前言
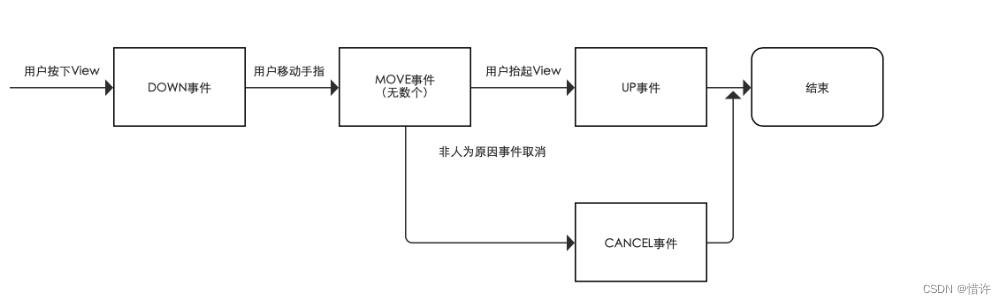
对于Android中的触摸事件即指手指触摸到屏幕时产生的点击事件;
类型如下:
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWNMotionEvent.ACTION_UPMotionEvent.ACTION_MOVEMotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL
Android事件处理流程
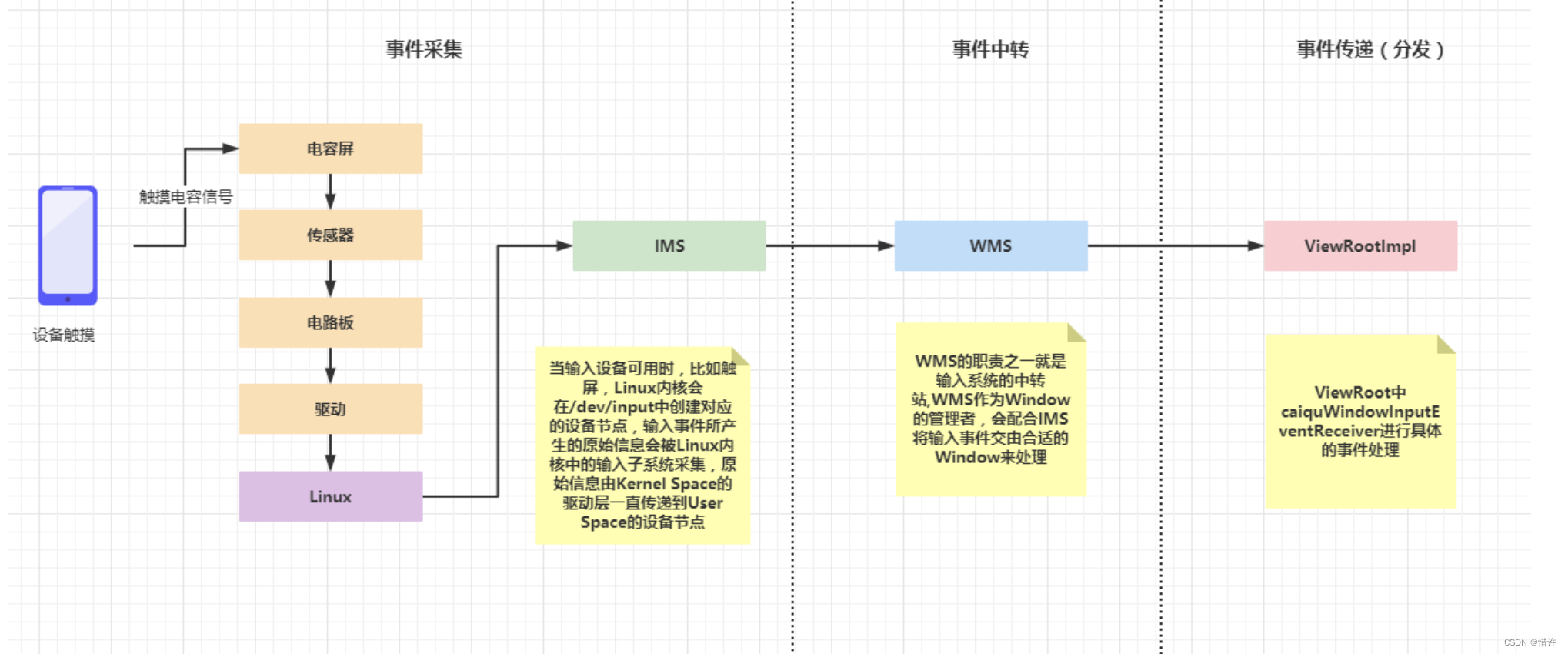
主要涉及三个流程:事件采集、事件中转以及事件分发;
在Android中,Touch事件的分发分服务端和应用端。在服务端由WindowManagerService(借助InputManagerService)负责采集和分发的,在应用端则是由ViewRootImpl(内部有一个mView变量指向View树的根,负责控制View树的UI绘制和事件消息的分发)负责分发的。
当输入设备可用时,比如触屏,Linux内核会在dev/input中创建对应的设备节点,输入事件所产生的原始信息会被Linux内核中的输入子系统采集,原始信息由Kernel Space的驱动层一直传递到User Space的设备节点;
IMS所做的工作就是监听/dev/input/下的所有设备节点,当设备节点有数据时会将数据进行加工处理并找到合适的Window,将输入事件分发给它;
Linux相关函数简介
IMS监听/dev/input设备节点,具体实现需要借助Linux相关函数,这里简单介绍下:
- epoll函数【更多详解请参考:epoll详解】
-
epoll_create:创建 epoll 对象,会占用一个fd值,在linux下可以通过查看/proc/进程id/fd/,可以看到具体的fd,在epoll使用完毕后,需要调用close()进行关闭; -
epoll_ctl:epoll的事件注册函数,它不同于select()函数是在监听事件时告诉内核要监听什么类型的事件,而是在这里先注册要监听的事件类型; -
epoll_wait:收集在epoll监控的事件中已经发送的事件;函数调用成功,返回对应I/O上已准备好的文件描述符数目。返回0表示已超时;
- iNotify函数【更多详解请参考:Linux inotify详解】
它是一个内核用于通知用户空间程序文件系统变化的机制;
在用户态,inotify 通过三个系统调用和在返回的文件描述符上的文件 I/ 操作来使用,使用 inotify 的第一步是创建 inotify 实例:
int fd = inotify_init ();
每一个 inotify 实例对应一个独立的排序的队列。
文件系统的变化事件被称做 watches 的一个对象管理,每一个 watch 是一个二元组(目标,事件掩码),目标可以是文件或目录,事件掩码表示应用希望关注的 inotify 事件,每一个位对应一个 inotify 事件。Watch 对象通过 watch描述符引用,watches 通过文件或目录的路径名来添加。目录 watches 将返回在该目录下的所有文件上面发生的事件。
下面函数用于添加一个 watch:
int wd = inotify_add_watch (fd, path, mask);
fd 是 inotify_init() 返回的文件描述符,path 是被监视的目标的路径名(即文件名或目录名),mask 是事件掩码, 在头文件 linux/inotify.h 中定义了每一位代表的事件。可以使用同样的方式来修改事件掩码,即改变希望被通知的inotify 事件。Wd 是 watch 描述符。
下面的函数用于删除一个 watch:
int ret = inotify_rm_watch (fd, wd);
fd 是 inotify_init() 返回的文件描述符,wd 是 inotify_add_watch() 返回的 watch 描述符。Ret 是函数的返回值。
源码分析
从内核到IMS过程
我们从SystemServer.startOtherServices()方法出发:
#SystemServer.startOtherServices
....
inputManager = new InputManagerService(context);
...
inputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(wm.getInputManagerCallback());
inputManager.start();
...
这里会启动InputManagerService,我们看下InputManagerService的构造方法以及start方法都做了些什么?
public InputManagerService(Context context) {
this.mContext = context;
this.mHandler = new InputManagerHandler(DisplayThread.get().getLooper());
mStaticAssociations = loadStaticInputPortAssociations();
...
mPtr = nativeInit(this, mContext, mHandler.getLooper().getQueue());//调用nativeInit方法
...
}
public void start() {
...
nativeStart(mPtr);//调用nativeStart方法
...
