目录
1.需要实现的项目需求(web服务器的工作原理)
2.实现过程:
1.编写套接字
2.多线程的代码和任务类
3.文件描述符的处理方法的框架
4.读取请求
4.1.读取请求行
4.2.读取请求报头
4.3.分析请求行和报头
请求行的方法、URI、版本放到承装容器;
4.4.读取正文
5.构建响应
5.1.根据请求方法和是否带参来判断是否需要进行CGI处理:
5.2.把URI处理合理
6.CGI处理
7.发送响应
9.源码链接
1.需要实现的项目需求(web服务器的工作原理)
实现:从用户输入网页地址,到建立连接、获取和分析请求、对有参数的请求进行CGI机制处理(CGI机制:用户会访问web服务器的任意文件,服务器需要依靠参数对文件进行处理,不能把处理方法放在web服务器的代码下,因为用户只会访问它需要的,那么大量的处理方法是无意义的,而且内容太多了)、构建和发送响应的全过程;
下面是我画的一个实现全过程的思维导图
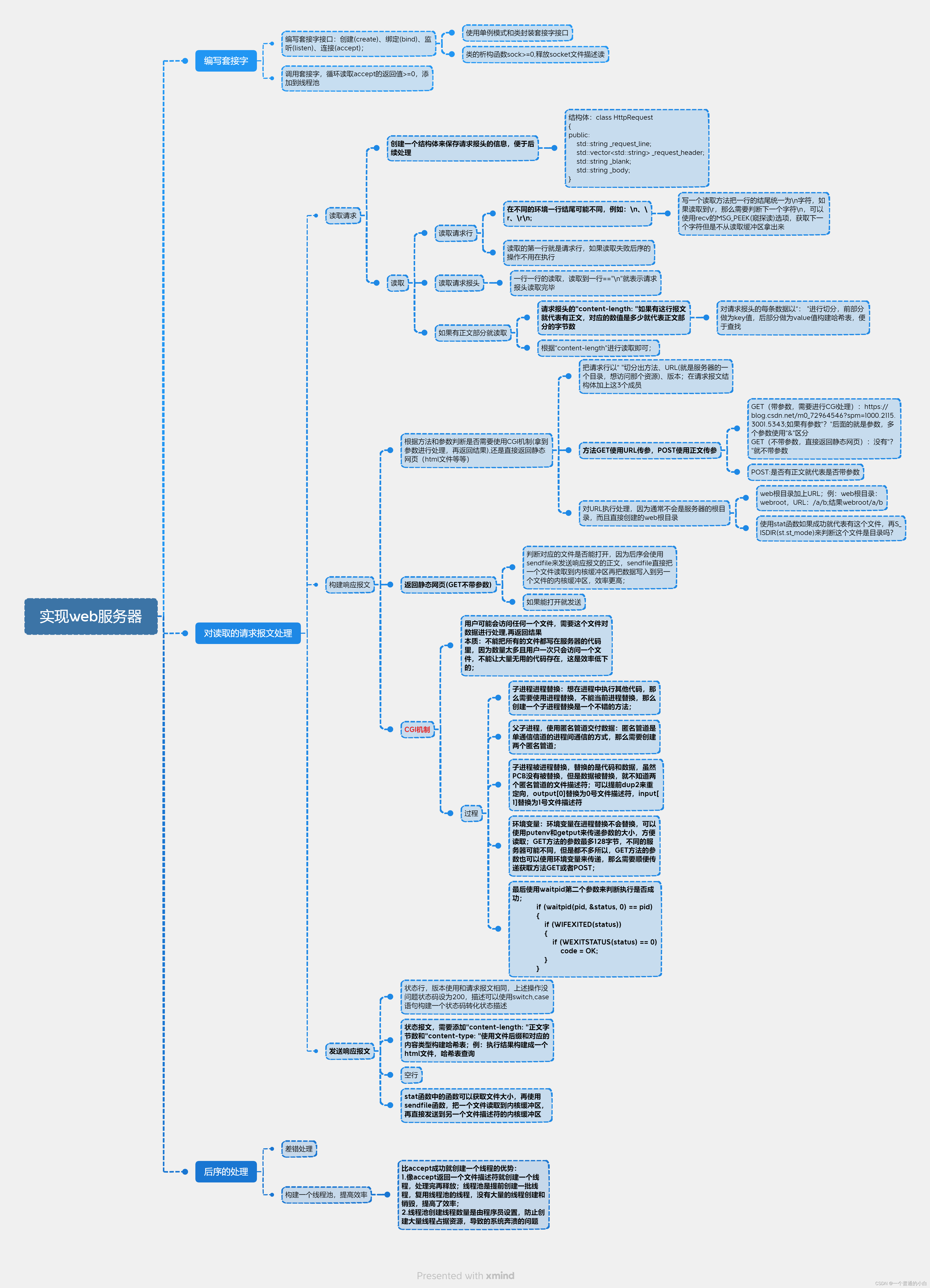
2.实现过程:
1.编写套接字
1. 使用单例模式类封装的一个套接字
#pragma once #include <iostream> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include"Log.hpp" #define Backlog 5 class TcpSocket { private: void Socket() { _socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (_socket < 0) { LOG(FATAL,"socket error"); exit(1); } // 快速重启 int opt = 1; setsockopt(_socket, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &opt, sizeof(opt)); } void Bind() { struct sockaddr_in local; // 把套接字置为0; memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local)); local.sin_family = AF_INET; local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; local.sin_port = htons(_port); if (bind(_socket, (struct sockaddr *)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0) { LOG(FATAL,"bind error"); exit(2); } } void Listen() { if (listen(_socket, Backlog) < 0) { LOG(FATAL,"listen error"); exit(3); } } public: void Init() { Socket(); Bind(); Listen(); } static TcpSocket *GetInstance(int port) { static pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; if (_sigleton == nullptr) { // 防止多进程访问临界资源 pthread_mutex_lock(&lock); if (_sigleton == nullptr) { _sigleton = new TcpSocket(port); _sigleton->Init(); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock); } return _sigleton; } int GetSocket() { return _socket; } ~TcpSocket() { if (_socket >= 0) close(_socket); } private: TcpSocket(int port) : _socket(-1), _port(port) { } TcpSocket(const TcpSocket &s) { } private: int _socket; int _port; // 单例模式指针 static TcpSocket *_sigleton; }; TcpSocket *TcpSocket::_sigleton = nullptr;2.获取请求,添加到多线程,sigpipe信号必须忽略,客服端可能随时关闭,读端关闭,写端收到sigpipe中止进程;
#include "TcpSocket.hpp" #include "Protocol.hpp" #include "Thread_pool.hpp" #include<signal.h> class HttpSocket { private: int _port; int _quit; public: HttpSocket(int port) : _port(port), _quit(false) { } void InitServer() { //信号SIGPIPE需要进行忽略,如果不忽略,在写入时候,可能直接崩溃server //客户端随时可能关闭连接, signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); } void loop() { TcpSocket *segleton = TcpSocket::GetInstance(_port); int listen_socket = segleton->GetSocket(); LOG(INFO,"build success,wait client"); while (!_quit) { struct sockaddr_in peer; socklen_t len = sizeof(peer); int new_socket = accept(listen_socket, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, &len); if(new_socket<0) continue; ThreadPool::GetInstance()->Push(new_socket); } } };主函数
