目录
一. 关于哈希表
二. 如何实现哈希表
1. 散列函数
2. 散列表
3. 散列函数的构造方法
4. 处理冲突的方法
三. 代码实现
1. 构造函数构造哈希表
2. 哈希表的查找
四. 代码展示
五. 数据测试编辑
六. 总结
一. 关于哈希表
在前面介绍的线性表的查找中,记录在表中的位置与记录的关键字之间不存在确定关系,因此,在这些表中查找记录时需进行一系列的关键字比较。这类查找方法建立在“比较”的基础上,查找的效率取决于比较的次数。
二. 如何实现哈希表
1. 散列函数
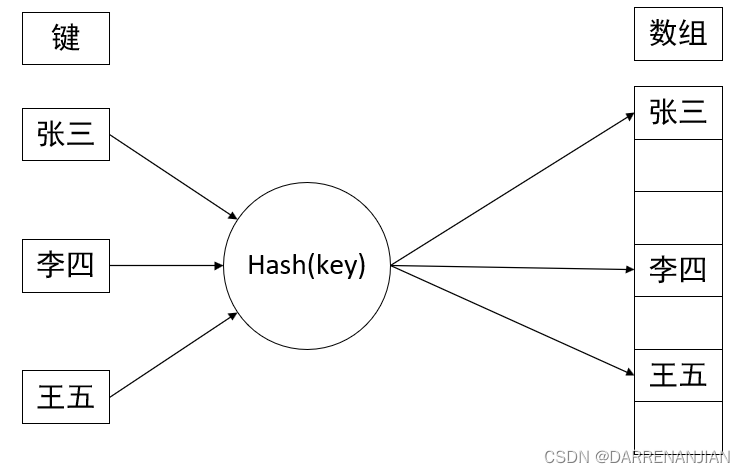
一个把查找表中的关键字映射成该关键字对应的地址的函数,记为(这里的地址可以是数组下标、有索引或内存地址等)。散列函数可能会把两个或两个以上的不同关键字映射到同一地址,称这种情况为冲突,这些发生碰撞的不同关键字称为同义词。一方面, 设计得好的散列函数应尽量减少这样的冲突;另一方面,由于这样的冲突总是不可避免的,所以还要设计好处理冲突的方法。
2. 散列表
根据关键字而直接进行访问的数据结构。也就是说,散列表建立了关键字和存储地址之间的一种直接映射关系。理想情况下,对散列表进行查找的时间复杂度为0(1),即与表中元素的个数无关。下面分别介绍常用的散列函数和处理冲突的方法。
3. 散列函数的构造方法
1)散列函数的定义域必须包含全部需要存储的关键字,而值域的范围则依赖于散列表的大小或地址范围。
2)散列函数计算出来的地址应该能等概率。均匀的分布在整个地址空间中,从而减少冲突的发生。
3)散列函数应尽量简单,能够在较短的时间内计算出任意一个关键字对应的散列地址。
以下是常用的散列函数:
4. 处理冲突的方法
线性探测法:冲突发生时,顺序查看表中下一个单元(探测到表尾地址m-1时,下一个探测地址是表首地址0),直到找出下一个空闲单元(当表未填满时一定能找到一个空闲单元)或查遍全表。线性探测法可能使第i个散列地址的同义词存入第i+1个散列地址,这样本应该存入i+1个散列地址的元素就争夺i+2个散列地址的元素地址...从而造成大量元素在相邻的散列地址上堆积起来,大大降低了查找效率。
除此之外再介绍一种拉链法处理冲突:当我们的同义词发生冲突之后,可以把所有的同义词存储在一个线性链表中,这个线性链表由其散列地址唯一标识。假设散列地址i的同义词链表的头指针存放在散列表的第i个单元中,因而查找、插入、删除操作主要在同义词链中进行。例如散列函数Hash(key)=key%13,用拉链法处理冲突建立如下的哈希表
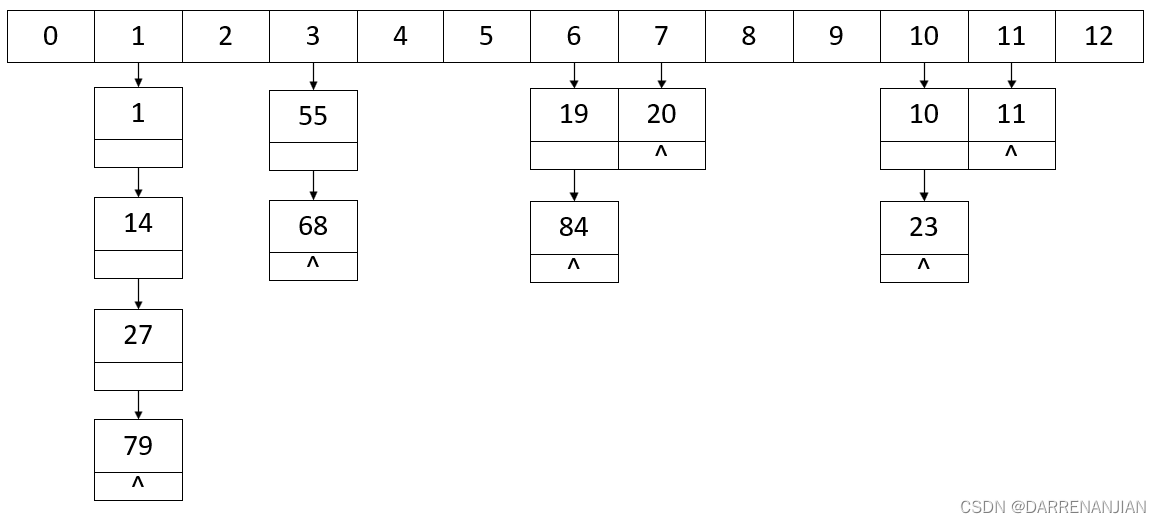
还有平方探测法,双散列法,伪随机探测法在这里就不一一赘述。
三. 代码实现
1. 构造函数构造哈希表
在这里设置了一个新的构造函数,传入标签数组paraKeyArray,对应的数据数组paraContentArray,还有哈希表长度paraLength。构造一个长度为paraLength的数组,每个位置上是用哈希函数得到的节点值。
/**
*********************
* The second constructor. For Hash code only. It is assumed that
* paraKeyArray.length <= paraLength.