}
我们找到InputManagerService.cpp文件里的nativeInit以及nativeStart方法:

找到InputManager.cpp文件,对应构造方法以及start方法如下:
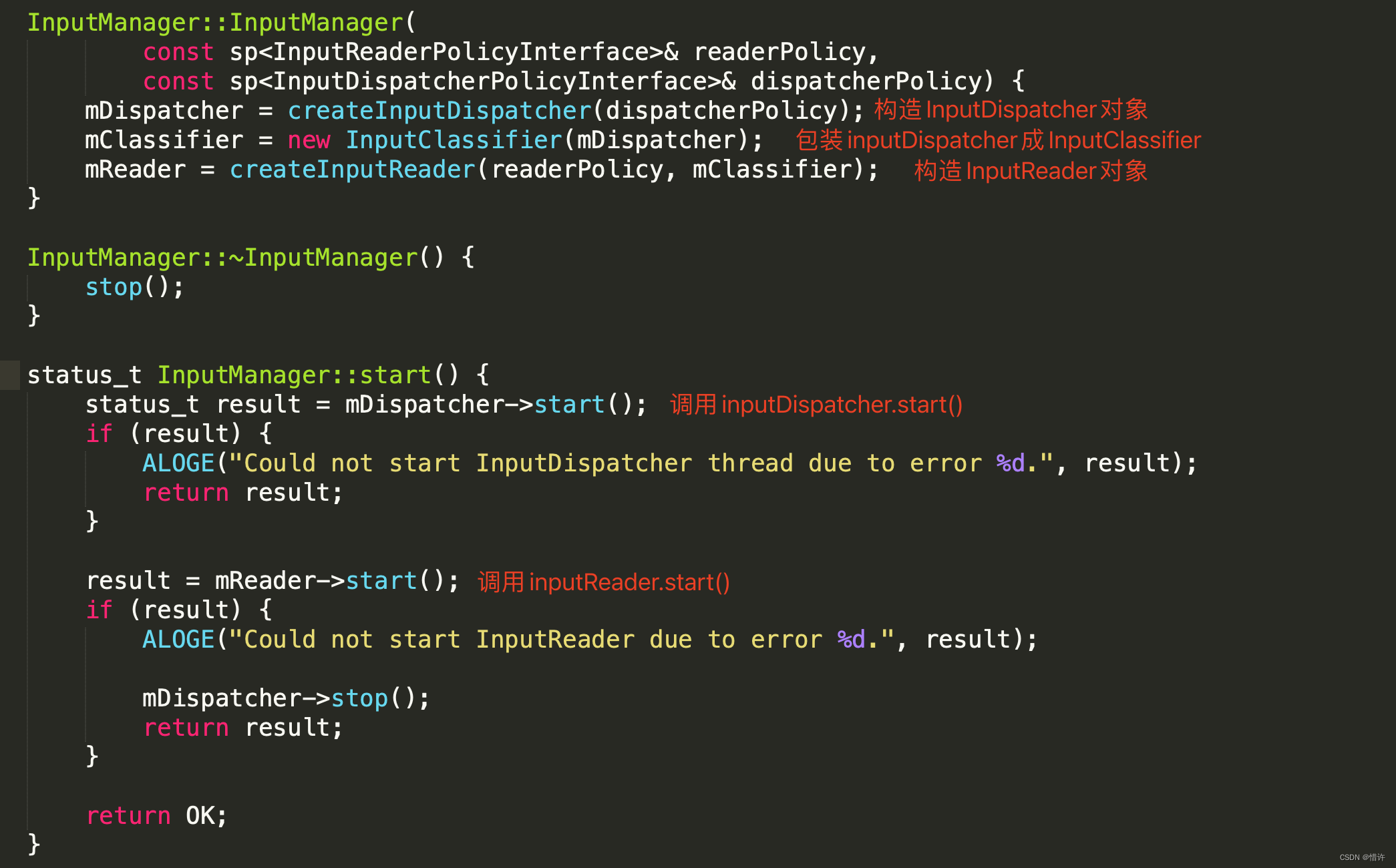
可以看到InputManager主要做以下几件事:
- 构造InputDispatcher对象;(用于后续事件分发处理)
- 构造InputReader对象;(用于事件输入监听)
- 调用InputDispatcher和InputReader的start()方法;
Q:那InputReader是如何监听事件输入的呢?
我们从InputReader::start方法入手!

我们看下loopOnce函数做了什么?
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
int32_t oldGeneration;
int32_t timeoutMillis;
bool inputDevicesChanged = false;
std::vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;
{
...
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE); //从EventHub中读取事件,需要注意内部使用epoll机制实现,调用了epoll_wait进行阻塞,当fd发生变化的时候执行后面的代码
{
....
if (count) {
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count); //处理事件
}
...
// 当输入设备的描述更改时发送一个消息
if (inputDevicesChanged) {
mPolicy->notifyInputDevicesChanged(inputDevices);
}
//将事件传递给InputDispatcher
mQueuedListener->flush();
}
先不着急分析 processEventsLocked方法是如何来处理事件的,我们先了解下EventHub
先看下EventHub的构造方法:
EventHub::EventHub(void)
: mBuiltInKeyboardId(NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD),
mNextDeviceId(1),
mControllerNumbers(),
mOpeningDevices(nullptr),
mClosingDevices(nullptr),
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan(false),
mNeedToReopenDevices(false),
mNeedToScanDevices(true),
