文章目录
前言
只是为方便学习,不做其他用途,
一、
1 组总刚main文件的断点
//=============================================//
// Assembling & solving //
//=============================================//
// creating assembler
gsElasticityAssembler<real_t> assembler(geometry, basis, bcInfo, g);
assembler.options().setReal("YoungsModulus", youngsModulus);
assembler.options().setReal("PoissonsRatio", poissonsRatio);
gsInfo << "Assembling...\n";
gsStopwatch clock;
clock.restart();
assembler.assemble();
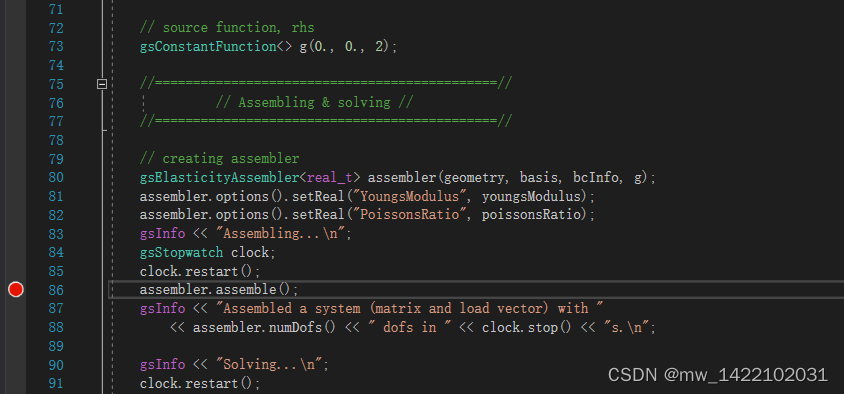
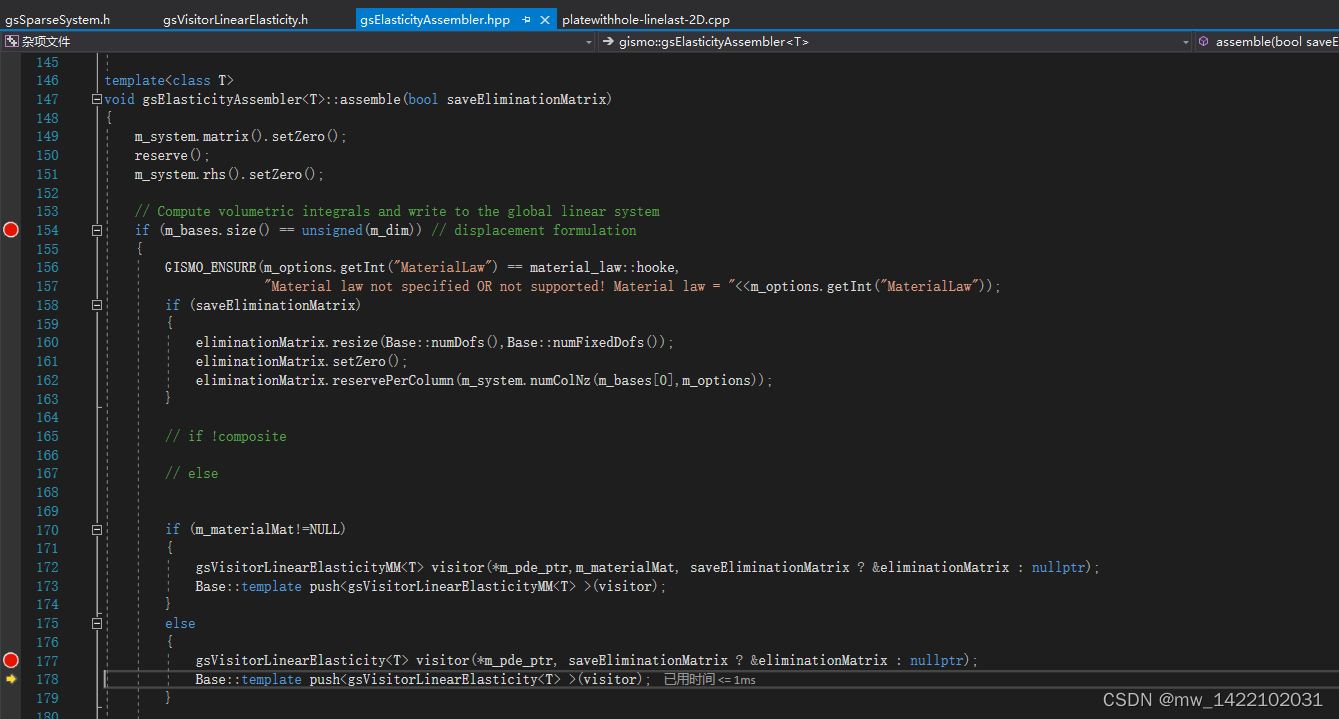
2 跳转到gsElasticityAssembler.hpp
147行:gsElasticityAssembler::assemble(bool saveEliminationMatrix)函数
//--------------------- SYSTEM ASSEMBLY ----------------------------------//
template<class T>
void gsElasticityAssembler<T>::assemble(bool saveEliminationMatrix)
{
m_system.matrix().setZero();
reserve();
m_system.rhs().setZero();
// Compute volumetric integrals and write to the global linear system计算体积积分并写入全局线性系统
if (m_bases.size() == unsigned(m_dim)) // displacement formulation
{
GISMO_ENSURE(m_options.getInt("MaterialLaw") == material_law::hooke,
"Material law not specified OR not supported! Material law = "<<m_options.getInt("MaterialLaw"));
if (saveEliminationMatrix)
{
eliminationMatrix.resize(Base::numDofs(),Base::numFixedDofs());
eliminationMatrix.setZero();