*
* @param paraKeyArray The array of the keys.
* @param paraContentArray The array of contents.
* @param paraLength The space for the Hash table.
*********************
*/
public DataArray(int[] paraKeyArray, String[] paraContentArray, int paraLength) {
// Step 1. Initialize.
length = paraLength;
data = new DataNode[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
data[i] = null;
} // Of for i
// Step 2. Fill the data.
int tempPosition;
for (int i = 0; i < paraKeyArray.length; i++) {
// Hash.
tempPosition = paraKeyArray[i] % paraLength;
// Find an empty position
while (data[tempPosition] != null) {
tempPosition = (tempPosition + 1) % paraLength;
System.out.println("Collision, move forward for key " + paraKeyArray[i]);
} // Of while
data[tempPosition] = new DataNode(paraKeyArray[i], paraContentArray[i]);
} // Of for i
}// Of the second constructor2. 哈希表的查找
构建完成哈希表之后,开始查找,输入需要查找的标签i,先查找i%paraLength的位置是不是i;若不是则将i自加1,再用(i+1)%paraLength查找第二个位置;继续如上循环直到查找到为止。
/**
*********************
* Hash search.
*
* @param paraKey The given key.
* @return The content of the key.
*********************
*/
public String hashSearch(int paraKey) {
int tempPosition = paraKey % length;
while (data[tempPosition] != null) {
if (data[tempPosition].key == paraKey) {
return data[tempPosition].content;
} // Of if
System.out.println("Not this one for " + paraKey);
tempPosition = (tempPosition + 1) % length;
} // Of while
return "null";
}// Of hashSearch四. 代码展示
主类
package Day_42;
import Day_41.DataArray;
public class demo1 {
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
// System.out.println("\r\n-------sequentialSearchTest-------");
int []paraKeyArray;
paraKeyArray=new int[]{1,2,3};
String[] paraContentArray = new String[]{"121","21","324"};
DataArray test=new DataArray(paraKeyArray,paraContentArray);
test.hashSearchTest();
}// Of main
}
调用类:
package Day_41;
/**
* Data array for searching and sorting algorithms.
*
* @author Jian An 2569222191@qq.com.
*/
public class DataArray {
/**
* An inner class for data nodes. The text book usually use an int value to
* represent the data. I would like to use a key-value pair instead.
*/
class DataNode {
/**
* The key.
*/
int key;
/**
* The data content.
*/
String content;
/**
* ********************
* The first constructor.
* ********************
*/
DataNode(int paraKey, String paraContent) {
key = paraKey;
content = paraContent;
}// Of the first constructor
/**
* ********************
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
* ********************
*/
public String toString() {
return "(" + key + ", " + content + ") ";
}// Of toString
}// Of class DataNode
/**
* The data array.
*/
DataNode[] data;
/**
* The length of the data array.
*/
int length;
/**
* ********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraKeyArray The array of the keys.
* @param paraContentArray The array of contents.
* ********************
*/
public DataArray(int[] paraKeyArray, String[] paraContentArray) {
length = paraKeyArray.length;
data = new DataNode[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
data[i] = new DataNode(paraKeyArray[i], paraContentArray[i]);
} // Of for i
}// Of the first constructor
/**
* ********************
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
* ********************
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "I am a data array with " + length + " items.\r\n";
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
resultString += data[i] + " ";
} // Of for i
return resultString;
}// Of toString
/**
* ********************
* Sequential search. Attention: It is assume that the index 0 is NOT used.
