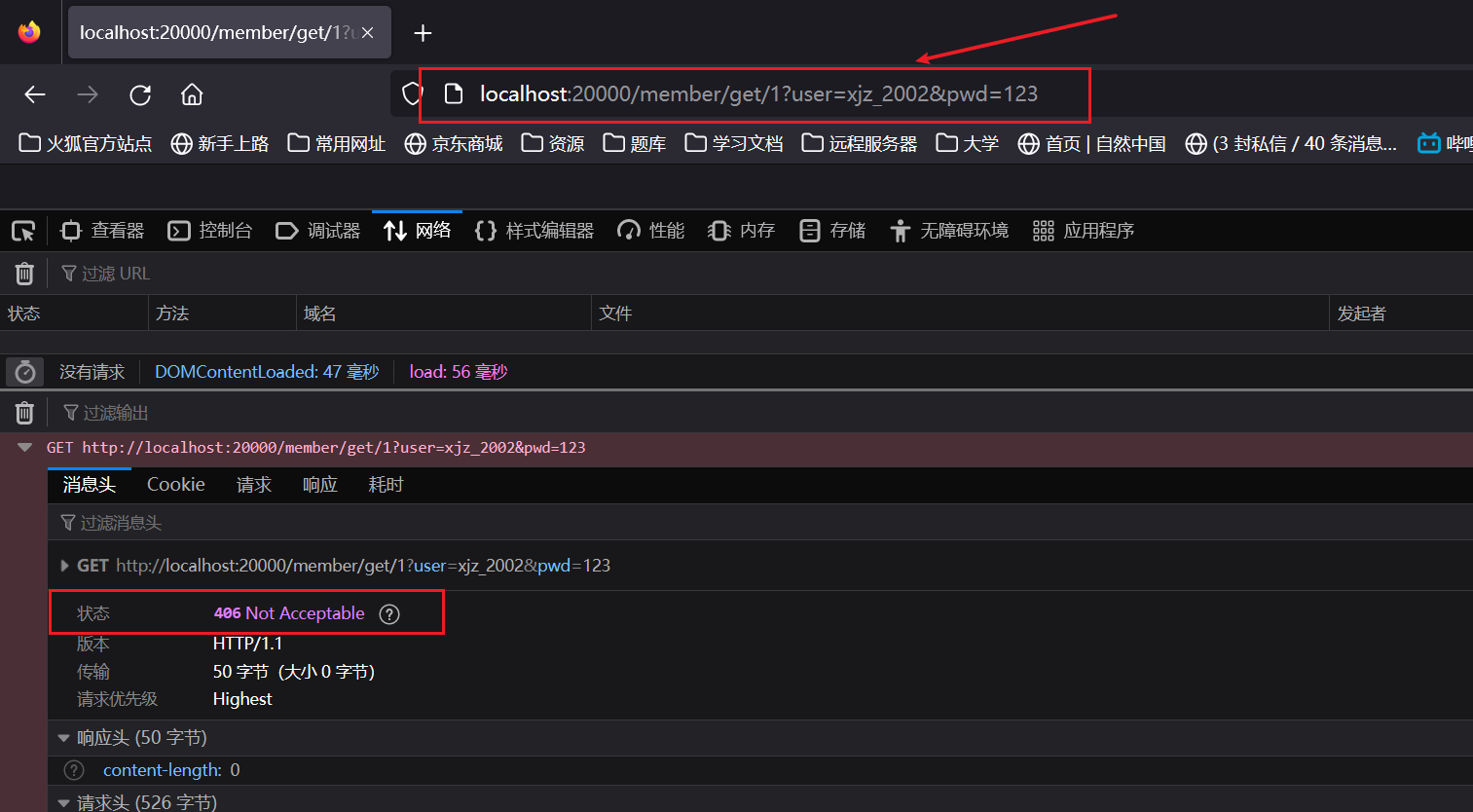
Problem - D - Codeforces
思路:
- 注意到bi+bj<=2*n,所以ai*aj<=2*n,即我们实际只需要枚举
个a的匹配即可
- 为了不重不漏,我们可以枚举x从1到
,寻找所有与x匹配且大于等于x的[a,b]对
- 这样复杂度就是
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
void mysolve()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<pii>a(n);
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i)cin>>a[i].first;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i)cin>>a[i].second;
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
ll ans=0;
for(int x=1; x*x<=2*n; ++x)
{
vector<int>cnt(n+1);//枚举x,x只与大于大于他的a匹配,显然在遇到pip前,如果真的存在a=x,我们可以存入每个x=a对应的b
for(auto [k,v]:a)
{
int b=k*x-v;
if(b>0&&b<=n)///b符合范围
{
ans+=cnt[b];
}
if(k==x)cnt[v]++;//在遇到a匹配前,先计入a=x的各个b的数目
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
int32_t main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);//使用read请把解绑注释了
int t=1;
cin >> t;
//read(t);
while (t--)
{
mysolve();
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
Problem - E - Codeforces
思路:
- 设左括号为1,右括号为-1
- 如果一个括号序列是合法的,必须满足所以前缀都是>=0的,而且所有后缀都是<=0的
- 要求[l,r]是合法序列,如果没有[l,r]之间的区间交,显然答案就是被割裂开的每个偶数段(存在奇数段就是无解)的卡特兰数乘积
- 如果[l1,r1]与[l2,r2]相交,观察出[l2,r1]也必须是合法括号序列,因为[l2,r1]同时满足第一个的后缀和<=0,又同时满足第二个区间的前缀和>=0,所以它同样是合法括号序列
- 那么存在相交,相当于在割裂出一段,变为[l1,l2],[l2,r1],[r1,r2]都要求是合法序列
- 所以最后答案就是所有割裂出的合法序列乘积
- 一个区间被操作多次最后属于哪个区间,我们可以使用异或的思想,显然,如果几个数异或值相同,他们属于一个区间。
- 为了避免异或出现冲突,我们可以在unsigned long long 的范围内取随机数取异或。操作进行差分即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f
#define eps 1e-9
#define int long long
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
inline int read(int &x);
//double 型memset最大127,最小128
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------//
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------//
const int N = 3e5 + 10;
const int mod = 998244353;
ll f[N];
ll fastmi(ll base,ll power)
{
ll ans=1;
while(power)
{
if(power&1)ans=ans*base%mod;
power>>=1,base=base*base%mod;
}
return ans;
}
void mysolve()
{
mt19937_64 rnd(random_device{}());
uniform_int_distribution<ull> dist(0, ULLONG_MAX);
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
vector<int>b(n+5);
int l,r;
for(int i=1; i<=k; ++i)
{
cin>>l>>r;
ull h=dist(rnd);
b[l]^=h,b[r+1]^=h;
}
if(n&1)
{
cout<<0<<endl;
return;
}
map<ull,int>mp;
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i)
{
b[i]^=b[i-1];
mp[b[i]]++;
}
int ans=1;
for(auto [k,v]:mp)
{
if(v&1)//要求被割裂的每个段都是偶数长度
{
cout<<0<<endl;
return;
}
ans=ans*f[v/2]%mod;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
int32_t main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);//使用read请把解绑注释了
int t=1;
cin >> t;
//read(t);
f[0]=1;
for(int i=1; i<=3e5; ++i)
f[i]=f[i-1]*(4*i-2)%mod*fastmi(i+1,mod-2)%mod;//预处理卡特兰数
while (t--)
{
mysolve();
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
inline int read(int &x)
{
x = 0;
char ch = 0;
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9')ch = getchar();
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
{
x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return x;
}