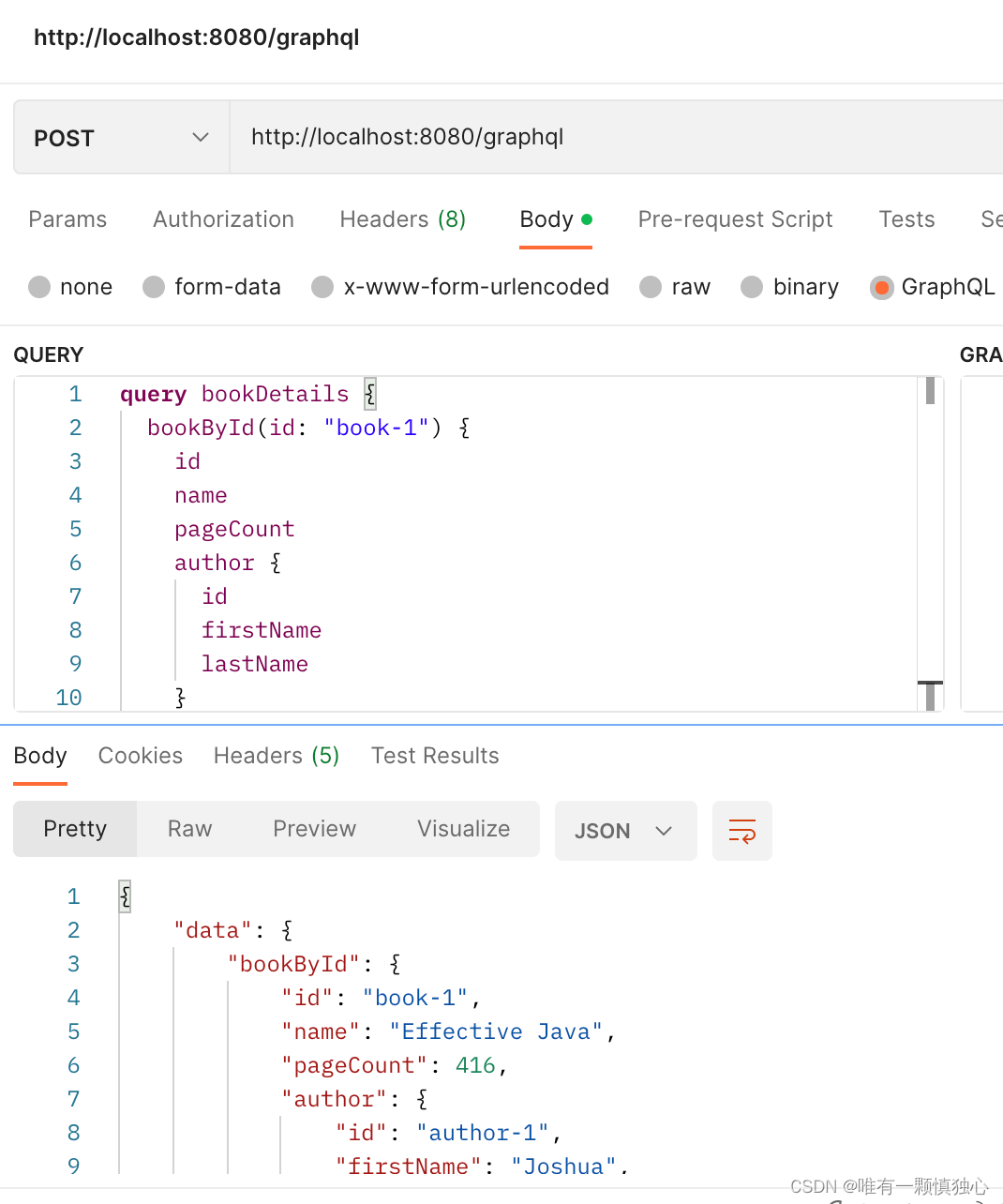
一、Set 接口(P518)
1. Set 接口基本介绍
(1)无序(添加和取出的顺序不一致),没有索引。
(2)不允许重复元素,所以最多包含一个 null。
2. Set 接口的常用方法
和 List 接口一样,Set 接口也是 Collection 的子接口,因此,常用方法和 Collection 接口一样。
3. Set 接口的遍历方式
同 Collection 的遍历方式一样,因为 Set 接口是 Collection 接口的子接口。
(1)可以使用选代器
(2)增强for
(3)不能使用索引的方式来获取
二、HashSet(P519)
1. Hashset 的说明
(1)HashSet 实现了 Set 接口。
(2)HashSet 实际上是 HashMap。(3)可以存放 null 值,但是只能有一个 null。
(4)HashSet 不保证元素是有序的,取决于 hash 后,再确定索引的结果。
(5)不能有重复元素/对象。
2. Hashset底层机制源码说明(P522)
分析 Hashset 底层是 HashMap,HashMap 底层是(数组+链表+红黑树)
public class HashMap_<K, V> { transient Node<K, V>[] table; transient int modCount; transient int size; public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); } static final int hash(Object key) { int h; return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); } final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K, V>[] tab; Node<K, V> p; int n, i; // 属性table为null或table的长度为0,就扩容 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) { n = (tab = resize()).length; } // 如果tab[i]为null,表示没有存放元素,就创建节点并赋值给tab[i] if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) { tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); } else { Node<K, V> e; K k; // p 和添加元素的hash值相同 并且 (key相同或equals相同),p赋值给e if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { e = p; } // 链表循环比较 else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { break; } p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) { e.value = value; } return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) { resize(); } return null; } int threshold; final float loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // 16 // 加载因子 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; final Node<K, V>[] resize() { Node<K, V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; int oldThr = threshold; int newCap, newThr = 0; if (oldCap > 0) { if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return oldTab; } else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) { newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold } } else if (oldThr > 0) { newCap = oldThr; } else { // 扩容 newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int) (DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); } if (newThr == 0) { float ft = (float) newCap * loadFactor; newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float) MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int) ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } threshold = newThr; // 初始化数组,并赋值给属性table Node<K, V>[] newTab = (Node<K, V>[]) new Node[newCap]; table = newTab; return newTab; } Node<K, V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) { return new Node<>(hash, key, value, next); } static class Node<K, V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K, V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.next = next; } } }
(1)HashSet 底层是 HashMap
(2)添加一个元素时,先得到hash值-会转成->索引值
(3)找到存储数据表 table,看这个索引位置是否已经存放的有元素
(4)如果没有,直接加入
(5)如果有,调用 equals 比较,如果相同,就放弃添加,如果不相同,则添加到最后
(6)在 Java8 中,如果一条链表的元素个数达到 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是8),并且 table 的大小 >= MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认64),就会进行树化(红黑树)
红黑树机制:
(1)HashSet 底层是 HashMap,第一次添加时,table 数组扩容到16,临界值(threshold)是16,加载因子(loadFactor)是0.75=12
(2)如果table数组使用到了临界值12,就会扩容到16*2=32,新的临界值就是32*0.75=24,依次类推
(3)在Java8中,如果一条链表的元素个数到达TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是8),并且table的大小>=MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认64)就会进行树化(红黑树),否则仍然采用数组扩容机制