文章目录
- 【LeetCode热题100】打卡第17天:接雨水&全排列&旋转图像
- ⛅前言
- 接雨水
- 🔒题目
- 🔑题解
- 全排列
- 🔒题目
- 🔑题解
- 旋转图像
- 🔒题目
- 🔑题解
【LeetCode热题100】打卡第17天:接雨水&全排列&旋转图像
⛅前言
大家好,我是知识汲取者,欢迎来到我的LeetCode热题100刷题专栏!
精选 100 道力扣(LeetCode)上最热门的题目,适合初识算法与数据结构的新手和想要在短时间内高效提升的人,熟练掌握这 100 道题,你就已经具备了在代码世界通行的基本能力。在此专栏中,我们将会涵盖各种类型的算法题目,包括但不限于数组、链表、树、字典树、图、排序、搜索、动态规划等等,并会提供详细的解题思路以及Java代码实现。如果你也想刷题,不断提升自己,就请加入我们吧!QQ群号:827302436。我们共同监督打卡,一起学习,一起进步。
博客主页💖:知识汲取者的博客
LeetCode热题100专栏🚀:LeetCode热题100
Gitee地址📁:知识汲取者 (aghp) - Gitee.com
Github地址📁:Chinafrfq · GitHub
题目来源📢:LeetCode 热题 100 - 学习计划 - 力扣(LeetCode)全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
PS:作者水平有限,如有错误或描述不当的地方,恳请及时告诉作者,作者将不胜感激
接雨水
🔒题目
原题链接:42. 接雨水
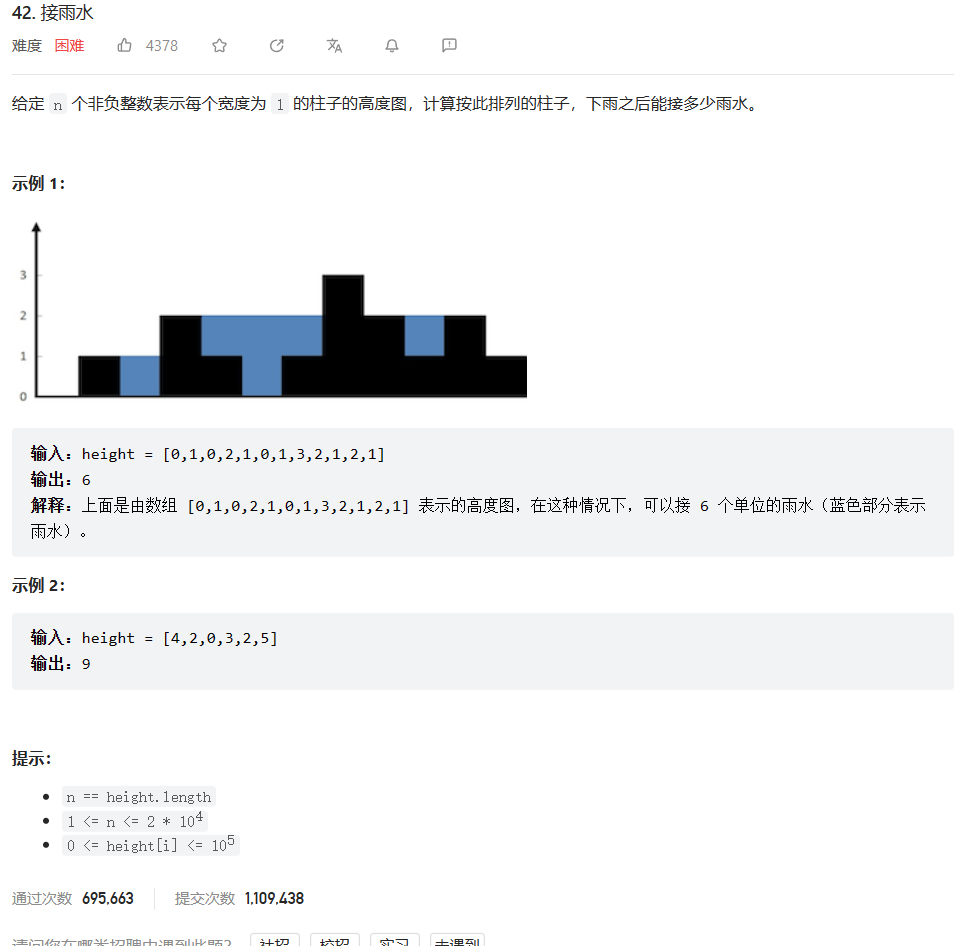
🔑题解
-
解法一:
待定复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( ) O() O()
- 空间复杂度: O ( ) O() O()
其中 n n n 为数组中元素的个数
全排列
🔒题目
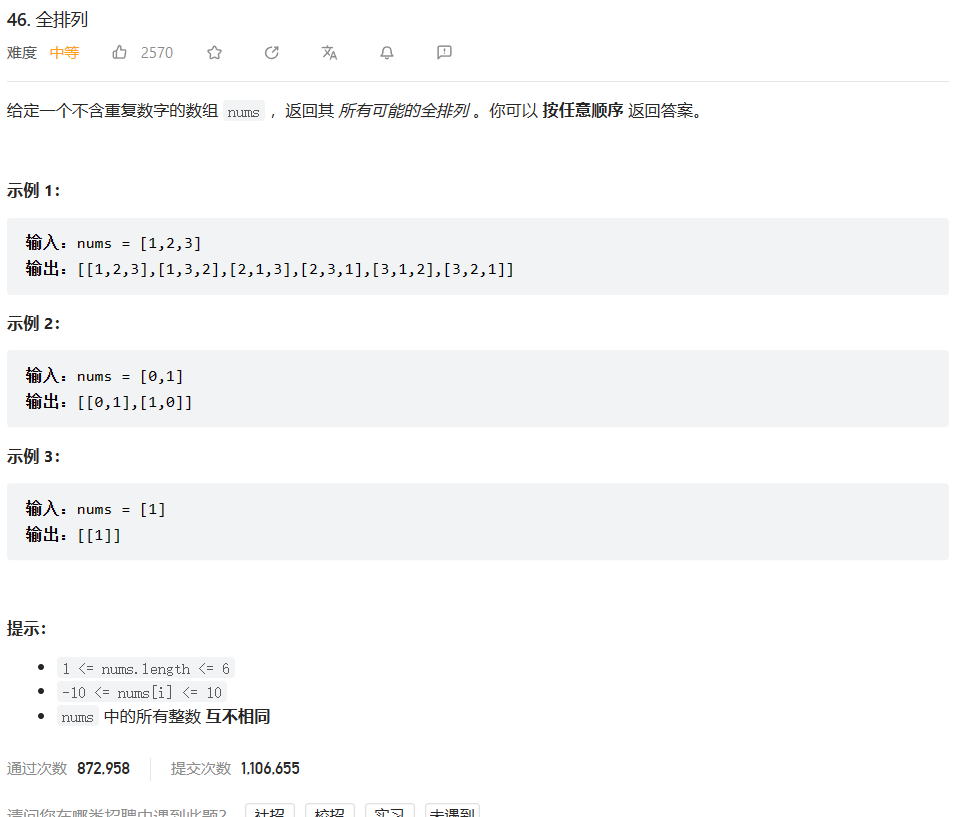
原题链接:46. 全排列
🔑题解
-
解法一:递归+回溯
看到这种全排列,一下就想到了BFS,这类题型算是很常规的题目了。这里就不再过多赘述了,毕竟时间宝贵
