🤔拷贝替换算法:
🙂1.copy 拷贝
在 C++ STL 中,copy()是一种常用的算法,用于将一个指定范围内的元素复制到目标位置中,不会改变原有序列的大小。
copy()的函数原型为:
template<class InputIt, class OutputIt>
OutputIt copy(InputIt first, InputIt last, OutputIt d_first);📖其中,first 和 last 分别表示被复制序列的起始位置和结束位置;d_first 表示目标序列的起始位置。
📖copy() 函数从源序列([first, last))中复制元素到目标序列([d_first, d_first+(last-first)))中。它返回目标序列中最后一个被写入元素的后继位置。
copy() 函数可以对标准数组、STL 容器等基本类型以及自定义类型进行操作。
🔍代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void print(int val)
{
cout << val<<" ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int>d1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
d1.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>d2;
d2.resize(10);
copy(d1.begin(), d1.end(), d2.begin());
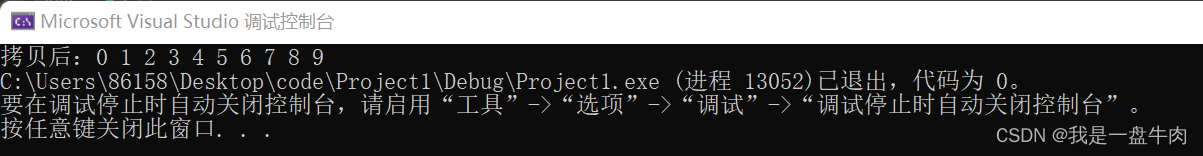
cout << "拷贝后:";
for_each(d2.begin(), d2.end(), print);
}
🔍运行结果:
🙂 2.replace 替换
在 C++ STL 中,replace()是一种常用的算法,用于在范围内以新值替换旧值。
replace()的函数原型为:
template<class ForwardIt, class T>
void replace(ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last, const T &old_value, const T &new_value);📖replace() 函数将输入范围 first 至 last-1 中等于 old_value 的元素替换为 new_value。
🔍代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void print(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int>d1;
d1.push_back(10);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_back(30);
d1.push_back(40);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_back(30);
d1.push_back(20);
//替换所有的20为2000
replace(d1.begin(),d1.end(),20 ,2000);
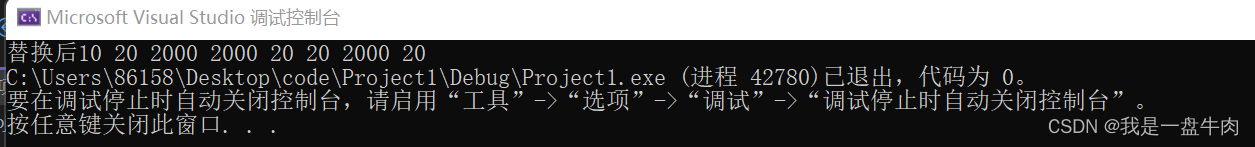
cout << "替换后";
for_each(d1.begin(), d1.end(), print);
}
🔍 运行结果:

🙂 3.replace_if 按条件替换
在 C++ STL 中,replace_if 是一种常用的算法,用于在指定的范围内以新值替换符合特定判定条件的值。
replace_if 的函数原型为:
template<class ForwardIt, class UnaryPredicate, class T>
void replace_if(ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last, UnaryPredicate p, const T &new_value);📖first 和 last 分别表示需要替换的序列的起始位置和结束位置;p 是一个一元谓词(即接受一个参数并返回 bool 值的函数),用于判断每个元素是否需要被替换;new_value 表示新值。
📖replace_if() 函数将输入范围 first 至 last-1 中满足 p 判定条件的元素替换为 new_value。
🔍代码示例:
我们把比30大的元素都替换为2000.
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class greater30
{
public:
bool operator() (int val)
{
if (val < 30)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
void print(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int>d1;
d1.push_back(10);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_back(30);
d1.push_back(40);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_back(30);
d1.push_back(20);
//替换所有的不符合条件的
replace_if(d1.begin(),d1.end(),greater30(), 2000);
cout << "替换后";
for_each(d1.begin(), d1.end(), print);
}🔍运行结果:
🙂 4.swap 交换
在 C++ STL 中,swap是一种常用的算法,用于交换两个对象的值,可以用于任何支持拷贝构造函数和赋值操作符的类型。
swap的函数原型为:
template<class T>
void swap(T& a, T& b);其中,a 和 b 分别表示需要交换的两个对象。
📖swap() 函数交换两个对象的值,不需要为对象分配新的内存空间。需要注意的是,对于大型对象,使用 swap() 函数比直接赋值更高效。
📖swap() 函数可以对任何支持拷贝构造函数和赋值操作符的类型进行操作,包括基本类型和自定义类型。
🔍代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void print(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int>d1;
vector<int>d2;
d1.push_back(10);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_back(30);
d1.push_back(40);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_back(30);
d1.push_back(20);
d2.push_back(100);
cout << "交换前";
cout << "d1:";
for_each(d1.begin(), d1.end(), print);
cout << endl;
cout << "d2:";
for_each(d2.begin(), d2.end(), print);
cout << endl;
cout << "交换后";
swap(d1,d2);
cout << "d1:";
for_each(d1.begin(), d1.end(), print);
cout << endl;
cout << "d2:";
for_each(d2.begin(), d2.end(), print);
}
🔍运行结果:
🤔结束!