1. 使用
1.1 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
1.2 定义切面类
定义一个切面类,指定增强的方法,方法前两个注解必须有
execution( * com.lzp..controller..(…)) 代表 com.lzp包下所有包下controller包下所有类的所有方法都会被代理,就代表所有,第一个是所有方法的返回值,第一个前面还有方法修饰符,public之类的,缺省就表示所有修饰符,最后一个代表所有方法名,(…)代表方法参数,…是指所有参数,倒数第二个代表类,第二个*代表包。这样调用对应包下的方法时就会被增强。
所以顺序就是 修饰符 返回值 包名 类名 方法名 方法参数
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class TestAspect {
@Around("execution( * com.lzp.*.controller.*.*(..))")
public void arround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
try {
log.info("1、Around:方法环绕开始.....");
Object o = pjp.proceed();
log.info("3、Around:方法环绕结束,结果是 :" + o);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 表达式多种多样,根据需求配置即可
- 表达式还可以针对注解使用 自定义和非自定义注解都可以
- 表达式参考
1.3 定义被增强的方法
在规则配置的包下的类中定义方法即可,这样在调用test01方法时,就会进行增强了。
@RestController
public class TestController {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
@GetMapping("/")
public String test01(){
if(logger.isDebugEnabled()){
logger.fatal(123);
}
return "hello11122222";
}
}
注意:切面类和被增强方法所在的类,都要注册到sping中。
2. 自动配置
2.1 AopAutoConfiguration
引入依赖后会自动配置aop
AopAutoConfiguration
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
//引入依赖后这里就会通过
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "auto", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
public class AopAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass(Advice.class)
static class AspectJAutoProxyingConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "false")
static class JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
//默认使用这个cglib创建代理 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy是开启aop功能
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true",
matchIfMissing = true)
static class CglibAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("org.aspectj.weaver.Advice")
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true",
matchIfMissing = true)
static class ClassProxyingConfiguration {
@Bean
static BeanFactoryPostProcessor forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying() {
return (beanFactory) -> {
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
};
}
}
}