#include "HttpServer.hpp" #include <cstdlib> #include <memory> void Usage() { std::cout << "usage: ./main port" << std::endl; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (argc != 2) { Usage(); return 1; } HttpSocket s(atoi(argv[1])); s.InitServer(); s.loop(); return 0; }
2.多线程的代码和任务类
线程池工作原理:一个生产消费模型的多线程线程池,accept成功后把sock文件描述符添加到线程池,由线程池构建一个Task类对象,Task类对象包含一个函数指针,这个指针指向对sock文件描述符的处理方法(读取请求报头、分析请求报头、构建响应报头等等);
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Task.hpp"
#define NUM 5
class ThreadPool
{
private:
void Lock()
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&_mt);
}
void Unlock()
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mt);
}
void Wait()
{
pthread_cond_wait(&_cond, &_mt);
}
void Wakeup()
{
pthread_cond_signal(&_cond);
}
bool IfEmpty()
{
_q.empty();
}
void Pop(Task &t)
{
t = _q.front();
_q.pop();
}
// 如果不是静态成员函数,那么参数实际有两个,一个是this指针
static void *handler(void *arg)
{
Task t;
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
ThreadPool *tp = (ThreadPool *)arg;
tp->Lock();
while (tp->IfEmpty())
{
tp->Wait();
}
tp->Pop(t);
tp->Unlock();
t.ProcessOn();
}
public:
void Push(int sock)
{
Task ts(sock);
_q.push(ts);
Wakeup();
}
void InitThread()
{
pthread_t pt[_num];
for (int i = 0; i < _num; i++)
{
if (pthread_create(&pt[i], nullptr, handler, this) != 0)
{
LOG(ERROR, "pthread_create fail");
exit(1);
}
}
}
static ThreadPool *GetInstance()
{
static pthread_mutex_t _mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
if (_sigleton == nullptr)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);
//双重判断,防止上面的判断成功线程被切换,调度回来时可能已经被其他线程new
if(_sigleton == nullptr)
{
_sigleton = new ThreadPool;
_sigleton->InitThread();
LOG(INFO,"thread init ok");
}
pthread_mutex_lock;
}
return _sigleton;
}
private:
ThreadPool() : _num(NUM)
{
pthread_mutex_init(&_mt, nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&_cond, nullptr);
}
ThreadPool(const ThreadPool &tp) = delete;
~ThreadPool()
{
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mt);
pthread_cond_destroy(&_cond);
}
private:
int _num;
std::queue<Task> _q;
pthread_mutex_t _mt;
pthread_cond_t _cond;
static ThreadPool *_sigleton;
};
ThreadPool *ThreadPool::_sigleton = nullptr;任务类:成员:1.accept返回的套接字文件描述符;2.对这个描述符的处理方法(读取请求报头、分析请求报头、构建响应报头等等);
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include "Protocol.hpp"
class Task
{
public:
Task()
{
}
Task(int sock) : _accept_sock(sock)
{
}
~Task()
{
}
void ProcessOn()
{
_cb.ProcessOn(_accept_sock);
}
private:
int _accept_sock;
Callback _cb;
};3.文件描述符的处理方法的框架
框架:分别承装请求和响应报文的类,把它们当做结构体,用做读取的请求、构建的响应的存放;对sock文件描述符需要做读取和分析请求、构建和发送响应;
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/sendfile.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include "Util.hpp"
