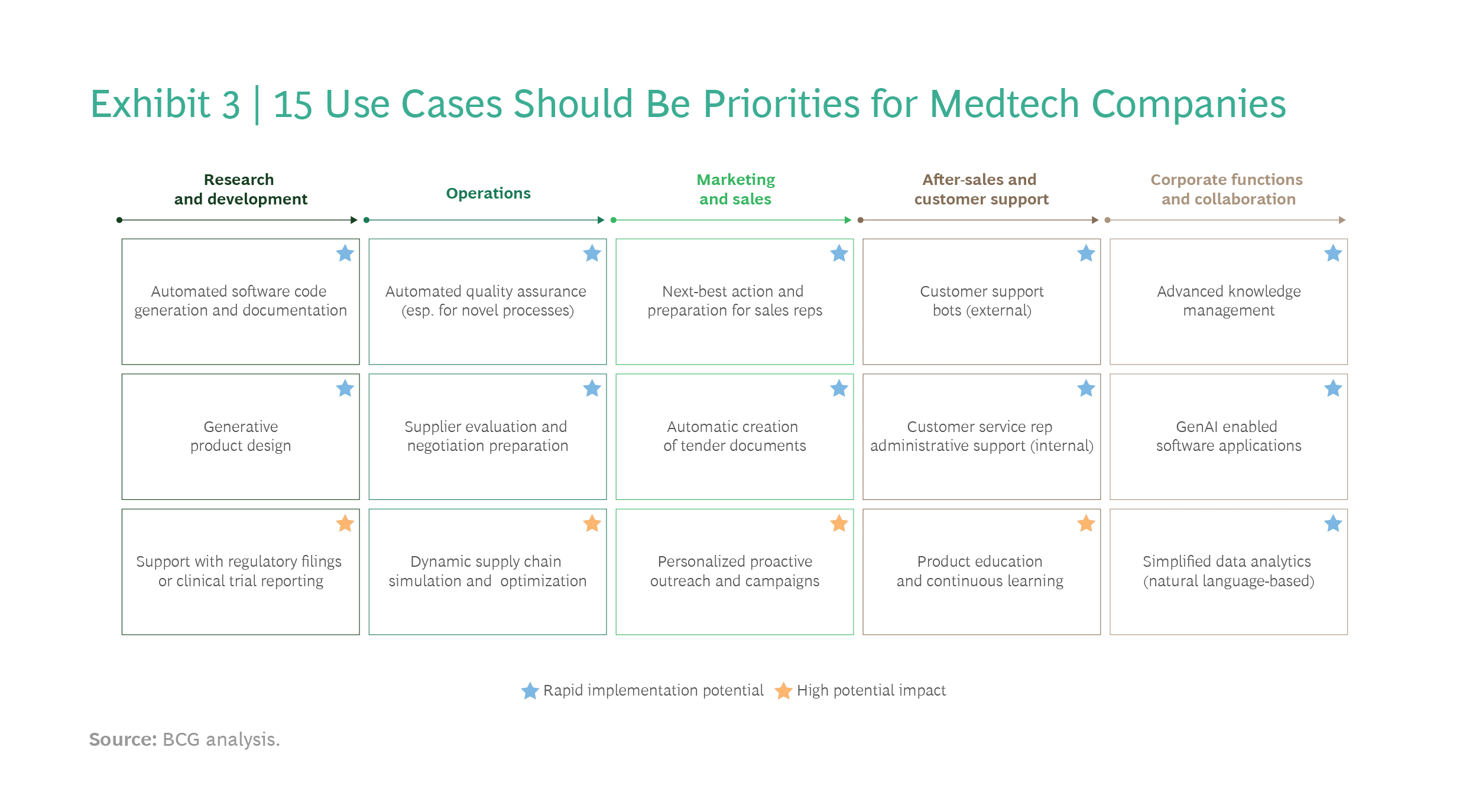
写在前面:
题目链接:LeetCode257. 二叉树的所有路径
题目难度:简单
编程语言:C++
一、题目描述
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
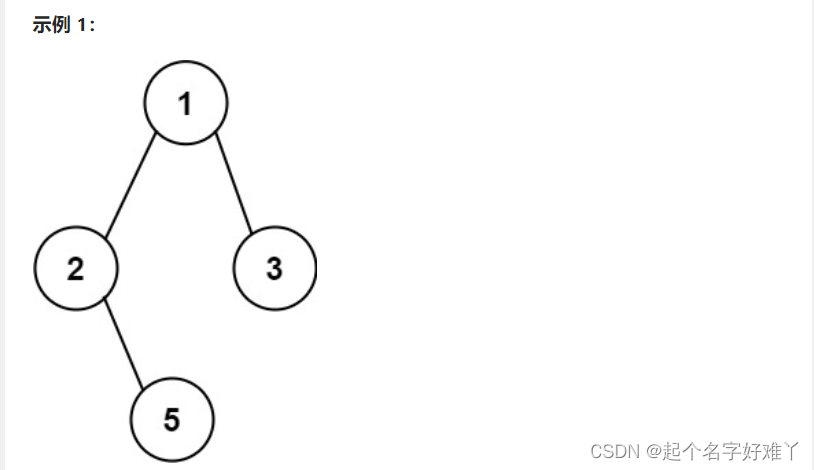
输入:root = [1,2,3,null,5]
输出:[“1->2->5”,“1->3”]
示例 2 :
输入:root = [1]
输出:[“1”]
二、题目分析&解题思路
由于是从回溯法里找了一道题,那么就话不多说直接上回溯
如果之前没有了解过回溯的可以先看看回溯的思路:
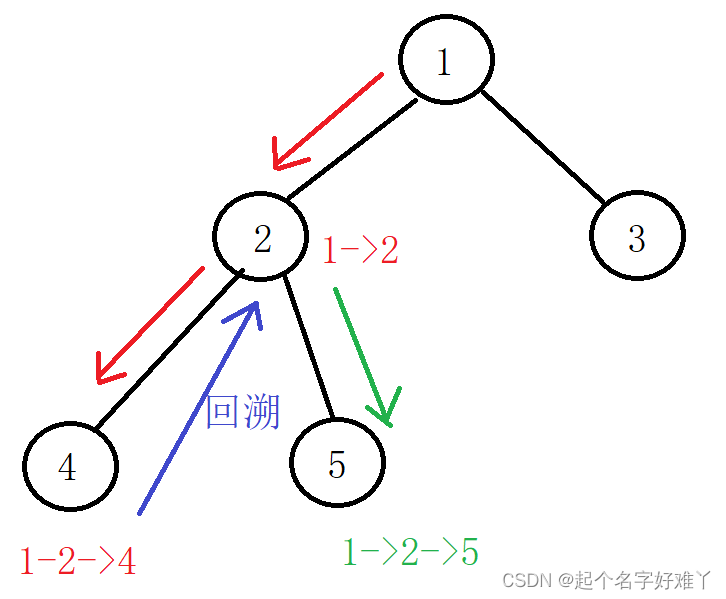
如果还是不太理解的话,可以参考下面这篇博客:
LeetCode.46. 全排列(回溯法入门)
不过每个节点的值需要从 int 转到 string
刚开始不知道 C++ 里面有专门 Int To string 的方法(大傻子本人了)
然后自己啥没写,先自己手写了一个 Int To string 的方法,感觉太傻了,各位献丑了:
vector<string> vctMap = {"0","1","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9"};
string IntToStr(int val)
{
if(val >=0 && val < 10)
{
return vctMap[val];
}
else if(val>-10 && val <0)
{
val = -val;
string strResult = "-" + vctMap[val];
return strResult;
}
else
{
bool isFushu = false;
if(val < 0)
{
isFushu = true;
val = -val;
}
//开始取每一位
string strResult = "";
while( val > 0)
{
int temp = val%10;
strResult.insert(0,vctMap[temp]);
val/=10;
}
if(isFushu)
{
strResult.insert(0, "-");
}
return strResult;
}
}
然后下面才是回溯的代码:
//回溯函数
void back(TreeNode* root, string strPath)
{
//终止条件
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr)
{
vctResult.push_back(strPath);
return;
}
//不断向递归终止条件逼近
//左
if(root->left != nullptr)
{
string strTemp = "->"+IntToStr(root->left->val);
