文章目录
- 前言
- 🌟一、建堆的两种方式:
- 🌏1.1 向上调整建堆(堆排序):
- 💫1.1.1 完整代码:
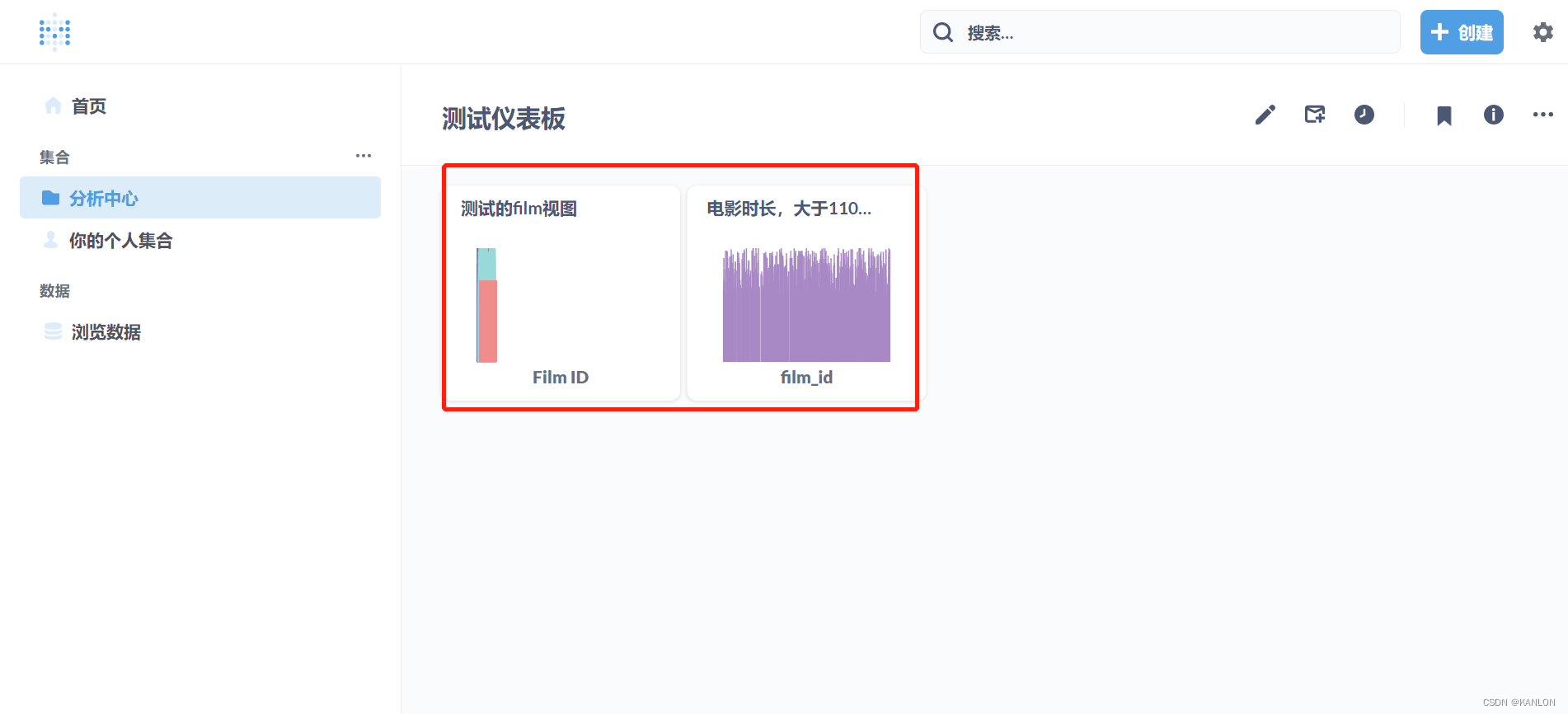
- 💫1.1.2 流程图(以小堆为例):升序:建大堆
- 💫1.1.3 流程图(以小堆为例):降序:建小堆
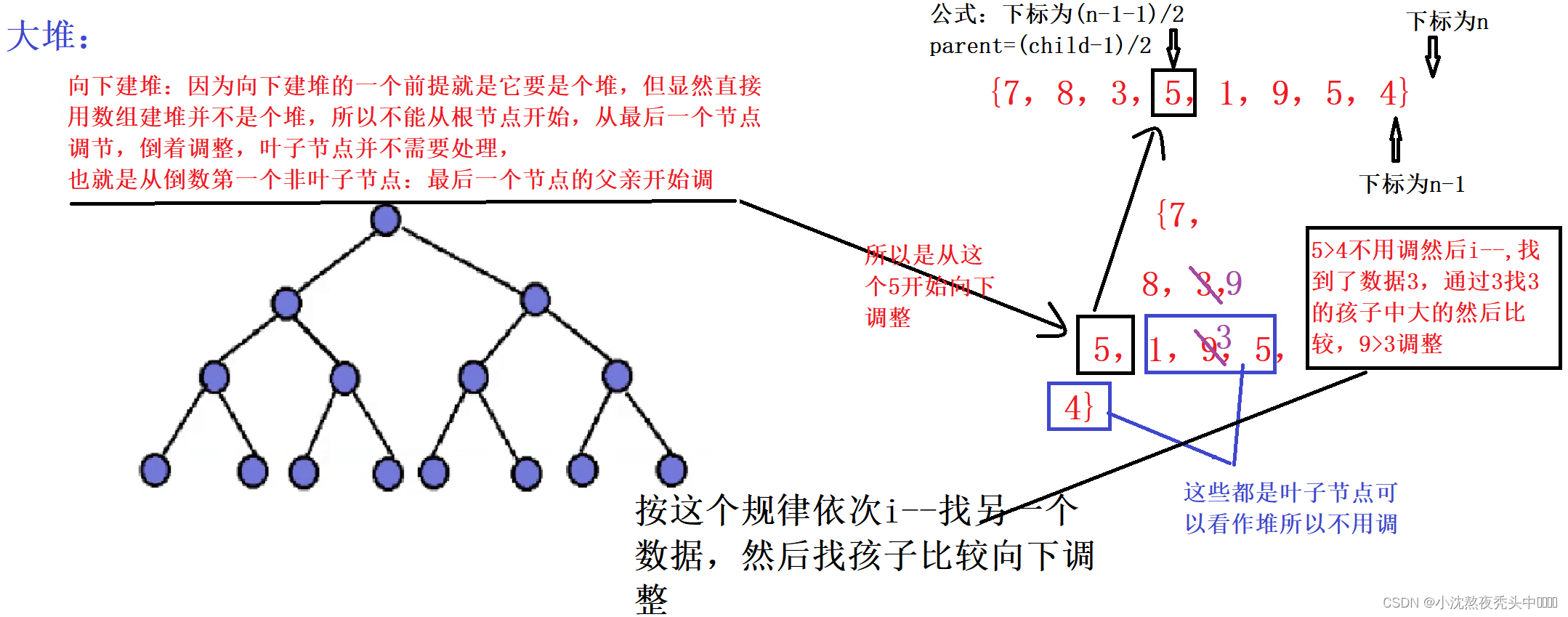
- 🌏1.2 向下调整建堆(堆排序):
- 💫1.2.1 完整代码:
- 💫1.2.2 流程图:
- 🌟二、两种建堆方式时间复杂度比较:
- 🌏2.1 向上调整建堆:
- 🌏2.2 向下调整建堆:
- 🌟三、堆排序的时间复杂度:O(N*logN)
- 🌟四、呼应一下上章节的部分:利用堆使数据有序(不建议)
- 🌟五、TOP-K问题:
- 🌏5.1 TOP-K问题思路:
- 🌏5.2 TOP-K问题代码:
- 🌟六、文件操作:
- 😽总结
前言
👧个人主页:@小沈熬夜秃头中୧⍤⃝❅
😚小编介绍:欢迎来到我的乱七八糟小星球🌝
📋专栏:数据结构
🔑本章内容:堆排序+TOP-K问题
送给各位💌:日落跌入昭昭星野 人间忽晚 山河以秋
记得 评论📝 +点赞👍 +收藏😽 +关注💞哦~
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
🌟一、建堆的两种方式:
🌏1.1 向上调整建堆(堆排序):
💫1.1.1 完整代码:
//Heap.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct Heap
{
HPDataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}HP;
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent);
//因为要在Test.c中调用这个函数而Test.c中包含#include"Heap.h"所以要在这里包含一下
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child);
void HeapInit(HP* php);
void HeapDestroy(HP* php);
void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x);
void HeapPop(HP* php);
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* php);
bool HeapEmpty(HP* php);
int HeapSize(HP* php);
//Heap.c
void HeapInit(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
php->a = NULL;
php->size = 0;
php->capacity = 0;
}
void Swap(HPDataType* p1, HPDataType* p2)
{
HPDataType tmp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = tmp;
}
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < n)
{
if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] < a[child])
{
child++;
}
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
//Test.c
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
{
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
for (int i = 1;i<n; i++)
{
//堆向上调整算法
AdjustUp(a, i);//当i=0时,也就是孩子下标是0此时一个数据可以看作一个堆所以从1开始向上调整
}
int end = n - 1;
while (end > 0)
{
//小堆为例通过建堆第一个肯定是最小数
Swap(&a[0], &a[end]);
//调整选出次小数
AdjustDown(a, end, 0);//这里的end是n-1是最后一个数据的下标也是除了最后一个数据外前面数据的个数,所以可以传end过去
end--;
}
}
int main()
{
//HPTest();
int a[] = { 7,8,3,5,1,9,5,4 };
HeapSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
return 0;
}
💫1.1.2 流程图(以小堆为例):升序:建大堆
最后得到的就是一个升序
💫1.1.3 流程图(以小堆为例):降序:建小堆
最后得到的就是一个降序
🌏1.2 向下调整建堆(堆排序):
💫1.2.1 完整代码:
//Heap.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct Heap
{
HPDataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}HP;
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent);
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child);
void HeapInit(HP* php);
void HeapDestroy(HP* php);
void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x);
void HeapPop(HP* php);
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* php);
bool HeapEmpty(HP* php);
int HeapSize(HP* php);
//Heap.c
void HeapInit(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
php->a = NULL;
php->size = 0;
php->capacity = 0;
}
void Swap(HPDataType* p1, HPDataType* p2)
{
HPDataType tmp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = tmp;
}
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < n)
{
if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] < a[child])
{
child++;
}
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
//Test.c
#include"Heap.h"
//直接建堆来调整---向下调整建堆
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
{
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
for (int i = (n-1-1)/2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(a, n, i);
}
int end = n - 1;
while (end > 0)
{
Swap(&a[0], &a[end]);
AdjustDown(a, end, 0);
end--;
}
}
int main()
{
//HPTest();
int a[] = { 7,8,3,5,1,9,5,4 };
HeapSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
return 0;
}
💫1.2.2 流程图:
🌟二、两种建堆方式时间复杂度比较:
通过对两种建堆方式的比较更建议使用向下调整建堆但是向上调整建堆更容易理解看个人情况
🌏2.1 向上调整建堆:
🌏2.2 向下调整建堆:
🌟三、堆排序的时间复杂度:O(N*logN)
🌟四、呼应一下上章节的部分:利用堆使数据有序(不建议)
利用创建的堆数组排序:我们可以采用下面这种方法 — 先建堆(NlogN)太麻烦,然后来回拷贝数据(空间复杂度高)—具体代码可以看【数据结构】— 博主拍了拍你并向你扔了一“堆”二叉树(堆的概念+结构+代码实现)其中只有Test.c文件中做了以下修改其余没变
void HeapSort(int* a,int n)
{
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
//建堆N*logN
for (int i = 0;i<n; i++)
{
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
}
//N*logN
int i = 0;
while (!HeapEmpty(&hp))
{
int top = HeapTop(&hp);
a[i++] = top;
HeapPop(&hp);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
HeapDestroy(&hp);
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 7,8,3,5,1,9,5,4 };
HeapSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
return 0;
}
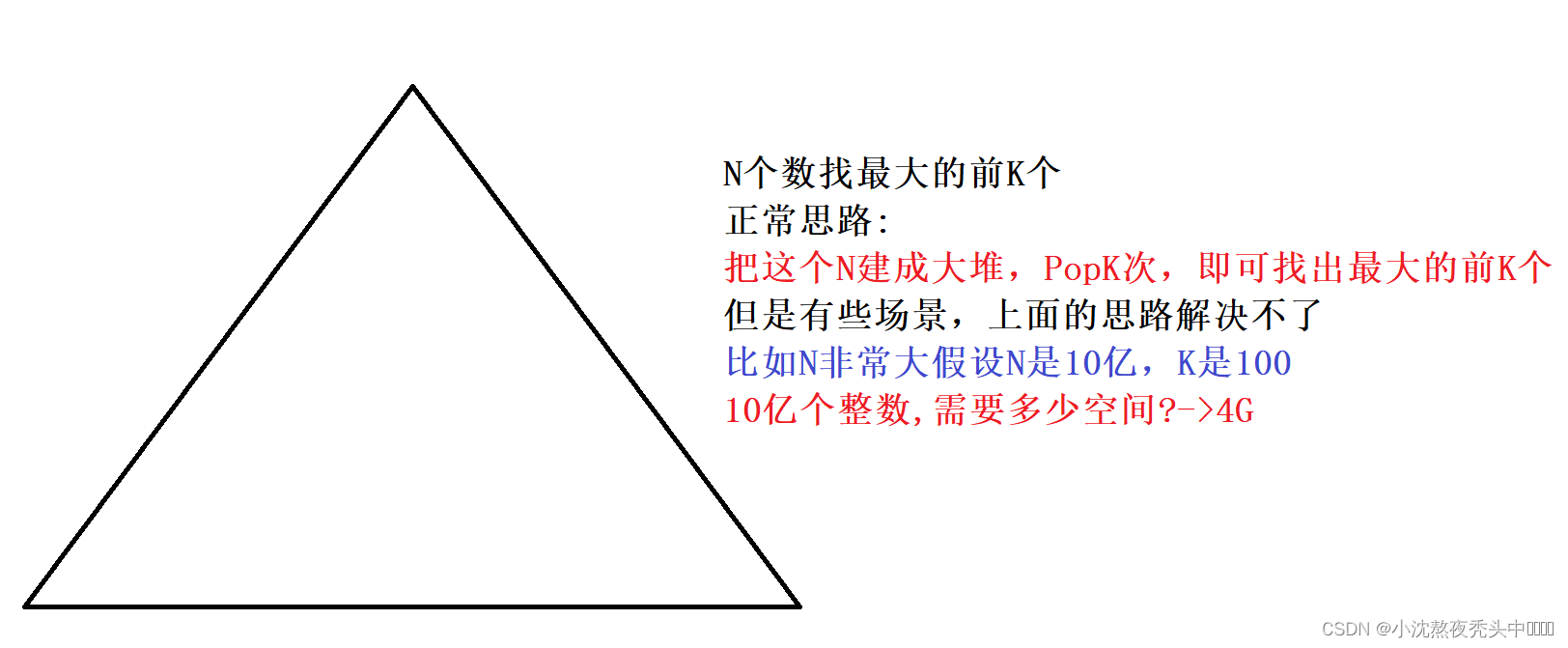
🌟五、TOP-K问题:
🌏5.1 TOP-K问题思路:
TOP-K问题:即求数据结合中前K个最大的元素或者最小的元素,一般情况下数据量都比较大。比如:专业前10名、世界500强、富豪榜、游戏中前100的活跃玩家等。
对于Top-K问题,能想到的最简单直接的方式就是排序
但是:如果数据量非常大,排序就不太可取了(可能数据都不能一下子全部加载到内存中)。
最佳的方式就是用堆来解决,基本思路如下:
🌏5.2 TOP-K问题代码:
在1000个数中找到前5个最大的数
除了Test.c作了以下改变Heap.h和Heap.c依据上面
//Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Heap.h"
#include<time.h>
void CreateNDate()
{
// 造数据
int n = 1000;
srand(time(0));//产生随机数
const char* file = "data.txt";
FILE* fin = fopen(file, "w");//以写的形式打开文件
if (fin == NULL)
{
perror("fopen error");
return;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
int x = rand() % 1000000;
fprintf(fin, "%d\n", x);//写
}
fclose(fin);
}
void PrintTopK(int k)
{
const char* file = "data.txt";
FILE* fout = fopen(file, "r");//以读的方式
if (fout == NULL)
{
perror("fopen error");
return;
}
//malloc空间
int* kminheap = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k);
if (kminheap == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
//读取前K个数据
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
fscanf(fout, "%d", &kminheap[i]);
}
//建堆(建小堆)
for (int i = (k - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(kminheap, k,i );
}
//比较覆盖
int val = 0;
while (!feof(fout))//文件读取结束就跳出循环
{
fscanf(fout, "%d", &val);//从k+1数据开始读取和堆顶数据比较
if (val > kminheap[0])
{
kminheap[0] = val;//覆盖
AdjustDown(kminheap, k, 0);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
printf("%d ",kminheap[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
CreateNDate();
PrintTopK(5);
return 0;
}
🌟六、文件操作:
可以看 C语言 — 文件操作(万字详解)
😽总结
😽Ending,今天的 堆排序+TOP-K问题 的内容就到此结束啦~,如果后续想了解更多,就请关注我吧,一键三连哦 ~