1. 基本数据结构
基础的node定义在LKH.h中

用于2-level tree的segment定义如下:

LKH可以使用3种数据结构,默认是2-level tree:
2-level tree的flip操作(即2-opt算子),在Flip_SL.c中,特殊的地方在于flip过程中涉及到重新分配segment的操作,其逻辑如下,其中P开头的是node对应的segment编号。

2. 读取问题数据
2.1 关键词清单
读数据代码在ReadProblem.c中,必须包含两部分:specification part和data part。specification part支持的关键词包括:
* NAME : <string>e
* Identifies the data file.
*
* TYPE : <string>。可以是非对称tsp问题,带时间窗的问题,经典VRP问题,非对称VRP问题,pickup-and-delivery TSP问题,开放VRP问题,。
* Specifies the type of data. Possible types are
* TSP Data for a symmetric traveling salesman problem
* ATSP Data for an asymmetric traveling salesman problem
* SOP Data for a sequence ordering problem
* HCP Hamiltonian cycle problem data
* HPP Hamiltonian path problem data (not available in TSPLIB)
* TSPTW Data for a TSP instance with time windows
* CCVRP Data for a cumulative capacitated vehicle routing problem
* CVRP Data for a symmetric capacitated vehicle routing problem
* ACVRP Data for an asymmetric capacitated vehicle routing problem
* ADCVRP Data for an asymmetric distance constrained vehicle
* routing problem
* CVRPTW Data for a capacitated vehicle routing problem with
* time windows
* VRPMPD Data for a mixed pickup and delivery problem with backhauls
* 1-PDTSP Data for a one-commodity pickup-and-delivery traveling
* salesman problem
* MLP Data for a minimum latency problem
* m-PDTSP Data for a mulity-commodity pickup-and-delivery traveling
* salesman problem
* m1-PDTSP Data for a mulity-commodity one-to-one pickup-and-delivery
* traveling salesman problem
* OVRP Data for an open vehicle routing problem
* PDTSP Data for a pickup and delivery traveling salesman problem
* PDTSPF Data for a pickup and delivery traveling salesman problem
* with FIFO loading
* PDTSPL Data for a pickup and delivery traveling salesman problem
* with LIFO loading
* PDPTW Data for a pickup and delivery problem with time windows
* RCTVRP Data for a risk-constrained cash-in-transit vehicle
* routing problem
* RCTVRPTW Data for a risk-constrained cash-in-transit vehicle
* routing problem with time windows
* TRP Data for a traveling repairman problem
* TSPDL Dara for a traveling salesman problem with draft limits
* TSPPD Data for a pickup and delivery travling salesman problem
* TSTSP Data for a Steiner traveling salesman problem
* VRPB Data for a vehicle routing problem with backhauls
* VRPBTW Data for a vehicle routing problem with backhauls and
* time windows
* CTSP Data for a colored traveling salesman problem
*
* COMMENT : <string>
* Additional comments (usually the name of the contributor or the creator of
* the problem instance is given here).
*
* DIMENSION : < integer>
* The number of nodes.
*
* CAPACITY : <integer>
* Specifies the truck capacity in a CVRP.
*
* DISTANCE : <real>
* The maximum length allowed for each route in a CVRP.
