项目结构

技术选型
flask 做后端, 提供数据和渲染html
暂时没有提供mysql, 后续会更新操作mysql和样式美化的版本
起一个flask服务
flask是python的一个web框架, 下面演示如何提供http接口, 并返回json数据
main.py
# flask创建http接口
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify,render_template
# 支持flask跨域
from flask_cors import CORS
# 创建flask服务
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app, resources=r'/*') # 注册CORS, "/*" 允许访问域名所有api
# 首页
@app.route('/',methods=['get'])
def index():
# 自动在templates里找对应名称的文件
return jsonify({"msg":"hello"})
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 运行web服务
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=10086)此时打开终端, 运行

python main.py打开浏览器, 输入 http://localhost:10086/

渲染模板
flask可以渲染html文件(自动往项目根目录的templates里找), 并往里面填数据

main.py
# flask创建http接口
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify,render_template
# 支持flask跨域
from flask_cors import CORS
# 创建flask服务
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app, resources=r'/*') # 注册CORS, "/*" 允许访问域名所有api
# 首页
@app.route('/',methods=['get'])
def index():
# 自动在templates里找对应名称的文件
return render_template('index.html',msg="hello world")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 运行web服务
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=10086)index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
{{msg}}
</body>
</html>浏览器

用对象数组来存放图书数据
main.py
通过模板渲染传递books到html里
# flask创建http接口
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify,render_template
# 支持flask跨域
from flask_cors import CORS
# 创建flask服务
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app, resources=r'/*') # 注册CORS, "/*" 允许访问域名所有api
# 暂时代替数据库
books = [
{
"id":'1',
"name":"hello world",
"author":"迭名",
"desc": "程序员入门第一本书",
"price": 11.99
},
{
"id":'2',
"name":"0基础学it",
"author":"xx程序员",
"desc": "某培训机构精心出品教程",
"price": 99.98
},
]
# 首页
@app.route('/',methods=['get'])
def index():
# 自动在templates里找对应名称的文件
return render_template('index.html',books=books)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 运行web服务
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=10086)index.html
html接收flask后端传来的数据, 渲染到table里
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<!-- 加样式,居中 -->
<style>
* {
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
<body>
<br>
<table border="1">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>书名</th>
<th>作者</th>
<th>描述</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for book in books %} {# 遍历 books 变量 #}
<tr id={{book.id}}>
<th>{{book.name}}</th>
<th>{{book.author}}</th>
<th>{{book.desc}}</th>
<th>{{book.price}}</th>
<th>
<button id={{book.id}}>删除</button>
<a href='http://localhost:10086/uptbook?id={{book.id}}'>修改</a>
</th>
</tr>
{% endfor %} {# 使用 endfor 标签结束 for 语句 #}
</tbody>
</table>
<br>
</body>
</html>查看效果

添加图书
使用a标签请求flask后端, flask后端返回html模板, 实现跳转添加页面(add.html)
这里add.html是在book下, 这是因为如果还有别的服务(比如用户的crud), 可以通过不同文件夹区分模块

添加两个接口, 我们的id就用book对象在books数组里的下标(索引/序号), 添加就直接append添加到books数组的末尾
# 跳转添加页面
@app.route('/addbook',methods=['get'])
def addbook_html():
# 自动在templates里找对应名称的文件
return render_template('book/add.html')
# 添加
@app.route('/addbook',methods=['post'])
def addbook():
# 获取json数据
book = request.get_json()
book['id']= str(len(book)-1)
books.append(book)
return jsonify({"books":books})main.py
# flask创建http接口
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify,render_template
# 支持flask跨域
from flask_cors import CORS
# 创建flask服务
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app, resources=r'/*') # 注册CORS, "/*" 允许访问域名所有api
# 暂时代替数据库
books = [
{
"id":'1',
"name":"hello world",
"author":"迭名",
"desc": "程序员入门第一本书",
"price": 11.99
},
{
"id":'2',
"name":"0基础学it",
"author":"xx程序员",
"desc": "某培训机构精心出品教程",
"price": 99.98
},
]
# 首页
@app.route('/',methods=['get'])
def index():
# 自动在templates里找对应名称的文件
return render_template('index.html',books=books)
# 跳转添加页面
@app.route('/addbook',methods=['get'])
def addbook_html():
# 自动在templates里找对应名称的文件
return render_template('book/add.html')
# 添加
@app.route('/addbook',methods=['post'])
def addbook():
# 获取json数据
book = request.get_json()
# 用数组下标表示id
book['id']= str(len(book)-1)
# 添加到books末尾
books.append(book)
return jsonify({"books":books})
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 运行web服务
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=10086)index.html
我们使用axios(js的一个库)来发送http请求
<!-- 引入axios发送请求给后端 -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>发送请求前, 通过input框的value获取数据, 然后axios发送post请求, 并传递一个json对象给后端
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form">
<lable>书名</lable>
<input type="text" name="book-name" id="book-name">
<label>作者</label>
<input type="text" name="book-author" id="book-author">
<label>描述</label>
<input type="text" name="book-desc" id="book-desc">
<label>价格</label>
<input type="text" name="book-price" id="book-price">
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</form>
<!-- 引入axios发送请求给后端 -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
const addform = document.querySelector("#form")
const bookName = document.querySelector("#book-name")
const bookDesc = document.querySelector("#book-desc")
const bookAuthor = document.querySelector("#book-author")
const bookPrice = document.querySelector("#book-price")
addform.addEventListener("submit", function (e) {
e.preventDefault();
// console.log(bookName.value);
// 发送请求给后端
axios.post('http://localhost:10086/addbook',
// 传递json数据给后端
{
name: bookName.value,
author: bookAuthor.value,
desc: bookDesc.value,
price: bookPrice.value
})
// axios请求完成后
.then((res) => {
// 后端处理完请求,axios拿到的结果
console.log(res);
alert('添加成功')
// 跳转首页
window.location.href = 'http://localhost:10086/'
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>查看效果




删除图书
我们通过axios发送delete请求给后端, 同时传递id, 后端遍历books, 找到对应id的元素下标, 然后删除
main.py
# flask创建http接口
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify,render_template
# 支持flask跨域
from flask_cors import CORS
# 创建flask服务
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app, resources=r'/*') # 注册CORS, "/*" 允许访问域名所有api
# 暂时代替数据库
books = [
{
"id":'1',
"name":"hello world",
"author":"迭名",
"desc": "程序员入门第一本书",
"price": 11.99
},
{
"id":'2',
"name":"0基础学it",
"author":"xx程序员",
"desc": "某培训机构精心出品教程",
"price": 99.98
},
]
# 首页
@app.route('/',methods=['get'])
def index():
# 自动在templates里找对应名称的文件
return render_template('index.html',books=books)
# 跳转添加页面
@app.route('/addbook',methods=['get'])
def addbook_html():
# 自动在templates里找对应名称的文件
return render_template('book/add.html')
# 添加
@app.route('/addbook',methods=['post'])
def addbook():
# 获取json数据
book = request.get_json()
# 用数组下标表示id
book['id']= str(len(book)-1)
# 添加到books末尾
books.append(book)
return jsonify({"books":books})
# 删除
@app.route('/delete',methods=['delete'])
def delbook():
id = request.args.get('id')
# 下标
index = -1
# 遍历,找到id相同的元素
for i in range(len(books)):
if books[i]['id'] == id:
# 记录元素下标
index = i
# id不是-1表示有找到要删除的元素
if i != -1:
# 删除
books.remove(books[index])
return jsonify({'books': books})
else:
return jsonify({'books': books})
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 运行web服务
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=10086)index.html
我们在渲染table的时候, 将每行(tr标签)的id设为book的id, 删除时, 可以通过tr的id获取要删除的book的id, 实现删除特定的book
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<!-- 加样式,居中 -->
<style>
* {
margin: 0 auto;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<body>
<br>
<table border="1">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>书名</th>
<th>作者</th>
<th>描述</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for book in books %} {# 遍历 books 变量 #}
<tr id={{book.id}}>
<th>{{book.name}}</th>
<th>{{book.author}}</th>
<th>{{book.desc}}</th>
<th>{{book.price}}</th>
<th>
<button id={{book.id}}>删除</button>
<a href='http://localhost:10086/uptbook?id={{book.id}}'>修改</a>
</th>
</tr>
{% endfor %} {# 使用 endfor 标签结束 for 语句 #}
</tbody>
</table>
<br>
<a href="http://localhost:10086/addbook">添加图书</a>
<!-- axios,可以发送请求给后端 -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
// 按钮
const btns = document.querySelectorAll('th > button')
// 遍历
btns.forEach((b) => {
console.log(b.id);
// 给按钮添加click事件
b.addEventListener('click', function (e) {
// todo 弹出确认框,是否删除
// 删除
axios.delete(("http://localhost:10086/delete?id=" + b.id))
.then((res) => {
if (res.status == 200 && res.data) {
// 刷新页面
location.reload();
alert('删除成功')
} else {
alert('删除失败')
}
})
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>查看效果