2.2 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy会引入AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar,这个Registrar会引入AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的bean定义信息。关键类,aop的功能就是由它和它的父类们实现的。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承了AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean方法在执行doCreateBean之前会执行本类的resolveBeforeInstantiation方法。
@Nullable
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object bean = null;
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd);
if (targetType != null) {
//关键方法
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
if (bean != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
}
mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null);
}
return bean;
}
resolveBeforeInstantiation方法会调用本类的applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation方法
遍历processors 调用对应postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法,这里的关键是AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator这个processor,上面自动配置引入的就是这个类,会执行他的父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法
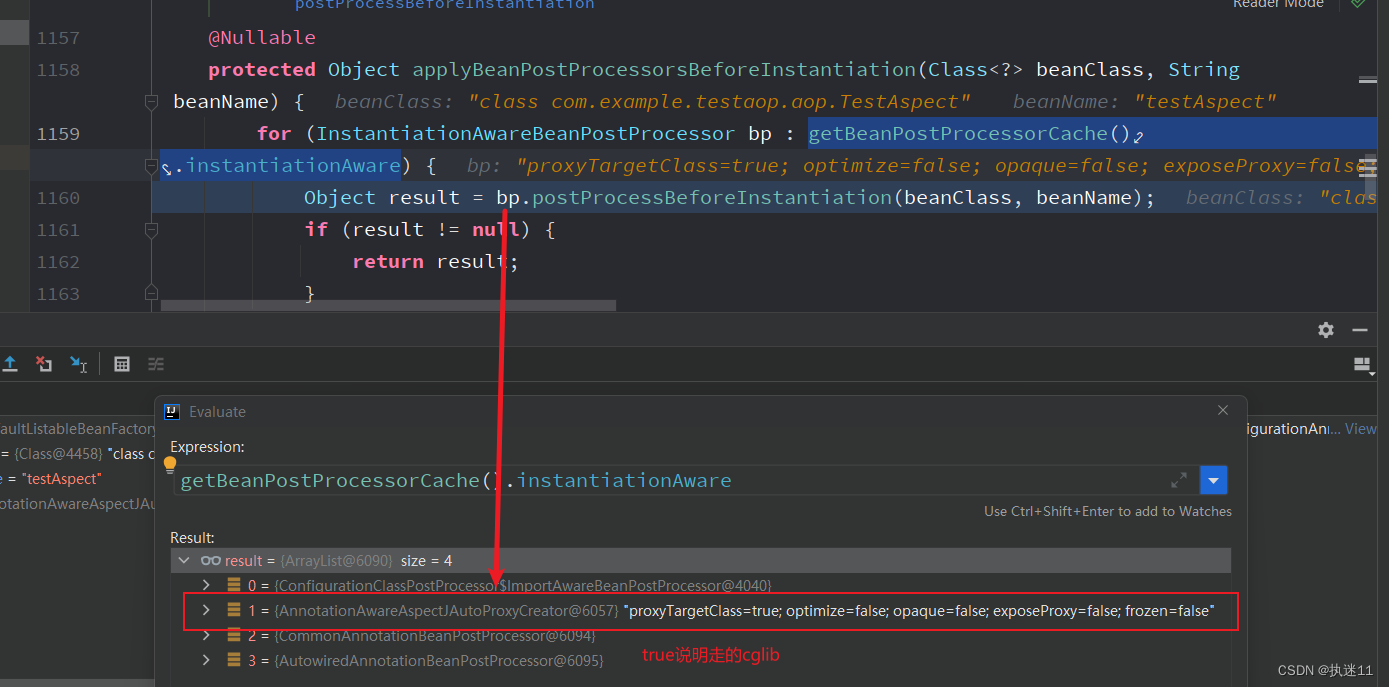
aop的功能由此开始实现
3. 原理
3.1 解析切面类
解析切面类由
AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessBeforeInstantiation完成
重写InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法
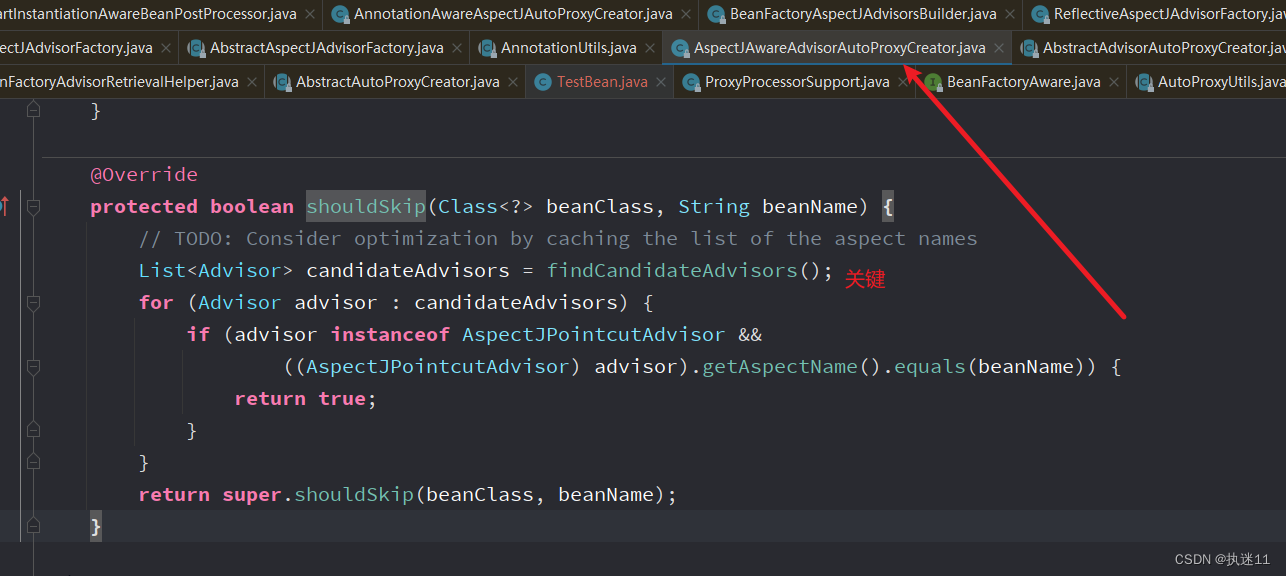
这里的逻辑是普通类进入判断,advisedBeans的value设置为false,需要增强的类不会进入判断,通过shouldSkip方法获取到切面中配置的增强方法(也就是加了@around注解的方法)
这里普通的类(包括切面类)会进入判断,但是切面类中配置的增强类不会进入判断,
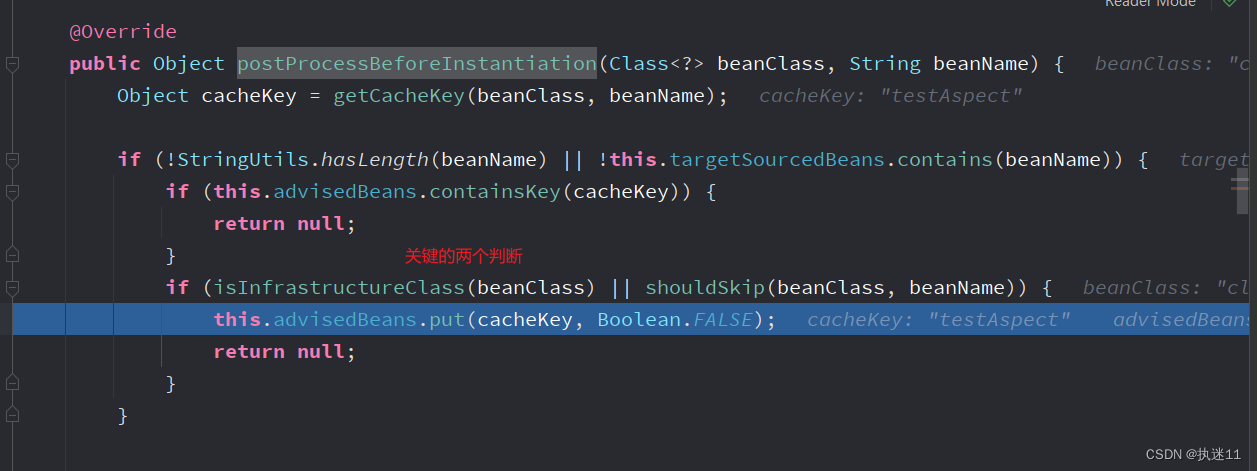
3.1.1 第一个判断
加了@aspect的类会通过
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator重写了isInfrastructureClass方法,所以会执行AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类的isInfrastructureClass方法
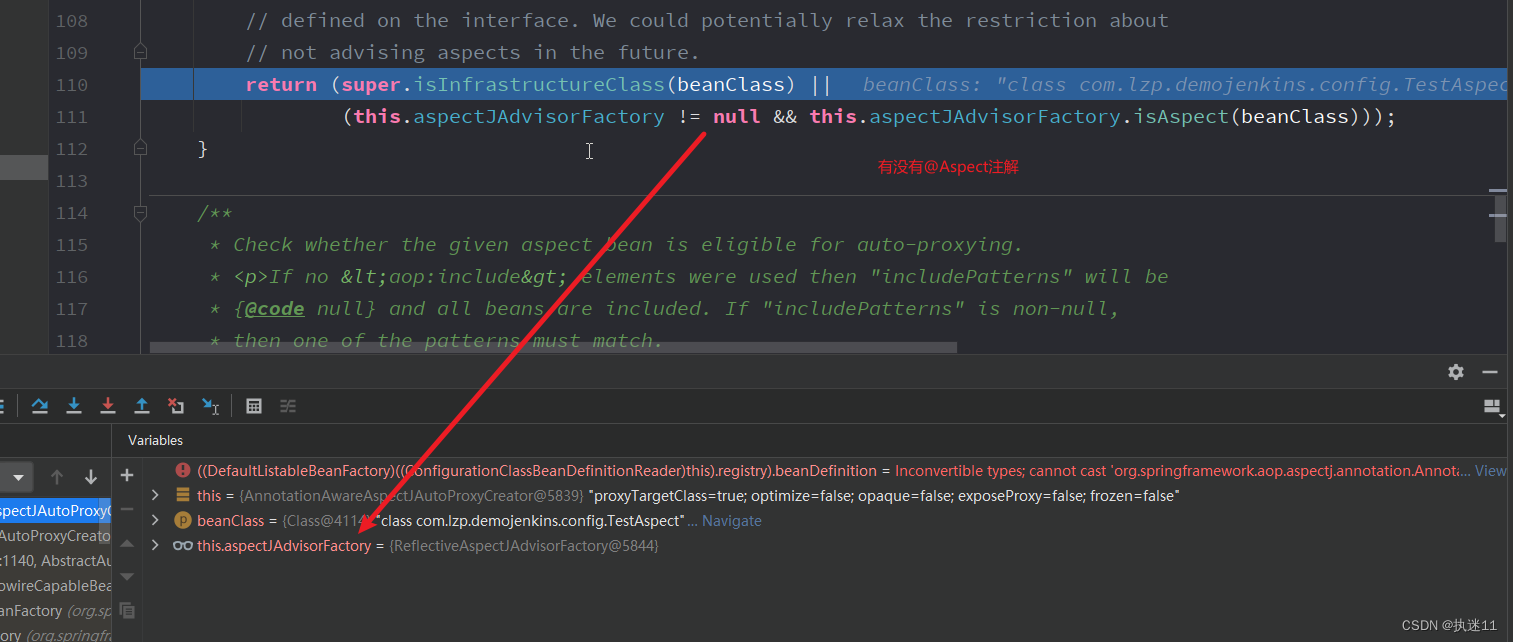
3.1.2 第二个判断
需要被增强的类 普通类会进入,步骤1的TestController不应该跳过
会调用子类的子类AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#shouldSkip方法
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator#findCandidateAdvisors
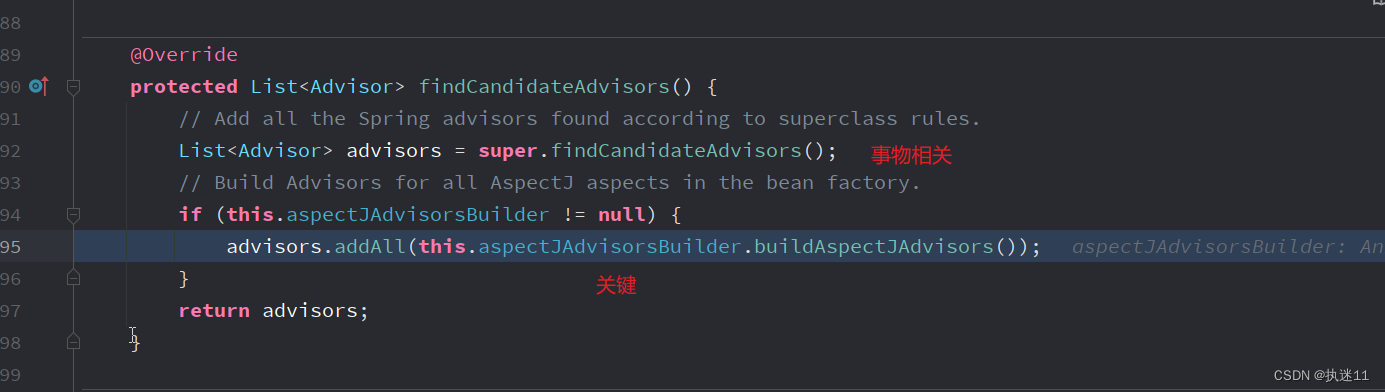
BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder#buildAspectJAdvisors
也就是找到切面类。步骤1的TestAspect类
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