mPendingEventCount(0),
mPendingEventIndex(0),
mPendingINotify(false) {
ensureProcessCanBlockSuspend();
mEpollFd = epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC);//调用epoll_create创建 eventpoll 对象
mINotifyFd = inotify_init(); //调用inotify_init
mInputWd = inotify_add_watch(mINotifyFd, DEVICE_PATH, IN_DELETE | IN_CREATE); //调用inotify_add_watch设置监听目标路径为DEVICE_PATH,即/dev/input/
...
int result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mINotifyFd, &eventItem);//调用epoll_ctl注册监听事件
...
}
再看下mEventHub->getEvents()方法:
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
...
for (;;) {
...
int pollResult = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, mPendingEventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);//调用epoll_wait监听事件输入
if (pollResult == 0) {
// Timed out.
mPendingEventCount = 0;
break;
}
if (pollResult < 0) {
// An error occurred.
mPendingEventCount = 0;
// Sleep after errors to avoid locking up the system.
// Hopefully the error is transient.
if (errno != EINTR) {
ALOGW("poll failed (errno=%d)\n", errno);
usleep(100000);
}
} else {
// Some events occurred.
mPendingEventCount = size_t(pollResult);
}
}
return event - buffer;
}
可以看到EventHub内部使用epoll函数以及inotify函数实现事件监听回调!
我们继续跟进事件处理函数:processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count)