*
* EDGE_WEIGHT_TYPE : <string>
* Specifies how the edge weights (or distances) are given. The values are:
* ATT Special distance function for problem att48 and att532
* CEIL_2D Weights are Euclidean distances in 2-D rounded up
* CEIL_3D Weights are Euclidean distances in 3-D rounded up
* EUC_2D Weights are Euclidean distances in 2-D
* EUC_3D Weights are Euclidean distances in 3-D
* EXACT_2D Weights are EUC_2D distances (SCALE = 1000 as default)
* EXACT_3D Weights are EUC_3D distances (SCALE = 1000 as default)
* EXPLICIT Weights are listed explicitly in the corresponding section
* FLOOR_2D Weights are Euclidean distances in 2-D rounded down
* FLOOR_3D Weights are Euclidean distances in 3-D rounded down
* GEO Weights are geographical distances in kilometers (TSPLIB)
* Coordinates are given in the form DDD.MM where DDD are the
* degrees and MM the minutes
* GEOM Weights are geographical distances in meters (used for the
* world TSP). Coordinates are given in decimal form
* GEO_MEEUS Weights are geographical distances in kilometers, computed
* according to Meeus' formula. Coordinates are given in the
* form DDD.MM where DDD are the degrees and MM the minutes
* GEOM_MEEUS Weights are geographical distances, computed according to
* Meeus' formula. Coordinates are given in decimal form
* MAN_2D Weights are Manhattan distances in 2-D
* MAN_3D Weights are Manhattan distances in 3-D
* MAX_2D Weights are maximum distances in 2-D
* MAX_3D Weights are maximum distances in 3-D
* TOR_2D Wirghes are toroidal distances in 2-D
* TOR_3D Wirghes are toroidal distances in 3-D
* XRAY1 Distance function for crystallography problems (Version 1)
* XRAY2 Distance function for crystallography problems (Version 2)
* SPECIAL There is a special distance function implemented in
* the Distance_SPECIAL function.
*
* EDGE-WEIGHT_FORMAT : <string>
* Describes the format of the edge weights if they are given explicitly.
* The values are
* FUNCTION Weights are given by a function (see above)
* FULL_MATRIX Weights are given by a full matrix
* UPPER_ROW Upper triangular matrix
* (row-wise without diagonal entries)
* LOWER_ROW Lower triangular matrix
* (row-wise without diagonal entries)
* UPPER_DIAG_ROW Upper triangular matrix
* (row-wise including diagonal entries)
* LOWER_DIAG_ROW Lower triangular matrix
* (row-wise including diagonal entries)
* UPPER_COL Upper triangular matrix
* (column-wise without diagonal entries)
* LOWER_COL Lower triangular matrix
* (column-wise without diagonal entries)
* UPPER_DIAG_COL Upper triangular matrix
* (column-wise including diagonal entries)
* LOWER_DIAG_COL Lower triangular matrix
* (column-wise including diagonal entries)
*
* EDGE_DATA_FORMAT : <string>
* Describes the format in which the edges of a graph are given, if the
* graph is not complete. The values are
* EDGE_LIST The graph is given by an edge list
* ADJ_LIST The graph is given by an adjacency list
*
* NODE_COORD_TYPE : <string>
* Specifies whether the coordinates are associated with each node
* (which, for example may be used for either graphical display or
* distance computations.
* The values are
* TWOD_COORDS Nodes are specified by coordinates in 2-D
* THREED_COORDS Nodes are specified by coordinates in 3-D
* NO_COORDS The nodes do not have associated coordinates
* The default value is NO_COORDS. In the current implementation, however,
* the value has no significance.
*
* DISPLAY_DATA_TYPE : <string>
* Specifies how a graphical display of the nodes can be obtained.
* The values are
* COORD_DISPLAY Display is generated from the node coordinates
* TWOD_DISPLAY Explicit coordinates in 2-D are given
* NO_DISPLAY No graphical display is possible
*
* The default value is COORD_DISPLAY if node coordinates are specifies and
* NO_DISPLAY otherwise. In the current implementation, however, the value
* has no significance.
*
* DEMAND_DIMENSION : <integer>
* The number of objects in an m1-PDTSP.
*
* GRID_SIZE : <real>
* The grid size for toroidal instances.
* Default: 1000000.0
*
* RISK_THRESHOLD : <integer>
* The maximum risk alllowed for each route in an RCTVRP or RCTVRPTW instance.
*
* SALESMEN : <integer>
* VEHICLES : <integer>
* The number of vehicles/salesmen in a CVRP.
*
* SCALE : <integer>
* Scale factor. Distances are multiplied by this factor.
*
* SERVICE_TIME : <real>
* Same service time for all nodes.
*
* EOF
* Terminates input data. The entry is optional.