strPath+=strTemp;
back(root->left, strPath);
//回溯 也就是把上一次的结果删除掉
strPath.resize(strPath.size() - strTemp.size());
}
//右
if(root->right != nullptr)
{
string strTemp = "->"+IntToStr(root->right->val);
strPath+=strTemp;
back(root->right, strPath);
//回溯
strPath.resize(strPath.size() - strTemp.size());
}
}
三、完整代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> vctResult;
string strPath = "";
vector<string> vctMap = {"0","1","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9"};
public:
//自己傻傻写的int to string 函数
string IntToStr(int val)
{
if(val >=0 && val < 10)
{
return vctMap[val];
}
else if(val>-10 && val <0)
{
val = -val;
string strResult = "-" + vctMap[val];
return strResult;
}
else
{
bool isFushu = false;
if(val < 0)
{
isFushu = true;
val = -val;
}
//开始取每一位
string strResult = "";
while( val > 0)
{
int temp = val%10;
strResult.insert(0,vctMap[temp]);
val/=10;
}
if(isFushu)
{
strResult.insert(0, "-");
}
return strResult;
}
}
//回溯函数
void back(TreeNode* root, string strPath)
{
//终止条件
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr)
{
vctResult.push_back(strPath);
return;
}
//不断向递归终止条件逼近
if(root->left != nullptr)
{
//保存每个路径上的节点值
string strTemp = "->"+IntToStr(root->left->val);
strPath+=strTemp;
back(root->left, strPath);
//回溯
strPath.resize(strPath.size() - strTemp.size());
