1、下载编译
官网:http://www.fftw.org/index.html
2、FFT基础知识
2.1 概念
-
FFT分辨率可以表示为:fs/Nfft
频率分辨率的物理量就是:观测信号的时间窗长度, 时间窗越长(N大), 对应频率分辨率就越高。
提高频率分辨率的两种方法:增加fft点数N(计算量大),降低采样率(时间分辨率降低了)。 -
输出取N/2个频点,N点fft的输出值也是N个(对称的),故只取一半。
-
时域上的补0相当于频域上的插值,通过补0增加的fft点数无法提高fft精度
-
幅度、相位

-
示例:fs =1024/10 N=1024 △f=0.1Hz
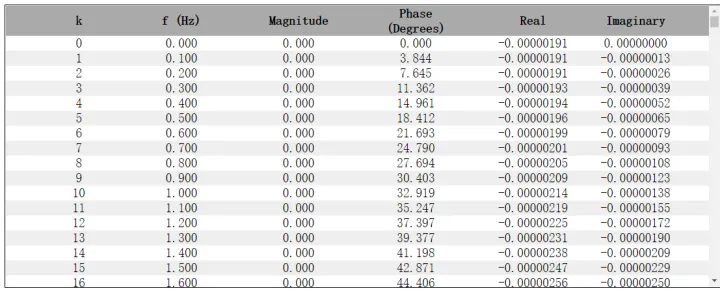
2.2 对1024个点的信号,做4次256点FFT和1次1024点FFT的区别
有信号如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
如果拆分成4个4点FFT,或者1个16点,其中的数学关系不能凭直觉发现,但是,如果把这段信号拆分成:
1 2 3 4 | 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 | 5 6 7 8 | 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 | 9 10 11 12 | 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 |13 14 15 16
然后做4次16点的FFT,那么这4次16点的FFT频谱叠加,最后得到的叠加后的频谱就=一次16点的FFT.
那么,问题就变成了: 1个带12个0的16点的FFT跟1个4点的FFT之间是什么关系?
1 2 3 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0和1 2 3 4,他们的频谱,就相当于1234的4点频谱做插值成16个点.
至于0 0 0 0 5 6 7 8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0和5 6 7 8 之间的关系,你知道根据时移定理,对频谱乘一个e^-i2pikm相当于时域上延迟k个点:0 0 0 0 5 6 7 8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0可以变形为5 6 7 8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
也就是说,4点4FFT与1点的16FFT的关系,大致相当于:
FFT(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16)=插值(FFT(1,2,3,4))+插值(FFT(5,6,7,8))*时移+插值(FFT(9,10,11,12))*时移^2+插值(FFT(13,14,15,16))*时移^3
3、FFTW基础
3.1 基本函数
plan= fftw_plan_dft_1d(_N,_in,_out,FFTW_BACKWARD,FFTW_MEASURE);//配置计算计划
倒数第二个参数sign, FFTW_FORWARD:正变换 ;FFTW_BACKWARD:逆变换。
最后的一个参数flags,FFTW_MEASURE:表示先计算一些FFT并测量所用的时间,以便为大小为n的变换寻找最优的计算方法。
//c-c
fftw_plan fftw_plan_dft_1d(int n, fftw_complex *in, fftw_complex *out, int sign, unsigned flags);
fftw_plan fftw_plan_dft_2d(int n0, int n1, fftw_complex *in, fftw_complex *out, int sign, unsigned flags);
fftw_plan fftw_plan_dft_3d(int n0, int n1, int n2, fftw_complex *in, fftw_complex *out, int sign, unsigned flags);
fftw_plan fftw_plan_dft(int rank, const int *n, fftw_complex *in, fftw_complex *out, int sign, unsigned flags);
//r-c
fftw_plan fftw_plan_dft_r2c_1d(int n, double *in, fftw_complex *out, unsigned flags);
fftw_plan fftw_plan_dft_r2c_2d(int n0, int n1, double *in, fftw_complex *out, unsigned flags);
fftw_plan fftw_plan_dft_r2c_3d(int n0, int n1, int n2, double *in, fftw_complex *out, unsigned flags);
fftw_plan fftw_plan_dft_r2c(int rank, const int *n, double *in, fftw_complex *out, unsigned flags);
//r-r
fftw_plan fftw_plan_r2r_1d(int n, double *in, double *out, fftw_r2r_kind kind, unsigned flags);
fftw_plan fftw_plan_r2r_2d(int n0, int n1, double *in, double *out, fftw_r2r_kind kind0, fftw_r2r_kind kind1, unsigned flags);
fftw_plan fftw_plan_r2r_3d(int n0, int n1, int n2, double *in, double *out, fftw_r2r_kind kind0, fftw_r2r_kind kind1, fftw_r2r_kind kind2, unsigned flags);
fftw_plan fftw_plan_r2r(int rank, const int *n, double *in, double *out, const fftw_r2r_kind *kind, unsigned flags);