//缓存中没有的话去获取,这里在第一个bean执行createBean方法时就会为空,然后创建缓存,后面的bean实例化时就可以直接获取了。
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
//获取到所有的beanName
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
//遍历所有的beanName
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this case they
// would be cached by the Spring container but would not have been weaved.
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName, false);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
//只有是加了@Aspect注解的类才会进入判断
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
//先把名字加到缓存中,方法开始就是从这里拿到切面类的名字
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
//构建工厂
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
//关键方法 解析切面类中的增强方法
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
//加到缓存中 classAdvisors也就是增强方法 可能有多个
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
//遍历完了 获取完了 直接返回了
return advisors;
}
}
}
if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
//缓存中有的话直接从缓存中拿 缓存是在上面创建好的
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {
List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);
if (cachedAdvisors != null) {
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
}
else {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
return advisors;
}
有的话直接从缓存中拿
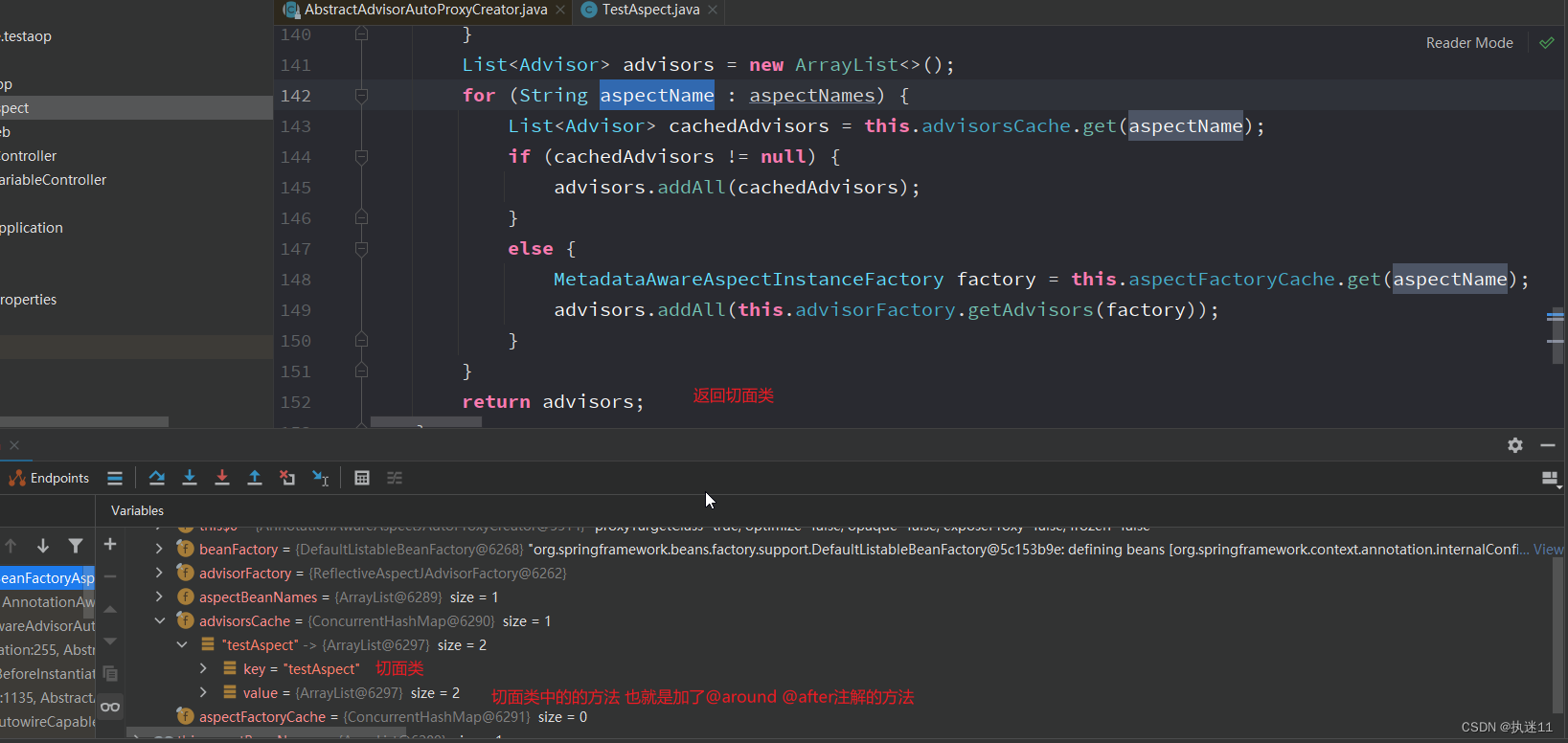
没有的话需要获取到切面类,然后解析。
3.2 解析切面类流程
在实例化第一个单例bean时,会对我们定义的切面类进行解析 然后缓存到advisorsCache中,key是beanName,value是advisor数组。每个切面类可能有多个增强方法
过程就是获取到切面类,然后获取到所有切面类的方法(除了pointcut注解的方法),然后遍历,封装成Advisor类型。
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory#getAdvisors
@Override
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
//获取到切面类
Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
//切面类的name
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
//我们需要用装饰器包装 MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory,以便它只实例化一次。
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
//获取遍历切面类所有的增强方法 @before @around @after
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
// Prior to Spring Framework 5.2.7, advisors.size() was supplied as the declarationOrderInAspect
// to getAdvisor(...) to represent the "current position" in the declared methods list.