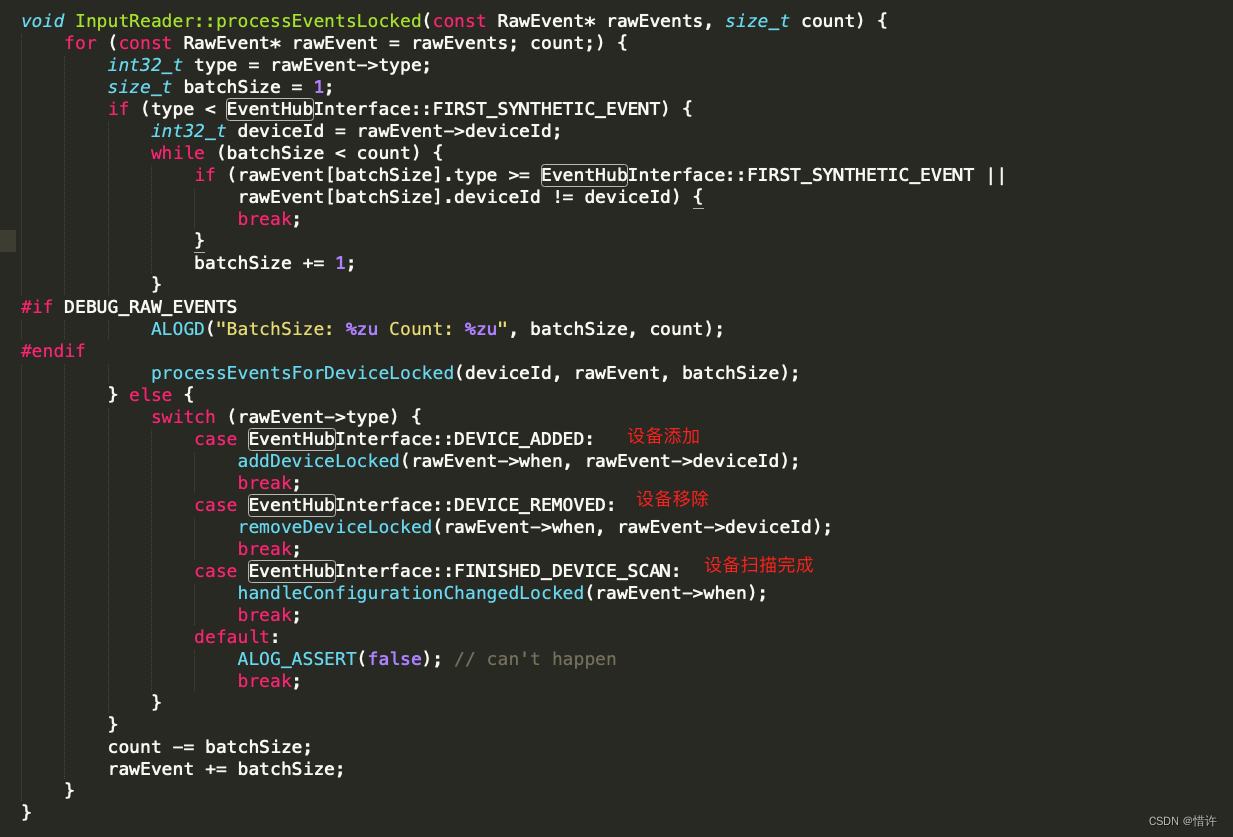
继续跟进processEventsForDeviceLocked()
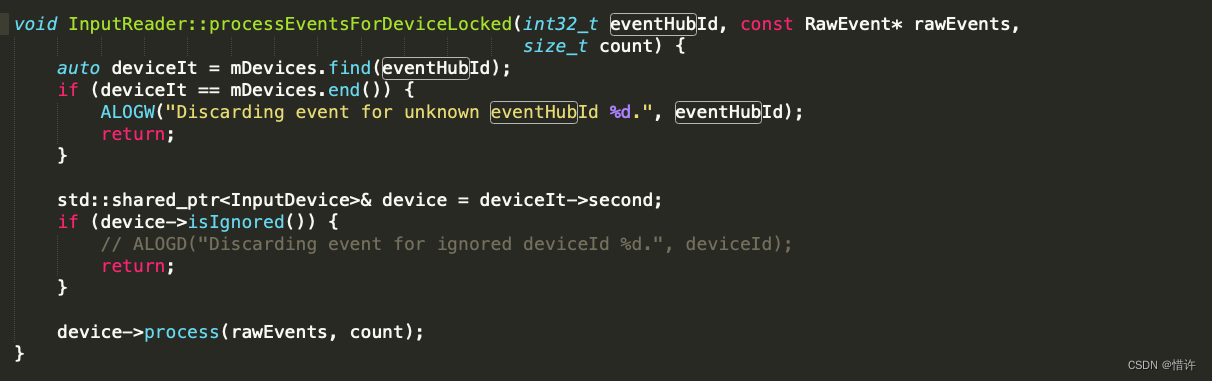
可以看到会交给device-->process方法处理:
我们找到InputDevice.cpp文件对应的process函数

而mapper.process会交给TouchInputMapper::process处理:
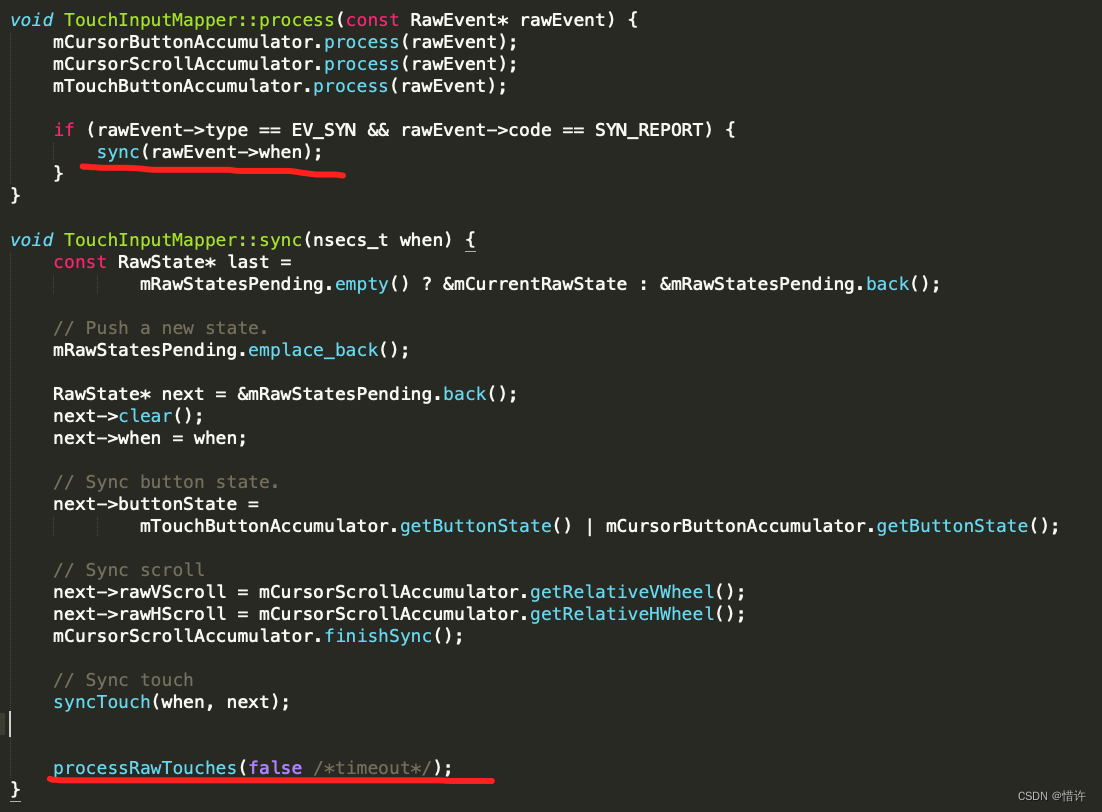
紧接着调用processRawTouches方法
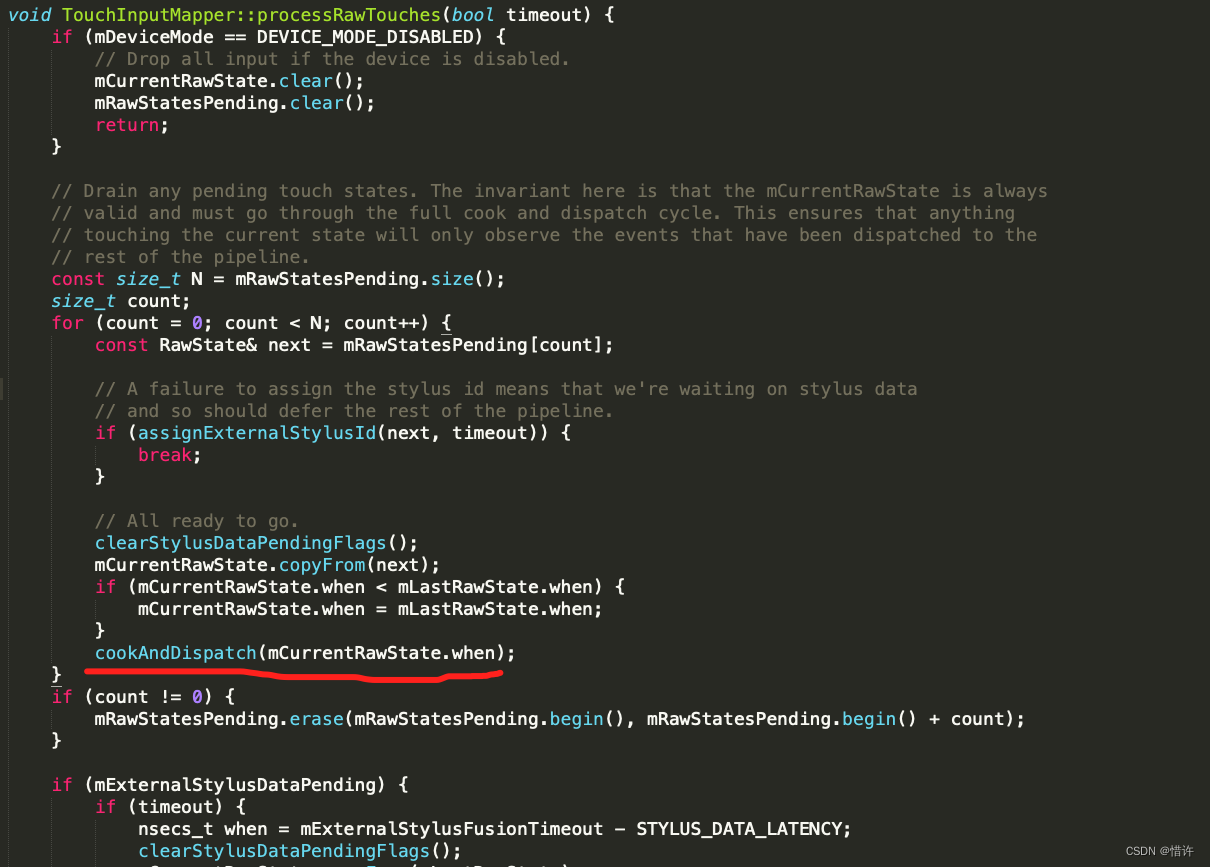
调用cookAndDispatch方法,最终会调用TouchInputMapper::dispatchMotion方法
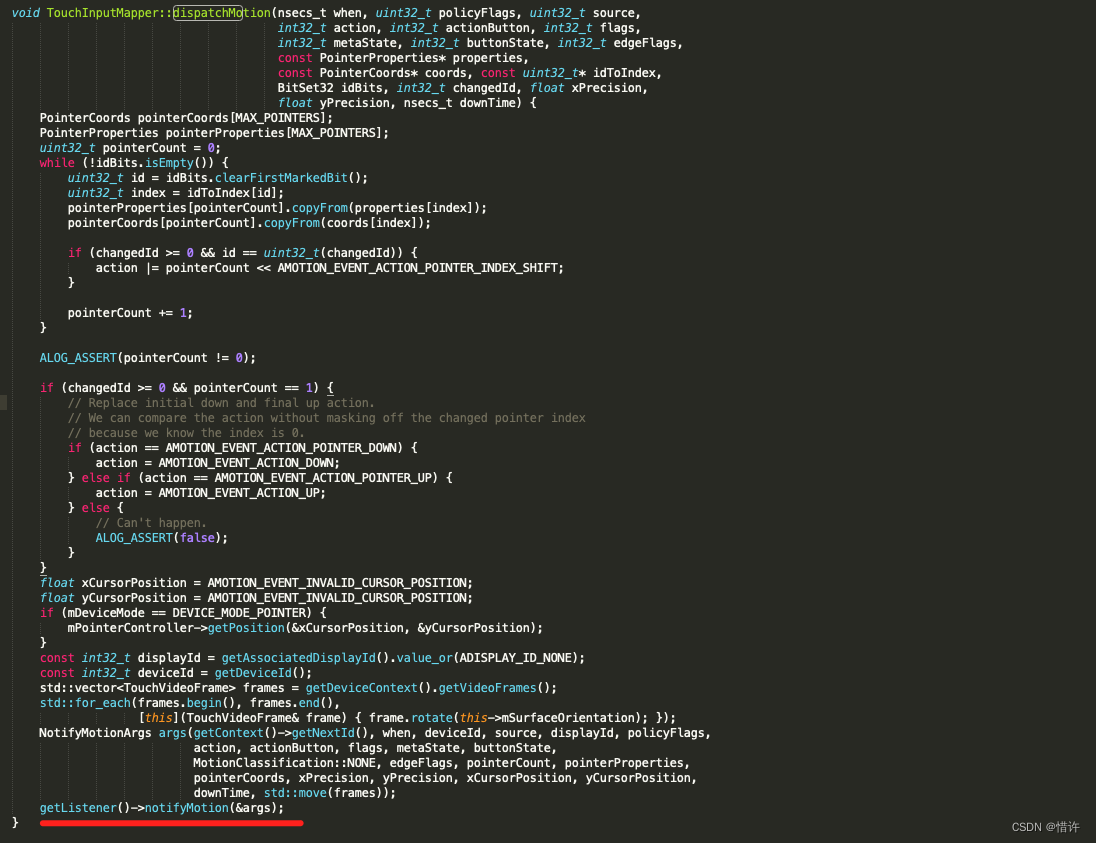
最终会执行getListener()-->notifyMotion方法,那这里的getListener()是谁呢?
InputListenerInterface* InputReader::ContextImpl::getListener() {
return mReader->mQueuedListener.get();
}
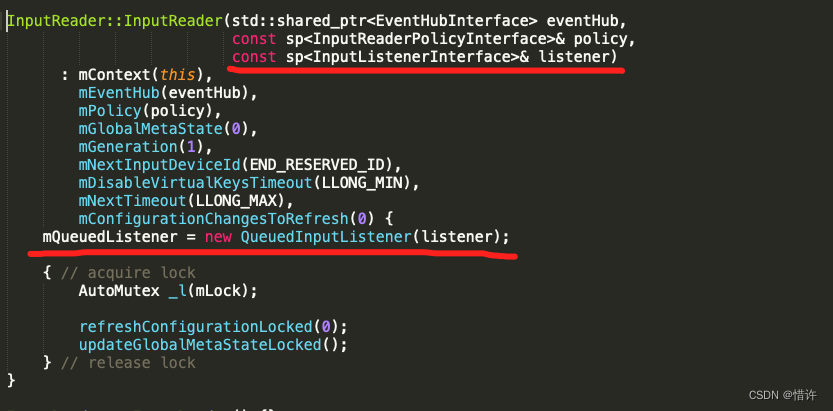
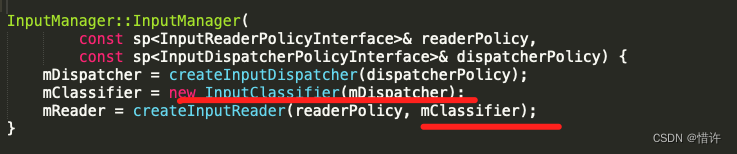
几者结合可以得出结论:getListener()即为InputDispatcher对象!
至此,InputReader完成事件的监听工作并后续交给InputDispatcher进行分发!
InputReader监听输入整体流程
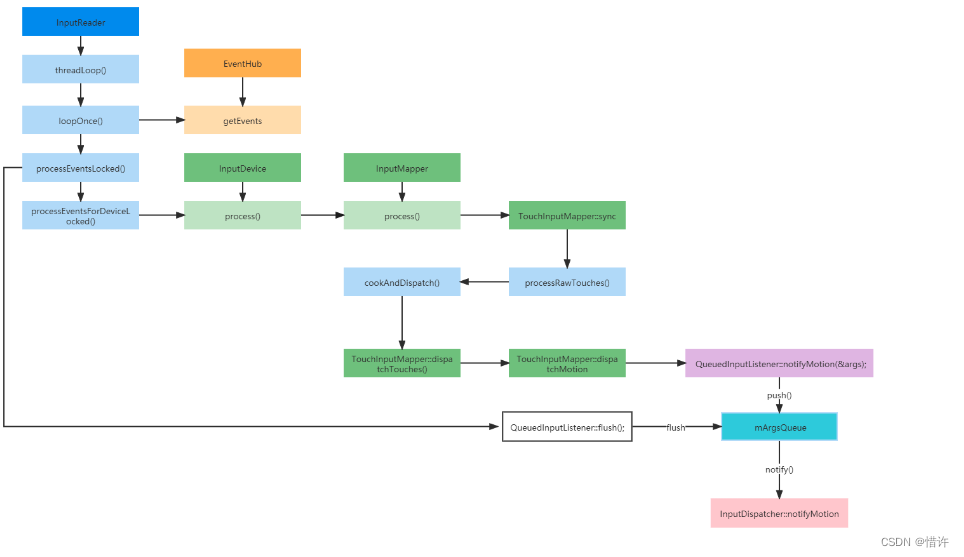
Q:InputDispatcher又是如何进行事件分发的呢?
我们先看下InputDispatcher::notifyMotion方法:
void InputDispatcher::notifyMotion(const NotifyMotionArgs* args) {
...
if (needWake) {
mLooper->wake(); //会调用mLooper->wake()唤醒InputDispatcher线程
}
}
和InputReader类似,InputDispatcher::start方法同样会开启一个线程,并执行dispatchOnce()函数

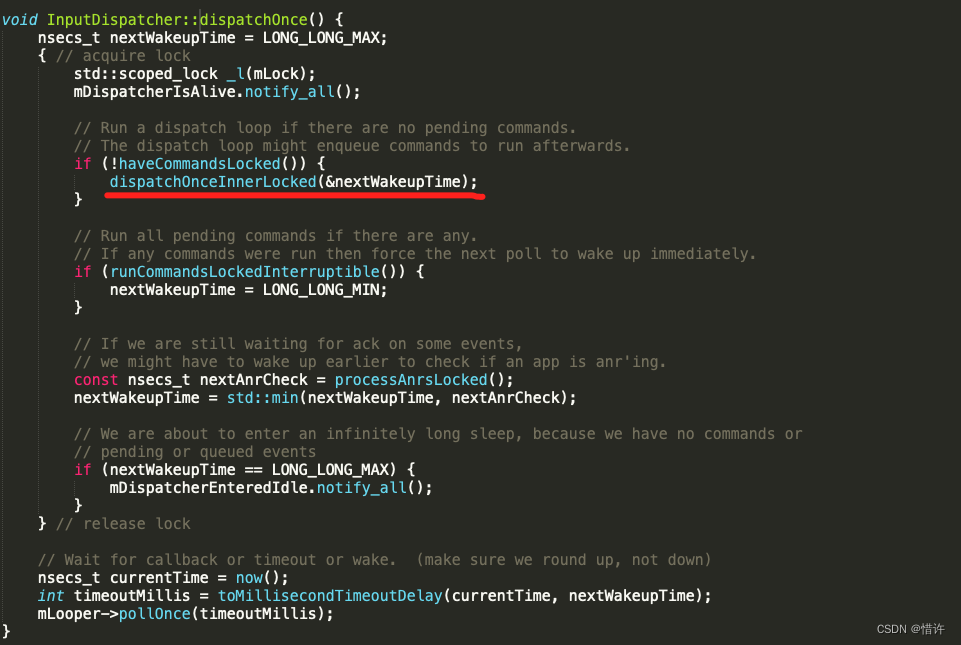
我们看下dispatchOnceInnnerLocked函数
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
...
switch (mPendingEvent->type) {
...
