A. 美丽的2

思路:
枚举 1 到 2020 的每个数,依次判断即可。
代码:
public class Main {
public static boolean check(int x) {
while (x != 0) {
if (x % 10 == 2) return true;
x /= 10;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2020; i++)
if (check(i))
cnt++;
System.out.println(cnt);
}
}
B. 扩散

解法一:(比较慢但是容易想)
b f s bfs bfs,先将给出的点加入队列中,并且加到集合里。记录扩散的步数,初始化为2020,然后对队列中的每一个同一层的节点在四个方向上扩散,当扩散的点不在集合里时,把它加到队列里,并加到集合里。每扩散一层就减1,当步数为0时,就结束 b f s bfs bfs,输出答案。
这种做法比较慢,当时跑了好几分钟,不过填空题也无关紧要了。
代码:
package L11;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Queue;
public class B {
static final int N = 10000;
static long ans = 0;
static int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
static HashSet<Point> set = new HashSet<Point>();
static Queue<Point> queue = new LinkedList<Point>();
static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
public static void bfs() {
int count = 2020;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = queue.size(); i >= 1; i--) {
Point p = queue.poll();
int x = p.x, y = p.y;
for (int u = 0; u < 4; u++) {
int a = x + dx[u], b = y + dy[u];
if (set.contains(new Point(a, b))) continue;
set.add(new Point(a, b));
queue.add(new Point(a, b));
}
}
count--;
System.out.println(count);
if (count == 0) break;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
queue.add(new Point(0, 0));
queue.add(new Point(2020, 11));
queue.add(new Point(11, 14));
queue.add(new Point(2000, 2000));
set.add(new Point(0, 0));
set.add(new Point(2020, 11));
set.add(new Point(11, 14));
set.add(new Point(2000, 2000));
bfs();
System.out.println(set.size());
}
static class Point {
int x, y;
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(x, y);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Point other = (Point) obj;
return x == other.x && y == other.y;
}
}
}
解法2:
统计在扩散范围内的点与那几个点距离小于2020的个数。
代码:
package L11;
public class B_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0 - 2020; i <= 2020 + 2020; i++)
for (int j = 0 - 2020; j <= 2020 + 2020; j++) {
if (Math.abs(i - 0) + Math.abs(j - 0) <= 2020 || Math.abs(i - 2020) + Math.abs(j - 11) <= 2020 ||
Math.abs(i - 11) + Math.abs(j - 14) <= 2020 || Math.abs(i - 2000) + Math.abs(j - 2000) <= 2020)
ans++;
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
C. 阶乘约数

思路:
复习了一下试除法求质约数个数与约数个数。
给定一个数
N
N
N,
p
i
p_i
pi为
N
N
N的质约数,则可以表示为:
N
=
p
1
α
1
×
p
2
α
2
×
p
3
α
3
×
.
.
.
×
p
k
α
k
N=p_{1}^{\alpha_1}\times p_{2}^{\alpha_2} \times p_{3}^{\alpha_3}\times... \times p_{k}^{\alpha_k}
N=p1α1×p2α2×p3α3×...×pkαk
N
N
N的每一个约数
d
i
d_i
di,可以表示为:
d
i
=
p
1
β
1
×
p
2
β
2
×
p
3
β
3
×
.
.
.
×
p
k
β
k
d_i=p_{1}^{\beta_1}\times p_{2}^{\beta_2} \times p_{3}^{\beta_3}\times... \times p_{k}^{\beta_k}
di=p1β1×p2β2×p3β3×...×pkβk
其中,
0
≤
β
i
≤
α
i
0 \le \beta_i \le \alpha_i
0≤βi≤αi,
β
i
\beta_i
βi的选法有
0
∼
α
i
0 \sim \alpha_i
0∼αi,共有
(
α
i
+
1
)
(\alpha_i + 1)
(αi+1)种选法 ,根据排列组合原理,约数个数为:
(
α
1
+
1
)
×
(
α
2
+
1
)
×
(
α
3
+
1
)
×
.
.
.
×
(
α
k
+
1
)
(\alpha_1 + 1) \times (\alpha_2 + 1) \times (\alpha_3 + 1) \times ... \times (\alpha_k + 1)
(α1+1)×(α2+1)×(α3+1)×...×(αk+1)
求 2 ∼ 100 2 \sim 100 2∼100 的质因数以及每个质因数的个数,每个质因数的个数加一相乘即可,答案为 ∏ 1 k ( α i + 1 ) \displaystyle\prod^{k}_{1}{(\alpha_i + 1)} 1∏k(αi+1)。
代码:
public class Main {
static int[] p = new int[110];
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i++) {
int x = i;
for (int j = 2; j <= i / j; j++) {
if (x % j == 0) {
while (x % j == 0) {
x /= j;
p[j]++;
}
}
}
if (x > 1) p[x]++;
}
long ans = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < 100; i++) ans *= (p[i] + 1);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
D. 本质上升序列

