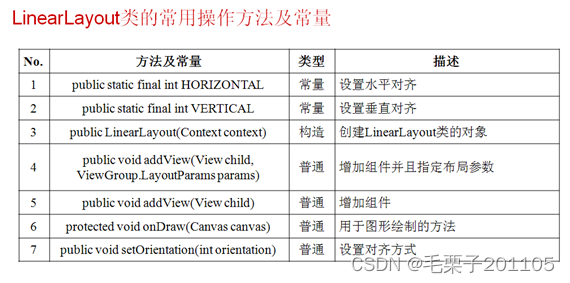
1. 线性布局管理器:LinearLayout
1.1 知识点
(1)布局管理器简介;
(2)线型布局管理器的配置;
(3)通过Activity程序进行线型布局
1.2 具体内容
在android中,只要定义了组件的话,这个组件就必须放在线性布局管理器中,另外一部分就是组件一般会存在事件处理操作。

先主要讲解线性布局管理器。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android=http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android—布局文件包含的是Android的命名空间
xmlns:tools=http://schemas.android.com/tools—命名空间的工具
android:layout_width="match_parent" –此布局宽度为全屏
android:layout_height="match_parent" – 此布局高度全屏
android:orientation="vertical"> --此布局中组件垂直码放
</LinearLayout>
线性布局管理器是android中最常用的布局管理器。

通过类的集成关系可以发现,线性布局管理器是一个特殊的组件,相比之前的组件来说,只是还可以放置其他的组件。

<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/but1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="爱科技有限公司" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/but2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="www.wanczy.com" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/but3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="毛栗子" />
</LinearLayout>
当然我们也可以通过Activity程序来配置我们的布局管理器,现在就不再使用布局文件了。
package com.example.linearlayoutproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
public class LinearLayoutActivity extends Activity {
private LinearLayout layout = null;
private Button but1 = null;
private Button but2 = null;
private Button but3 = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
this.layout = new LinearLayout(this);
LinearLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams =
new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
LinearLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);//准备布局管理器布局参数
this.layout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);//设置为垂直码放
this.layout.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);//设置布局参数
this.but1 = new Button(this);
this.but1.setText("爱科技有限公司");
this.but2 = new Button(this);
this.but2.setText("www.aikeji.com");
this.but3 = new Button(this);
this.but3.setText("毛栗子");
LinearLayout.LayoutParams butParams =
new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);//准备按钮布局参数
this.layout.addView(this.but1,butParams);
this.layout.addView(this.but2,butParams);
this.layout.addView(this.but3,butParams);
super.setContentView(layout);//此Activity程序使用的就是我们定义的布局管理器
}
}
以上程序就是使用Activity程序完成线性布局,没有使用任何的布局文件,但是在开发中,布局管理器一般都是需要配置在布局文件中。
1.3 小结
(1)线型布局有两种排列方式:水平和垂直
(2)可以通过LinearLayout 类定义线型布局,而布局参数可以使用LinearLayout.LayoutParams类完成。
2. 框架布局管理器:FrameLayout
2.1 知识点
(1)掌握框架布局管理器的使用特点;
(2)可以在布局管理器之中使用框架布局进行排列;
(3)可以使用FrameLayout和FrameLayout.LayoutParams类在Activity程序之中动态生成布局。
2.2 具体内容
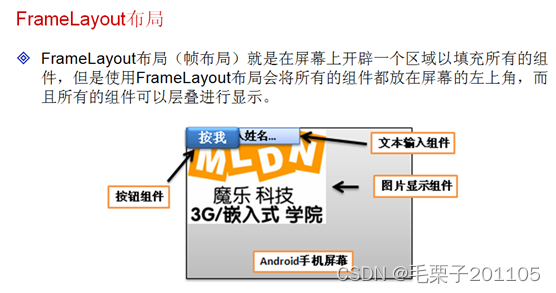
<FrameLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/android02" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="请输入您的姓名"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="你点我呀"
/>
</FrameLayout>
对于以上的程序来说,我们是感觉不到作用在哪里。

我们现在也可以不使用布局文件,而是直接在Activity程序中生成布局。
package com.example.framelayoutproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
import android.widget.ImageView;
public class FrameLayoutActivity extends Activity {
private FrameLayout layout = null;
private ImageView imgView = null;
private EditText editText = null;
private Button but = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
this.layout = new FrameLayout(this);
FrameLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams = new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
FrameLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
FrameLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);// 准备FrameLayout布局参数
this.layout.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);// 设置FrameLayout布局参数
this.imgView = new ImageView(this);
imgView.setImageResource(R.drawable.android02);// 设置图片组件要显示的图片
this.editText = new EditText(this);
this.editText.setText("请输入姓名:");
this.but = new Button(this);
this.but.setText("你点我呀");
// 准备组件的布局参数
FrameLayout.LayoutParams childParams = new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
FrameLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
FrameLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);//准备了组件的布局参数
this.layout.addView(this.imgView,childParams);
this.layout.addView(this.editText,childParams);
this.layout.addView(this.but,childParams);
setContentView(layout);
}
}
效果仍然是一样的,但是还是那句话,在以后的开发中,布局还是需要在布局文件中进行。很少写在Activity中。
2.3 小结
(1)框架布局是在一个指定的区域内使用组件进行填充;
(2)可以使用FrameLayout和FrameLayout.LayoutParams类手工配置布局。
3. 表格布局管理器:TableLayout
3.1 知识点
(1)掌握表格布局管理器的基本使用;
(2)掌握TableLayout和TableRow的操作关系;
(3)掌握表格布局管理器中常见属性的作用。
3.2 具体内容
一般在进行操作的时候,会经常使用到表格对数据进行排版,这样的好处在于阅读数据更加方便及美观。