*
* @param paraKey The given key.
* @return The content of the key.
* ********************
*/
public String sequentialSearch(int paraKey) {
data[0].key = paraKey;
int i;
// Note that we do not judge i >= 0 since data[0].key = paraKey.
// In this way the runtime is saved about 1/2.
// This for statement is equivalent to
//for (i = length - 1; data[i].key != paraKey; i--);
for (i = length - 1; data[i].key != paraKey; i--) {
;
}//Of for i
return data[i].content;
}// Of sequentialSearch
/**
* ********************
* Test the method.
* ********************
*/
public static void sequentialSearchTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = {-1, 5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9};
String[] tempContents = {"null", "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while"};
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
System.out.println("Search result of 10 is: " + tempDataArray.sequentialSearch(10));
System.out.println("Search result of 5 is: " + tempDataArray.sequentialSearch(5));
System.out.println("Search result of 4 is: " + tempDataArray.sequentialSearch(4));
}// Of sequentialSearchTest
/**
* ********************
* Binary search. Attention: It is assume that keys are sorted in ascending
* order.
*
* @param paraKey The given key.
* @return The content of the key.
* ********************
*/
public String binarySearch(int paraKey) {
int tempLeft = 0;
int tempRight = length - 1;
int tempMiddle = (tempLeft + tempRight) / 2;
while (tempLeft <= tempRight) {
tempMiddle = (tempLeft + tempRight) / 2;
if (data[tempMiddle].key == paraKey) {
return data[tempMiddle].content;
} else if (data[tempMiddle].key <= paraKey) {
tempLeft = tempMiddle + 1;
} else {
tempRight = tempMiddle - 1;
}
} // Of while
// Not found.
return "null";
}// Of binarySearch
/**
* ********************
* Test the method.
* ********************
*/
public static void binarySearchTest() {
int[] tempSortedKeys = {1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10};
String[] tempContents = {"if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while"};
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempSortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
System.out.println("Search result of 10 is: " + tempDataArray.binarySearch(10));
System.out.println("Search result of 5 is: " + tempDataArray.binarySearch(5));
System.out.println("Search result of 4 is: " + tempDataArray.binarySearch(4));
}// Of binarySearchTest
/**
*********************
* The second constructor. For Hash code only. It is assumed that
* paraKeyArray.length <= paraLength.
*
* @param paraKeyArray The array of the keys.
* @param paraContentArray The array of contents.
* @param paraLength The space for the Hash table.
*********************
*/
public DataArray(int[] paraKeyArray, String[] paraContentArray, int paraLength) {
// Step 1. Initialize.
length = paraLength;
data = new DataNode[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
data[i] = null;
} // Of for i
// Step 2. Fill the data.
int tempPosition;
for (int i = 0; i < paraKeyArray.length; i++) {
// Hash.
tempPosition = paraKeyArray[i] % paraLength;
// Find an empty position
while (data[tempPosition] != null) {
tempPosition = (tempPosition + 1) % paraLength;
System.out.println("Collision, move forward for key " + paraKeyArray[i]);
} // Of while
data[tempPosition] = new DataNode(paraKeyArray[i], paraContentArray[i]);
} // Of for i
}// Of the second constructor
/**
*********************
* Hash search.
*
* @param paraKey The given key.
* @return The content of the key.
*********************
*/
public String hashSearch(int paraKey) {
int tempPosition = paraKey % length;
while (data[tempPosition] != null) {
if (data[tempPosition].key == paraKey) {
return data[tempPosition].content;
} // Of if
System.out.println("Not this one for " + paraKey);
tempPosition = (tempPosition + 1) % length;
} // Of while
return "null";
}// Of hashSearch
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void hashSearchTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { 16, 33, 38, 69, 57, 95, 86 };
String[] tempContents = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents, 19);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
System.out.println("Search result of 95 is: " + tempDataArray.hashSearch(95));
System.out.println("Search result of 38 is: " + tempDataArray.hashSearch(38));
System.out.println("Search result of 57 is: " + tempDataArray.hashSearch(57));
System.out.println("Search result of 4 is: " + tempDataArray.hashSearch(4));
}// Of hashSearchTest
}// Of class DataArray五. 数据测试
六. 总结
这一小节的代码比较简单,这一节的知识体现不在代码上,而在于构造哈希函数,处理冲突方法的结构上。一个好的哈希表处理查找的效率是O(1),即瞬间可以得到传入标签的数据值,这在我们无论哪一个查找算法中无疑都是最快的。但是缺点也还是有的,若构造哈希函数没有构造好,或者冲突的没有处理好,那将造成大范围的“聚集”现象,大大降低查找效率。
除此之外,现目前很多的编程环境已经自带了哈希表的包,例如哈希表在JDK中有不少的实现,例如HahsMap、HashTable等,对哈希表感兴趣的可以阅读本文后去查看JDK的相应实现,相信这可以增强你对哈希表的理解。