python 计算程序运行的耗时,主要有三种方法:
time.time() 、 time.perf_counter() 和 datetime.datetime.now()方法
使用方法如下:
1. time.time()
import time
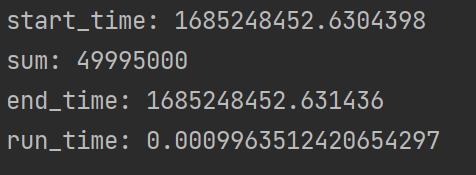
start = time.time() # 程序开始时间,单位为秒
print("start_time:", start)
# function() 运行的程序
summ = 0
for i in range(0, 10000):
summ = summ + i
print("sum:", summ)
end = time.time() # 程序结束时间
print("end_time:", end)
run_time = end - start # 程序的运行时间,单位为秒
print("run_time:", run_time)
2. time.perf_counter()
与time.time()用法一致。
import time
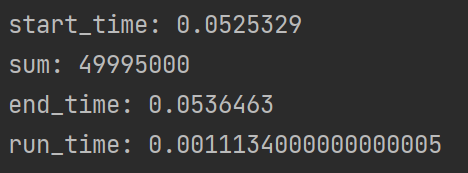
start = time.perf_counter() # 程序开始时间
print("start_time:", start)
# function() 运行的程序
summ = 0
for i in range(0, 10000):
summ = summ + i
print("sum:", summ)
end = time.perf_counter() # 程序结束时间
print("end_time:", end)
run_time = end - start # 程序的运行时间,单位为秒
print("run_time:", run_time)
附:time.sleep() 让程序暂停指定的秒数,如 time.sleep(0.5)
二者的区别为:
time.time() 为wall time(墙上时钟),是系统时钟的时间戳(1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC 后经过的浮点秒数)。
time.perf_counter() 为该程序运行后CPU运行的浮点秒数。不包含sleep用时。
所以在统计程序运行用时时,应按照自身需求进行选用。
3、datetime.datetime.now()方法
生成一个datetime.datetime对象,包含了年、月、日、时、分、秒、毫秒七个参数
t.year, t.month, t.day, t.hour, t.minute, t.second, t.microsecond
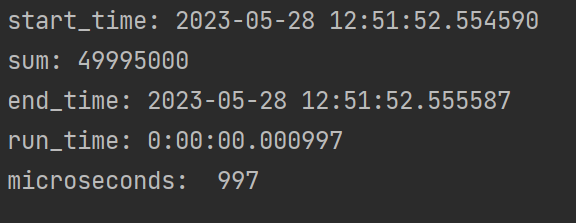
from datetime import datetime
# start = datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') #设置格式
start = datetime.now()
print("start_time:", start)
# function() 运行的程序
summ = 0
for i in range(0, 10000):
summ = summ + i
print("sum:", summ)
end = datetime.now()
print("end_time:", end)
run_time = end - start # 程序的运行时间
print("run_time:", run_time)
print("microseconds: ", (end-start).microseconds) # 毫秒
![C++ [STL之list的使用]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/84e4fd60d85a42619862f999bd6ec9ea.png#pic_center)