eliminationMatrix.reservePerColumn(m_system.numColNz(m_bases[0],m_options));
}
// if !composite
// else
if (m_materialMat!=NULL)
{
gsVisitorLinearElasticityMM<T> visitor(*m_pde_ptr,m_materialMat, saveEliminationMatrix ? &eliminationMatrix : nullptr);
Base::template push<gsVisitorLinearElasticityMM<T> >(visitor);
}
else
{
gsVisitorLinearElasticity<T> visitor(*m_pde_ptr, saveEliminationMatrix ? &eliminationMatrix : nullptr);
Base::template push<gsVisitorLinearElasticity<T> >(visitor);
}
if (saveEliminationMatrix)
{
Base::rhsWithZeroDDofs = m_system.rhs();
eliminationMatrix.makeCompressed();
}
}
else // mixed formulation (displacement + pressure)
{
GISMO_ENSURE(m_options.getInt("MaterialLaw") == material_law::mixed_hooke,
"Material law not specified OR not supported!");
gsVisitorMixedLinearElasticity<T> visitor(*m_pde_ptr);
Base::template push<gsVisitorMixedLinearElasticity<T> >(visitor);
}
// Compute surface integrals and write to the global rhs vector
Base::template push<gsVisitorElasticityNeumann<T> >(m_pde_ptr->bc().neumannSides());
m_system.matrix().makeCompressed();
}
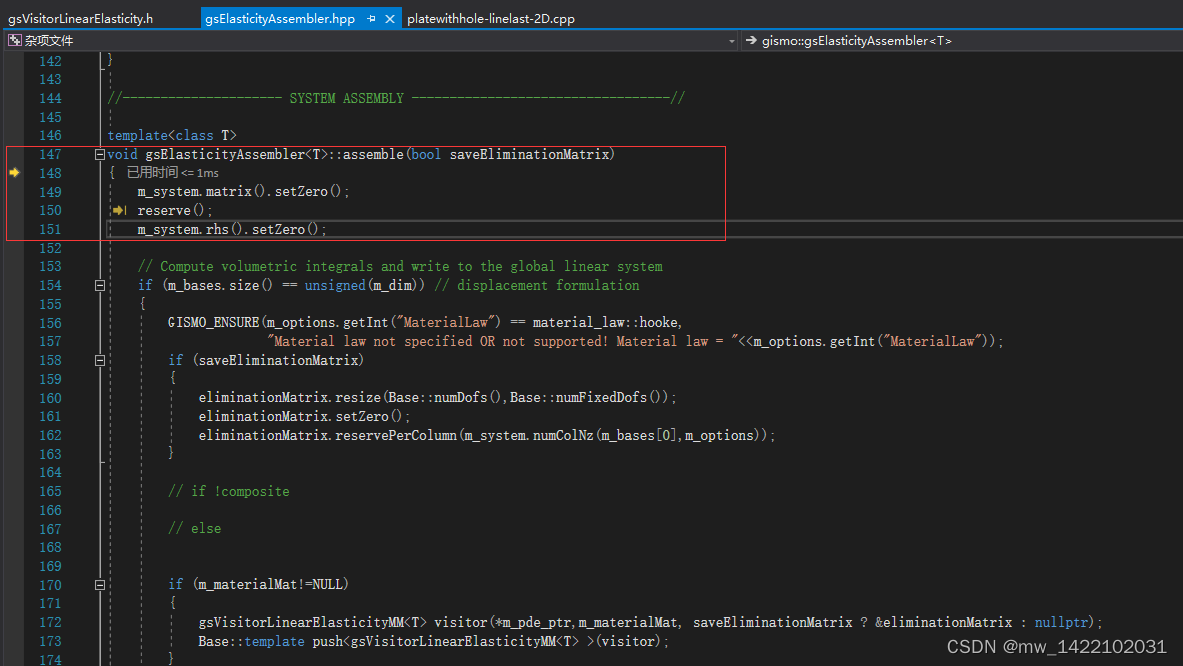
3 gsElasticityAssembler.hpp的177行进入gsVisitorLinearElasticity.h
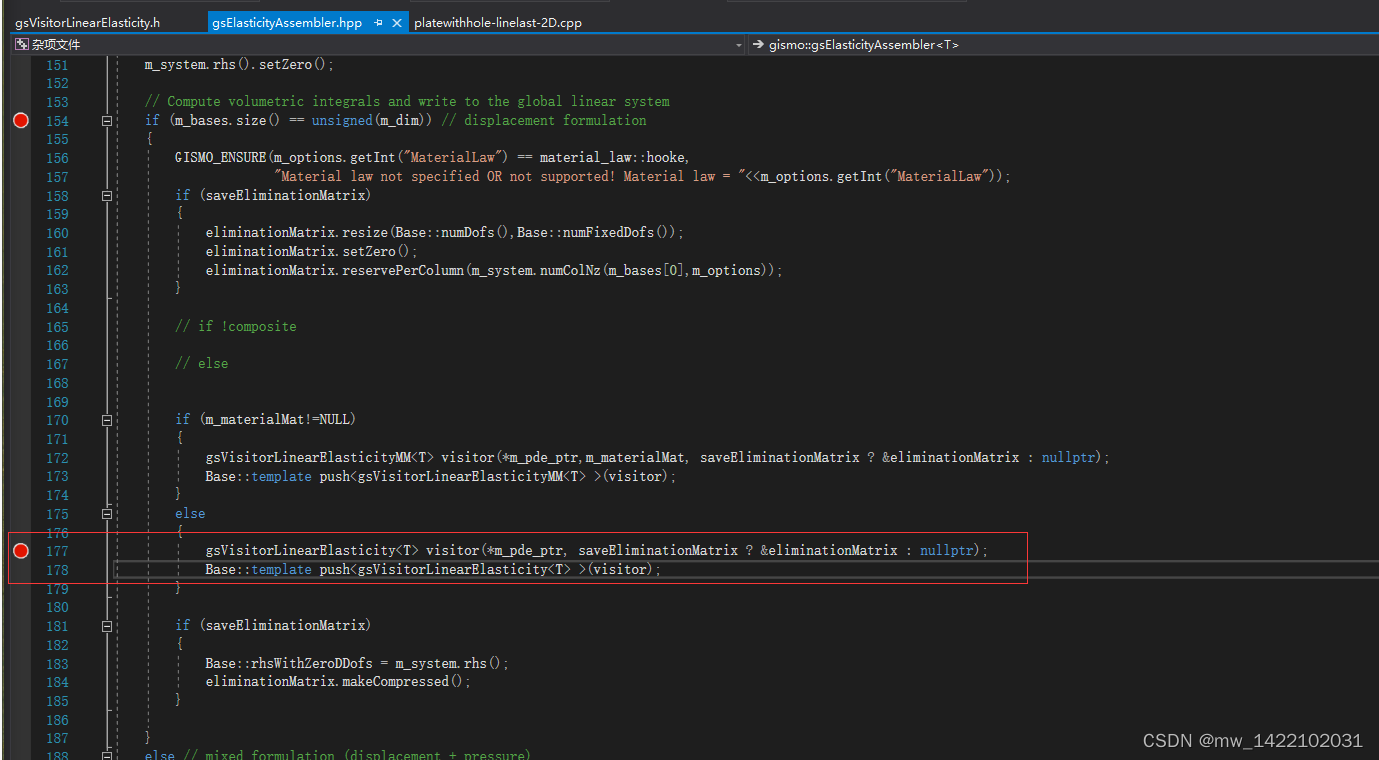
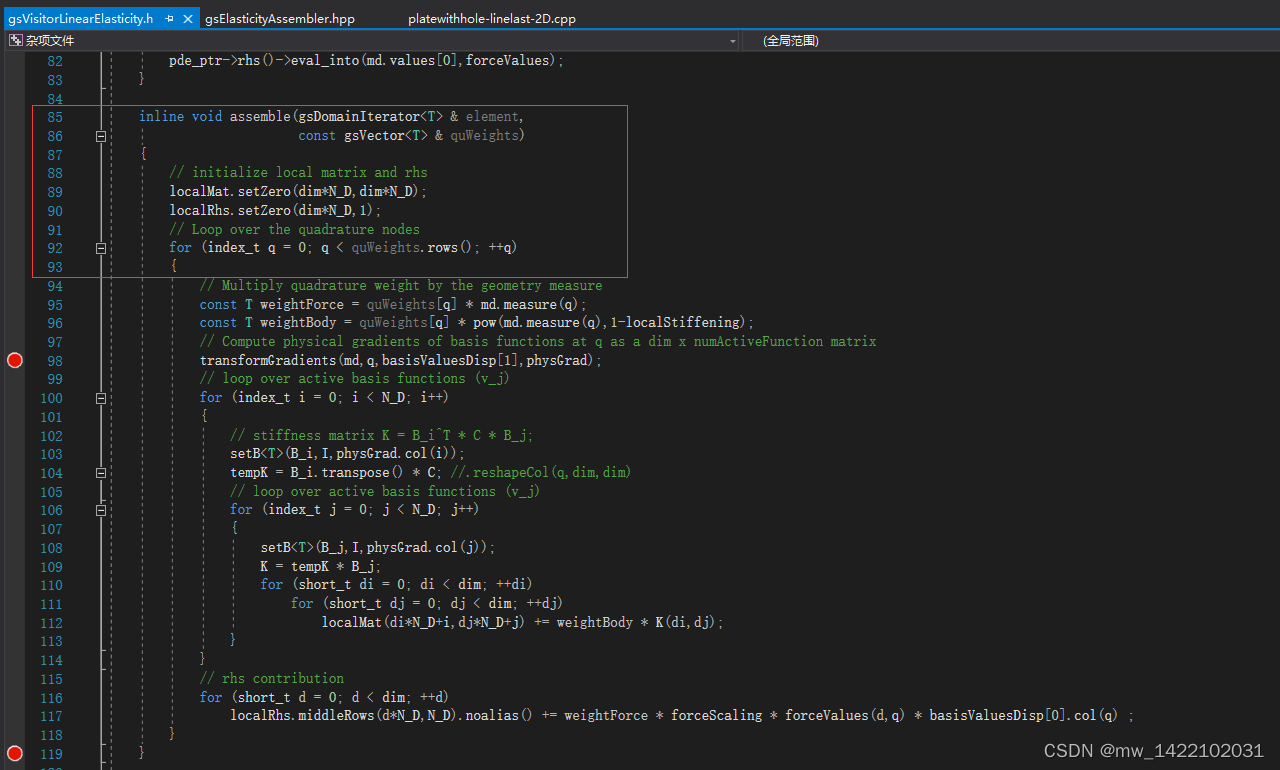
inline void assemble(gsDomainIterator<T> & element,
const gsVector<T> & quWeights)