import java.util.*; /** * @author ghp * @title 全排列 */ class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>(10); Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); boolean[] vis = new boolean[nums.length]; bfs(ans, nums, path, vis); return ans; } private void bfs(List<List<Integer>> ans, int[] nums, Deque<Integer> path, boolean[] vis) { // 递归结束条件 if (path.size() == nums.length) { // 此时已经遍历到最后一层了 ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { if (!vis[i]) { // 当前元素没有没被遍历,则添加到path中 path.addLast(nums[i]); vis[i] = true; bfs(ans, nums, path, vis); // 恢复现场,用于回溯 vis[i] = false; path.removeLast(); } } } }备注:这里有一点小疑问?明明LinkedList删除和新增的性能要高于ArrayList,但是为什么使用ArrayList提交能够击败100%,但是使用LinkedList只能击败92%?有懂的大佬吗,希望能够为我解答一下疑惑w(゚Д゚)w
-
解法二:
这个解法是LeetCode官方提供的,我也是参考官方给出的思路,重新写了一遍。他是通过不断两两交换实现,思路比较新颖,十分值得借鉴。
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; import java.util.stream.Collectors; /** * @author ghp * @title 全排列 */ class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>(10); List<Integer> path = Arrays.stream(nums).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList()); bfs(ans, path, 0); return ans; } private void bfs(List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> path, int