//这里我们只关注motion事件
case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: {
MotionEntry* typedEntry = static_cast<MotionEntry*>(mPendingEvent);
if (dropReason == DropReason::NOT_DROPPED && isAppSwitchDue) {
dropReason = DropReason::APP_SWITCH;
}
if (dropReason == DropReason::NOT_DROPPED && isStaleEvent(currentTime, *typedEntry)) {
dropReason = DropReason::STALE;
}
if (dropReason == DropReason::NOT_DROPPED && mNextUnblockedEvent) {
dropReason = DropReason::BLOCKED;
}
done = dispatchMotionLocked(currentTime, typedEntry, &dropReason, nextWakeupTime);
break;
}
}
...
}
}
在dispatchOnceInnerLocked函数中会调用dispatchMotionLocked方法
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchMotionLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, MotionEntry* entry,
DropReason* dropReason, nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchMotionLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, MotionEntry* entry,
DropReason* dropReason, nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
ATRACE_CALL();
...
if (isPointerEvent) {
// 1.findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked 负责找到要进行分发的window
injectionResult =findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime, *entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime,
&conflictingPointerActions);
} else {
injectionResult = findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime, *entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime);
}
if (injectionResult == INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING) {
return false;
}
setInjectionResult(entry, injectionResult);
...
//2.具体事件分发
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);
return true;
}
}