#include "Log.hpp"
#define WEB_ROOT "webroot"
#define PAGE_404 "webroot/page_404.html"
#define PAGE_400 "webroot/page_400.html"
#define PAGE_500 "webroot/page_500.html"
#define HOME_PAGE "index.html"
#define OK 202
#define CLIENT_ERR 400
#define SERVER_ERR 500
#define NOT_FOUND 404
#define END_LINE "\n"
// 做为承装请求报文的容器
class HttpRequest
{
public:
std::string _request_line;
std::vector<std::string> _request_header;
std::string _blank;
std::string _body;
};
// 做为承装构建响应报文的容器
class HttpResponse
{
public:
std::string _status_line;
std::vector<std::string> _status_header;
std::string _blank;
std::string _body;
};
class EndPoint
{
private:
// 读取请求报头
bool RecvRequestLine()
{}
bool RecvRequestHeader()
{}
// 分析请求报头
void ParseRequestLine()
{}
bool RecvRequestBody()
{}
private:
void BuildStatusLine(int code)
{}
public:
// 读取
void RecvRequest()
{}
// 构建
void BuildResponse()
{}
void SendResponse()
{}
public:
EndPoint(int sock) : _new_socket(sock), _stop(false)
{}
~EndPoint()
{
if (_new_socket >= 0)
close(_new_socket);
}
private:
HttpRequest _http_request;
HttpResponse _http_response;
int _new_socket;
bool _stop;
};
class Callback
{
public:
void ProcessOn(int new_socket)
{
EndPoint ep(new_socket);
std::cout << "begin.........." << std::endl;
ep.RecvRequest();
if (ep.GetStop() == false)
{
ep.BuildResponse();
ep.SendResponse();
}
std::cout << "end.........." << std::endl;
}
};4.读取请求
4.1.读取请求行
读取函数:不同的环境下,http协议的结尾的区分可能不同,可能为'\n'、'\r\n'、'\r',需要统一为'\n',方便后序处理;下面使用了一个小技巧:recv的MSG_PEEK选项:窥探读,读取下一个字节,但是不从内核缓冲区拿出来,所以后序可以继续读这个字节;
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <string>
class Util
{
public:
static bool RecvLine(int sock, std::string &buffer)
{
char ch;
while (ch != '\n')
{
ssize_t s = recv(sock, &ch, 1, 0);
if (s > 0)
{
if (ch == '\r')
{
// 窥探下一个元素但是不拿取;
recv(sock, &ch, 1, MSG_PEEK);
if (ch == '\n') // 处理\r\n->\n
{
recv(sock, &ch, 1, 0);
}
else // 处理\r->\n
{
ch = '\n';
}
}
buffer.push_back(ch);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};读取请求报行 ,保存在承装类中,LOG是一个日志;
// 读取请求行
bool RecvRequestLine()
{
if (Util::RecvLine(_new_socket, _http_request._request_line))
{
// 去除\n
_http_request._request_line.pop_back();
LOG(INFO, _http_request._request_line);
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}4.2.读取请求报头
- 去除\n",后序要把请求报头的每行报文的类型和数据做哈希表;
// 读取请求报头
bool RecvRequestHeader()
{
std::string tmp;
while (tmp != "\n")
{
tmp.clear();
if (Util::RecvLine(_new_socket, tmp))
{
if (tmp != "\n")
{
// 去除\n
tmp.pop_back();
_http_request._request_header.push_back(tmp);
// LOG(INFO, tmp);
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}4.3.分析请求行和报头
-
请求行的方法、URI、版本放到承装容器;
- 请求报文的类型和数据,做哈希表,例:“content-length: 100”,key:content-length value:100;
// 分析请求行
void ParseRequestLine()
{
std::stringstream ss(_http_request._request_line);