{
// initialize local matrix and rhs
localMat.setZero(dim*N_D,dim*N_D);
localRhs.setZero(dim*N_D,1);
// Loop over the quadrature nodes
for (index_t q = 0; q < quWeights.rows(); ++q)
{
// Multiply quadrature weight by the geometry measure
const T weightForce = quWeights[q] * md.measure(q);
const T weightBody = quWeights[q] * pow(md.measure(q),1-localStiffening);
// Compute physical gradients of basis functions at q as a dim x numActiveFunction matrix
transformGradients(md,q,basisValuesDisp[1],physGrad);
// loop over active basis functions (v_j)
for (index_t i = 0; i < N_D; i++)
{
// stiffness matrix K = B_i^T * C * B_j;
setB<T>(B_i,I,physGrad.col(i));
tempK = B_i.transpose() * C; //.reshapeCol(q,dim,dim)
// loop over active basis functions (v_j)
for (index_t j = 0; j < N_D; j++)
{
setB<T>(B_j,I,physGrad.col(j));
K = tempK * B_j;
for (short_t di = 0; di < dim; ++di)
for (short_t dj = 0; dj < dim; ++dj)
localMat(di*N_D+i,dj*N_D+j) += weightBody * K(di,dj);
}
}
// rhs contribution
for (short_t d = 0; d < dim; ++d)
localRhs.middleRows(d*N_D,N_D).noalias() += weightForce * forceScaling * forceValues(d,q) * basisValuesDisp[0].col(q) ;
}
}
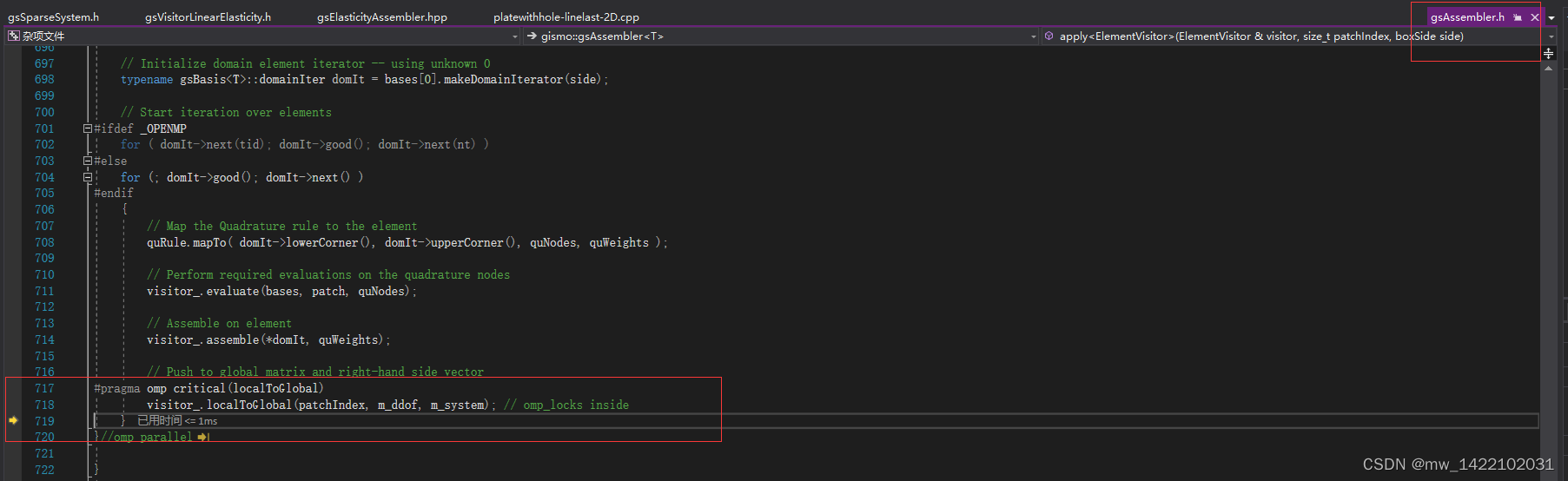
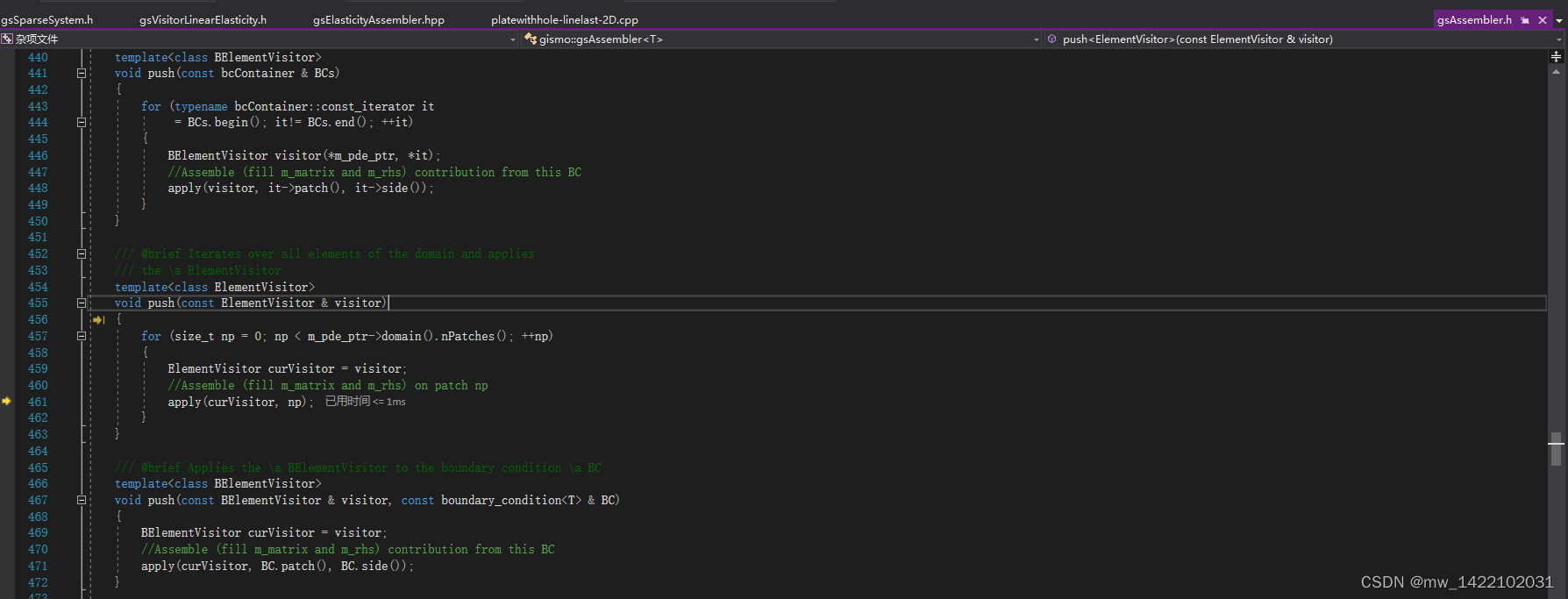
4 进入gsAssembler.h
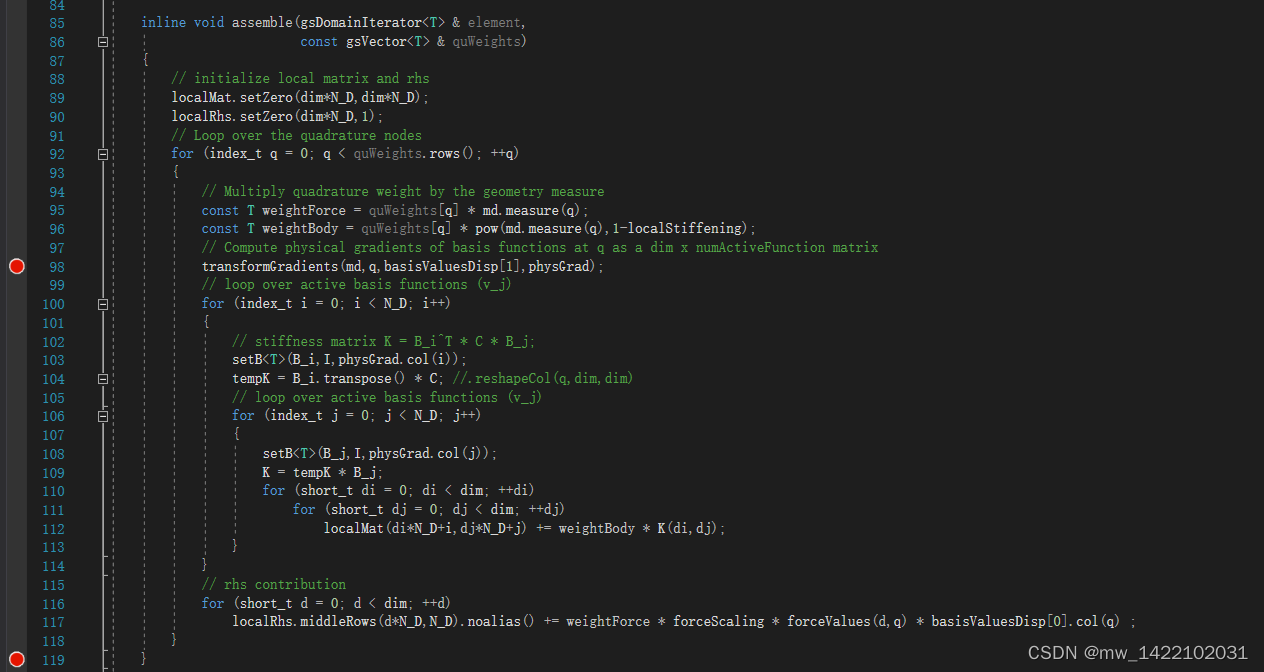
gsVisitorLinearElasticity.h的119行结束进入gsAssembler.h
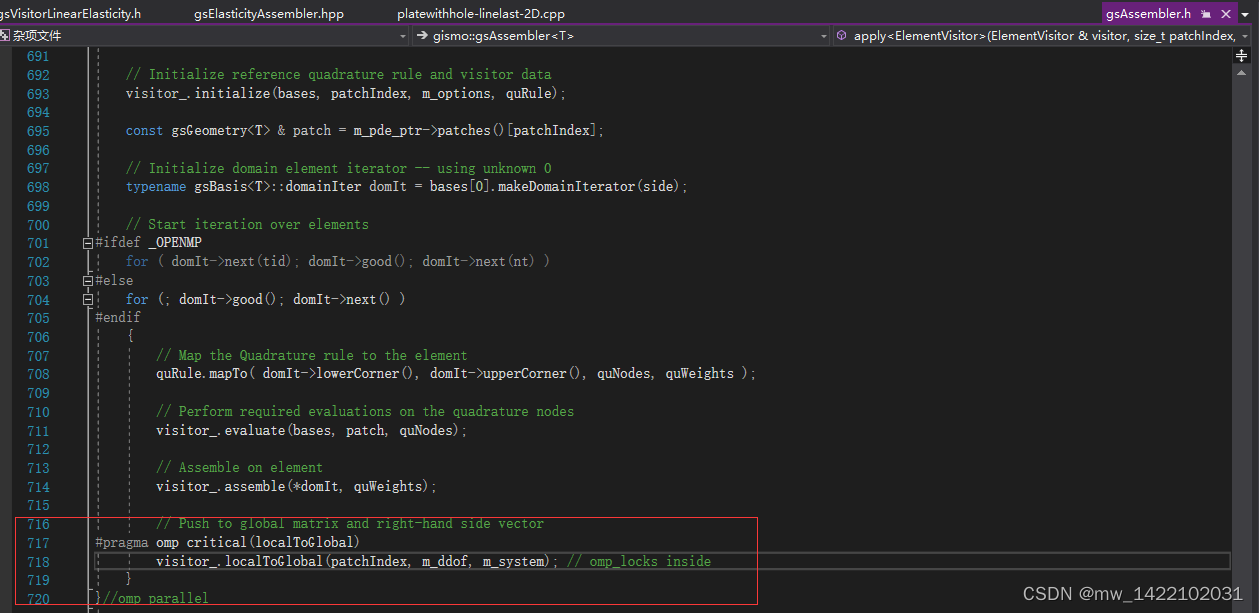
template <class T>
template<class ElementVisitor>
void gsAssembler<T>::apply(ElementVisitor & visitor,
size_t patchIndex,
boxSide side)
{
//gsDebug<< "Apply to patch "<< patchIndex <<"("<< side <<")\n";
const gsBasisRefs<T> bases(m_bases, patchIndex);
#pragma omp parallel
{
gsQuadRule<T> quRule ; // Quadrature rule
gsMatrix<T> quNodes ; // Temp variable for mapped nodes
gsVector<T> quWeights; // Temp variable for mapped weights
ElementVisitor
#ifdef _OPENMP
// Create thread-private visitor
visitor_(visitor);
const int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
const int nt = omp_get_num_threads();
#else
&visitor_ = visitor;
#endif
// Initialize reference quadrature rule and visitor data
visitor_.initialize(bases, patchIndex, m_options, quRule);
const gsGeometry<T> & patch = m_pde_ptr->patches()[patchIndex];
// Initialize domain element iterator -- using unknown 0
typename gsBasis<T>::domainIter domIt = bases[0].makeDomainIterator(side);
// Start iteration over elements
#ifdef _OPENMP
for ( domIt->next(tid); domIt->good(); domIt->next(nt) )
#else
for (; domIt->good(); domIt->next() )
#endif
{
// Map the Quadrature rule to the element
quRule.mapTo( domIt->lowerCorner(), domIt->upperCorner(), quNodes, quWeights );
// Perform required evaluations on the quadrature nodes
visitor_.evaluate(bases, patch, quNodes);
// Assemble on element
visitor_.assemble(*domIt, quWeights);
// Push to global matrix and right-hand side vector
#pragma omp critical(localToGlobal)
visitor_.localToGlobal(patchIndex, m_ddof, m_system); // omp_locks inside
}
}//omp parallel
}
重新进入gsVisitorLinearElasticity.h
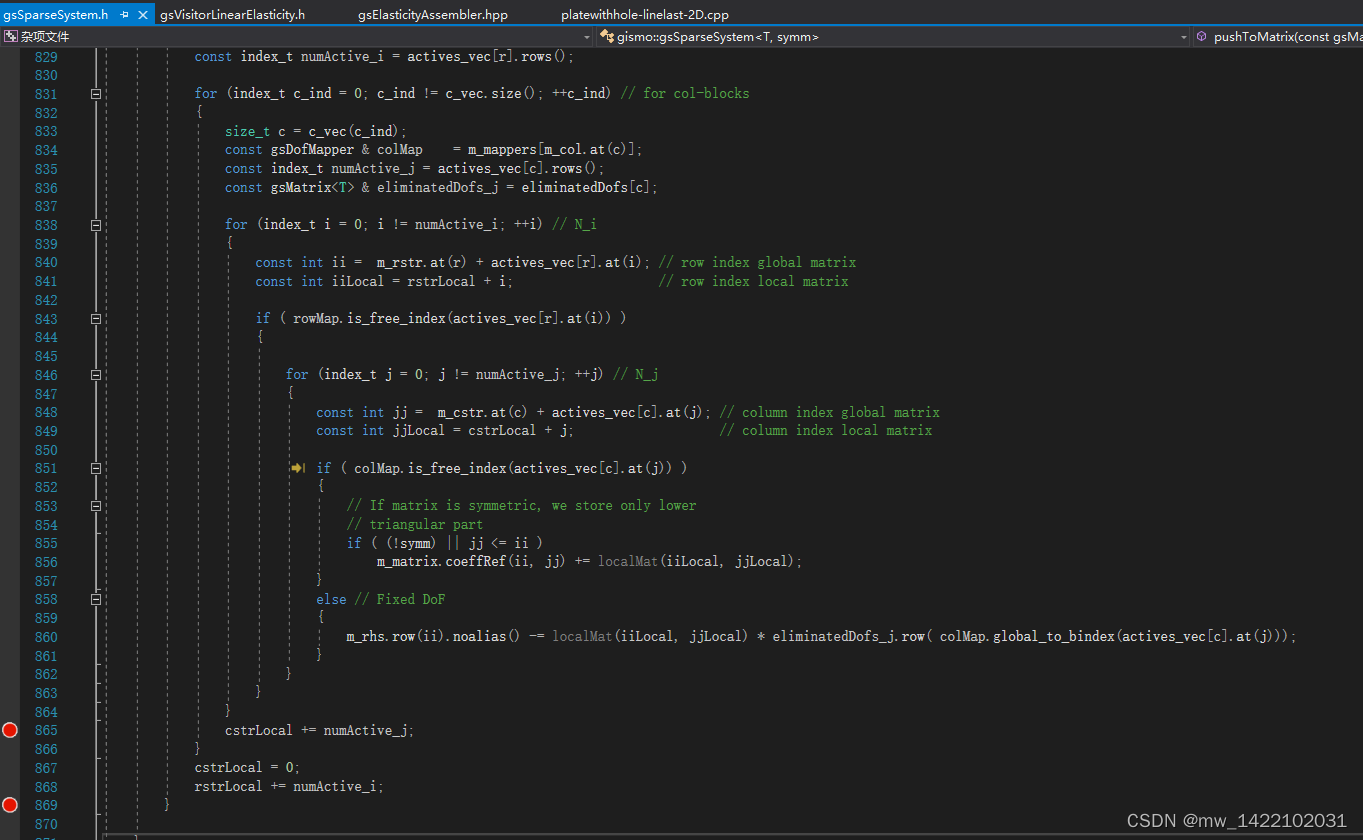
进入函数:inline void localToGlobal
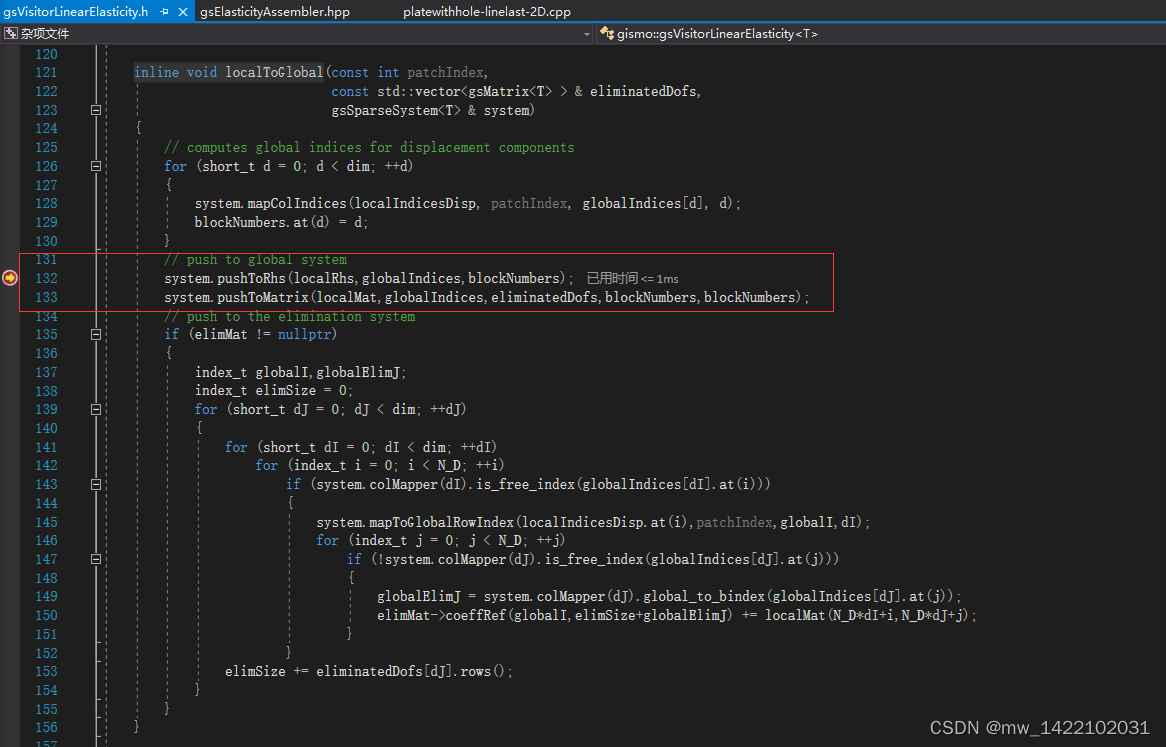
PushToMatrix 推出一个局部矩阵,该矩阵由若干块组成,这些块对应于全局系统的各个块
进入gsSparseSystem.h
进入gsSparseSystem.h函数816行:void pushToMatrix
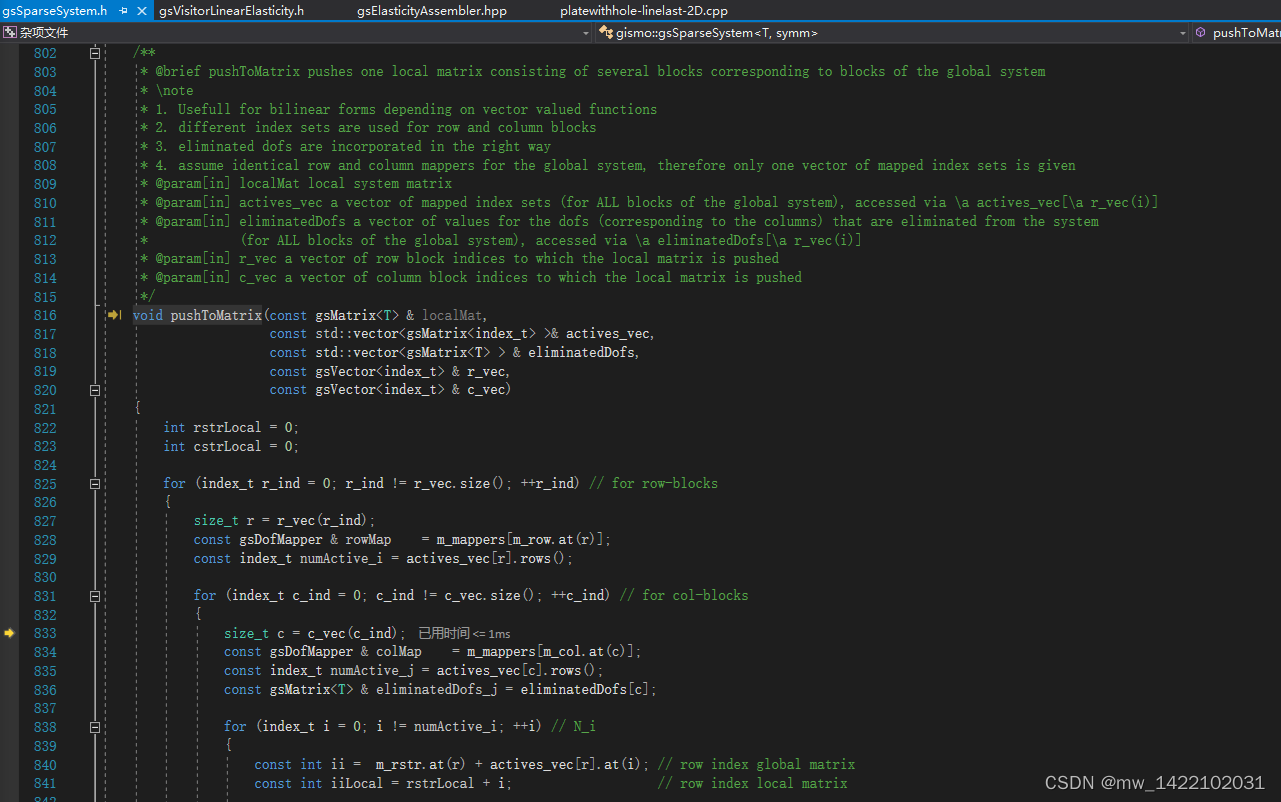
/**
* @brief pushToMatrix pushes one local matrix consisting of several blocks corresponding to blocks of the global system
* \note
* 1. Usefull for bilinear forms depending on vector valued functions
* 2. different index sets are used for row and column blocks
* 3. eliminated dofs are incorporated in the right way
* 4. assume identical row and column mappers for the global system, therefore only one vector of mapped index sets is given
* @param[in] localMat local system matrix
* @param[in] actives_vec a vector of mapped index sets (for ALL blocks of the global system), accessed via \a actives_vec[\a r_vec(i)]
* @param[in] eliminatedDofs a vector of values for the dofs (corresponding to the columns) that are eliminated from the system