修改图书信息

前端点击修改后跳转修改页面
<a href='http://localhost:10086/uptbook?id={{book.id}}'>修改</a>main.py
# flask创建http接口
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify,render_template
# 支持flask跨域
from flask_cors import CORS
# 创建flask服务
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app, resources=r'/*') # 注册CORS, "/*" 允许访问域名所有api
# 暂时代替数据库
books = [
{
"id":'1',
"name":"hello world",
"author":"迭名",
"desc": "程序员入门第一本书",
"price": 11.99
},
{
"id":'2',
"name":"0基础学it",
"author":"xx程序员",
"desc": "某培训机构精心出品教程",
"price": 99.98
},
]
# 首页
@app.route('/',methods=['get'])
def index():
# 自动在templates里找对应名称的文件
return render_template('index.html',books=books)
# 跳转添加页面
@app.route('/addbook',methods=['get'])
def addbook_html():
# 自动在templates里找对应名称的文件
return render_template('book/add.html')
# 添加
@app.route('/addbook',methods=['post'])
def addbook():
# 获取json数据
book = request.get_json()
# 用数组下标表示id
book['id']= str(len(book)-1)
# 添加到books末尾
books.append(book)
return jsonify({"books":books})
# 删除
@app.route('/delete',methods=['delete'])
def delbook():
id = request.args.get('id')
# 下标
index = -1
# 遍历,找到id相同的元素
for i in range(len(books)):
if books[i]['id'] == id:
# 记录元素下标
index = i
# id不是-1表示有找到要删除的元素
if i != -1:
# 删除
books.remove(books[index])
return jsonify({'books': books})
else:
return jsonify({'books': books})
# 跳转修改页面
@app.route('/uptbook',methods=['get'])
def uptbook_html():
id = request.args.get('id')
book = {}
for b in books:
if b['id'] == id:
book = b
return render_template('book/update.html',book=book)
# 修改
@app.route('/uptbook',methods=['patch'])
def uptbook():
id = request.args.get('id')
book = request.get_json()
index = -1
for i in range(len(books)):
if books[i]['id'] == id:
index = i
if index == -1:
return jsonify({"books":books})
else:
if(book['name']!=None):
books[index]['name'] = book['name']
if(book['author']!=None):
books[index]['author'] = book['author']
if(book['desc']!=None):
books[index]['desc'] = book['desc']
if(book['price']!=None):
books[index]['price'] = book['price']
return jsonify({"books":books})
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 运行web服务
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=10086)update.html
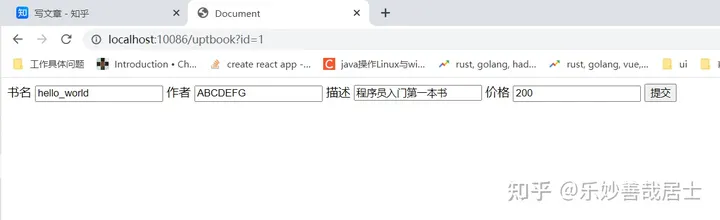
和添加图书页面基本相同
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 自定义属性,值为book.id -->
<form id="form" data-id={{book.id}}>
<lable>书名</lable>
<input type="text" name="book-name" value={{book.name}} id="book-name">
<label for="">作者</label>
<input type="text" name="book-author" value={{book.author}} id="book-author">
<label for="">描述</label>
<input type="text" name="book-desc" value={{book.desc}} id="book-desc">
<label for="">价格</label>
<input type="text" name="book-price" value={{book.price}} id="book-price">
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</form>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
const uptform = document.querySelector("#form")
const bookName = document.querySelector("#book-name")
const bookDesc = document.querySelector("#book-desc")
const bookAuthor = document.querySelector("#book-author")
const bookPrice = document.querySelector("#book-price")
// 自定义属性
const id = uptform.dataset.id
uptform.addEventListener("submit", function (e) {
e.preventDefault();
// console.log(bookName.value);
// 发送请求给后端
axios.patch(("http://localhost:10086/uptbook?id=" + id), {
name: bookName.value,
author: bookAuthor.value,
desc: bookDesc.value,
price: bookPrice.value
}).then((res) => {
console.log(res);
alert('修改成功')
// 跳转回首页
window.location.href = 'http://localhost:10086/'
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>查看效果



完结, 恭喜