ss >> _http_request._method >> _http_request._uri >> _http_request._version;
auto &method = _http_request._method;
std::transform(method.begin(), method.end(), method.begin(), ::toupper); //::是全局作用域符
}
//分析请求报头
void ParseRequestHeader()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _http_request._request_header.size(); i++)
{
std::string sub_out1;
std::string sub_out2;
if (Util::CutString(_http_request._request_header[i], ": ", sub_out1, sub_out2))
{
_http_request._um_header[sub_out1] = sub_out2;
}
else
break;
}
}4.4.读取正文
- 根据请求报头是否有content-length来判断是否有正文;
bool IsNeedRecvBody()
{
if (_http_request._method == "POST")
{
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string>::iterator it = _http_request._um_header.find("Content-Length");
_http_request._content_length = atoi(it->second.c_str());
if (_http_request._content_length > 0)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool RecvRequestBody()
{
if (IsNeedRecvBody())
{
char ch;
int num = _http_request._content_length;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
if (recv(_new_socket, &ch, 1, 0) > 0)
{
_http_request._body.push_back(ch);
// LOG(INFO, _http_request._body);
}
else
return false;
}
}
return true;
}5.构建响应
5.1.根据请求方法和是否带参来判断是否需要进行CGI处理:
- 如果不是GET和POST直接构建400(CLIENT_ERROR)响应;
- GET如果不带参就返回静态网页(读取对应文件的内容,再把内容发送给客户端);
- GET如果带参就需要进行CGI处理(GET使用URI传参,只能传递一些比较小的参数);
- POST需要进行CGI处理(传递任意大小的参数);
void BuildResponse()
{
auto &method = _http_request._method;
if (method != "GET" && method != "POST")
{
_http_response._stat_code = CLIENT_ERR;
LOG(RISK, "method is not right");
goto END;
}
if (method == "GET")
{
auto &uri = _http_request._uri;
if (uri.find('?') != std::string::npos)
{
_http_response._cgi = true;
Util::CutString(uri, "?", _http_request._url, _http_request._uri_argments);
}
else
_http_request._url = uri;
}
else if (method == "POST")
{
_http_request._url = _http_request._uri;
_http_response._cgi = true;
}
else
{
// do nothing
}5.2.把URI处理合理
- 访问的一定的是服务器想让你访问的资源,服务器会建立webroot目录(就是一个不同目录,webroot就是它的名字),存在这些可以访问的资源;
- 让webroot+=请求路径,才是合理的路径;
- 加后webroot/请求路径/,像这样格式就访问这个目录下的index.html(首页),webroot/请求路径/index.html
- 使用stat来判断文件是否存在,顺便使用se.st_size来获取文件大小保存在承装类中
// 不一定是根目录,把url处理为符合服务器的url
_http_request._request_path = WEB_ROOT;
_http_request._request_path += _http_request._url;
if (_http_request._request_path[_http_request._request_path.size() - 1] == '/')
{
// 把"/"或者"a/b/c/"这种目录都处理为,访问目录下的index.html
_http_request._request_path += HOME_PAGE;
}
// 判断路径是否存在
struct stat st;
// 等于0代表执行函数成功,也等于有这个文件
if (stat(_http_request._request_path.c_str(), &st) == 0)
{
if (S_ISDIR(st.st_mode))
{
// 处理最后不是'/'的路径,例:/a/b/c
_http_request._request_path += "/";
_http_request._request_path += HOME_PAGE;
stat(_http_request._request_path.c_str(), &st);
}
if ((st.st_mode & S_IXUSR) || (st.st_mode & S_IXGRP) || (st.st_mode & S_IXOTH))