* (for ALL blocks of the global system), accessed via \a eliminatedDofs[\a r_vec(i)]
* @param[in] r_vec a vector of row block indices to which the local matrix is pushed
* @param[in] c_vec a vector of column block indices to which the local matrix is pushed
*/
void pushToMatrix(const gsMatrix<T> & localMat,
const std::vector<gsMatrix<index_t> >& actives_vec,
const std::vector<gsMatrix<T> > & eliminatedDofs,
const gsVector<index_t> & r_vec,
const gsVector<index_t> & c_vec)
{
int rstrLocal = 0;
int cstrLocal = 0;
for (index_t r_ind = 0; r_ind != r_vec.size(); ++r_ind) // for row-blocks
{
size_t r = r_vec(r_ind);
const gsDofMapper & rowMap = m_mappers[m_row.at(r)];
const index_t numActive_i = actives_vec[r].rows();
for (index_t c_ind = 0; c_ind != c_vec.size(); ++c_ind) // for col-blocks
{
size_t c = c_vec(c_ind);
const gsDofMapper & colMap = m_mappers[m_col.at(c)];
const index_t numActive_j = actives_vec[c].rows();
const gsMatrix<T> & eliminatedDofs_j = eliminatedDofs[c];
for (index_t i = 0; i != numActive_i; ++i) // N_i
{
const int ii = m_rstr.at(r) + actives_vec[r].at(i); // row index global matrix
const int iiLocal = rstrLocal + i; // row index local matrix
if ( rowMap.is_free_index(actives_vec[r].at(i)) )
{
for (index_t j = 0; j != numActive_j; ++j) // N_j
{
const int jj = m_cstr.at(c) + actives_vec[c].at(j); // column index global matrix