}
if(root->right != nullptr)
{
//保存每个路径上的节点值
string strTemp = "->"+IntToStr(root->right->val);
strPath+=strTemp;
back(root->right, strPath);
//回溯
strPath.resize(strPath.size() - strTemp.size());
}
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)
{
return vctResult;
}
else
{
//先开始把根节点加上
strPath = IntToStr(root->val);
back(root, strPath);
return vctResult;
}
}
};
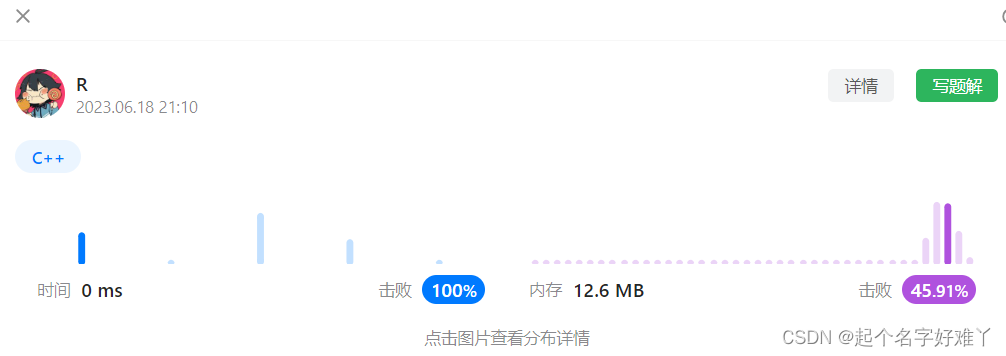
运行结果:
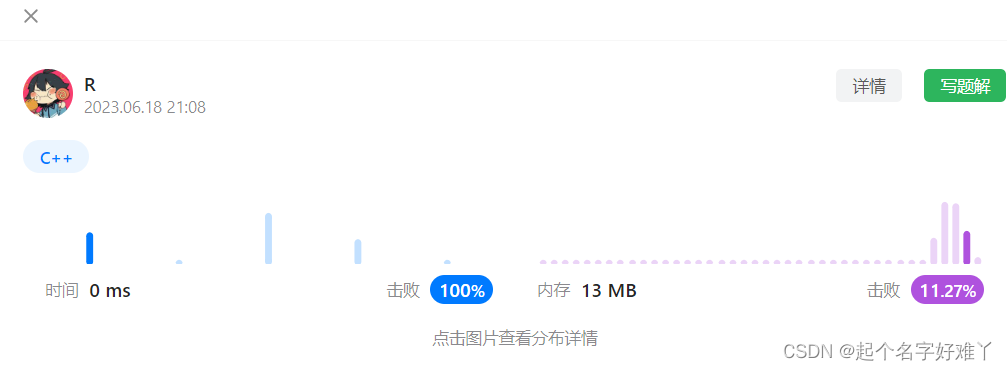
我们再使用c++ 自己的to_string 接口试试:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> vctResult;
string strPath = "";
public:
//回溯函数
void back(TreeNode* root, string strPath)
{
//终止条件
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr)
{
vctResult.push_back(strPath);
return;
}
//不断向递归终止条件逼近
//向左
if(root->left != nullptr)
{
string strTemp = "->"+to_string(root->left->val);
strPath+=strTemp;
back(root->left, strPath);
//回溯 也就是把上次的结果删除掉
strPath.resize(strPath.size() - strTemp.size());
}
//向右
if(root->right != nullptr)
{
string strTemp = "->"+to_string(root->right->val);
strPath+=strTemp;
back(root->right, strPath);
//回溯
strPath.resize(strPath.size() - strTemp.size());
}
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)
{
return vctResult;
}
else
{
//先开始把根节点加上
strPath = to_string(root->val);
back(root, strPath);
return vctResult;
}
}
};
运行结果: