目录
- Extractive: Single-Doc
- Extractive: Multi-Doc
- Abstractive: Single-Doc
- Evaluation
- Conclusion
- summarisation
- Distill the most important information from a text to produce shortened or abridged version
- Examples
- outlines of a document
- abstracts of a scientific article
- headlines of a news article
- snippets of search result
- what to summarise
- Single-document summarisation
- Input: a single document
- Output: summary that characterise the content
- Multi-document summarisation(find overlapping information)
- Input: multiple documents
- Output: summary that captures the gist(要点,主旨) of all documents
- E.g. summarise a news event from multiple sources or perspectives
- Single-document summarisation
- how to summarise
- Extractive summarisation
- Summarise by selecting representative sentences from documents
- Abstractive summarisation
- Summarise the content in your own words
- Summaries will often be paraphrases of the original content
- Extractive summarisation
- goal of summarisation
- Generic summarisation
- Summary gives important information in the document(s)
- Query-focused summarisation
- Summary responds to a user query
- “Non-factoid” QA
- Answer is much longer than factoid QA

- Generic summarisation
Extractive: Single-Doc
- summarisation system
-
Content selection: select what sentences to extract from the document
-
Information ordering: decide how to order extracted sentences
-
Sentence realisation: cleanup to make sure combined sentences are fluent

-
We will focus on content selection
-
For single-document summarisation, information ordering not necessary
- present extracted sentences in original order
-
Sentence realisation also not necessary if they are presented in dot points
-
- content selection
-
Not much data with ground truth extractive sentences
-
Mostly unsupervised methods
-
Goal: Find sentences that are important or salient(显著的,突出的)
-
method1: TF-IDF
- Frequent words in a doc → \to → salient
- But some generic words are very frequent but uninformative
- function words
- stop words
- Weigh each word
w
w
w in document
d
d
d by its inverse document frequency:
- w e i g h t ( w ) = t f d , w × i d f w weight(w)=tf_{d,w} \times idf_w weight(w)=tfd,w×idfw
-
method 2: Log Likelihood Ratio
- Intuition: a word is salient if its probability in the input corpus is very different to a background corpus(e.g. Wikipedia)
- f ( n ) = { 1 , i f − 2 l o g λ ( w ) > 10 0 , o t h e r w i s e f(n)= \begin{cases} 1, & {if -2log\lambda(w)>10} \\ 0, & {otherwise} \end{cases} f(n)={1,0,if−2logλ(w)>10otherwise
-
λ
(
w
)
\lambda(w)
λ(w) is the ratio between:
- numerator: P(observing w w w in I I I) → ( N I x ) p x ( 1 − p ) N I − x \to \begin{pmatrix} N_I \\ x \\ \end{pmatrix}p^x(1-p)^{N_I-x} →(NIx)px(1−p)NI−x and P(observing w w w in B B B) → ( N B y ) p y ( 1 − p ) N B − y \to \begin{pmatrix} N_B \\ y \\ \end{pmatrix}p^y(1-p)^{N_B-y} →(NBy)py(1−p)NB−y, assuming P ( w ∣ I ) = P ( w ∣ B ) = p → x + y N I + N B P(w|I)=P(w|B)=p \to \frac{x+y}{N_I+N_B} P(w∣I)=P(w∣B)=p→NI+NBx+y
- denominato: P(observing w w w in I I I) → ( N I x ) p I x I ( 1 − p I ) N I − x \to \begin{pmatrix} N_I \\ x \\ \end{pmatrix}p_I^{x_I}(1-p_I)^{N_I-x} →(NIx)pIxI(1−pI)NI−x and P(observing w w w in B B B) → ( N B y ) p B y ( 1 − p B ) N B − y \to \begin{pmatrix} N_B \\ y \\ \end{pmatrix}p_B^y(1-p_B)^{N_B-y} →(NBy)pBy(1−pB)NB−y, assuming P ( w ∣ I ) = p I → x N I a n d P ( w ∣ B ) = p B → y N B P(w|I)=p_I \to \frac{x}{N_I} \ and \ P(w|B)=p_B \to \frac{y}{N_B} P(w∣I)=pI→NIx and P(w∣B)=pB→NBy
- saliency of a sentence
- w e i g h t ( s ) = 1 ∣ S ∣ ∑ w ∈ S w e i g h t ( w ) weight(s)=\frac{1}{|S|}\sum_{w\in{S}}weight(w) weight(s)=∣S∣1∑w∈Sweight(w)
- only consider non-stop words in S S S
-
method 3: sentence centrality(find sentence )
- Alternative approach to ranking sentences
- Measure distance between sentences, and choose sentences that are closer to other sentences
- Use tf-idf BOW to represent sentence
- Use cosine similarity to measure distance
- c e n t r a l i t y ( s ) = 1 # s e n t ∑ s ′ c o s t f i d f ( s , s ′ ) centrality(s)=\frac{1}{\# sent}\sum_{s'}cos_{tfidf}(s,s') centrality(s)=#sent1∑s′costfidf(s,s′)
- final extracted summary
- Use top-ranked sentences as extracted summary
- Saliency (tf-idf or log likelihood ratio)
- Centrality
- Use top-ranked sentences as extracted summary
-
method 4: RST parsing

-
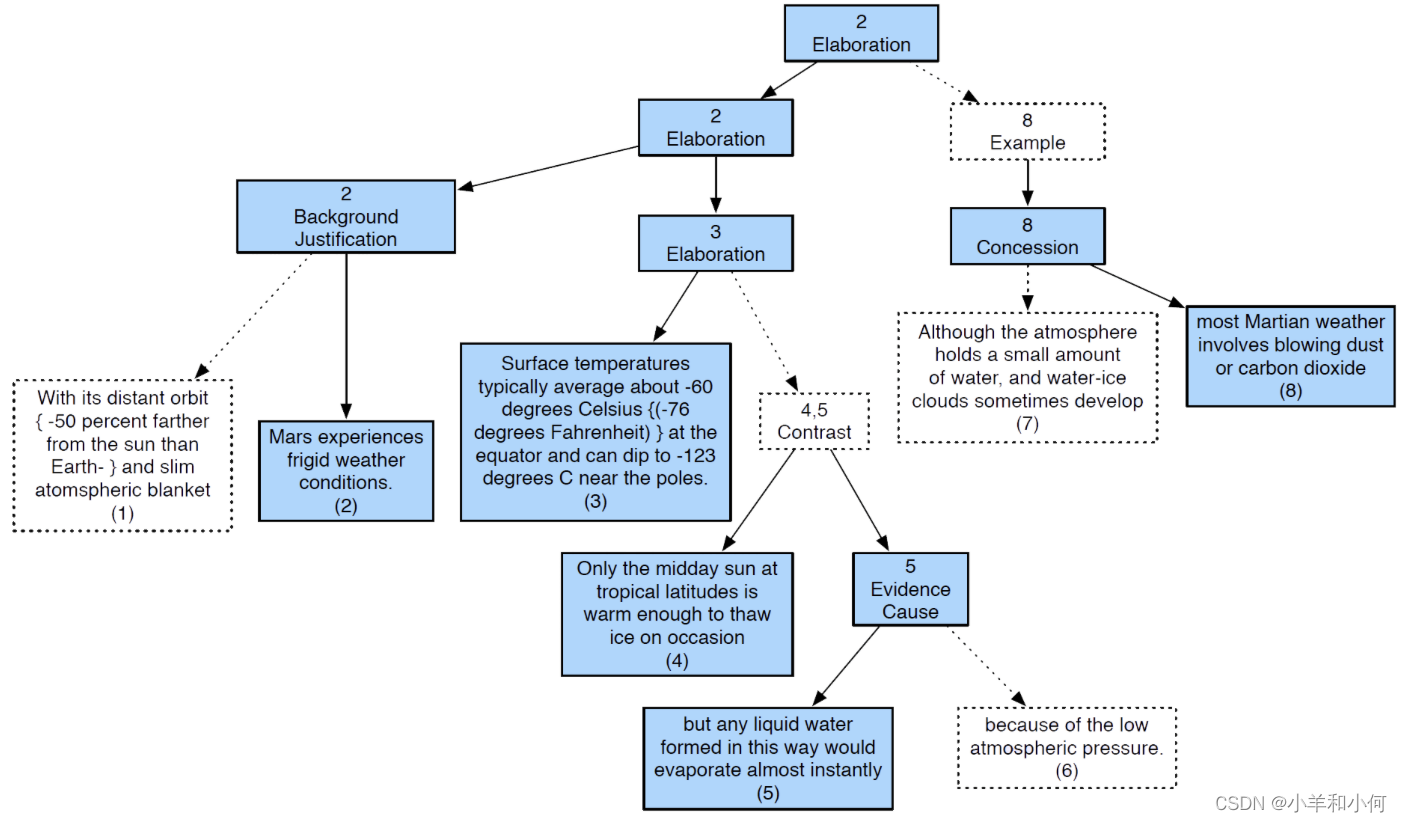
Rhetorical structure theory (L12, Discourse): explain how clauses are connected
-
Define the types of relations between a nucleus (main clause) and a satellite (supporting clause)