*
数据部分的格式如下,可以是
NODE_COORD_SECTION:node坐标
EDGE_DATA_SECTION:edge清单(如果是3个整数,最后一个表示weight),临近edge清单(第一个数据是当前点,后面是临近点,以-1结束)
FIXED_EDGES_SECTION:必须出现的edge清单
* NODE_COORD_SECTION :
* Node coordinates are given in this section. Each line is of the form
*
* <integer> <real> <real>
*
* if NODE_COORD_TYPE is TWOD_COORDS, or
*
* <integer> <real> <real> <real>
*
* if NODE_COORD_TYPE is THREED_COORDS. The integers give the number of the
* respective nodes. The real numbers are the associated coordinates.
*
* EDGE_DATA_SECTION :
* Edges of the graph are specified in either of the two formats allowed in
* the EDGE_DATA_FORMAT entry. If the type is EDGE_LIST, then the edges are
* given as a sequence of lines of one of the forms
*
* <integer> <integer>
* <integer> <integer> <integer>
*
* each entry giving the terminal nodes of some edge, and if three integers are
* given, the last one specifies its weight. The list is terminated by a -1.
* If the type is ADJ_LIST, the section consists of adjacency lists for nodes.
* The adjacency list of a node x is specified as
*
* <integer> <integer> ... <integer> -1
*
* where the first integer gives the number of node x and the following
* integers (terminated by -1) the numbers of the nodes adjacent to x.
* The list of adjacency lists are terminated by an additional -1.
*
* FIXED_EDGES_SECTION :
* In this section, edges are listed that are required to appear in each
* solution to the problem. The edges to be fixed are given in the form
* (per line)
*
* <integer> <integer>
*
* meaning that the edge (arc) from the first node to the second node has
* to be contained in a solution. This section is terminated by a -1.
*
* DISPLAY_DATA_SECTION :
* If DISPLAY_DATA_TYPE is TWOD_DISPLAY, the 2-dimensional coordinates from
* which a display can be generated are given in the form (per line)
*
* <integer> <real> <real>
*
* The integers specify the respective nodes and the real numbers give the
* associated coordinates. The contents of this section, however, has no
* significance in the current implementation.
*
* EDGE_WEIGHT_SECTION :
* The edge weights are given in the format specifies by the EDGE_WEIGHT_FORMAT
* entry. At present, all explicit data are integral and is given in one of the
* (self-explanatory) matrix formats, with explicitly known lengths.
*
* TOUR_SECTION :
* A tour is specified in this section. The tour is given by a list of
* integers giving the sequence in which the nodes are visited in the tour.
* The tour is terminated by a -1. Note: In contrast to the TSPLIB format,
* only one tour can be given in this section. The tour is used to limit
* the search (the last edge to be excluded in a non-gainful move must not
* belong to the tour). In addition, the Alpha field of its edges is set to
* -1.
*
* BACKHAUL_SECTION :
* This section is used for specifying VRPB instances.
* It contains a list of backhaul nodes. This list is terminated by a -1.
*
* CTSP_SET_SECTION :
* This section is used for specifying CTSP instances.
* Each entry has the following format:
* c v1 v2 ... vk -1, where c is the color number (colors are numbered
* from 1 to SALESMEN), and v1 v2 ... vk are vertices with color c
* (vertices are numbered from 1 to Dimension).
*
* DEMAND_SECTION :
* The demands of all nodes of a CVRP are given in the form (per line)
*
* <integer> <integer>
*
* The first integer spcifies a node number, the second its demand. The depot
* nodes must also occcur in this section. Their demands are 0.
*
* DEPOT_SECTION :
* Contains a list of possible alternate depot nodes. This list is terminated
* by a -1. The current implementation allows only one depot.
*
* DRAFT_LIMIT_SECTION :
* The draft limits of all nodes of a CVRP are give in the form (per line)
*
* <integer> <integer>
*
* The first integer spcifies a node number, the second its draft limit.
* The depot nodes must also occcur in this section. Their demands are 0.
*
* PICKUP_AND_DELIVERY_SECTION :
* This section is used for specifying specifying pickup-and-delivery
* instances. Each line is of the form
*
* <integer> <integer> <real> <real> <real> <integer> <integer>
*
* The first integer gives the number of the node.