解法1:
暴力枚举。因为本质上升序列最长为26,所有的序列个数为 2 26 2^{26} 226,可以二进制枚举所有的序列,判断在字符串中是否存在该序列,如果存在答案就加一,时间复杂度为 O ( 2 26 × 200 ) O(2^{26} × 200) O(226×200)。
代码:
public class D {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int ans = 0;
//String s = "lanqiao";
String s = "tocyjkdzcieoiodfpbgcncsrjbhmugdnojjddhllnofawllbhfiadgdcdjstemphmnjihecoapdjjrprrqnhgccevdarufmliqijgihhfgdcmxvicfauachlifhafpdccfseflcdgjncadfclvfmadvrnaaahahndsikzssoywakgnfjjaihtniptwoulxbaeqkqhfwl";
for (int i = 1; i < (1 << 26); i++) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {
if (((i >> j) & 1) == 1)
sb.append((char)('a' + j));
}
int j = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < s.length(); k++) {
if (s.charAt(k) == sb.charAt(j)) {
j++;
if (j == sb.length()) {
ans++;
break;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
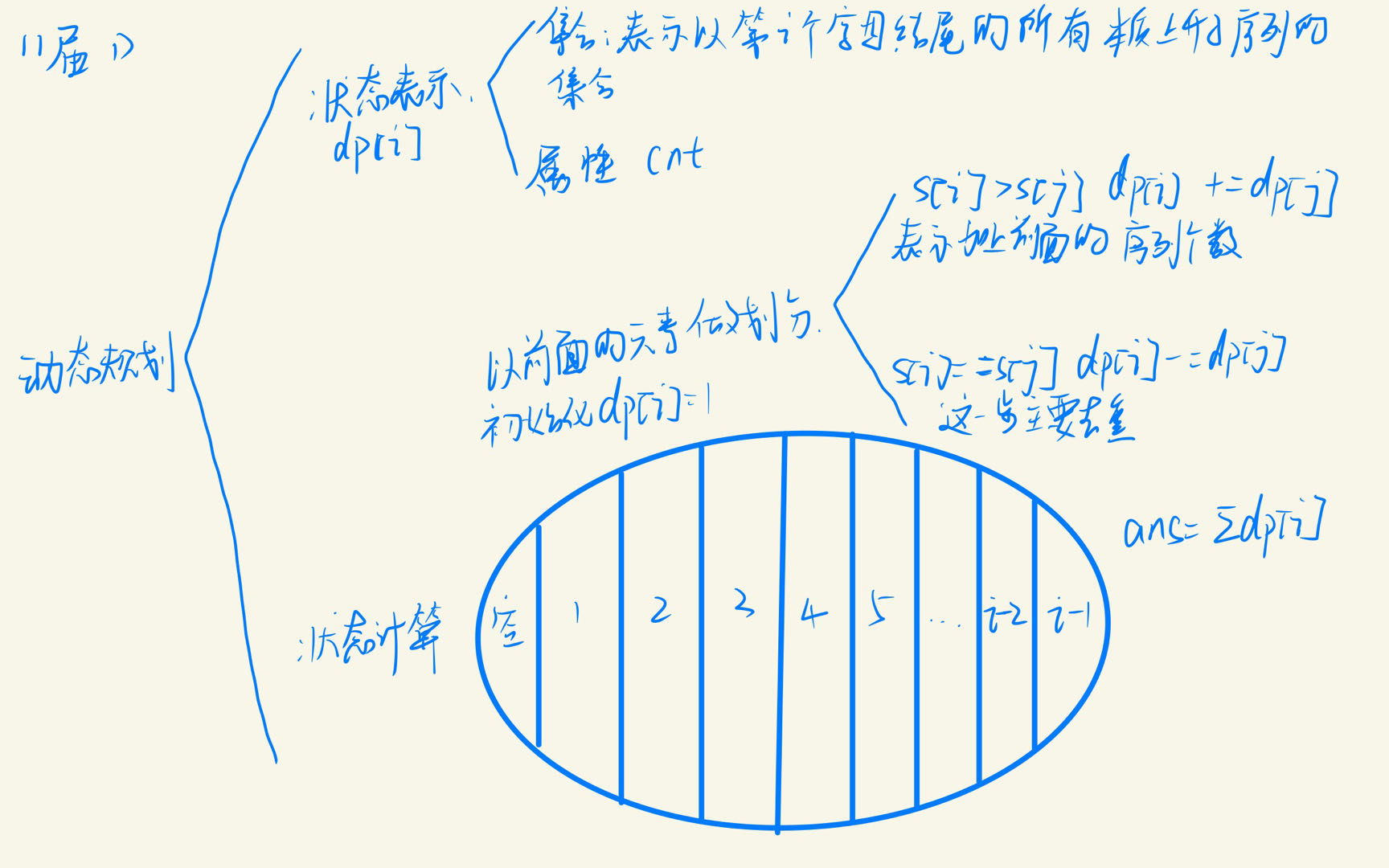
解法2:
动态规划,分析如下,时间复杂度为
O
(
N
)
O(N)
O(N)
代码:
public class Main {
static int[] dp = new int[200];
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String s = "tocyjkdzcieoiodfpbgcncsrjbhmugdnojjddhllnofawllbhfiadgdcdjstemphmnjihecoapdjjrprrqnhgccevdarufmliqijgihhfgdcmxvicfauachlifhafpdccfseflcdgjncadfclvfmadvrnaaahahndsikzssoywakgnfjjaihtniptwoulxbaeqkqhfwl";