-
Nucleus more important than satellite
-
A sentence that functions as a nucleus to more sentences = more salient (dashed arrow is satellite, solid arrow is nucleus)
-
which sentence is the best summary sentence?
- Mars experiences frigid conditions
-
-
Extractive: Multi-Doc
- summarisation system
-
Similar to single-document extractive summarisation system
-
Challenges:
- Redundancy in terms of information(multiple documents contains the same information)
- Sentence ordering(can on longer use the original order)

-
content selection
- We can use the same unsupervised content selection methods (tf-idf, log likelihood ratio, centrality) to select salient sentences from each of these documents individually
- But ignore sentences that are redundant
-
Maximum Marginal Relevance
- Iteratively select the best sentence to add to summary
- Sentences to be added must be novel(new information)
- Penalise a candidate sentence if it’s similar to extracted sentences:
- M M R − p e n a l t y ( s ) = λ m a x s i ∈ S s i m ( s , s i ) MMR-penalty(s)=\lambda max_{s_i\in{S}}sim(s,s_i) MMR−penalty(s)=λmaxsi∈Ssim(s,si)
- s i s_i si is a extracted sentence
- s s s is a candidate sentence
- S S S is the set of extracted sentences
- Stop when a desired number of sentences are added
-
Information Ordering
- Chronological ordering:
- Order by document dates
- Coherence:
- Order in a way that makes adjacent sentences similar
- Order based on how entities are organised (centering theory, L12)

- Chronological ordering:
-
Sentence Realisation
- Make sure entities are referred coherently
- Full name at first mention
- Last name at subsequent mentions
- Apply coreference methods to first extract names
- Write rules to clean up


- Make sure entities are referred coherently
-
Abstractive: Single-Doc
-
example

- Paraphrase
- A very difficult task
- Can we train a neural network to generate summary?
-
Encoder-Decoder?

- What if we treat:
- Source sentence = “document”
- Target sentence = “summary”

- What if we treat:
-
data
-
News headlines
-
Document: First sentence of article
-
Summary: News headline/title
-
Technically more like a “headline generation task”
-
and it kind of works…

-
More Summarisation Data
- But headline generation isn’t really exciting…
- Other summarisation data:
- CNN/Dailymail: 300K articles, summary in bullets
- Newsroom: 1.3M articles, summary by authors
- Diverse; 38 major publications
- XSum: 200K BBC articles
- Summary is more abstractive than other datasets
-
-
improvements
- Attention mechanism
- Richer word features: POS tags, NER tags, tf-idf
- Hierarchical encoders
- One LSTM for words
- Another LSTM for sentences

-
Potential issues of an attention encoder-decoder summarisation system?
- Has the potential to generate new details not in the source document (yes)
- Unable to handle unseen words in the source document (yes, can only generate a closed set of words)
- Information bottleneck: a vector is used to represent the source document (no, use attention)
- Can only generate one summary (no)


- Copy Mechanism
- Generate summaries that reproduce details in the document
- Can produce out-of-vocab words in the summary by copying them in the document
- e.g. smergle = out of vocabulary
- p(smergle) = attention probability + generation probability = attention probability
- latest development
- State-of-the-art models use transformers instead of RNNs
- Lots of pre-training
- Note: BERT not directly applicable because we need a unidirectional decoder (BERT is only an encoder)
Evaluation
- ROUGE (Recall Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation)
- Similar to BLEU, evaluates the degree of word overlap between generated summary and reference/human summary
- But recall oriented(BLEU is precision-oriented)
- Measures overlap in N-grams separately (e.g. from 1 to 3)
- ROUGE-2: calculates the percentage of bigrams from the reference that are in the generated summary
- ROUGE-2: example

Conclusion
- Research focus on single-document abstractive summarisation
- Mostly news data
- But many types of data for summarisation:
- Images, videos
- Graphs
- Structured data: e.g. patient records, tables
- Multi-document abstractive summarisation