会调用dispatchEventLocked方法,后续又经过层层调用最终会调用InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked方法
void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection) {
...
case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: { //这里,只关注Motion事件
MotionEntry* motionEntry = static_cast<MotionEntry*>(eventEntry);
// Publish the motion event.
status = connection->inputPublisher.publishMotionEvent(...);
break;
}
...
}
}
而inputPublisher.publishMotionEvent会执行InputPublisher::publishMotionEvent方法
status_t InputPublisher::publishMotionEvent(
uint32_t seq, int32_t eventId, int32_t deviceId, int32_t source, int32_t displayId,
std::array<uint8_t, 32> hmac, int32_t action, int32_t actionButton, int32_t flags,
int32_t edgeFlags, int32_t metaState, int32_t buttonState,
MotionClassification classification, float xScale, float yScale, float xOffset,
float yOffset, float xPrecision, float yPrecision, float xCursorPosition,
float yCursorPosition, nsecs_t downTime, nsecs_t eventTime, uint32_t pointerCount,
const PointerProperties* pointerProperties, const PointerCoords* pointerCoords) {
...
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::Type::MOTION;
msg.body.motion.seq = seq;
msg.body.motion.eventId = eventId;
msg.body.motion.deviceId = deviceId;
msg.body.motion.source = source;
msg.body.motion.displayId = displayId;
msg.body.motion.hmac = std::move(hmac);
msg.body.motion.action = action;
msg.body.motion.actionButton = actionButton;
msg.body.motion.flags = flags;
msg.body.motion.edgeFlags = edgeFlags;
msg.body.motion.metaState = metaState;
msg.body.motion.buttonState = buttonState;
msg.body.motion.classification = classification;
msg.body.motion.xScale = xScale;