// However, since Java 7 the "current position" is not valid since the JDK no longer
// returns declared methods in the order in which they are declared in the source code.
// Thus, we now hard code the declarationOrderInAspect to 0 for all advice methods
// discovered via reflection in order to support reliable advice ordering across JVM launches.
// Specifically, a value of 0 aligns with the default value used in
// AspectJPrecedenceComparator.getAspectDeclarationOrder(Advisor).
//遍历每个方法 一个一个解析
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, 0, aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
// If it's a per target aspect, emit the dummy instantiating aspect.
if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);
advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);
}
// Find introduction fields.
for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
return advisors;
}
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory#getAdvisor
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
//找到注解及注解配置的表达式 @around @after @before
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null) {
return null;
}
//针对每个增强方法 构建一个对象
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}
@Nullable
private AspectJExpressionPointcut getPointcut(Method candidateAdviceMethod, Class<?> candidateAspectClass) {
//找到注解及注解配置的表达式 @around @after @before
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
//构建对象
AspectJExpressionPointcut ajexp =
new AspectJExpressionPointcut(candidateAspectClass, new String[0], new Class<?>[0]);
ajexp.setExpression(aspectJAnnotation.getPointcutExpression());
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
ajexp.setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory);
}
return ajexp;
}
InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl#InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut,
Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
//当前的切点表达式
this.declaredPointcut = declaredPointcut;
//切面的class对象
this.declaringClass = aspectJAdviceMethod.getDeclaringClass();
//切面方法的名称
this.methodName = aspectJAdviceMethod.getName();
//切面方法的参数类型
this.parameterTypes = aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterTypes();
//切面方法对象
this.aspectJAdviceMethod = aspectJAdviceMethod;
//aspectj的通知工厂
this.aspectJAdvisorFactory = aspectJAdvisorFactory;
//aspect的实例工厂
this.aspectInstanceFactory = aspectInstanceFactory;
//切面的顺序
this.declarationOrder = declarationOrder;
//切面的名称
this.aspectName = aspectName;
//是否需要延时加载
if (aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
// Static part of the pointcut is a lazy type.
Pointcut preInstantiationPointcut = Pointcuts.union(
aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getPerClausePointcut(), this.declaredPointcut);
// Make it dynamic: must mutate from pre-instantiation to post-instantiation state.
// If it's not a dynamic pointcut, it may be optimized out
// by the Spring AOP infrastructure after the first evaluation.
this.pointcut = new PerTargetInstantiationModelPointcut(
this.declaredPointcut, preInstantiationPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
this.lazy = true;
}
else {
// A singleton aspect.
this.pointcut = this.declaredPointcut;
this.lazy = false;
//将切面中的通知构造为advice通知对象
this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);
}
}
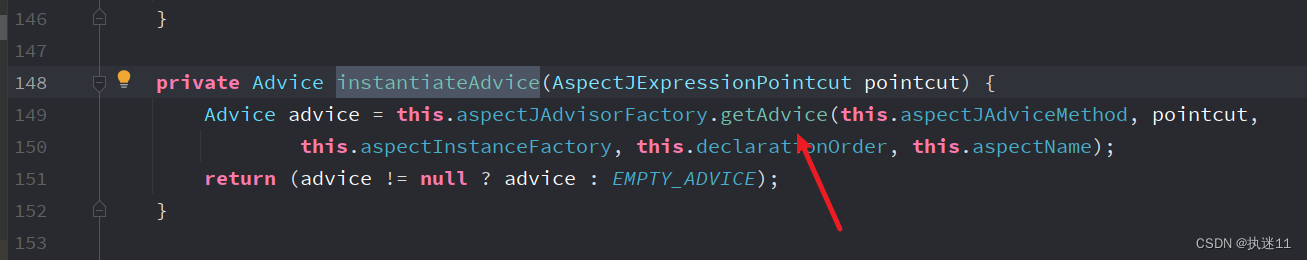
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory#getAdvice
getAdvisors方法中的getAdvisor方法需要的对象了。每个增强方法都会是一个Advice类型
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
//切面类的class
Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
//获取切面方法上的注解
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// If we get here, we know we have an AspectJ method.