step) { // 递归结束条件 if (step == path.size()) { // 此时已经遍历到最后一层了 ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for (int i = step; i < path.size(); i++) { // 交换当前层元素(也就是第step个元素)与当前第i个元素 Collections.swap(path, step, i); // 遍历下一层 bfs(ans, path, step+1); // 恢复现场,用于回溯 Collections.swap(path, step, i); } } }
旋转图像
🔒题目
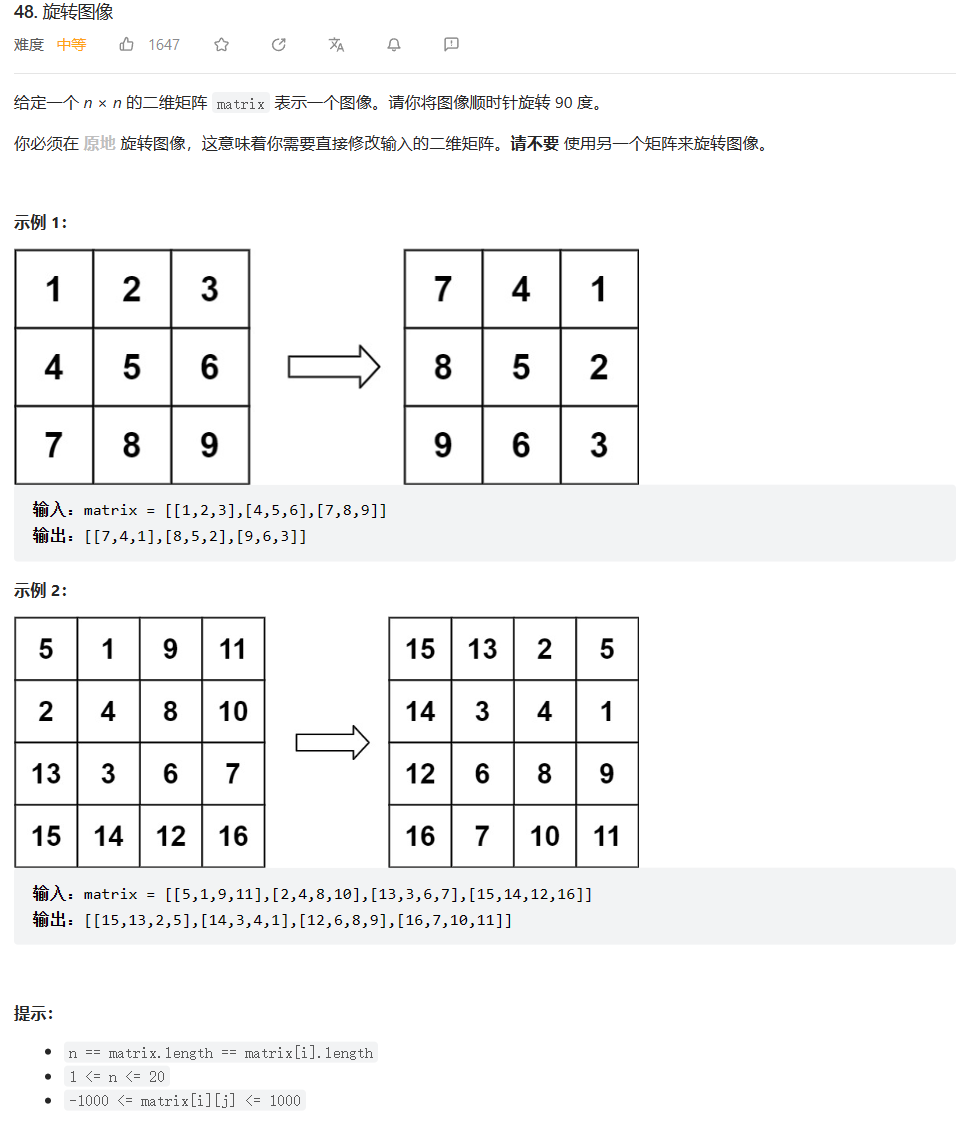
原题链接:48. 旋转图像
🔑题解
-
解法一:通过找出规律,进行替换
通过枚举,可以发现替换的规律,如下所示:
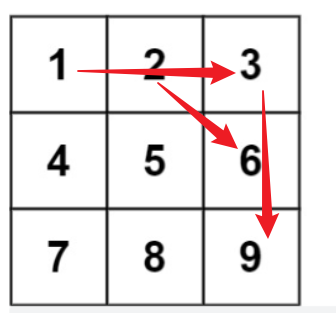
( 0 , 0 ) → ( 0 , n − 1 ) ( 0 , 1 ) → ( 1 , n − 1 ) ( 0 , 2 ) → ( 2 , n − 1 ) ( 1 , 0 ) → ( 0 , n − 2 ) ( 1 , 1 ) → ( 1 , n − 2 ) ( 1 , 2 ) → ( 2 , n − 2 ) . . . (0,0) → (0, n-1) \\ (0,1) → (1, n-1) \\ (0,2) → (2, n-1) \\ \\ (1,0) → (0, n-2) \\ (1,1) → (1, n-2) \\ (1,2) → (2, n-2) \\ ... (0,0)→(0,n−1)(0,1)→(1,n−1)(0,2)→(2,n−1)(1,0)→(0,n−2)(1,1)→(1,n−2)(1,2)→(2,n−2)...
经过枚举,我们可以得到替换公式: ( i , j ) → ( j , n − 1 − i ) (i, j)→(j, n-1-i) (i,j)→(j,n−1−i)import java.util.Arrays; /** * @author ghp * @title 旋转图像 */ class Solution { public void rotate(int[][] matrix) { int n = matrix.length; int[][] tempArr = new int[matrix.length][matrix.length]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { int t = matrix[i][j]; tempArr[j][n-1-i] = matrix[i][j]; } } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { matrix[i] = Arrays.copyOf(tempArr[i], tempArr[i].length); } } }复杂度分析
时间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
空间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
-
解法二:先水平翻转,后根据主对角线翻转
不得不佩服,这个思路真的是太巧妙了😫我怎么就想不到呢
class Solution { public void rotate(int[][] matrix) { int n = matrix.length; // 水平翻转 for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { int temp = matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j] = matrix[n - i - 1][j]; matrix[n - i - 1][j] = temp; } } // 主对角线翻转 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) { int temp = matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i]; matrix[j][i] = temp; } } } } 作者:LeetCode-Solution 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/rotate-image/solution/xuan-zhuan-tu-xiang-by-leetcode-solution-vu3m/ 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。复杂度分析
时间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)