char[] str = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
dp[i] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (str[i] > str[j]) dp[i] += dp[j];
if (str[i] == str[j]) dp[i] -= dp[j];
}
}
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) ans += dp[i];
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
E. 玩具蛇
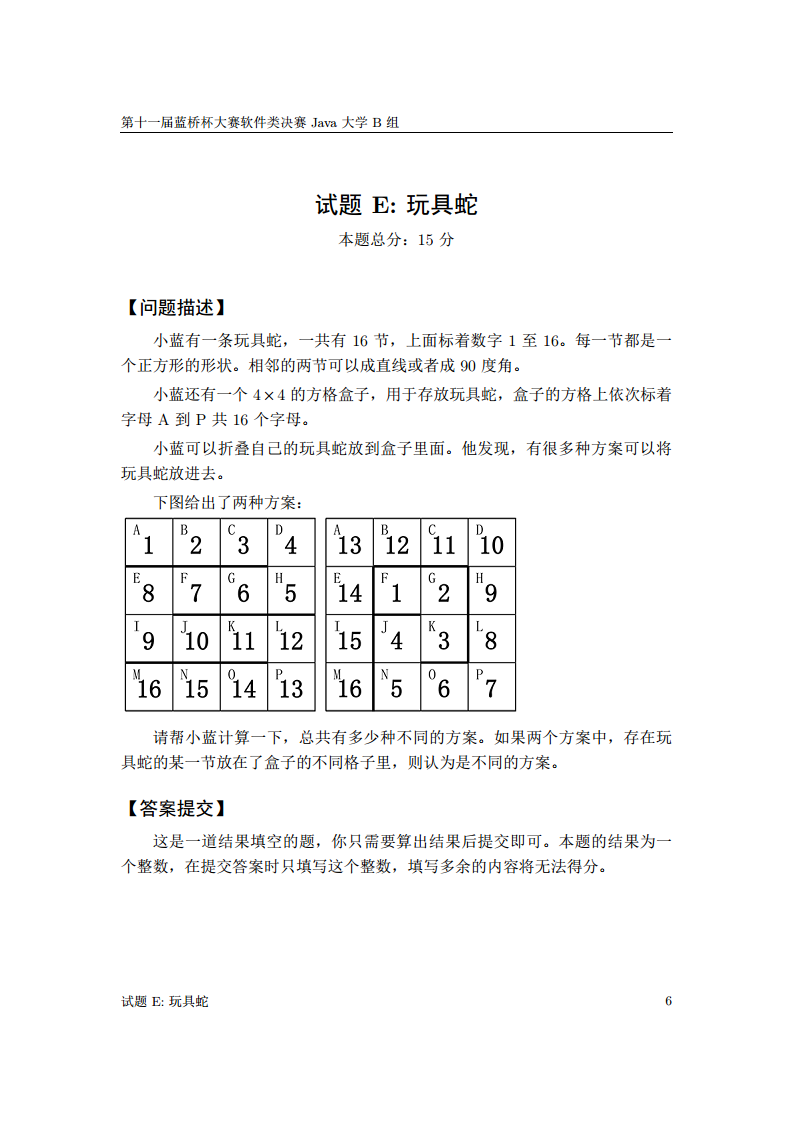
思路:
从 4 × 4 4 \times 4 4×4 的小方格中每一个位置放置 1 1 1, 接着按上下左右 4 个方向 d f s dfs dfs。在搜索的过程中记得回溯,因为求的是方案的个数。枚举每一个位置都要先标记起点,搜索之后再删除标记。
代码:
public class Main {
static int ans;
static int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
static boolean[][] st = new boolean[4][4];
public static void dfs(int x, int y, int ch) {
if (ch == 16) {
ans++;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (a < 0 || a >= 4 || b < 0 || b >= 4) continue;
if (st[a][b]) continue;
st[a][b] = true;
dfs(a, b, ch + 1);
st[a][b] = false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
st[i][j] = true;
dfs(i, j, 1);
st[i][j] = false;
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}










![[前端语法]js原型链有关的继承问题](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/82e7a5c121ea483fbfc6b74aea83fd16.png)