一、概念
informer 是 client-go 中的核心工具包,在kubernetes中,各个组件通过HTTP协议跟 API Server 进行通信。如果各组件每次都直接和API Server 进行交互,会给API Server 和ETCD造成非常大的压力。在不依赖任何中间件的情况下,通过informer保证了消息的实时性、可靠性和顺序性。
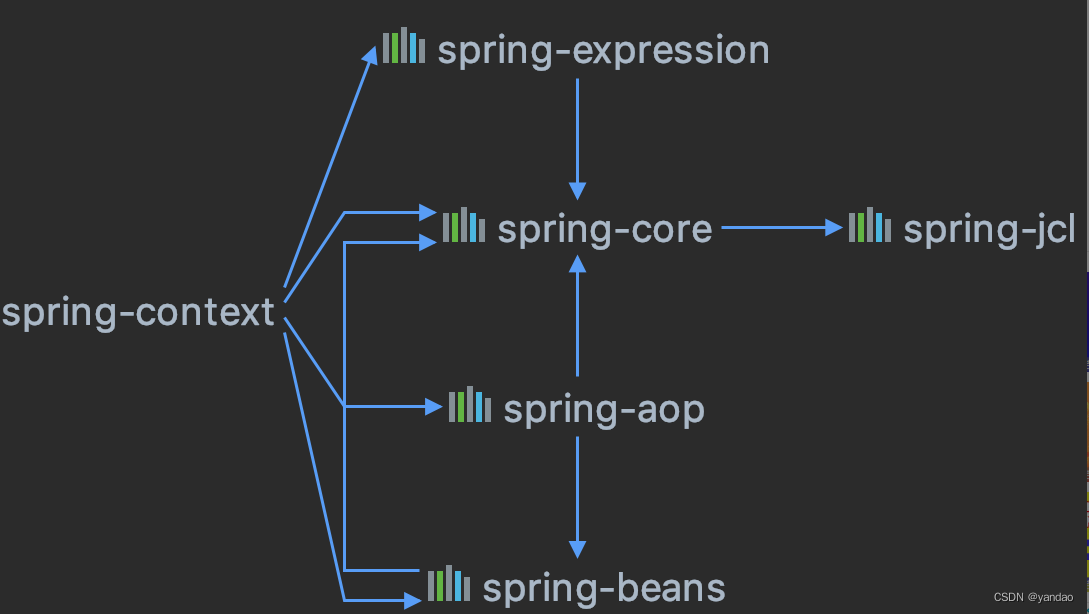
二、架构设计
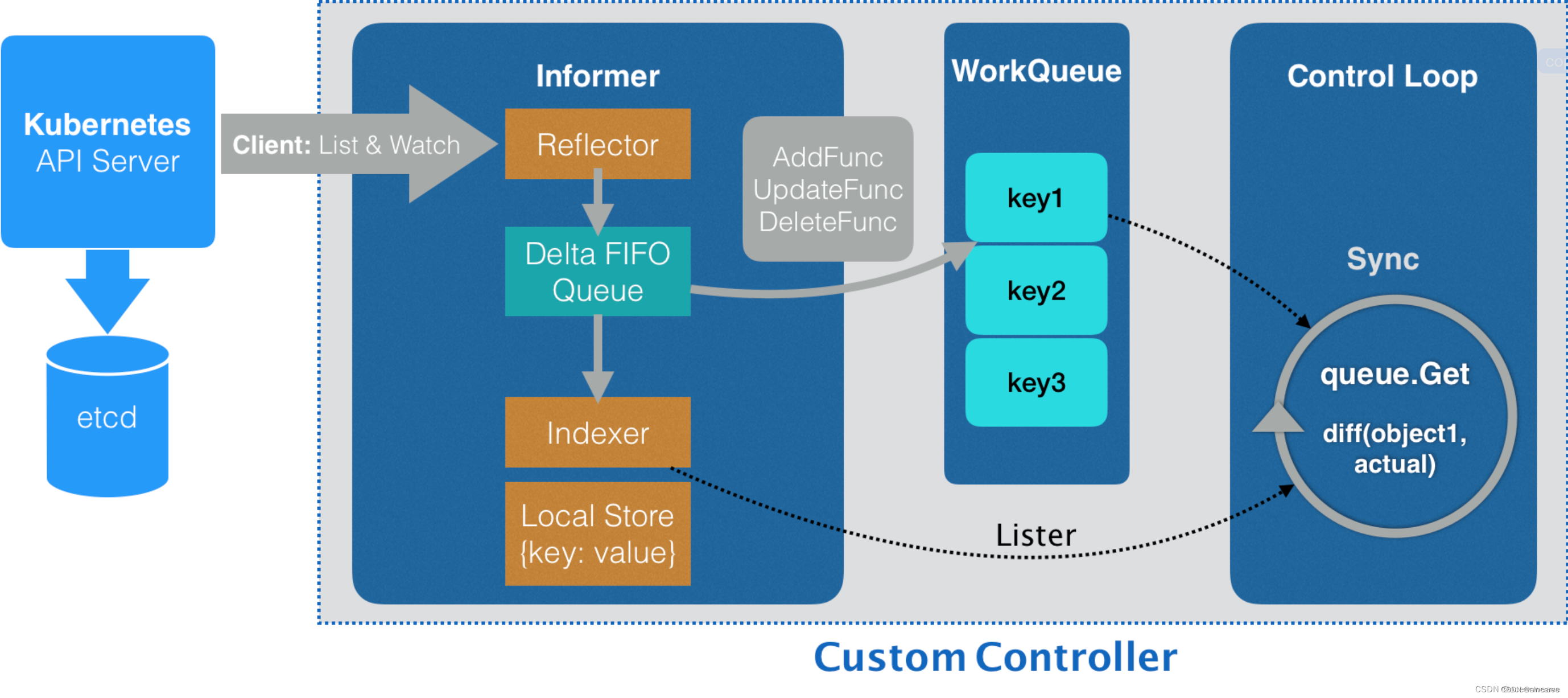
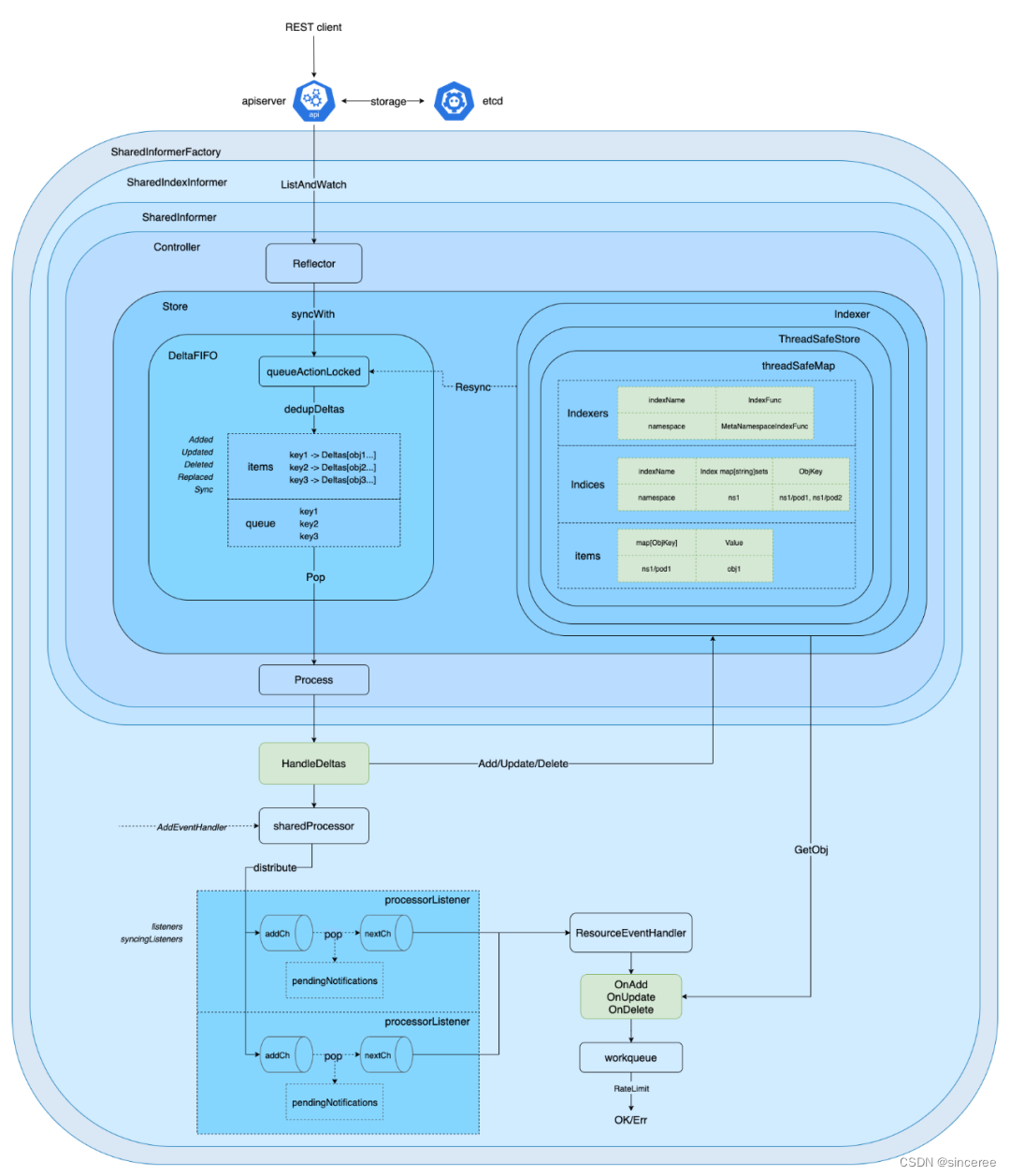
informer运行原理
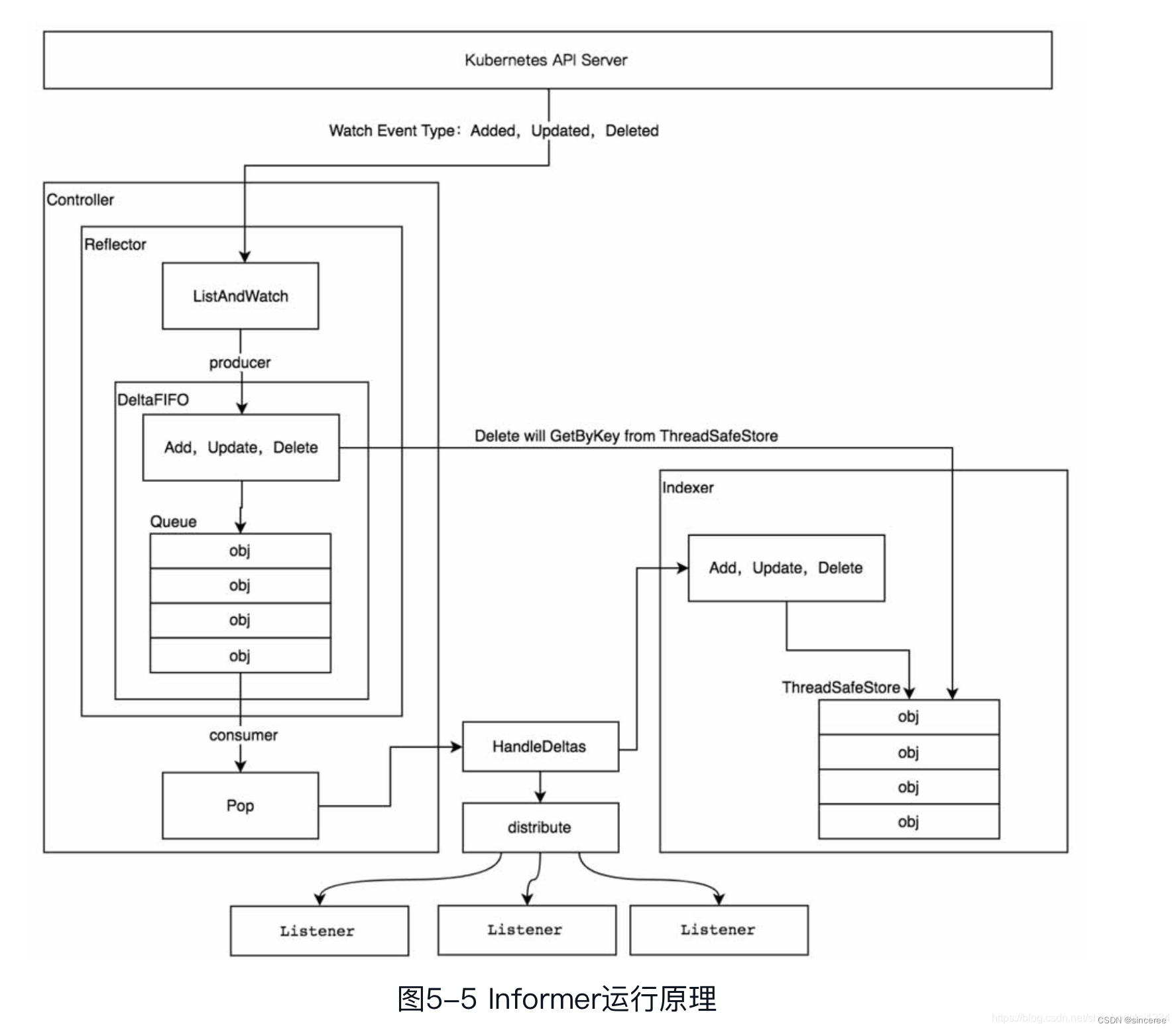
三、源码分析
3.1 informer启动
informer启动有以下步骤:
- 注册及启动processLoop和reflector
- reflector开始LIST和WATCH,watch到的数据进行对比处理,存入到queue中