const int jjLocal = cstrLocal + j; // column index local matrix
if ( colMap.is_free_index(actives_vec[c].at(j)) )
{
// If matrix is symmetric, we store only lower
// triangular part
if ( (!symm) || jj <= ii )
m_matrix.coeffRef(ii, jj) += localMat(iiLocal, jjLocal);
}
else // Fixed DoF
{
m_rhs.row(ii).noalias() -= localMat(iiLocal, jjLocal) * eliminatedDofs_j.row( colMap.global_to_bindex(actives_vec[c].at(j)));
}
}
}
}
cstrLocal += numActive_j;
}
cstrLocal = 0;
rstrLocal += numActive_i;
}
}
gsSparseSystem.h函数816行:void pushToMatrix结束后进入gsVisitorLinearElasticity.h 的函数inline void localToGlobal的135行
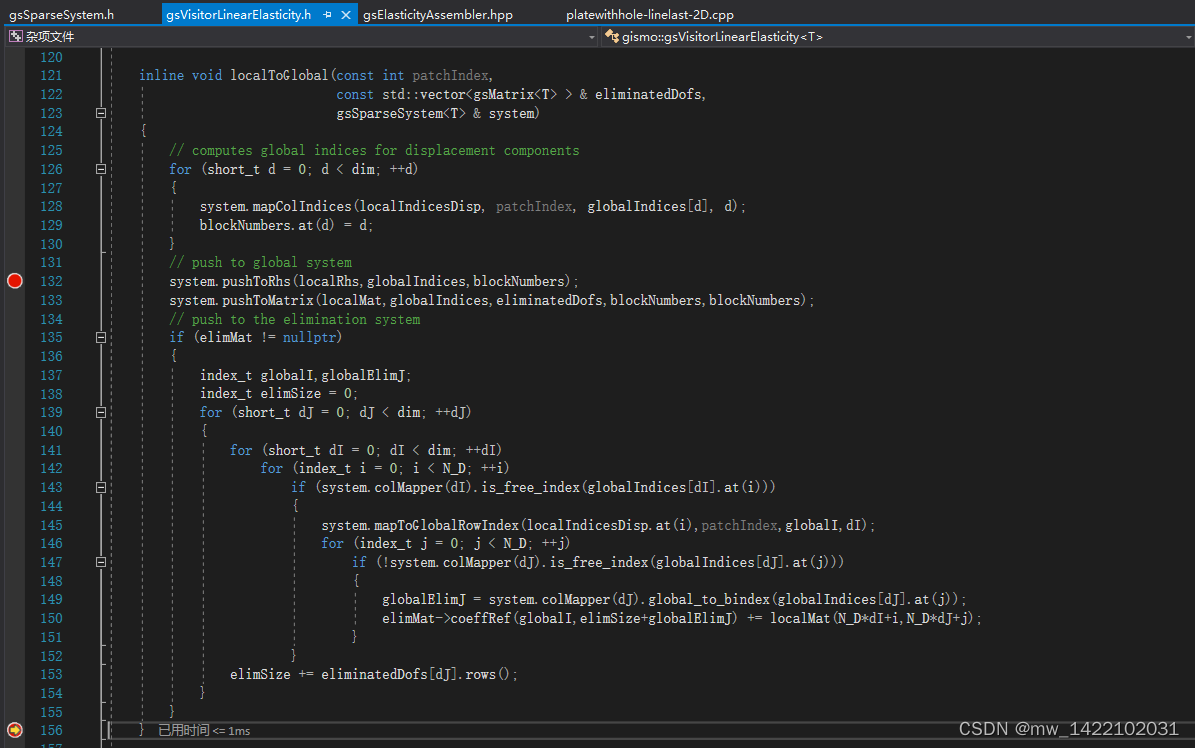
进入gsAssembler.h的718行
进入gsAssembler.h的455行函数
遍历域的所有单元并应用
template<class ElementVisitor>
void push(const ElementVisitor & visitor)
gsElasticityAssembler.hpp中 gsElasticityAssembler::assemble(bool saveEliminationMatrix) 函数运行完200行结束:
进入到主程序文件中:
gsElasticityAssembler.hpp
1.1
gsSparseSystem.h函数816行:void pushToMatrix结束后进入gsVisitorLinearElasticity.h 的函数inline void localToGlobal的135行
:
4 进入gsAssembler.h
1.2
:
1.3
:
1.4
:
二、
2.1
:
2.2
:
2.3
<f :
2.4
:
代码
/// This is the 2D linear elasticity benchmark "Infinite plate with circular hole"
/// as described in V.P.Nguyen, C.Anitescu, S.P.A.Bordas, T.Rabczuk, 2015
/// "Isogeometric analysis: An overview and computer implementation aspects".