msg.body.motion.yScale = yScale;
msg.body.motion.xOffset = xOffset;
msg.body.motion.yOffset = yOffset;
msg.body.motion.xPrecision = xPrecision;
msg.body.motion.yPrecision = yPrecision;
msg.body.motion.xCursorPosition = xCursorPosition;
msg.body.motion.yCursorPosition = yCursorPosition;
msg.body.motion.downTime = downTime;
msg.body.motion.eventTime = eventTime;
msg.body.motion.pointerCount = pointerCount;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < pointerCount; i++) {
msg.body.motion.pointers[i].properties.copyFrom(pointerProperties[i]);
msg.body.motion.pointers[i].coords.copyFrom(pointerCoords[i]);
}
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}
status_t InputPublisher::publishFocusEvent(uint32_t seq, int32_t eventId, bool hasFocus,
bool inTouchMode) {
if (ATRACE_ENABLED()) {
std::string message =
StringPrintf("publishFocusEvent(inputChannel=%s, hasFocus=%s, inTouchMode=%s)",
mChannel->getName().c_str(), toString(hasFocus),
toString(inTouchMode));
ATRACE_NAME(message.c_str());
}
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::Type::FOCUS;
msg.body.focus.seq = seq;
msg.body.focus.eventId = eventId;
msg.body.focus.hasFocus = hasFocus ? 1 : 0;
msg.body.focus.inTouchMode = inTouchMode ? 1 : 0;
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}
可以看到主要是将数据进行封装成InputMessage对象,并最终交给InputChannel进行发送;
InputDispatcher分发事件流程
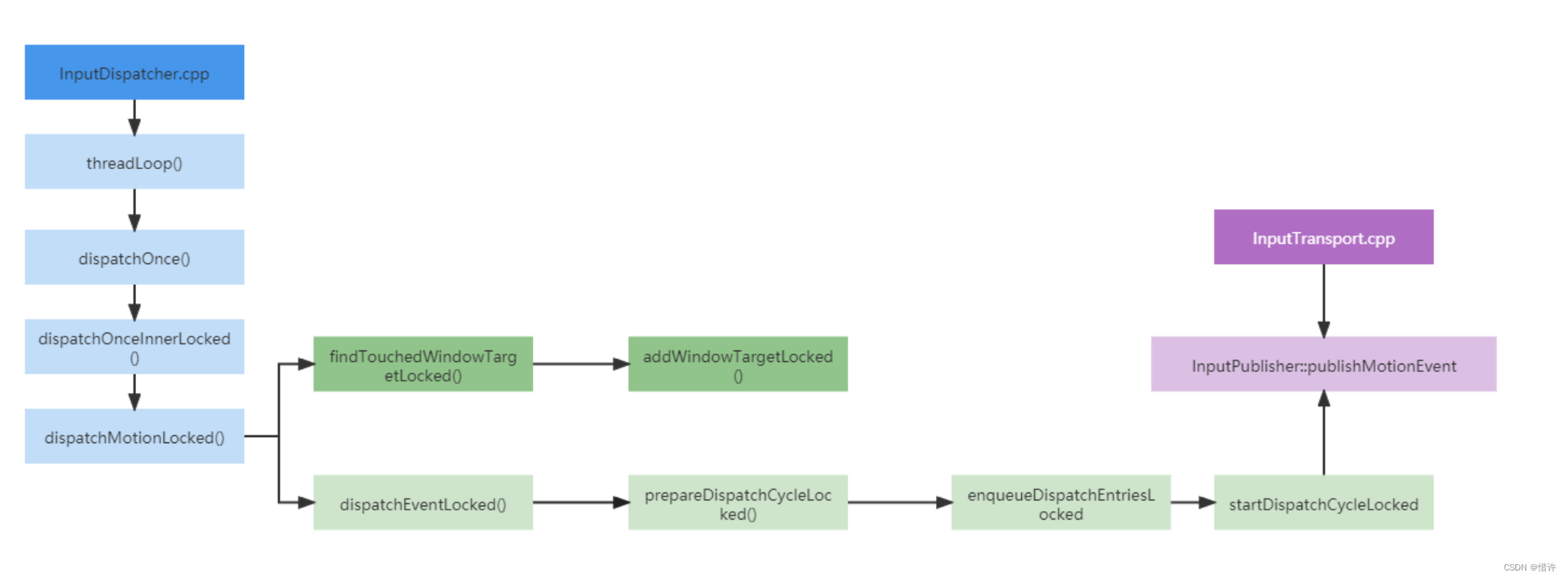
从IMS到WMS过程
从上面可以知道:InputReaderThread和InputDispatcherThread是运行在SystemServer进程中的;
和用户进程并不在同一个进程中,那中间一定存在进程间通信机制;
InputChannel目的正是为了与用户进程进行通信,InputChannel是由WMS管理,触发构建生成;
-
首先,在ViewRootImpl中的setView函数中会调用
mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser()方法;

这里在java层面构建了一个InputChannel对象; -