- processLoop开始循环pop队列数据
factory := informers.NewSharedInformerFactory(clientset, 0)
podInformer := factory.Core().V1().Pods().Informer()
podInformer.AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
mObj := obj.(v1.Object)
log.Printf("New pod added: %s", mObj.GetName())
},
UpdateFunc: func(oldObj, newObj interface{}) {
oObj := oldObj.(v1.Object)
nObj := newObj.(v1.Object)
log.Printf("%s pod updated to %s", oObj.GetName(), nObj.GetName())
},
DeleteFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
mObj := obj.(v1.Object)
log.Printf("pod deleted from store: %s", mObj.GetName())
},
})
//启动informer
podInformer.Run(stopCh)
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
......
fifo := NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(DeltaFIFOOptions{
KnownObjects: s.indexer,
EmitDeltaTypeReplaced: true,
})
cfg := &Config{
Queue: fifo,
ListerWatcher: s.listerWatcher,
ObjectType: s.objectType,
FullResyncPeriod: s.resyncCheckPeriod,
RetryOnError: false,
ShouldResync: s.processor.shouldResync,
//注册回调函数HandleDeltas,后面从queue弹出数据的时候要用到
Process: s.HandleDeltas,
WatchErrorHandler: s.watchErrorHandler,
}
......
s.controller.Run(stopCh)
}
代码位置:client-go/tools/cache/controller.go
func (c *controller) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
go func() {
<-stopCh
c.config.Queue.Close()
}()
r := NewReflector(
c.config.ListerWatcher,
c.config.ObjectType,
c.config.Queue,
c.config.FullResyncPeriod,
)
// 省略代码
......