{
// 特殊处理
_http_request._cgi = true;
}
_http_request._size = st.st_size;
}
else
{
// 文件不存在
LOG(RISK, _http_request._request_path);
_http_response._stat_code = CLIENT_ERR;
goto END;
}
// CGI处理
if (_http_response._cgi)
{
_http_response._stat_code = ProcessCgi();
}
else
{
// 不需要CGI处理,返回静态网页
_http_response._stat_code = ProcessNonCgi();
}
END:
auto &code = _http_response._stat_code;
// 构建状态行
BuildStatusLine(code);
// 构建响应报文
switch (code)
{
case OK:
HandlerOK();
break;
case NOT_FOUND:
HandlerError(code);
break;
case CLIENT_ERR:
HandlerError(code);
break;
case SERVER_ERR:
HandlerError(code);
break;
default:
break;
}
return;
}6.CGI处理
- CGI机制的原因:CGI机制:用户会访问web服务器的任意文件,服务器需要依靠参数对文件进行处理;不能把处理方法放在web服务器的代码下,因为用户只会访问它需要的,那么大量的处理方法是无意义的,而且内容太多了;
- CGI机制的本质:使用子进程进程替换,使用环境变量传递参数大小,匿名管道传递参数和执行结果;
- 匿名管道需要两个,因为匿名管道是单信道通信;
int ProcessCgi() //(重点)
{
int code = SERVER_ERR;
auto &path = _http_request._request_path;
auto &method = _http_request._method;
auto &get_arguments = _http_request._uri_argments;
auto &post_arguments = _http_request._body;
auto &body = _http_response._body;
// 把数据大小添加到环境变量内,返回被替换的子进程拿取
std::string arguments_size;
arguments_size += "ARGUMENTS_SIZE=";
if (method == "GET")
arguments_size += std::to_string(get_arguments.size());
else if (method == "POST")
arguments_size += std::to_string(post_arguments.size());
putenv((char *)arguments_size.c_str());
// 匿名管道是单信道通信,站在父进程的视角
int output[2];
int input[2];
if (pipe(output) == -1)
{
LOG(ERROR, "pipe output[2] create fail");
return SERVER_ERR;
}
if (pipe(input) == -1)
{
LOG(ERROR, "pipe input[2] create fail");
return SERVER_ERR;
}
// 创建子进程后续用来进程替换
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == 0)
{
close(output[1]);
close(input[0]);
// 站在子进程的视角,进程替换数据被替换,提前使用dup2把:
// output[0]->标准输入
// input[1]->标准输出
dup2(output[0], 0);
dup2(input[1], 1);
if (execl(path.c_str(), path.c_str(), nullptr) == -1)
{
std::cout << 2 << std::endl;
}
exit(0);
}
else if (pid > 0)
{
close(output[0]);
close(input[1]);
if (method == "GET")
{
write(output[1], get_arguments.c_str(), get_arguments.size());
}
if (method == "POST")
{
// post参数的大小可能很多,一次可能写不完
int psize = post_arguments.size();
int total = 0;
ssize_t s = 0;
while (total < psize && (s = write(output[1], post_arguments.c_str() + total, psize - total)) > 0)
{
if (s <= 0)
{
LOG(ERROR, "write error");
break;
}
total += s;
// std::cout << psize << ":" << s << ":" << total << std::endl;
}
}
// 读取cgi结果
char ch;
while (read(input[0], &ch, 1) > 0)
{
body.push_back(ch);
}
// std::cout<<body<<std::endl;
int status;
if (waitpid(pid, &status, 0) == pid)
{
if (WIFEXITED(status))
{
if (WEXITSTATUS(status) == 0)
code = OK;
else
LOG(error, "error code discontinue");
}
else
LOG(error, "signal discontinue");
}
else
{
LOG(ERROR, "waitpid fail");