addToDisplayAsUser会调用到WindowlessWindowManager.addToDisplay()方法;
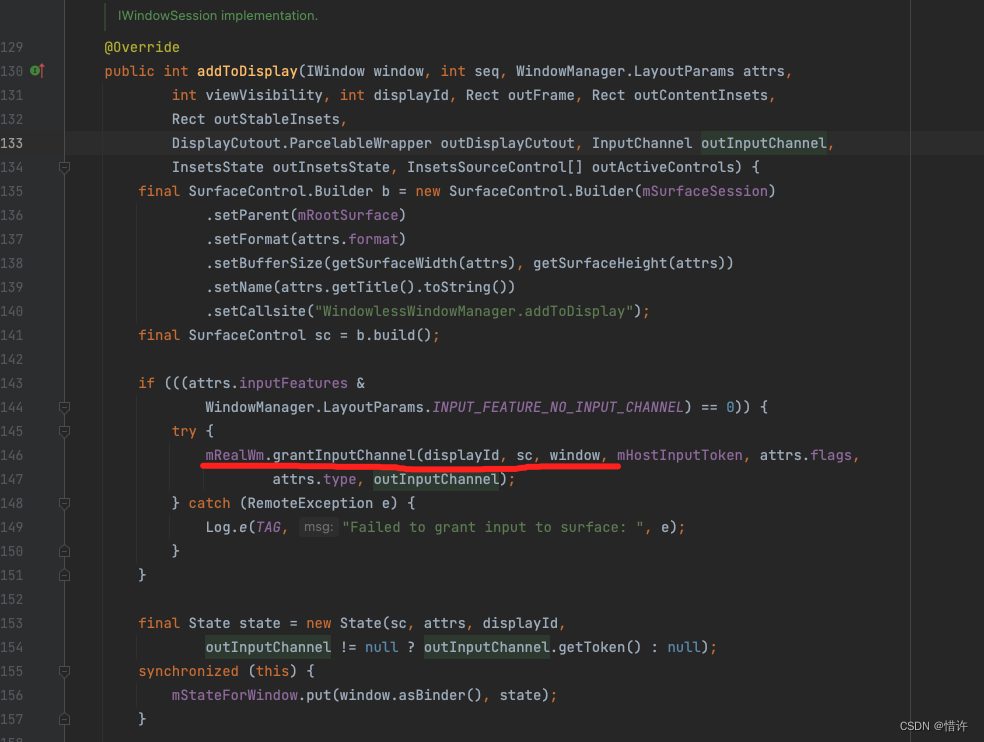
这里mRealWm是IWindowSession,我们知道它其实是WMS的代理,mRealWm.grantInputChannel()方法实际上调用的是WindowManagerService.grantInputChannel()方法;
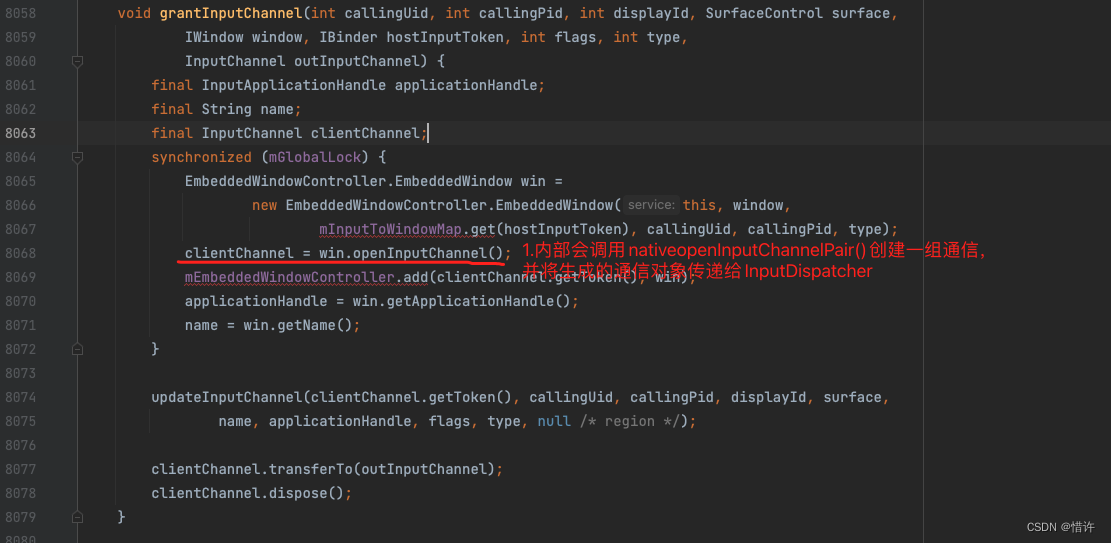
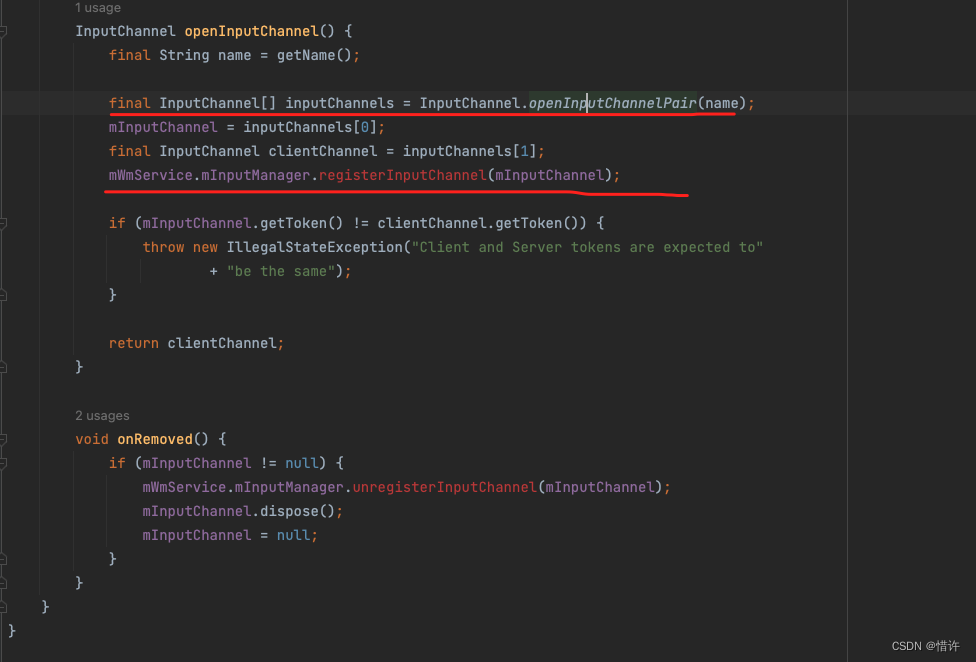
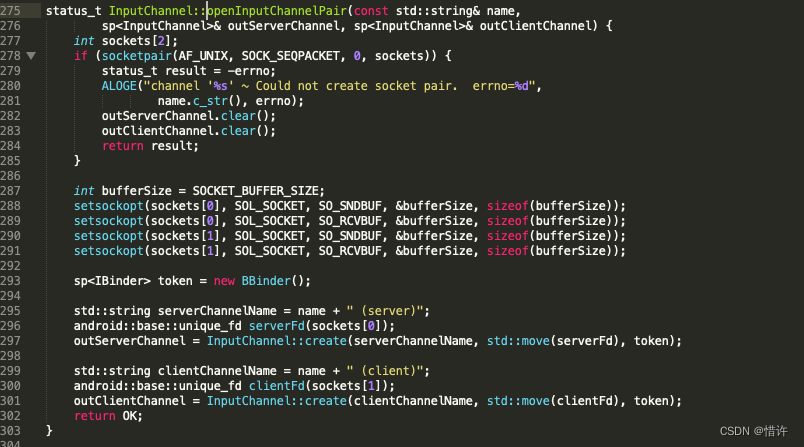
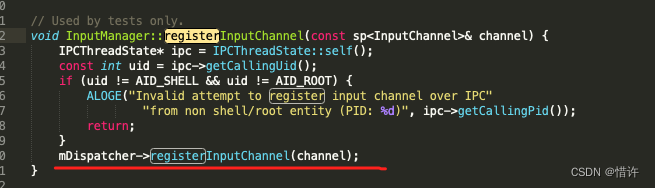
SocketPair:Linux实现了一个socketpair调用支持在同一个文件描述符中进行读写功能;
简单理解下:InputChannel内部使用Linux的socketpair实现不同进程间通信机制; -
继续回到setView中,在创建了
InputChannel之后,就开启了对InputChannel中输入事件的监听:
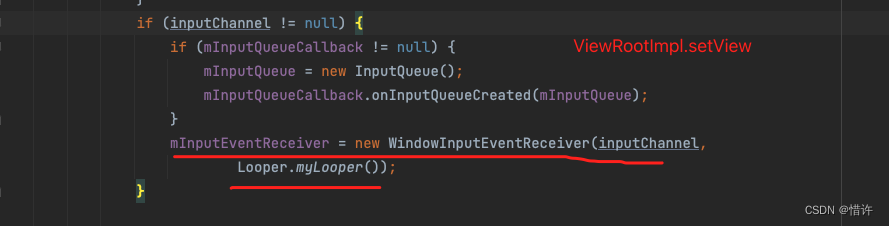
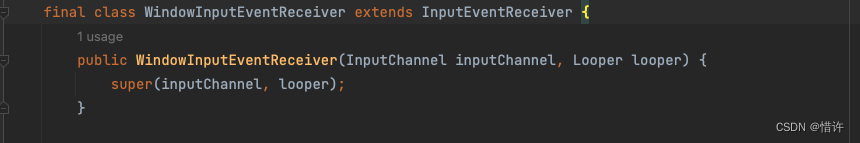
WindowInputEventReceiver继承于InputEventReceiver
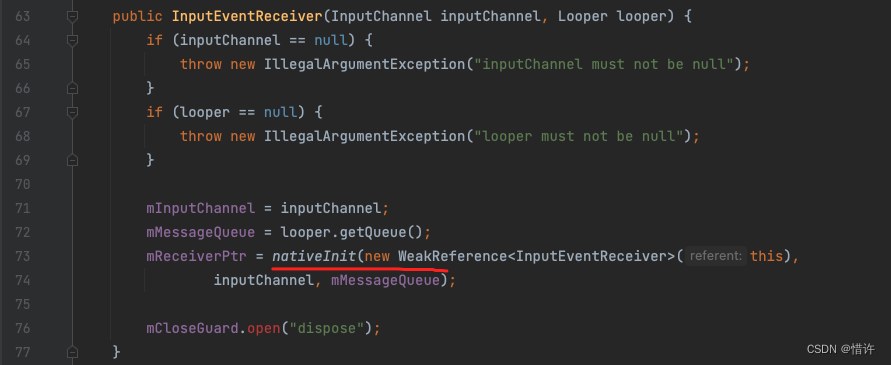
我们看下InputEventReceiver的构造方法:
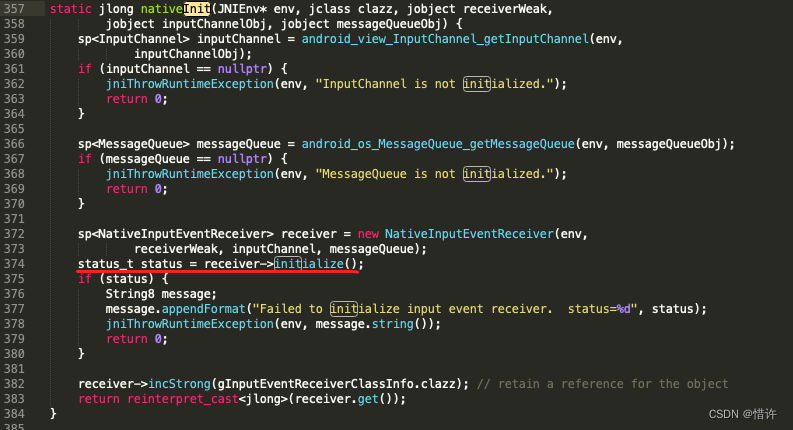
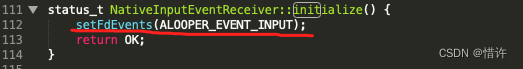

最终会调用Looper::addFd():该方法会对传递的fd添加epoll监控,Looper会循环调用pollOnce 方法,会等待消息的到来,当消息到来后,会根据消息类型一些判断处理,然后调用对应的callback函数;
这里我们当前是对开启的socket进行监听,当有数据到来时,我们会执行对应的回调,这里对于InputChannel的回调对应NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent方法:
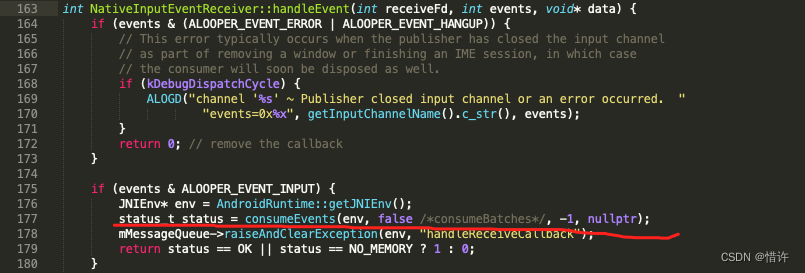
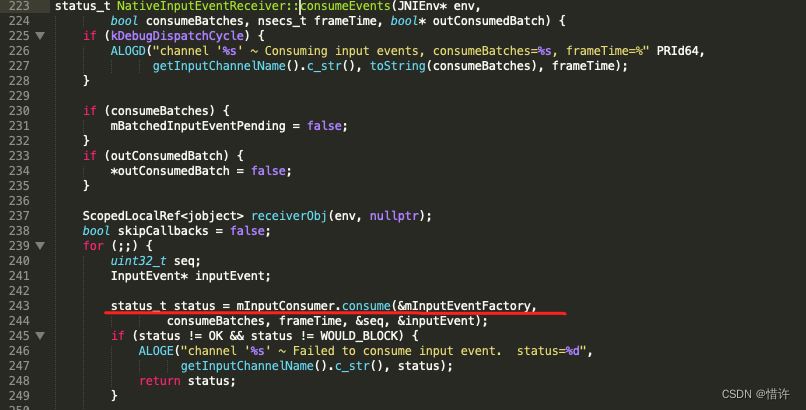
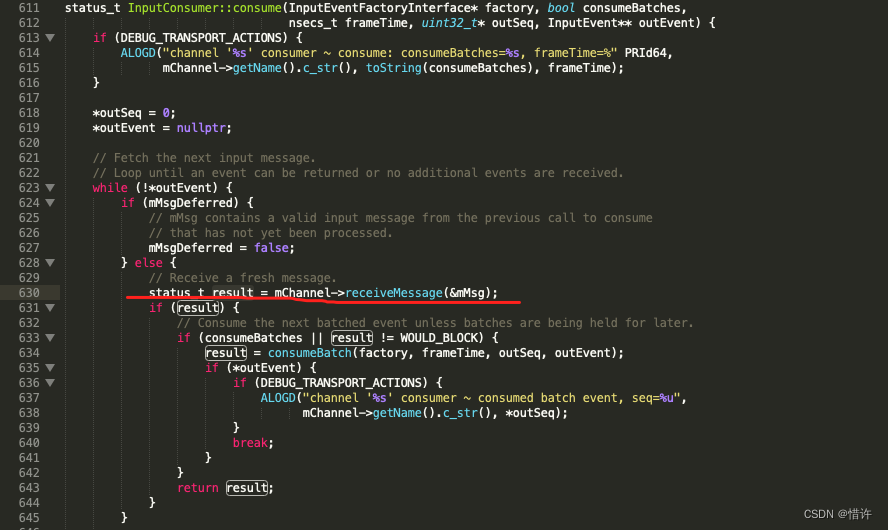
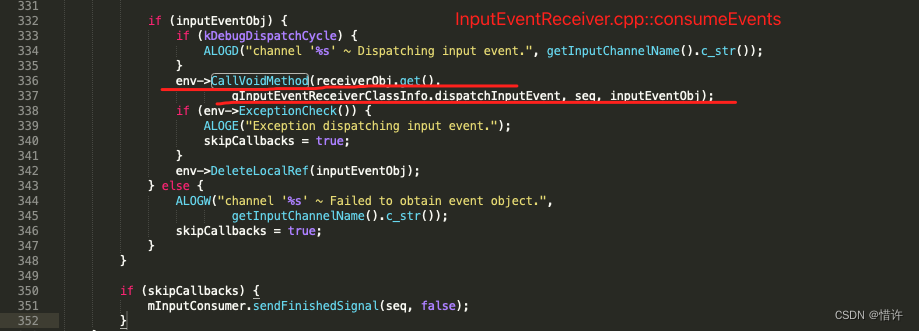
当mChannel->receiveMessage接收完毕后回到consumeEvent方法中,进行数据相关判断,最终会执行CallVoidMethod方法,回调JAVA函数:dispatchInputEvent
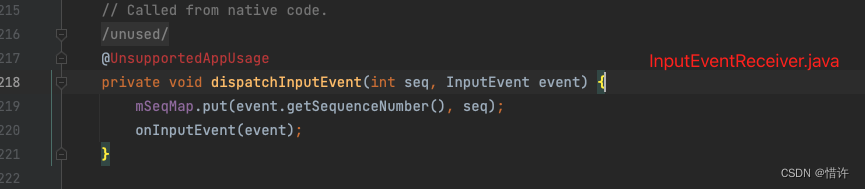
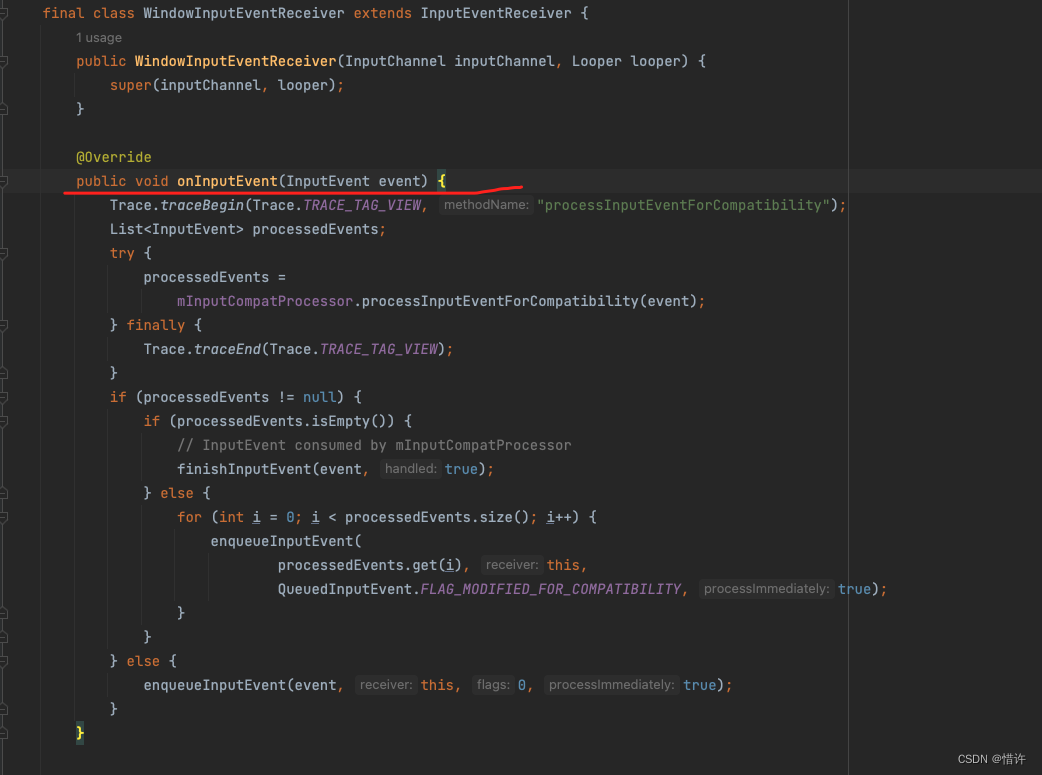
最终交给WindowInputEventReceiver.onInputEvent方法完成后续逻辑处理
IMS到WMS流程图
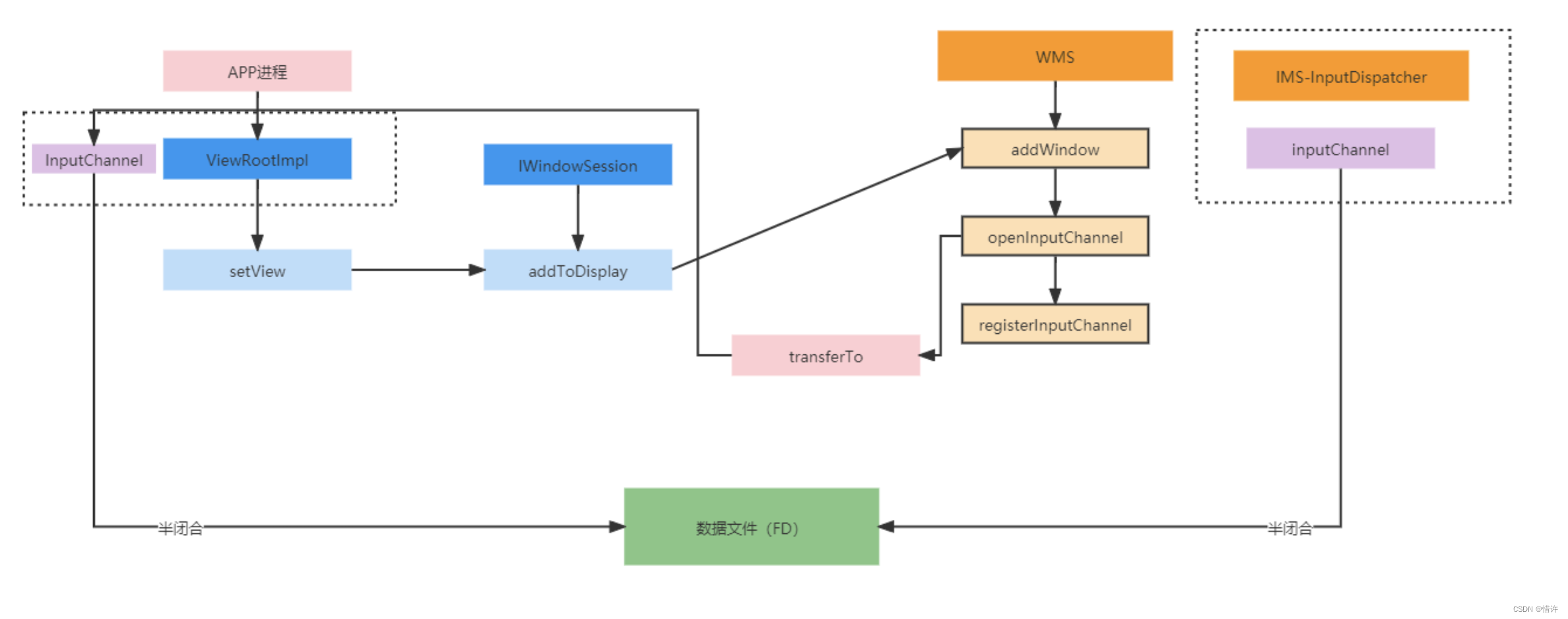
从WMS到ViewRootImpl过程
这一块相关流程之前在Android WMS工作原理浅析(二)分析过,这里不在赘述;
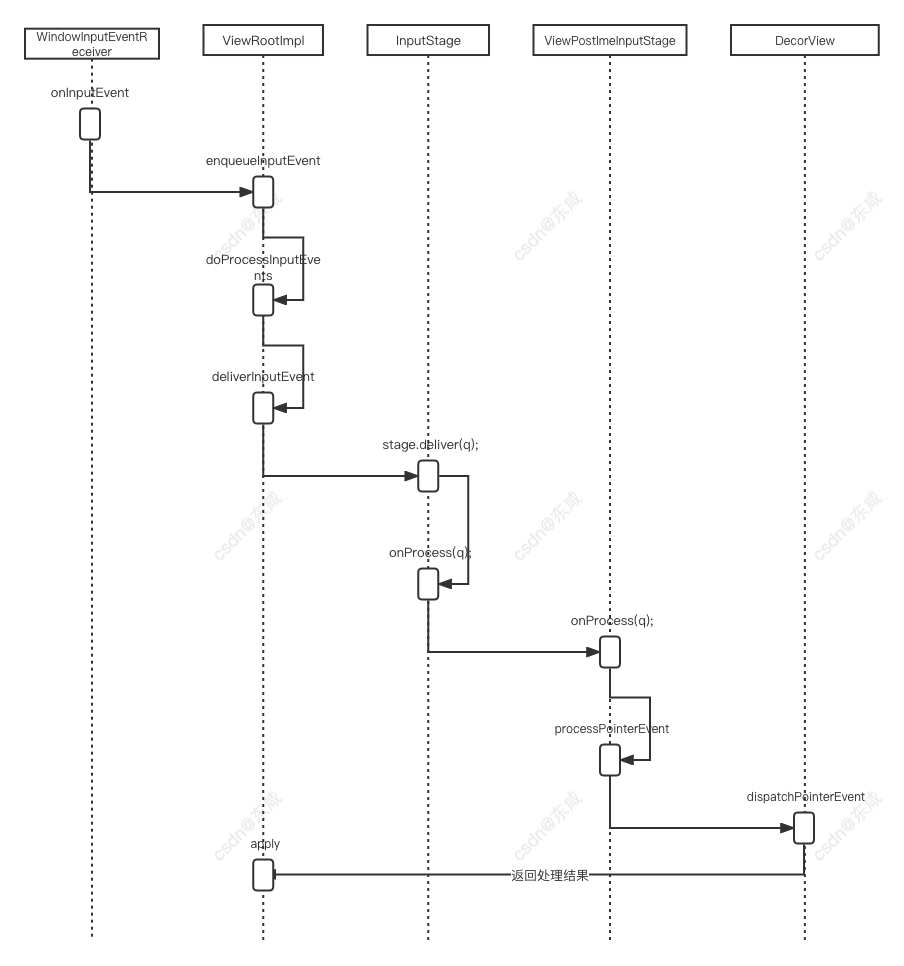
结语
如果以上文章对您有一点点帮助,希望您不要吝啬的点个赞加个关注,您每一次小小的举动都是我坚持写作的不懈动力!ღ( ´・ᴗ・` )