范例:
<TableLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TableRow –表示行
android:orientation="horizontal"
>
<EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="请输入检索关键字"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="检索"
/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:orientation="horizontal"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="请选择编码"
/>
<RadioGroup
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:checkedButton="@+id/rb2"—默认选中rb2
>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rb1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="UTF编码"
/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rb2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="GBK编码"
/>
</RadioGroup>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
以上的程序只是实现了简单的排版,对于表格来说,除了一些基本的排版之外呢,显示数据也是用的比较多的。
<TableLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TableRow
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView
android:layout_column="0"—定义列号
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="ID"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_column="1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="姓名"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_column="2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Email"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_column="3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="地址"
/>
</TableRow>
<View –这边是定义一根横线
android:layout_height="2px"
android:background="#330033"
/>
<TableRow
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Wanczy"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_column="1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="爱科技"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_column="2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="888888@qq.com"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_column="3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="光明大道1号"
/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="MLZ"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_column="1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="毛栗子"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_column="2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="mlz_fc@163.com"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_column="3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="光明大道2号"
/>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
如果屏幕的宽度不够,显示不下,这个时候我们可以设置伸缩列。
<TableLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:shrinkColumns="3">--表示设置第3列为伸缩列
现在是设置了一列为伸缩列,那么想要设置多列呢?
<TableLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:shrinkColumns="0,1,2,3">--设置了4个伸缩列
除了可以设置伸缩列之外,还可以设置隐藏列。
<TableLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:shrinkColumns="3"
android:collapseColumns="0">--隐藏第0列
为表格设置背景。
<TableLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:shrinkColumns="3"
android:collapseColumns="0"
android:background="@drawable/background">--设置背景图片
从整个的代码来看,表格布局是非常灵活的,但是如果想要使用Activity程序去完成表格操作的话,那将是一个非常繁琐的一个过程。
package com.example.tablelayoutproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TableLayout;
import android.widget.TableRow;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class TableLayoutActivity extends Activity {
private String titleData[][] = new String[][] {
{ "ID", "姓名", "EMAIL", "地址" }, // 标题头
{ "爱科技", "888888@139.com","光明大道1号" },
{"毛栗子", "mlz_fc.com", "光明大道2号" } };// 显示数据
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TableLayout layout = new TableLayout(this); // 表格布局
TableLayout.LayoutParams layoutParam = new TableLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, // 布局管理器宽度为屏幕宽度
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);// 布局管理器高度为屏幕高度
layout.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.background);// 设置背景图片
for (int x = 0; x < this.titleData.length; x++) {
TableRow row = new TableRow(this); // 定义表格行
for (int y = 0; y < this.titleData[x].length; y++) {
TextView text = new TextView(this);// 创建文本组件
text.setText(this.titleData[x][y]); // 设置文本内容
row.addView(text, y); // 增加组件
}
layout.addView(row); // 增加表格行
}
super.setContentView(layout, layoutParam); // 定义组件
}
}
3.3 小结
(1)表格布局管理器使用TableRow控制表格行;
(2)表格布局的几个属性:
定义伸缩列:android:shrinkColumns="3"
设置不显示列:android:collapseColumns="0,3"
增加背景图片:android:background="@drawable/mldn_logo"
(3)表格布局也可以使用Activity程序动态生成。
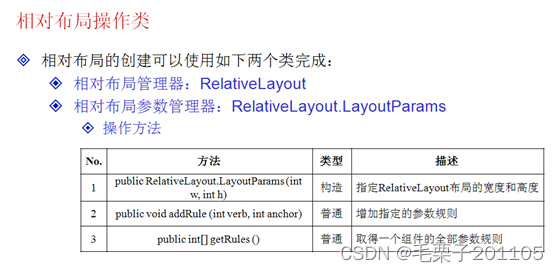
4. 相对布局管理器:RelativeLayout
4.1 知识点
(1)掌握相对布局管理器的主要特点及使用;
(2)可以使用Activity程序动态增加组件。
4.2 具体内容
相对布局管理器对于之前我们将的3种来说,用的会比较少,但是我们还是需要了解,相对布局就是以一个组件作为参照物,放在其上下左右,或者以其为对其方式的参考。

<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="这是一个文本显示组件" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/but"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="这是一个按钮"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/text"--放在text组件的右边
android:layout_below="@+id/text"/>--放在text组件的下边
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/img"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/text"—放在text组件的右边
android:layout_above="@+id/but"—放在but组件的上边
/>
</RelativeLayout>
以上的程序都是通过布局文件进行配置的,当然也可以通过程序控制相对布局管理器。
package com.example.relativelayoutproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
public class RelativeLayoutActivity extends Activity {
private RelativeLayout layout = null;
private Button but2 = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.activity_relative_layout);
this.layout = (RelativeLayout)super.findViewById(R.id.mylayout);
this.but2 = new Button(this);
this.but2.setText("我也是一个按钮");
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams butParams = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);//准备组件布局参数
butParams.addRule(RelativeLayout.LEFT_OF, R.id.img);//添加规则放在text组件的右边
butParams.addRule(RelativeLayout.BELOW, R.id.text);//添加规则放在text组件的下边
this.layout.addView(this.but2,butParams);//加入组件
}
}
4.3 小结
(1)相对布局管理器是以一个组件进行定位的参考;
(2)使用RelativeLayout和RelativeLayout.LayoutParams类可以在Activity程序中动态配置布局管理器。