// Check that it's an AspectJ-annotated class
if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) {
throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: " +
"Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" +
candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
//最终返回的类型
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
//根据注解类型构建
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
}
return null;
// 参数是 当前方法 切点表达式 工厂
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}
这样就把切面类的增强方法都解析完了。除了@pointcut的方法。
3.3 注意
父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator 实现了两个接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor。
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法在createBean方法doCreateBean之前会调用。作用就是解析切面类BeanPostProcessor接口的postProcessAfterInitialization方法在创建完bean,初始化(initializeBean)时调用。作用是为需要增强的类创建代理
AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization
重写接口BeanPostProcessor接口的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
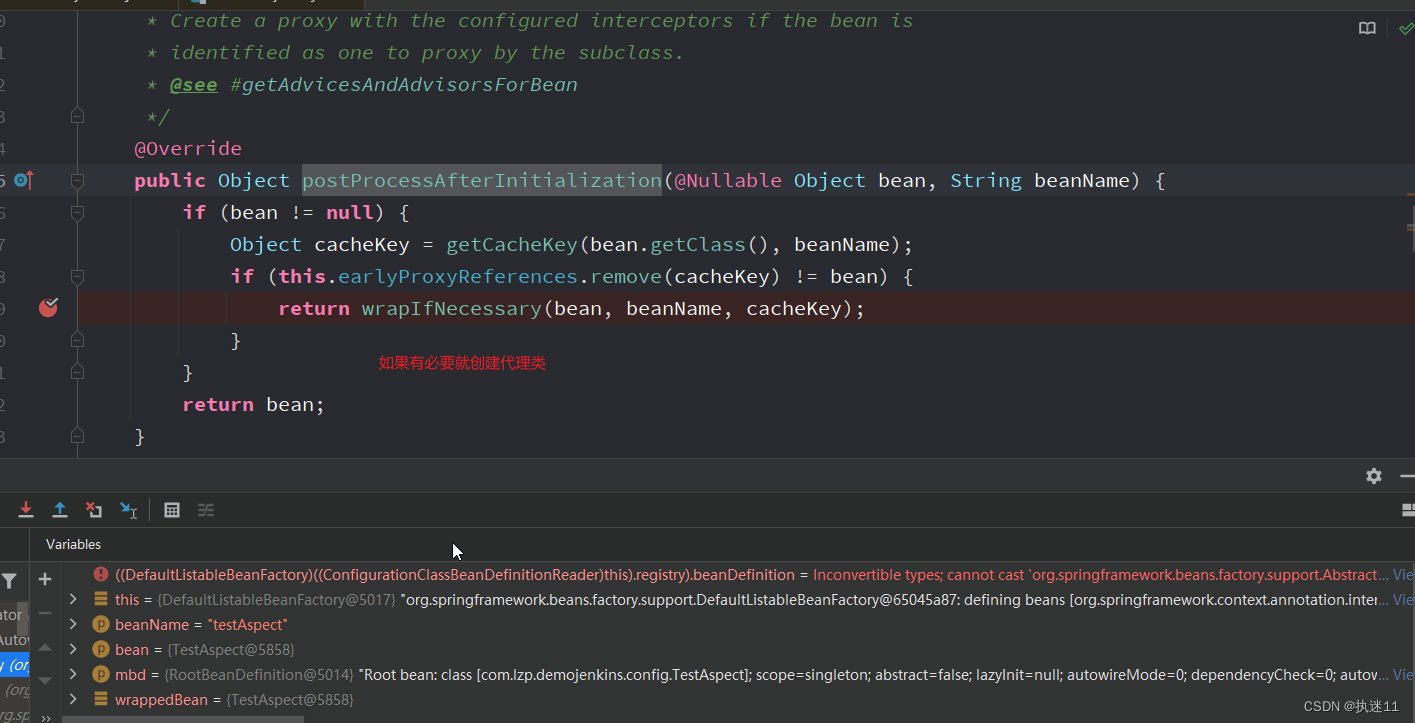
3.4 创建代理
在createBean方法的doCreateBean方法中执行实例化bean,填充bean,和初始化bean,在初始化bean方法initializeBean中,会执行postProcessBeforeInitialization、postProcessAfterInitialization方法,关于aop创建代理是在AbstractAutoProxyCreator类的postProcessAfterInitialization方法中。
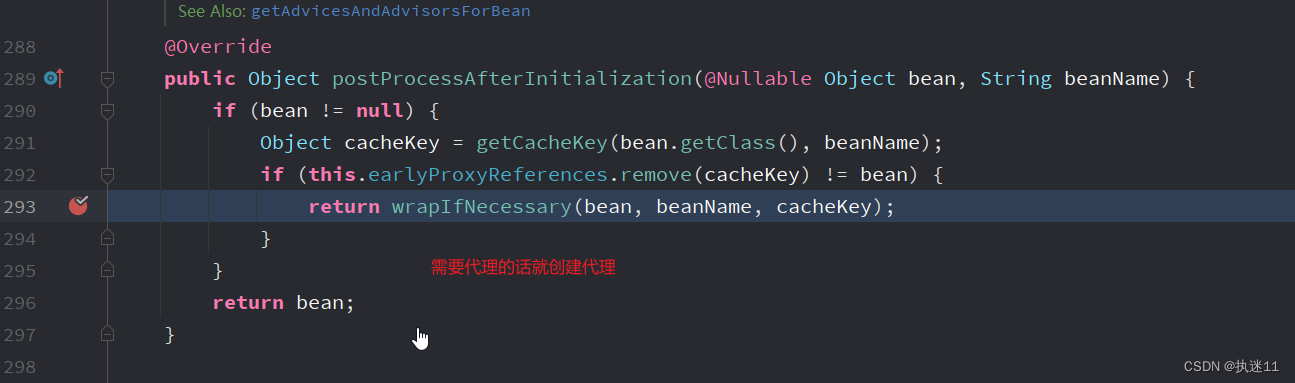
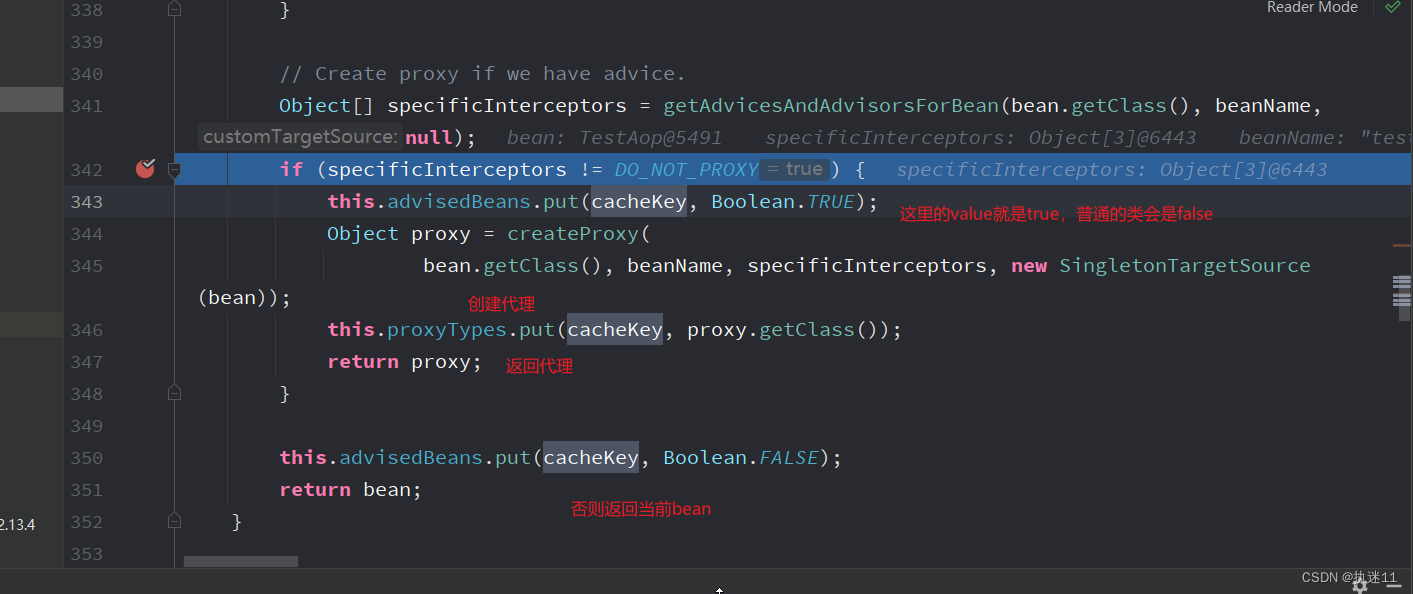
AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
//普通类会把advisedBeans中对应的bean的value设置为false,而切面类中指定的增强类则不会