///
/// Author: A.Shamanskiy (2016 - ...., TU Kaiserslautern)
#include <gismo.h>
#include <gsElasticity/gsElasticityAssembler.h>
#include <gsElasticity/gsWriteParaviewMultiPhysics.h>
using namespace gismo;
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
gsInfo << "This is the 2D linear elasticity benchmark: infinite plate with circular hole.\n";
//=====================================//
// Input //
//=====================================//
std::string filename = "plateWithHole.xml";
index_t numUniRef = 0;
index_t numDegElev = 0;
index_t numPlotPoints = 10000;
bool plotMesh = false;
// minimalistic user interface for terminal
gsCmdLine cmd("This is the 2D linear elasticity benchmark: infinite plate with circular hole.");
cmd.addInt("r", "refine", "Number of uniform refinement application", numUniRef);
cmd.addInt("d", "degelev", "Number of degree elevation application", numDegElev);
cmd.addInt("p", "points", "Number of points to plot to Paraview", numPlotPoints);
cmd.addSwitch("m", "mesh", "Plot computational mesh", plotMesh);
try { cmd.getValues(argc, argv); }
catch (int rv) { return rv; }
//=============================================//
// Scanning geometry and creating bases //
//=============================================//
// scanning geometry
gsMultiPatch<> geometry;
gsReadFile<>(filename, geometry);
// creating basis
gsMultiBasis<> basis(geometry);
for (index_t i = 0; i < numDegElev; ++i)
basis.degreeElevate();
for (index_t i = 0; i < numUniRef; ++i)
basis.uniformRefine();
gsInfo << basis;
//=============================================//
// Setting loads and boundary conditions //
//=============================================//
gsFunctionExpr<> analyticalStresses("1-1/(x^2+y^2)*(3/2*cos(2*atan2(y,x)) + cos(4*atan2(y,x))) + 3/2/(x^2+y^2)^2*cos(4*atan2(y,x))",
"-1/(x^2+y^2)*(1/2*cos(2*atan2(y,x)) - cos(4*atan2(y,x))) - 3/2/(x^2+y^2)^2*cos(4*atan2(y,x))",
"-1/(x^2+y^2)*(1/2*sin(2*atan2(y,x)) + sin(4*atan2(y,x))) + 3/2/(x^2+y^2)^2*sin(4*atan2(y,x))", 2);
// boundary load neumann BC
gsFunctionExpr<> traction("(-1+1/(x^2+y^2)*(3/2*cos(2*atan2(y,x)) + cos(4*atan2(y,x))) - 3/2/(x^2+y^2)^2*cos(4*atan2(y,x))) * (x==-4) +"
"(-1/(x^2+y^2)*(1/2*sin(2*atan2(y,x)) + sin(4*atan2(y,x))) + 3/2/(x^2+y^2)^2*sin(4*atan2(y,x))) * (y==4)",
"(1/(x^2+y^2)*(1/2*sin(2*atan2(y,x)) + sin(4*atan2(y,x))) - 3/2/(x^2+y^2)^2*sin(4*atan2(y,x))) * (x==-4) +"
"(-1/(x^2+y^2)*(1/2*cos(2*atan2(y,x)) - cos(4*atan2(y,x))) - 3/2/(x^2+y^2)^2*cos(4*atan2(y,x))) * (y==4)", 2);
// material parameters
real_t youngsModulus = 1.0e3;
real_t poissonsRatio = 0.3;
// boundary conditions
gsBoundaryConditions<> bcInfo;
bcInfo.addCondition(0, boundary::north, condition_type::neumann, &traction);
bcInfo.addCondition(0, boundary::west, condition_type::dirichlet, nullptr, 1); // last number is a component (coordinate) number
bcInfo.addCondition(0, boundary::east, condition_type::dirichlet, nullptr, 0);
// source function, rhs
gsConstantFunction<> g(0., 0., 2);
//=============================================//
// Assembling & solving //
//=============================================//
// creating assembler
gsElasticityAssembler<real_t> assembler(geometry, basis, bcInfo, g);
assembler.options().setReal("YoungsModulus", youngsModulus);
assembler.options().setReal("PoissonsRatio", poissonsRatio);
gsInfo << "Assembling...\n";
gsStopwatch clock;
clock.restart();
assembler.assemble();
gsInfo << "Assembled a system (matrix and load vector) with "
<< assembler.numDofs() << " dofs in " << clock.stop() << "s.\n";
gsInfo << "Solving...\n";
clock.restart();
#ifdef GISMO_WITH_PARDISO
gsSparseSolver<>::PardisoLLT solver(assembler.matrix());
gsVector<> solVector = solver.solve(assembler.rhs());
gsInfo << "Solved the system with PardisoLDLT solver in " << clock.stop() << "s.\n";
#else
gsSparseSolver<>::SimplicialLDLT solver(assembler.matrix());
gsVector<> solVector = solver.solve(assembler.rhs());
gsInfo << "Solved the system with EigenLDLT solver in " << clock.stop() << "s.\n";
#endif
//=============================================//
// Output //
//=============================================//
// constructing displacement as an IGA function
gsMultiPatch<> solution;
assembler.constructSolution(solVector, assembler.allFixedDofs(), solution);
// constructing stress tensor
gsPiecewiseFunction<> stresses;
assembler.constructCauchyStresses(solution, stresses, stress_components::all_2D_vector);
if (numPlotPoints > 0)
{
// constructing an IGA field (geometry + solution) for displacement
gsField<> solutionField(assembler.patches(), solution);
// constructing an IGA field (geometry + solution) for stresses
gsField<> stressField(assembler.patches(), stresses, true);
// analytical stresses
gsField<> analyticalStressField(assembler.patches(), analyticalStresses, false);
// creating a container to plot all fields to one Paraview file
std::map<std::string, const gsField<> *> fields;
fields["Deformation"] = &solutionField;
fields["Stress"] = &stressField;
fields["StressAnalytical"] = &analyticalStressField;
gsWriteParaviewMultiPhysics(fields, "plateWithHole", numPlotPoints, plotMesh);
gsInfo << "Open \"plateWithHole.pvd\" in Paraview for visualization. Stress wiggles on the left side are caused by "
"a singularity in the parametrization.\n";
}
// eval stress at the top of the circular cut
gsMatrix<> A(2, 1);
A << 1., 0.; // parametric coordinates for the isogeometric solution
gsMatrix<> res;
stresses.piece(0).eval_into(A, res);
A << 0., 1.; // spatial coordinates for the analytical solution
gsMatrix<> analytical;
analyticalStresses.eval_into(A, analytical);
gsInfo << "XX-stress at the top of the circle: " << res.at(0) << " (computed), " << analytical.at(0) << " (analytical)\n";
gsInfo << "YY-stress at the top of the circle: " << res.at(1) << " (computed), " << analytical.at(1) << " (analytical)\n";
gsInfo << "XY-stress at the top of the circle: " << res.at(2) << " (computed), " << analytical.at(2) << " (analytical)\n";
return 0;
}
总结 #pic_center
空格 空格
:
| 二维数 |
| 1 |
| 1 |
| 1 |