void fftw_execute(const fftw_plan p);
void fftw_execute_dft(const fftw_plan p, fftw_complex *in, fftw_complex *out);
void fftw_execute_split_dft(const fftw_plan p, double *ri, double *ii, double *ro, double *io);
void fftw_execute_dft_r2c(const fftw_plan p,double *in, fftw_complex *out);
void fftw_execute_split_dft_r2c(const fftw_plan p, double *in, double *ro, double *io);
void fftw_execute_dft_c2r(const fftw_plan p, fftw_complex *in, double *out);
void fftw_execute_split_dft_c2r(const fftw_plan p, double *ri, double *ii, double *out);
void fftw_execute_r2r(const fftw_plan p, double *in, double *out);
单序列正反变换的归一化处理时:除以N/2
3.2数据类型
FFTW有三个版本的数据类型:double、float、long double,
使用方法如下:
- 链接对应的库(比如libfftw3-3、libfftw3f-3、或ibfftw3l-3) 包含同样的头文件fftw3.h
单精度 前缀 “-fftwf” 编译选项 “-lfftw3f”
双精度 前缀 “-fftwl” 编译选项 “-lfftw3l”- 将所有以小写"fftw_“开头的名字替换为"fftwf_”(float版本)或"fftwl_"(long double版本)。
比如将fftw_complex替换为fftwf_complex,
将fftw_execute替换为fftwf_execute等。- 所有以大写"FFTW_"开头的名字不变,将函数参数中的double替换为float或long double
最后,虽然long double是C99的标准,但你的编译器可能根本不支持该类型,或它并不能提供比double更高的精度。
3、示例
Qt中用fftw对音频数据变换
全球最快的傅里叶变换算法(FFTW)
#include <fftw3.h>
...
{
fftw_complex *in, *out;
fftw_plan p;
...
in = (fftw_complex*) fftw_malloc(sizeof(fftw_complex) * N);
out = (fftw_complex*) fftw_malloc(sizeof(fftw_complex) * N);
...
p = fftw_plan_dft_1d(N, in, out, FFTW_FORWARD, FFTW_ESTIMATE); //变换类型
fftw_execute(p); // 执行变换
...
fftw_destroy_plan(p);
fftw_free(in);
fftw_free(out);
}
音频变换的例子:
int N = filesize/2; //计算数据个数
short *in_buf; //自己存输入数据
//为fft输入计算分配空间
double * in = (double*)fftw_malloc(sizeof(double) * N);
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
in[i] = in_buf[i]; //将pcm文件中的数据复制到fft的输入
}
//为fft输出算分配空间
fftw_complex * out = (fftw_complex*)fftw_malloc(sizeof(fftw_complex) * N);
//进行fft变换,fftw_plan_dft_c2r_1d函数进行反变换
fftw_plan p = FFTW3_H::fftw_plan_dft_r2c_1d(N, in, out, FFTW_ESTIMATE);
fftw_execute(p);
double dx3 = (double)SAMPLE_RATE / N;
polt_1->xAxis->setRange(0, SAMPLE_RATE/2, Qt::AlignLeft);
//根据FFT计算的复数计算振幅谱
for( int i=0; i<N/2; i++ )
{
double val = sqrt(out[i][0] * out[i][0] + out[i][1] * out[i][1]);
val = val / (N / 2);
polt_1->graph(0)->addData( dx3 * i, val );
if( val > val_max )
{
val_max = val;
}
double db = log(val);
//qDebug("frequency = %f, amplitude = %f, db = %f", dx3 * i, val / (N / 2), db);
}
polt_1->yAxis->setRange(val_max*0.6, val_max*1.2, Qt::AlignBottom);
polt_1->replot();
//根据FFT计算的复数计算相位谱
polt_2->xAxis->setRange(0, SAMPLE_RATE/2, Qt::AlignLeft);
polt_2->yAxis->setRange(0, 10, Qt::AlignBaseline);
for( int i=0; i<N/2; i++ )
{
double val = atan2(out[i][1], out[i][0]);
polt_2->graph(0)->addData( dx3 * i, val );
}
polt_2->replot();
//fftw销毁
fftw_destroy_plan(p);
fftw_free(in);
fftw_free(out);
N点的FFT,以 “采样率/N” 为频率间隔,


![【PWN · ret2libc】[NISACTF 2022]ezstack](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/76eec20bacf64802b26555cc148dd806.png)