var wg wait.Group
//启动reflector
wg.StartWithChannel(stopCh, r.Run)
//启动processLoop
wait.Until(c.processLoop, time.Second, stopCh)
wg.Wait()
}
reflector开始list and watch,代码位置:client-go/tools/cache/reflector.go
func (r *Reflector) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
klog.V(3).Infof("Starting reflector %s (%s) from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.resyncPeriod, r.name)
wait.BackoffUntil(func() {
if err := r.ListAndWatch(stopCh); err != nil {
r.watchErrorHandler(r, err)
}
}, r.backoffManager, true, stopCh)
klog.V(3).Infof("Stopping reflector %s (%s) from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.resyncPeriod, r.name)
}
switch event.Type {
//watch到add事件
case watch.Added:
err := r.store.Add(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to add watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
//watch到modified事件
case watch.Modified:
err := r.store.Update(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to update watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
//watch到delete事件
case watch.Deleted:
// TODO: Will any consumers need access to the "last known
// state", which is passed in event.Object? If so, may need
// to change this.
err := r.store.Delete(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to delete watch event object (%#v) from store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Bookmark:
// A `Bookmark` means watch has synced here, just update the resourceVersion
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
}
以update为例
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Update(obj interface{}) error {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
f.populated = true
return f.queueActionLocked(Updated, obj)
}
func (f *DeltaFIFO) queueActionLocked(actionType DeltaType, obj interface{}) error {
id, err := f.KeyOf(obj)
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
oldDeltas := f.items[id]
newDeltas := append(oldDeltas, Delta{actionType, obj})
newDeltas = dedupDeltas(newDeltas)
if len(newDeltas) > 0 {
if _, exists := f.items[id]; !exists {
//将key放入到queue
f.queue = append(f.queue, id)
}
//将newDeltas放入到items中
f.items[id] = newDeltas
//事件到达广播
f.cond.Broadcast()
} else {
// This never happens, because dedupDeltas never returns an empty list
// when given a non-empty list (as it is here).
// If somehow it happens anyway, deal with it but complain.
if oldDeltas == nil {
klog.Errorf("Impossible dedupDeltas for id=%q: oldDeltas=%#+v, obj=%#+v; ignoring", id, oldDeltas, obj)
return nil
}
klog.Errorf("Impossible dedupDeltas for id=%q: oldDeltas=%#+v, obj=%#+v; breaking invariant by storing empty Deltas", id, oldDeltas, obj)
f.items[id] = newDeltas
return fmt.Errorf("Impossible dedupDeltas for id=%q: oldDeltas=%#+v, obj=%#+v; broke DeltaFIFO invariant by storing empty Deltas", id, oldDeltas, obj)
}
return nil
}
DeltaFIFO的数据结构如下:
type DeltaFIFO struct {
// lock/cond protects access to 'items' and 'queue'.
lock sync.RWMutex
cond sync.Cond
// `items` maps a key to a Deltas.
// Each such Deltas has at least one Delta.
items map[string]Deltas
// `queue` maintains FIFO order of keys for consumption in Pop().
// There are no duplicates in `queue`.
// A key is in `queue` if and only if it is in `items`.
queue []string
// populated is true if the first batch of items inserted by Replace() has been populated
// or Delete/Add/Update/AddIfNotPresent was called first.
populated bool
// initialPopulationCount is the number of items inserted by the first call of Replace()
initialPopulationCount int
// keyFunc is used to make the key used for queued item
// insertion and retrieval, and should be deterministic.
keyFunc KeyFunc
// knownObjects list keys that are "known" --- affecting Delete(),
// Replace(), and Resync()
knownObjects KeyListerGetter
// Used to indicate a queue is closed so a control loop can exit when a queue is empty.