return SERVER_ERR;
}
close(output[1]);
close(input[0]);
}
else
{
// fork错误
LOG(ERROR, "fork fail");
return SERVER_ERR;
}
return code;
}我执行的文件是一个简单的加法;
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdlib>
bool GetArguments(std::string &arguments)
{
char ch;
int size = atoi(getenv("ARGUMENTS_SIZE"));
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
read(0, &ch, 1);
arguments.push_back(ch);
}
if (arguments.size() == size)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void CutArguments(const std::string &in, const std::string &op, std::string& arg1, std::string& arg2)
{
int pos = in.find(op);
arg1 = in.substr(0, pos);
arg2 = in.substr(pos + op.size());
}
void CutArguments(const std::string &in, const std::string &op, std::string &name, int &value)
{
int pos = in.find(op);
name = in.substr(0, pos);
value = atoi(in.substr(pos + op.size()).c_str());
}
bool PutCGIResult(int arg1, int arg2)
{
std::string s;
s+=std::to_string(arg1);
s+="+";
s+=std::to_string(arg2);
s+="=";
s+=std::to_string(arg1+arg2);
if (write(1, s.c_str(), s.size()) < 0)
return false;
// if (write(1, arg2.c_str(), arg2.size()) < 0)
// return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
std::cerr<<12<<std::endl;
std::string arguments;
if (GetArguments(arguments) == false)
return 1;
std::cerr<<arguments<<std::endl;
// 处理参数
std::string arg1, arg2;
CutArguments(arguments, "&", arg1, arg2);
std::string name1, name2;
int value1, value2;
CutArguments(arg1, "=", name1, value1);
CutArguments(arg2, "=", name2, value2);
// 返回结果
if (PutCGIResult(value1, value2) == false)
return 2;
return 0;
}7.发送响应
void SendResponse()
{
if (send(_new_socket, _http_response._status_line.c_str(), _http_response._status_line.size(), 0) <= 0)
return;
std::cout << _http_response._status_line;
for (auto &at : _http_response._status_header)
{
if (send(_new_socket, at.c_str(), at.size(), 0) <= 0)
return;
std::cout << at;
}
send(_new_socket, _http_response._blank.c_str(), _http_response._blank.size(), 0);
std::cout << _http_response._blank;
if (_http_response._cgi)
{
int size = _http_response._body.size();
int total = 0;
ssize_t s;
std::cout << _http_response._body << std::endl;
while (total < size && (s = send(_new_socket, _http_response._body.c_str() + total, size - total, 0)) > 0)
{
if (s <= 0)
{
LOG(ERROR, "write error");
break;
}
total += s;
// std::cout << size << ":" << s << ":" << total << std::endl;
}
}
else
{
int fd = open(_http_request._request_path.c_str(), O_RDONLY);
if (fd >= 0)
sendfile(_new_socket, fd, 0, _http_request._size);
}
}8.执行结果
这个项目注重理解的是 建立连接、获取和分析请求、对有参数的请求进行CGI机制处理(CGI机制:用户会访问web服务器的任意文件,服务器需要依靠参数对文件进行处理,不能把处理方法放在web服务器的代码下,因为用户只会访问它需要的,那么大量的处理方法是无意义的,而且内容太多了)、构建和发送响应的全过程;
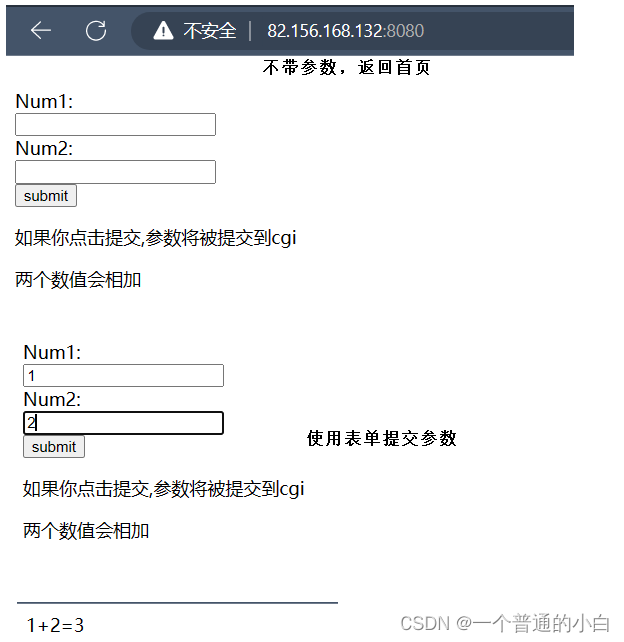
9.源码链接
Linux/web_server at main · lijinggai/Linux · GitHub