* The second integer gives its demand (ignored for PDTSPF, PDTSPL, VRPMPD
* and VRPSPD instances).
* The third and fourth number give the earliest and latest time for the node.
* The fifth number specifies the service time for the node.
* The last two integers are used to specify pickup and delivery. For a PDPTW,
* PDTSP, PDTSPF and PDTSPL instance, the first of these integers gives the
* index of the pickup sibling, whereas the second integer gives the index of
* the delivery sibling. For a VRPMPD and VRPSPD instance, the two integers
* simply give the size of the pickup and delivery for the node.
*
* REIQUIRED_NODES_SECTION :
* Contains a list of required nodes for a Steiner traveling salesman problem.
* This list is terminated * by a -1.
*
* SERVICE_TIME_SECTION :
* The service times of all nodes of a CVRP are given in the form (per line)
*
* <integer> <real>
*
* The integer specifies a node number, the real its service time.
* The depot node must also occur in this section. Its service time is 0.
*
* TIME_WINDOW_SECTION :
* Time windows are given in this section. Each line is of the form
*
* <integer> <real> <real>
*
* The first integer specifies a node number. The two reals specify
* earliest and latest arrival time for the node, respectively.
2.2 示例
直接使用点坐标(node_coord_section):
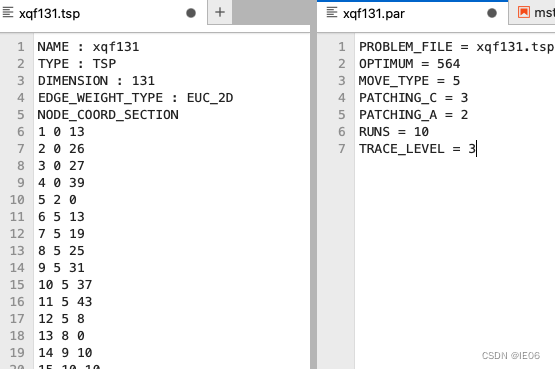