// Currently, not used to gate any of CRUD operations.
closed bool
// emitDeltaTypeReplaced is whether to emit the Replaced or Sync
// DeltaType when Replace() is called (to preserve backwards compat).
emitDeltaTypeReplaced bool
}
到这里,已经将最新的数据推送到了DeltaFIFO的queue中,接下来看下怎么处理queue中的数据。
queue出队:
回到之前注册的processLoop
func (c *controller) processLoop() {
for {
//从queue弹出数据,交由process处理,也就是之前注册的handleDeltas
obj, err := c.config.Queue.Pop(PopProcessFunc(c.config.Process))
if err != nil {
if err == ErrFIFOClosed {
return
}
if c.config.RetryOnError {
// This is the safe way to re-enqueue.
// 重新入队queue
c.config.Queue.AddIfNotPresent(obj)
}
}
}
}
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Pop(process PopProcessFunc) (interface{}, error) {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
for {
for len(f.queue) == 0 {
// When the queue is empty, invocation of Pop() is blocked until new item is enqueued.
// When Close() is called, the f.closed is set and the condition is broadcasted.
// Which causes this loop to continue and return from the Pop().
if f.closed {
return nil, ErrFIFOClosed
}
//如果queue中没有数据,阻塞等待
f.cond.Wait()
}
id := f.queue[0]
f.queue = f.queue[1:]
depth := len(f.queue)
if f.initialPopulationCount > 0 {
f.initialPopulationCount--
}
item, ok := f.items[id]
if !ok {
// This should never happen
klog.Errorf("Inconceivable! %q was in f.queue but not f.items; ignoring.", id)
continue
}
delete(f.items, id)
// Only log traces if the queue depth is greater than 10 and it takes more than
// 100 milliseconds to process one item from the queue.
// Queue depth never goes high because processing an item is locking the queue,
// and new items can't be added until processing finish.
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/103789
if depth > 10 {
trace := utiltrace.New("DeltaFIFO Pop Process",
utiltrace.Field{Key: "ID", Value: id},
utiltrace.Field{Key: "Depth", Value: depth},
utiltrace.Field{Key: "Reason", Value: "slow event handlers blocking the queue"})
defer trace.LogIfLong(100 * time.Millisecond)
}
//处理数据,重点看下这个方法,进入HandleDeltas
err := process(item)
if e, ok := err.(ErrRequeue); ok {
f.addIfNotPresent(id, item)
err = e.Err
}
// Don't need to copyDeltas here, because we're transferring
// ownership to the caller.
return item, err
}
}
代码位置 client-go/tools/cache/shared_informer.go
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) HandleDeltas(obj interface{}) error {
s.blockDeltas.Lock()
defer s.blockDeltas.Unlock()
// from oldest to newest
for _, d := range obj.(Deltas) {
switch d.Type {
case Sync, Replaced, Added, Updated:
s.cacheMutationDetector.AddObject(d.Object)
//从本地缓存indexer中查询数据是否存在
if old, exists, err := s.indexer.Get(d.Object); err == nil && exists {
//如果存在,则更新indexer中该数据
if err := s.indexer.Update(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
isSync := false
switch {
case d.Type == Sync:
// Sync events are only propagated to listeners that requested resync
isSync = true
case d.Type == Replaced:
if accessor, err := meta.Accessor(d.Object); err == nil {
if oldAccessor, err := meta.Accessor(old); err == nil {
// Replaced events that didn't change resourceVersion are treated as resync events
// and only propagated to listeners that requested resync
isSync = accessor.GetResourceVersion() == oldAccessor.GetResourceVersion()
}
}
}
//分发监听者,通知监听update
s.processor.distribute(updateNotification{oldObj: old, newObj: d.Object}, isSync)
} else {
//如果不存在,则在indexer中添加该数据
if err := s.indexer.Add(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
//分发监听者,通知监听add
s.processor.distribute(addNotification{newObj: d.Object}, false)
}
case Deleted:
if err := s.indexer.Delete(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
//分发监听者,通知监听delete
s.processor.distribute(deleteNotification{oldObj: d.Object}, false)
}
}
return nil
}
func (p *sharedProcessor) distribute(obj interface{}, sync bool) {
p.listenersLock.RLock()
defer p.listenersLock.RUnlock()
if sync {
for _, listener := range p.syncingListeners {
//往监听者加入数据
listener.add(obj)
}
} else {
for _, listener := range p.listeners {
//往监听者加入数据
listener.add(obj)
}
}
}
func (p *processorListener) add(notification interface{}) {
p.addCh <- notification
}
数据分发到了监听者,那么监听者是什么时候注册的,又是怎么工作的呢?
联系到前面informer注册的eventHandler
podInformer.AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
mObj := obj.(v1.Object)
log.Printf("New pod added: %s", mObj.GetName())
},
UpdateFunc: func(oldObj, newObj interface{}) {
oObj := oldObj.(v1.Object)
nObj := newObj.(v1.Object)
log.Printf("%s pod updated to %s", oObj.GetName(), nObj.GetName())
},
DeleteFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
mObj := obj.(v1.Object)
log.Printf("pod deleted from store: %s", mObj.GetName())
},
})
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) AddEventHandler(handler ResourceEventHandler) {
s.AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod(handler, s.defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod)
}
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod(handler ResourceEventHandler, resyncPeriod time.Duration) {
//省略代码
//......
//创建监听者
listener := newProcessListener(handler, resyncPeriod, determineResyncPeriod(resyncPeriod, s.resyncCheckPeriod), s.clock.Now(), initialBufferSize)
if !s.started {
s.processor.addListener(listener)
return
}
// in order to safely join, we have to
// 1. stop sending add/update/delete notifications
// 2. do a list against the store
// 3. send synthetic "Add" events to the new handler
// 4. unblock
s.blockDeltas.Lock()
defer s.blockDeltas.Unlock()
//添加监听者
s.processor.addListener(listener)
for _, item := range s.indexer.List() {
listener.add(addNotification{newObj: item})
}
}
func (p *sharedProcessor) addListener(listener *processorListener) {
p.listenersLock.Lock()
defer p.listenersLock.Unlock()
p.addListenerLocked(listener)
if p.listenersStarted {
//在不同的协程使监听者运行起来
p.wg.Start(listener.run)
p.wg.Start(listener.pop)
}
}
func (p *sharedProcessor) addListenerLocked(listener *processorListener) {
p.listeners = append(p.listeners, listener)
p.syncingListeners = append(p.syncingListeners, listener)
}
func (p *processorListener) pop() {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
defer close(p.nextCh) // Tell .run() to stop
var nextCh chan<- interface{}
var notification interface{}
for {
select {
case nextCh <- notification:
// Notification dispatched
var ok bool
notification, ok = p.pendingNotifications.ReadOne()
if !ok { // Nothing to pop
nextCh = nil // Disable this select case
}
//联系前面distribute分发监听者的时候将notification发送到addCh
case notificationToAdd, ok := <-p.addCh:
if !ok {
return
}
if notification == nil { // No notification to pop (and pendingNotifications is empty)
// Optimize the case - skip adding to pendingNotifications
notification = notificationToAdd
nextCh = p.nextCh
} else { // There is already a notification waiting to be dispatched
p.pendingNotifications.WriteOne(notificationToAdd)
}
}
}
}
func (p *processorListener) run() {
// this call blocks until the channel is closed. When a panic happens during the notification
// we will catch it, **the offending item will be skipped!**, and after a short delay (one second)
// the next notification will be attempted. This is usually better than the alternative of never
// delivering again.
stopCh := make(chan struct{})
wait.Until(func() {
for next := range p.nextCh {
//这里调用到用户定义的handler方法
switch notification := next.(type) {
case updateNotification:
p.handler.OnUpdate(notification.oldObj, notification.newObj)
case addNotification:
p.handler.OnAdd(notification.newObj)
case deleteNotification:
p.handler.OnDelete(notification.oldObj)
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unrecognized notification: %T", next))
}
}
// the only way to get here is if the p.nextCh is empty and closed
close(stopCh)
}, 1*time.Second, stopCh)
}
最后看一下informer的详细全局设计