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
//如果有匹配的通知,就创建代理对象 关键方法
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
//创建代理
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法会调用AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findEligibleAdvisors方法
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//找到Spring IoC容器中所有的候选通知 也就是切面类中加了@around @beafore @after注解的方法
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
//判断找到的通知能不能作用到当前的类上 关键
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
//对我们的advisor进行排序
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findAdvisorsThatCanApply
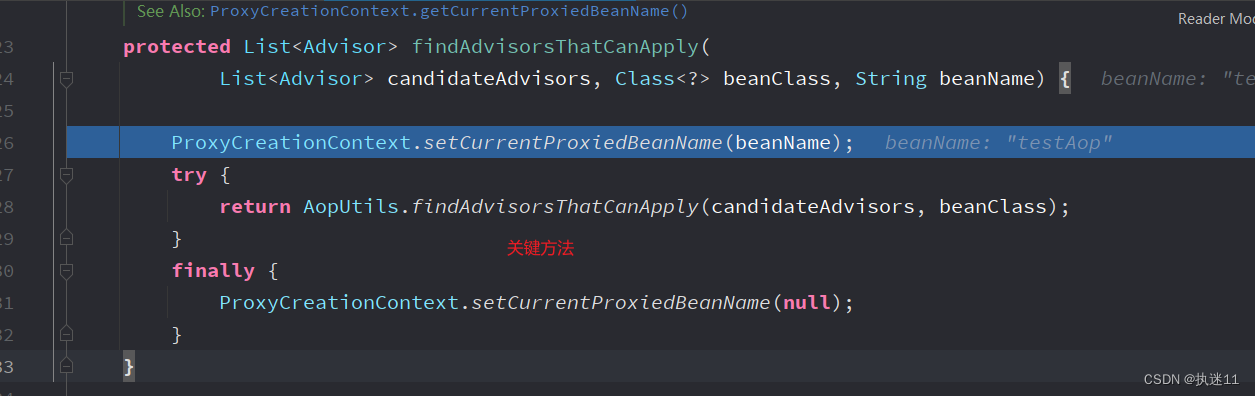
AopUtils#findAdvisorsThatCanApply
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
//为空直接返回
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
//这里不会进入 因为没有实现IntroductionAdvisor
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
//遍历
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
//这里不会进入 因为没有实现IntroductionAdvisor
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed
continue;
}
//会进这个判断
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
AopUtils#canApply
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
//这里不会进入 因为没有实现IntroductionAdvisor
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
//继续重载的canApply
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
AopUtils#canApply(org.springframework.aop.Pointcut, java.lang.Class<?>, boolean)
如果该方法返回true就表示匹配,就添加到合适的集合eligibleAdvisors中,然后为当前类创建代理
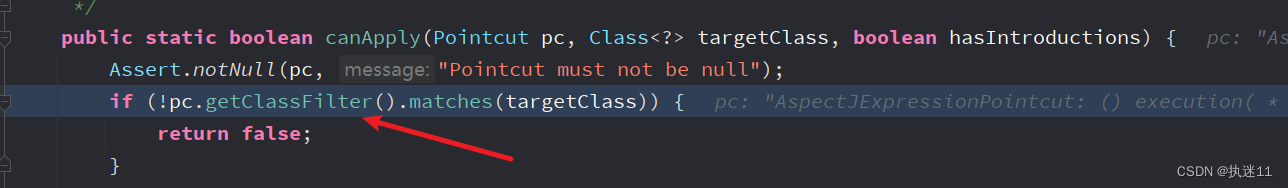
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
//这里会构建切面类中的表达式
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
//通过切点获取到一个方法匹配器对象
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
//断当前class是不是代理的class对象 不是的话加到classes
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
}
//把当前类实现的接口的class都加进来
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
//遍历当前类和当前类实现的接口
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
//获取到当前类的所有方法
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
//遍历看当前方法是否满足增强条件 也就是能否满足表达式的配置 能满足就返回true
//@Around("execution( * com.lzp.*.controller.*.*(..))")
for (Method method : methods) {
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
3.4.1 构建切点表达式
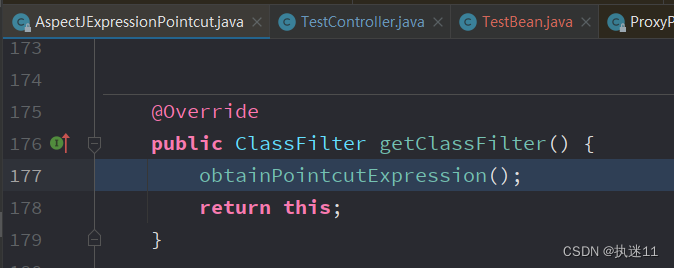
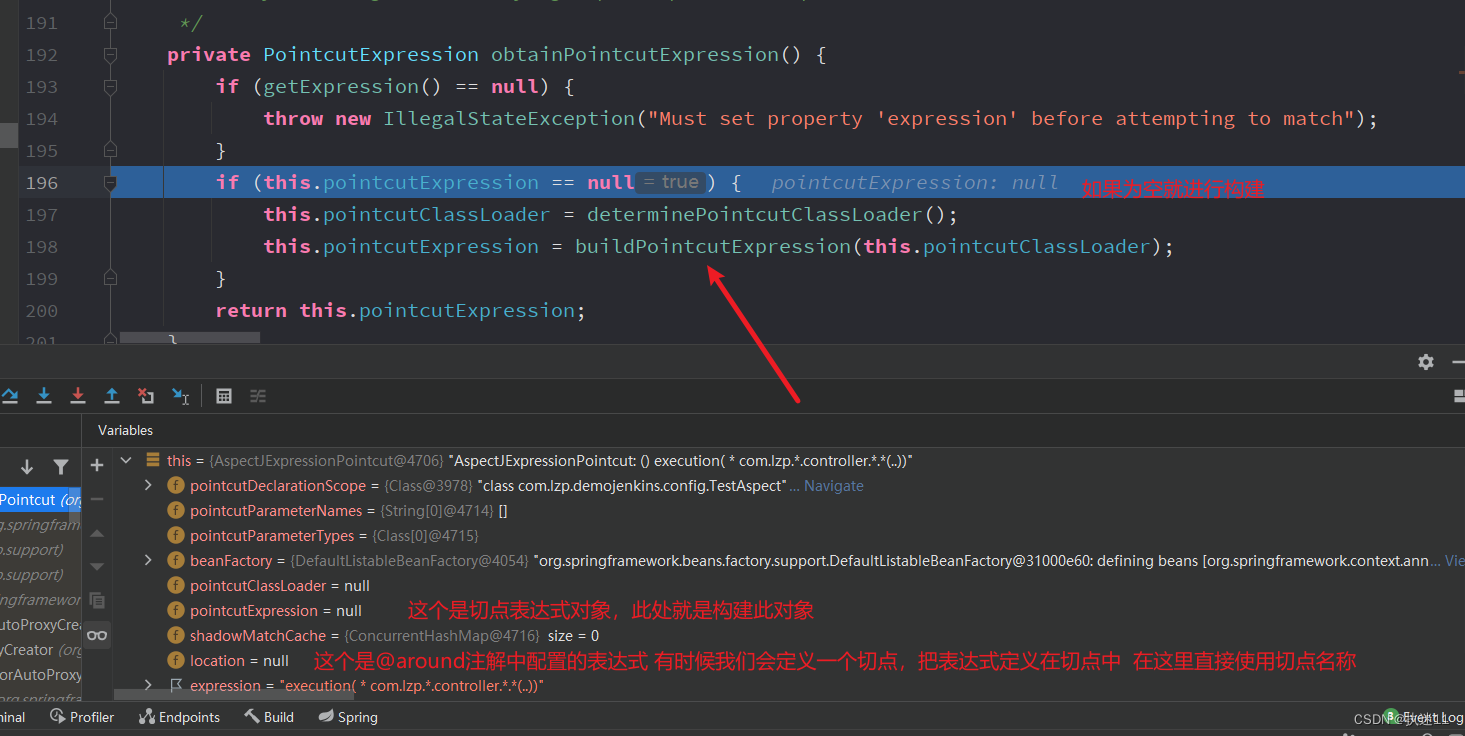
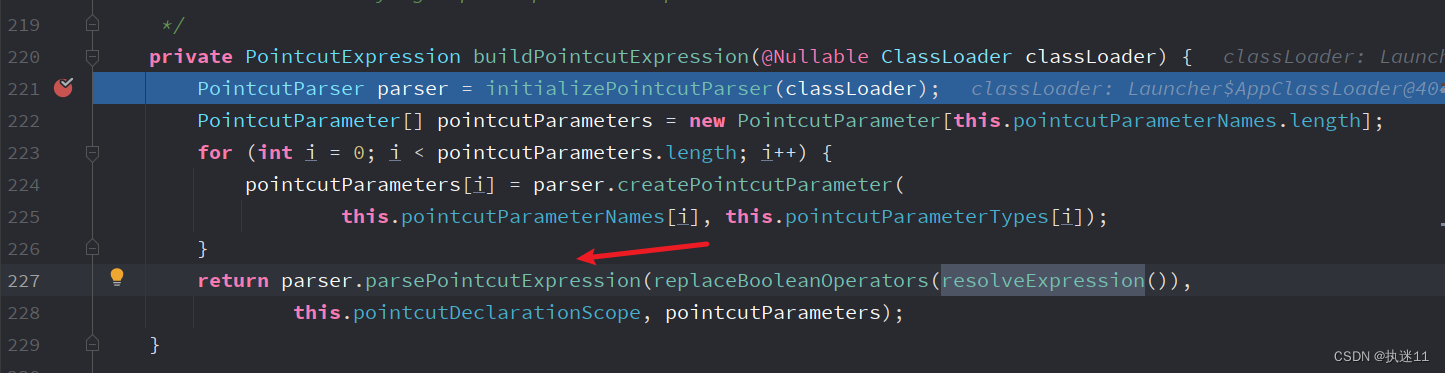
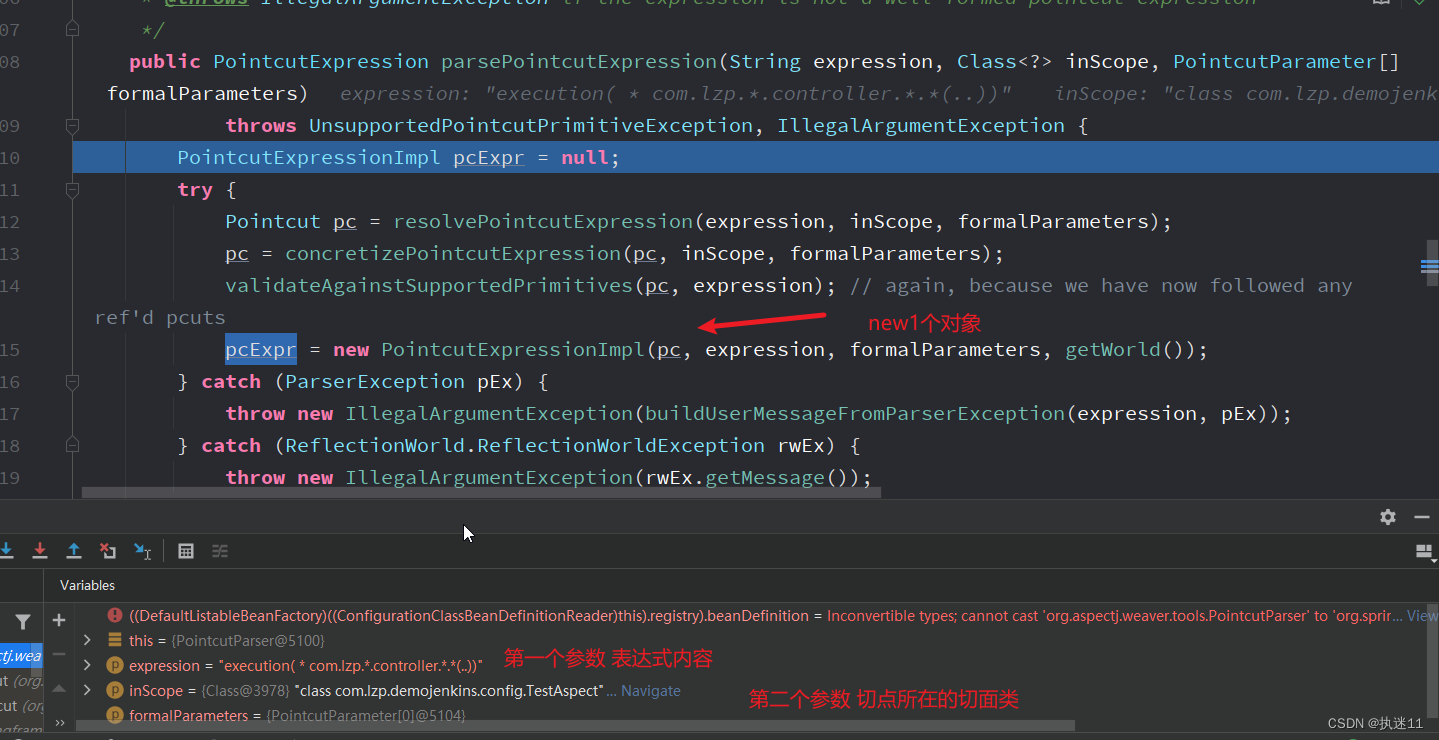
回到AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary方法,获取到specificInterceptors了,然后会创建当前类的代理对象,然后返回
AbstractAutoProxyCreator#createProxy
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
//创建代理工厂
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
//cglib
if (proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
// Explicit handling of JDK proxy targets and lambdas (for introduction advice scenarios)
if (Proxy.isProxyClass(beanClass) || ClassUtils.isLambdaClass(beanClass)) {
// Must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to the proxy's interfaces only.
for (Class<?> ifc : beanClass.getInterfaces()) {
proxyFactory.addInterface(ifc);
}
}
}
//jdk
else {
// No proxyTargetClass flag enforced, let's apply our default checks...
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
//添加增强方法 也就是@around @after @before
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
//目标类
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// Use original ClassLoader if bean class not locally loaded in overriding class loader
ClassLoader classLoader = getProxyClassLoader();
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && classLoader != beanClass.getClassLoader()) {
classLoader = ((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).getOriginalClassLoader();
}
//执行代理工厂的创建代理方法
return proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader);
}
ProxyFactory#getProxy(java.lang.ClassLoader)
创建方法肯定是创建了cglib代理工厂
注:springboot aop默认使用cglib动态代理,切换为jdk动态代理的方法是
spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false
jdk动态代理时:如果代理类没有实现接口也创建cglib代理,否则创建jdk代理
CglibAopProxy#getProxy(java.lang.ClassLoader)
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
//创建代理
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}
protected Object createProxyClassAndInstance(Enhancer enhancer, Callback[] callbacks) {
enhancer.setInterceptDuringConstruction(false);
enhancer.setCallbacks(callbacks);
return (this.constructorArgs != null && this.constructorArgTypes != null ?
enhancer.create(this.constructorArgTypes, this.constructorArgs) :
enhancer.create());
}
最终创建的代理
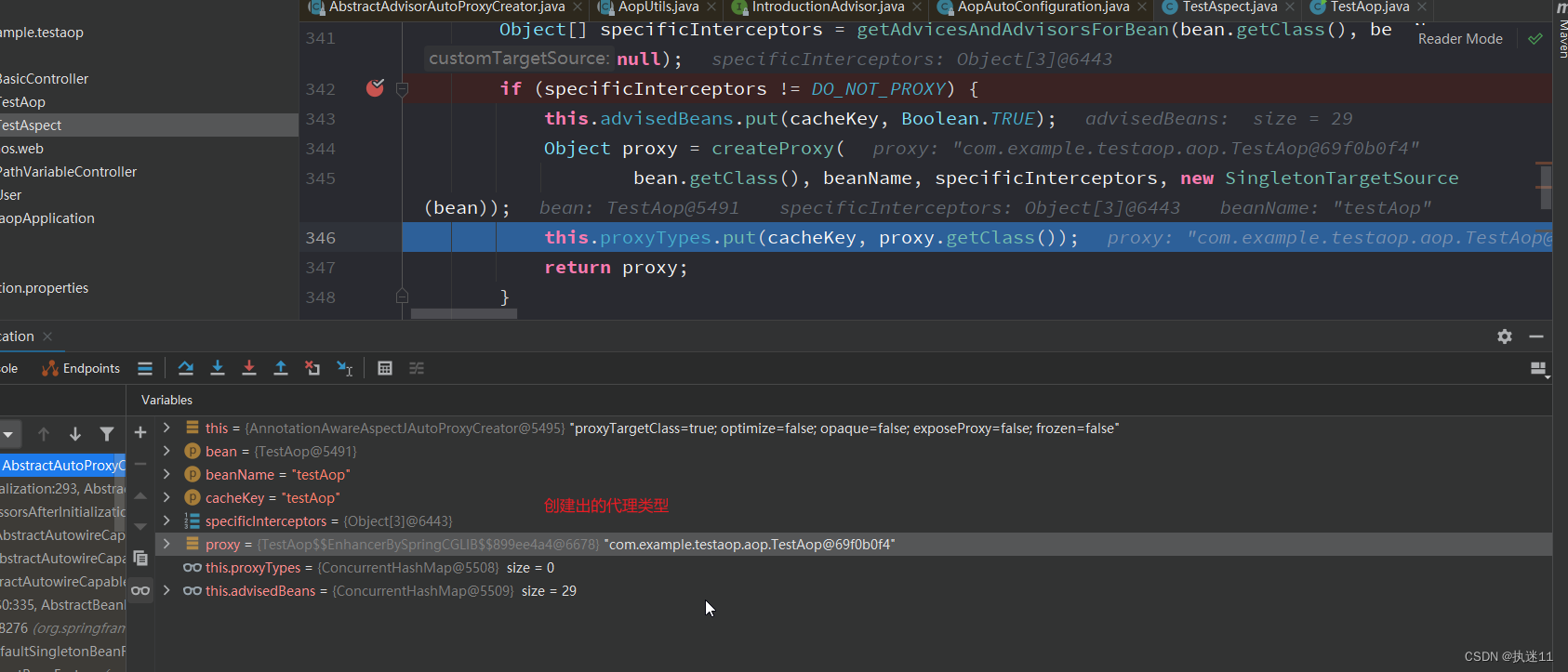
4.总结
aop的功能就是不改变原方法内容,对原方法进行增强,想要实现这个功能一定就是动态代理了。
实现原理:
1.关键类:AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,自动配置中的@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解会引入这个类,aop的功能就是通过这个类以及它的父类们共同完成的。
2.关键方法:
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的父类(不是直接父类)AbstractAutoProxyCreator 实现了两个接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor。
1.1.AbstractAutoProxyCreator类实现接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor重写的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法。
这个方法在bean实例化时的createBean方法中执行,在doCreateBean方法之前,在实例化第一个单例bean时,对所有我们自定义的切面类进行解析。然后放到缓存中,key是切面类name,value是advisor类型的数组,因为一个切面类可以有多个增强方法。
1.2.AbstractAutoProxyCreator类实现接口BeanPostProcessor重写了postProcessAfterInitialization方法。
这个方法在bean实例化时的initializeBean方法完成,在doCreateBean方法中,populateBean方法之后。对所有正在实例化的bean进行判断,看能否和1.1中生成的增强方法进行匹配,能匹配的话就对当前类创建代理。