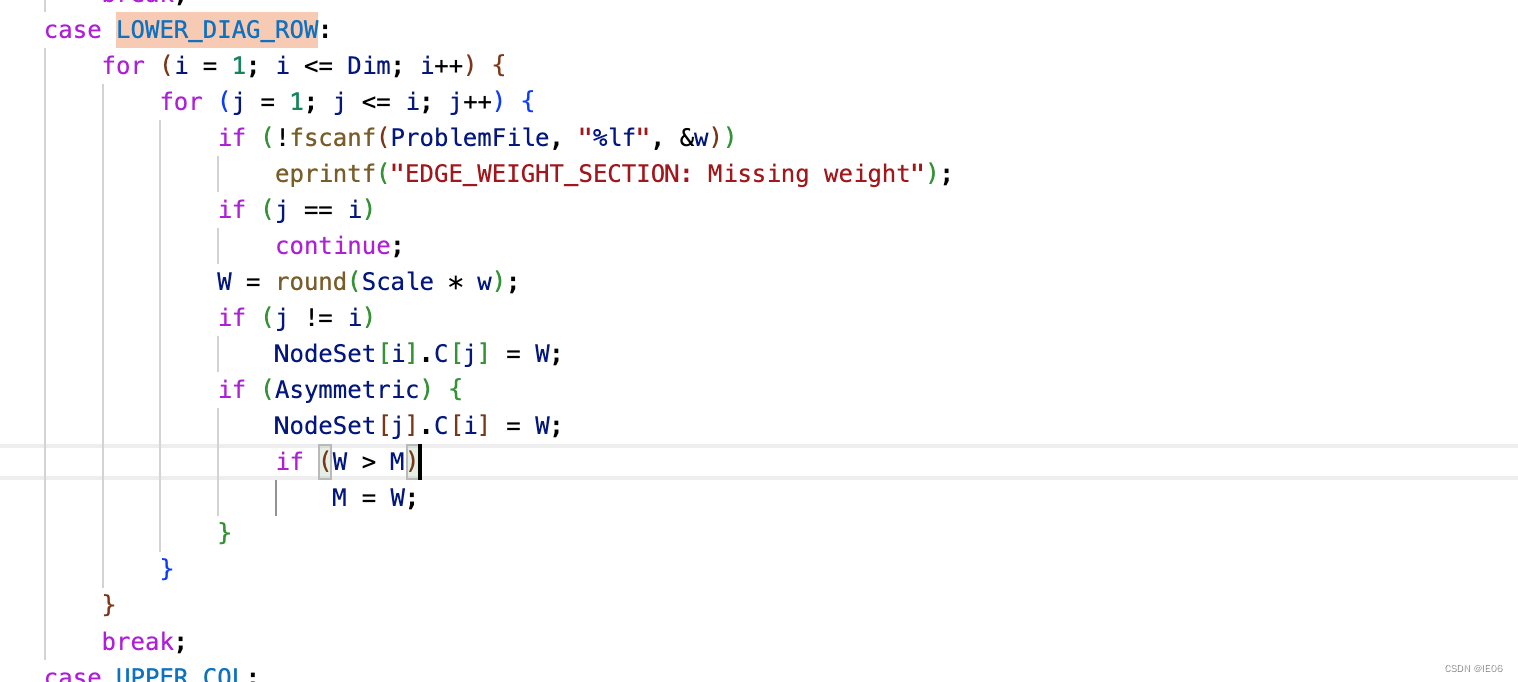
使用距离矩阵,我们以lower diag row为例,代码如下,
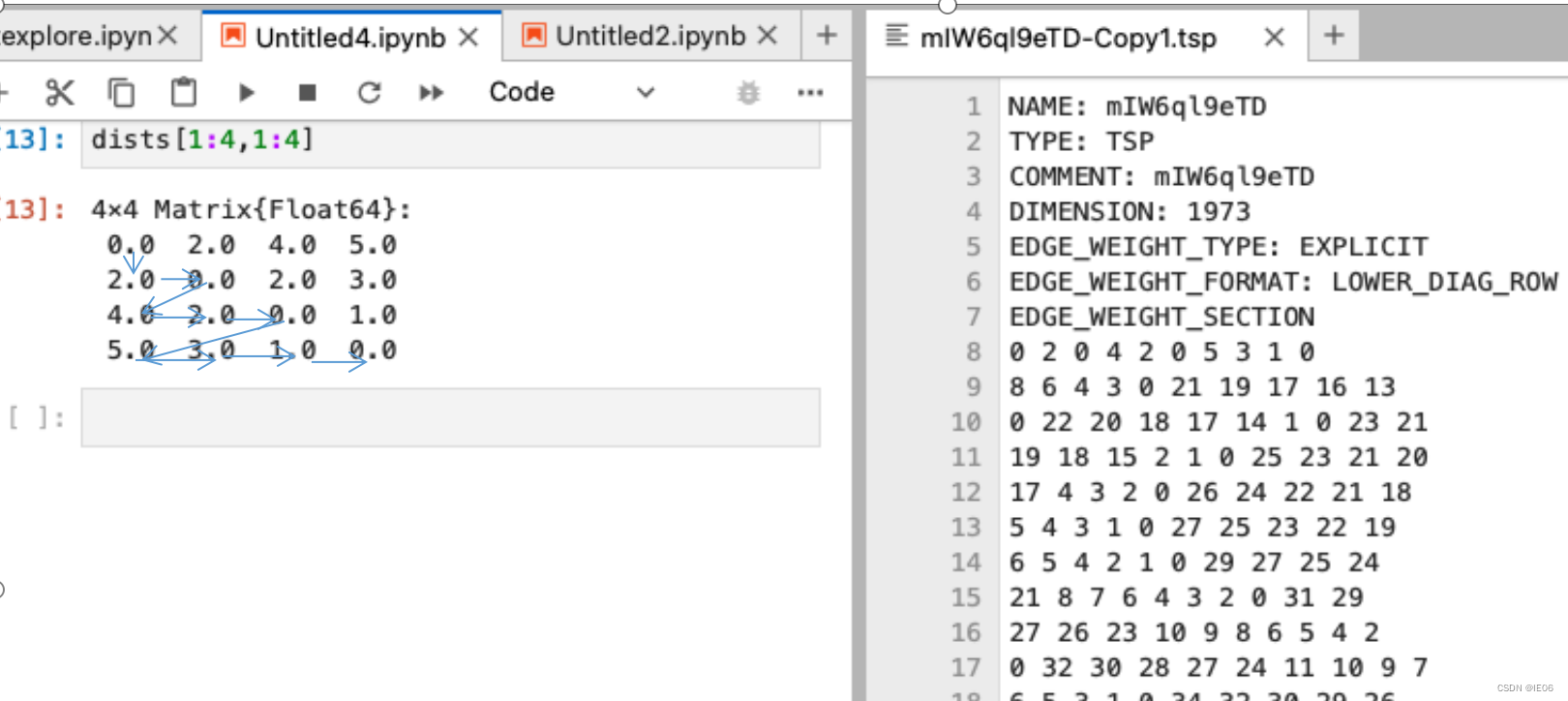
示例如下:
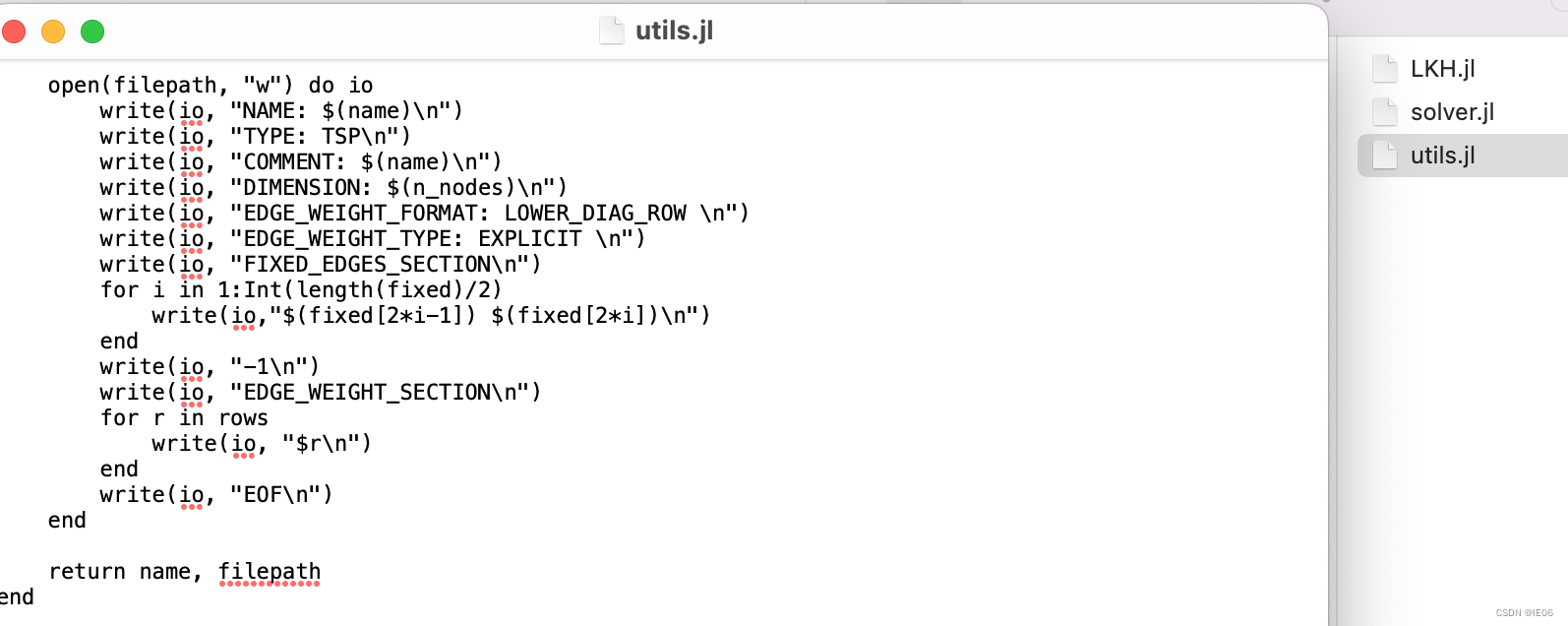
如果想要固定某些边,可以参考下面的代码,在tsp文件中添加fixed edge section
2.3 示例2
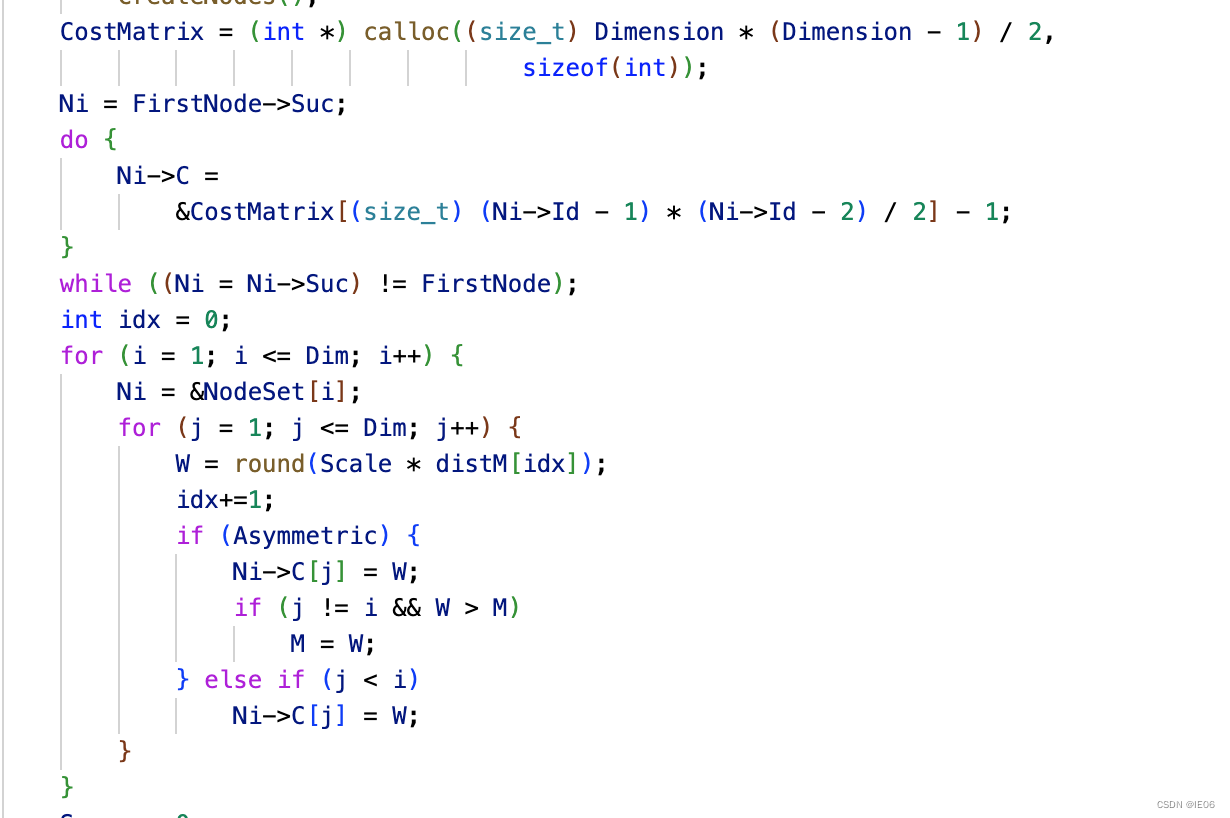
上面是通过读写文件的方式来传递问题数据的,下面说下直接通过库文件传递问题数据的方法。
首先在LKHmain.c中添加函数,例如double run_matrix(int* distM, int Dim),然后将readParameters和readProblem两个函数的内容修改后粘贴进函数中。读取数据的部分修改为从内存中读取: