文章目录
- 先决条件
- 硬件
- 软件
- 网络端口
- 安装docker
- 签发证书
- 生成证书颁发机构证书
- 生成服务器证书
- 向 Harbor 和 Docker 提供证书
- 下载harbor安装包
- containerd 配置私有仓库(二选一)
- 分发证书(如上文只是路径变了)
- 配置
- 登录
- 加密登录
- 打标签并推送与拉取
- docker 配置私有仓库
- 创建或编辑Docker配置文件
- 分发证书(如上文)
- 登录
- 加密登录(同上文)
- 打标签并推送与拉取
- 总结
先决条件
Harbor 被部署为多个 Docker 容器。因此,您可以将其部署在任何支持 Docker 的 Linux 发行版上。目标主机需要安装 Docker 和 Docker Compose。
硬件
下表列出了部署 Harbor 的最低和推荐硬件配置。
| 资源 | 最低限度 | 受到推崇的 |
|---|---|---|
| 中央处理器 | 2个中央处理器 | 4个中央处理器 |
| 内存 | 4GB | 8GB |
| 磁盘 | 40GB | 160GB |
软件
下表列出了目标主机上必须安装的软件版本。
| 软件 | 版本 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 码头工人引擎 | 版本 17.06.0-ce+ 或更高版本 | 有关安装说明,请参阅 Docker 引擎文档 |
| 码头工人组成 | docker-compose (v1.18.0+) 或 docker-compose v2 (docker-compose-plugin) | 有关安装说明,请参阅 Docker Compose 文档 |
| 打开SSL | 最新的优先 | 用于为Harbor生成证书和密钥 |
网络端口
Harbor 要求在目标主机上打开以下端口。
| 港口 | 协议 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 443 | HTTPS | Harbor 门户和核心 API 在此端口上接受 HTTPS 请求。您可以在配置文件中更改此端口。 |
| 4443 | HTTPS | 连接到 Harbor 的 Docker Content Trust 服务。只有在启用 Notary 时才需要。您可以在配置文件中更改此端口。 |
| 80 | HTTP | Harbor 门户和核心 API 在此端口上接受 HTTP 请求。您可以在配置文件中更改此端口。 |
安装docker
yum -y update
sudo yum remove docker docker-client docker-client-latest docker-common docker-latest docker-latest-logrotate docker-logrotate docker-engine
sudo yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
sudo yum install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
mkdir -p /etc/docker/
vim /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"registry-mirrors":["http://hub-mirror.c.163.com","https://registry.docker-cn.com"],
"data-root" : "/opt/docker"
}
systemctl daemon-reload && systemctl restart docker
签发证书
默认情况下,Harbor 不附带证书。可以在没有安全保护的情况下部署 Harbor,以便您可以通过 HTTP 连接到它。但是,只有在没有连接到外部互联网的气隙测试或开发环境中才可以使用 HTTP。在非气隙环境中使用 HTTP 会使您面临中间人攻击。在生产环境中,始终使用 HTTPS。如果启用 Content Trust with Notary 以正确签署所有图像,则必须使用 HTTPS。
要配置 HTTPS,您必须创建 SSL 证书。您可以使用由受信任的第三方 CA 签名的证书,也可以使用自签名证书。本节介绍如何使用 OpenSSL创建 CA,以及如何使用您的 CA 签署服务器证书和客户端证书。您可以使用其他 CA 提供商,例如 Let’s Encrypt。
下面的过程假设您的 Harbor 注册表的主机名是yourdomain.com,并且它的 DNS 记录指向您运行 Harbor 的主机。
生成证书颁发机构证书
在生产环境中,您应该从 CA 获得证书。在测试或开发环境中,您可以生成自己的 CA。要生成 CA 证书,请运行以下命令。
-
生成 CA 证书私钥。
openssl genrsa -out ca.key 4096 -
生成 CA 证书。
调整选项中的值
-subj以反映您的组织。如果使用 FQDN 连接 Harbor 主机,则必须将其指定为通用名称 (CN) 属性。openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -sha512 -days 3650 \ -subj "/C=CN/ST=Beijing/L=Beijing/O=example/OU=Personal/CN=yourdomain.com" \ -key ca.key \ -out ca.crt
生成服务器证书
证书通常包含一个.crt文件和一个.key文件,例如,yourdomain.com.crt和yourdomain.com.key。
-
生成私钥。
openssl genrsa -out yourdomain.com.key 4096 -
生成证书签名请求 (CSR)。
调整选项中的值
-subj以反映您的组织。如果使用 FQDN 连接 Harbor 主机,则必须将其指定为通用名称 (CN) 属性,并在密钥和 CSR 文件名中使用它。openssl req -sha512 -new \ -subj "/C=CN/ST=Beijing/L=Beijing/O=example/OU=Personal/CN=yourdomain.com" \ -key yourdomain.com.key \ -out yourdomain.com.csr -
生成 x509 v3 扩展文件。
无论您是使用 FQDN 还是 IP 地址连接到您的 Harbor 主机,您都必须创建此文件,以便您可以为您的 Harbor 主机生成符合主题备用名称 (SAN) 和 x509 v3 的证书扩展要求。替换
DNS条目以反映您的域。cat > v3.ext <<-EOF authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer basicConstraints=CA:FALSE keyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth subjectAltName = @alt_names [alt_names] DNS.1=yourdomain.com DNS.2=yourdomain DNS.3=hostname EOF -
使用该
v3.ext文件为您的 Harbor 主机生成证书。yourdomain.com将CRS 和 CRT 文件名中的替换为 Harbor 主机名。openssl x509 -req -sha512 -days 3650 \ -extfile v3.ext \ -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial \ -in yourdomain.com.csr \ -out yourdomain.com.crt
向 Harbor 和 Docker 提供证书
生成ca.crt、yourdomain.com.crt和yourdomain.com.key文件后,您必须将它们提供给 Harbor 和 Docker,并重新配置 Harbor 以使用它们。
-
将服务器证书和密钥复制到 Harbor 主机上的 certificates 文件夹中。
cp yourdomain.com.crt /data/cert/ cp yourdomain.com.key /data/cert/ -
转换
yourdomain.com.crt为yourdomain.com.cert, 供 Docker 使用。Docker 守护进程将
.crt文件解释为 CA 证书,.cert将文件解释为客户端证书。openssl x509 -inform PEM -in yourdomain.com.crt -out yourdomain.com.cert -
将服务器证书、密钥和 CA 文件复制到 Harbor 主机上的 Docker 证书文件夹中。您必须先创建适当的文件夹。
cp yourdomain.com.cert /etc/docker/certs.d/yourdomain.com/ cp yourdomain.com.key /etc/docker/certs.d/yourdomain.com/ cp ca.crt /etc/docker/certs.d/yourdomain.com/如果您将默认
nginx端口 443 映射到其他端口,请创建文件夹/etc/docker/certs.d/yourdomain.com:port或/etc/docker/certs.d/harbor_IP:port。 -
重新启动 Docker 引擎。
systemctl restart docker
下载harbor安装包
手动下载 harbor 离线安装包上传到服务器
tar -xf harbor-offline-installer-v2.3.1.tgz
cd harbor
编辑harbor.yml
vim harbor.yml
# Configuration file of Harbor
# The IP address or hostname to access admin UI and registry service.
# DO NOT use localhost or 127.0.0.1, because Harbor needs to be accessed by external clients.
hostname: harbor.test.com
# http related config
http:
# port for http, default is 80. If https enabled, this port will redirect to https port
port: 80
# https related config
https:
# https port for harbor, default is 443
port: 443
# The path of cert and key files for nginx
certificate: /data/cert/yourdomain.com.crt
private_key: /data/cert/yourdomain.com.key
# # Uncomment following will enable tls communication between all harbor components
# internal_tls:
# # set enabled to true means internal tls is enabled
# enabled: true
# # put your cert and key files on dir
# dir: /etc/harbor/tls/internal
# Uncomment external_url if you want to enable external proxy
# And when it enabled the hostname will no longer used
# external_url: https://reg.mydomain.com:8433
# The initial password of Harbor admin
# It only works in first time to install harbor
# Remember Change the admin password from UI after launching Harbor.
harbor_admin_password: harbor123
# Harbor DB configuration
database:
# The password for the root user of Harbor DB. Change this before any production use.
password: root123
# The maximum number of connections in the idle connection pool. If it <=0, no idle connections are retained.
max_idle_conns: 100
# The maximum number of open connections to the database. If it <= 0, then there is no limit on the number of open connections.
# Note: the default number of connections is 1024 for postgres of harbor.
max_open_conns: 900
# The default data volume
data_volume: /opt/harbor/data
# Harbor Storage settings by default is using /data dir on local filesystem
# Uncomment storage_service setting If you want to using external storage
# storage_service:
# # ca_bundle is the path to the custom root ca certificate, which will be injected into the truststore
# # of registry's and chart repository's containers. This is usually needed when the user hosts a internal storage with self signed certificate.
# ca_bundle:
# # storage backend, default is filesystem, options include filesystem, azure, gcs, s3, swift and oss
# # for more info about this configuration please refer https://docs.docker.com/registry/configuration/
# filesystem:
# maxthreads: 100
# # set disable to true when you want to disable registry redirect
# redirect:
# disabled: false
# Trivy configuration
#
# Trivy DB contains vulnerability information from NVD, Red Hat, and many other upstream vulnerability databases.
# It is downloaded by Trivy from the GitHub release page https://github.com/aquasecurity/trivy-db/releases and cached
# in the local file system. In addition, the database contains the update timestamp so Trivy can detect whether it
# should download a newer version from the Internet or use the cached one. Currently, the database is updated every
# 12 hours and published as a new release to GitHub.
trivy:
# ignoreUnfixed The flag to display only fixed vulnerabilities
ignore_unfixed: false
# skipUpdate The flag to enable or disable Trivy DB downloads from GitHub
#
# You might want to enable this flag in test or CI/CD environments to avoid GitHub rate limiting issues.
# If the flag is enabled you have to download the `trivy-offline.tar.gz` archive manually, extract `trivy.db` and
# `metadata.json` files and mount them in the `/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/db` path.
skip_update: false
#
# insecure The flag to skip verifying registry certificate
insecure: false
# github_token The GitHub access token to download Trivy DB
#
# Anonymous downloads from GitHub are subject to the limit of 60 requests per hour. Normally such rate limit is enough
# for production operations. If, for any reason, it's not enough, you could increase the rate limit to 5000
# requests per hour by specifying the GitHub access token. For more details on GitHub rate limiting please consult
# https://developer.github.com/v3/#rate-limiting
#
# You can create a GitHub token by following the instructions in
# https://help.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/creating-a-personal-access-token-for-the-command-line
#
# github_token: xxx
jobservice:
# Maximum number of job workers in job service
max_job_workers: 10
notification:
# Maximum retry count for webhook job
webhook_job_max_retry: 10
chart:
# Change the value of absolute_url to enabled can enable absolute url in chart
absolute_url: disabled
# Log configurations
log:
# options are debug, info, warning, error, fatal
level: info
# configs for logs in local storage
local:
# Log files are rotated log_rotate_count times before being removed. If count is 0, old versions are removed rather than rotated.
rotate_count: 50
# Log files are rotated only if they grow bigger than log_rotate_size bytes. If size is followed by k, the size is assumed to be in kilobytes.
# If the M is used, the size is in megabytes, and if G is used, the size is in gigabytes. So size 100, size 100k, size 100M and size 100G
# are all valid.
rotate_size: 200M
# The directory on your host that store log
location: /var/log/harbor
# Uncomment following lines to enable external syslog endpoint.
# external_endpoint:
# # protocol used to transmit log to external endpoint, options is tcp or udp
# protocol: tcp
# # The host of external endpoint
# host: localhost
# # Port of external endpoint
# port: 5140
#This attribute is for migrator to detect the version of the .cfg file, DO NOT MODIFY!
_version: 2.3.0
# Uncomment external_database if using external database.
# external_database:
# harbor:
# host: harbor_db_host
# port: harbor_db_port
# db_name: harbor_db_name
# username: harbor_db_username
# password: harbor_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# max_idle_conns: 2
# max_open_conns: 0
# notary_signer:
# host: notary_signer_db_host
# port: notary_signer_db_port
# db_name: notary_signer_db_name
# username: notary_signer_db_username
# password: notary_signer_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# notary_server:
# host: notary_server_db_host
# port: notary_server_db_port
# db_name: notary_server_db_name
# username: notary_server_db_username
# password: notary_server_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# Uncomment external_redis if using external Redis server
# external_redis:
# # support redis, redis+sentinel
# # host for redis: <host_redis>:<port_redis>
# # host for redis+sentinel:
# # <host_sentinel1>:<port_sentinel1>,<host_sentinel2>:<port_sentinel2>,<host_sentinel3>:<port_sentinel3>
# host: redis:6379
# password:
# # sentinel_master_set must be set to support redis+sentinel
# #sentinel_master_set:
# # db_index 0 is for core, it's unchangeable
# registry_db_index: 1
# jobservice_db_index: 2
# chartmuseum_db_index: 3
# trivy_db_index: 5
# idle_timeout_seconds: 30
# Uncomment uaa for trusting the certificate of uaa instance that is hosted via self-signed cert.
# uaa:
# ca_file: /path/to/ca
# Global proxy
# Config http proxy for components, e.g. http://my.proxy.com:3128
# Components doesn't need to connect to each others via http proxy.
# Remove component from `components` array if want disable proxy
# for it. If you want use proxy for replication, MUST enable proxy
# for core and jobservice, and set `http_proxy` and `https_proxy`.
# Add domain to the `no_proxy` field, when you want disable proxy
# for some special registry.
proxy:
http_proxy:
https_proxy:
no_proxy:
components:
- core
- jobservice
- trivy
# metric:
# enabled: false
# port: 9090
# path: /metrics
最后运行sudo ./install.sh --with-notary --with-trivy即可,成功如下:
Note: stopping existing Harbor instance ...
Stopping harbor-db ... done
Stopping harbor-log ... done
Removing harbor-jobservice ... done
Removing nginx ... done
Removing harbor-core ... done
Removing trivy-adapter ... done
Removing registryctl ... done
Removing harbor-portal ... done
Creating harbor-log ... done
Removing redis ... done
Removing harbor-db ... done
Removing harbor-log ... done
Removing network harbor_harbor
Creating redis ... done
Creating registry ... done
Creating harbor-core ... done
Creating network "harbor_harbor" with the default driver
Creating nginx ... done
Creating registryctl ...
Creating redis ...
Creating registry ...
Creating harbor-db ...
Creating harbor-portal ...
Creating trivy-adapter ...
Creating harbor-core ...
Creating nginx ...
Creating harbor-jobservice ...
✔ ----Harbor has been installed and started successfully.----
可以通过docker ps查看:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
087ca29bad5f goharbor/harbor-jobservice:v2.3.1 "/harbor/entrypoint.…" About an hour ago Up About an hour (healthy) harbor-jobservice
5f90ef6b4cb9 goharbor/nginx-photon:v2.3.1 "nginx -g 'daemon of…" About an hour ago Up About an hour (healthy) 0.0.0.0:80->8080/tcp, :::80->8080/tcp nginx
ca1246eb6973 goharbor/harbor-core:v2.3.1 "/harbor/entrypoint.…" About an hour ago Up About an hour (healthy) harbor-core
7d6de32b3e69 goharbor/trivy-adapter-photon:v2.3.1 "/home/scanner/entry…" About an hour ago Up About an hour (healthy) trivy-adapter
d82428517498 goharbor/harbor-registryctl:v2.3.1 "/home/harbor/start.…" About an hour ago Up About an hour (healthy) registryctl
ec48fa6ac024 goharbor/harbor-portal:v2.3.1 "nginx -g 'daemon of…" About an hour ago Up About an hour (healthy) harbor-portal
1016cbdf3b4c goharbor/registry-photon:v2.3.1 "/home/harbor/entryp…" About an hour ago Up About an hour (healthy) registry
f83d39db01c7 goharbor/redis-photon:v2.3.1 "redis-server /etc/r…" About an hour ago Up About an hour (healthy) redis
bf8291c83c06 goharbor/harbor-db:v2.3.1 "/docker-entrypoint.…" About an hour ago Up About an hour (healthy) harbor-db
8afe93e0dd32 goharbor/harbor-log:v2.3.1 "/bin/sh -c /usr/loc…" About an hour ago Up About an hour (healthy) 127.0.0.1:1514->10514/tcp harbor-log
访问本机ip即可查看 如 127.0.0.1账号密码为admin/harbor123
containerd 配置私有仓库(二选一)
分发证书(如上文只是路径变了)
cp yourdomain.com.cert /etc/containerd/certs.d/yourdomain.com/
cp yourdomain.com.key /etc/containerd/certs.d/yourdomain.com/
cp ca.crt /etc/containerd/certs.d/yourdomain.com/
配置
修改配置文件
vim /etc/containerd/config.toml
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors."your.harbor.registry"]
endpoint = ["https://your.harbor.registry"]
-
将
your.harbor.registry替换为您私有Harbor Registry的URL。 -
保存并关闭配置文件。
-
重新启动containerd服务以使更改生效。可以使用以下命令之一:
-
使用systemd:
sudo systemctl restart containerd -
使用Docker Compose(如果您是使用Docker Compose运行的):
docker-compose restart
-
现在,containerd将使用您配置的私有Harbor源作为容器镜像的默认来源。您可以验证配置是否生效,通过拉取和运行一个位于Harbor Registry上的镜像来测试。
登录
-
打开终端或命令行界面。
-
使用
crictl命令登录到Harbor Registry。crictl是与containerd集成的容器运行时CLI工具。命令的基本格式如下:crictl login <harbor-registry-url>将
<harbor-registry-url>替换为您私有Harbor Registry的URL。例如:
crictl login example.com执行该命令后,您将被提示输入用户名和密码。
-
输入您在Harbor Registry上配置的用户名和密码,并按Enter键确认。
Username: <your-username> Password: <your-password>如果您提供的用户名和密码正确,您将看到一条消息表示登录成功。
-
您现在已成功登录到私有Harbor源。之后,您可以使用
crictl pull命令拉取位于Harbor Registry上的镜像。
请注意,与Docker类似,crictl登录到Harbor Registry将在您的本地配置文件中创建一个身份验证令牌,以便将来进行身份验证。
如果您希望退出登录,可以使用以下命令:
crictl logout <harbor-registry-url>
将<harbor-registry-url>替换为您私有Harbor Registry的URL。执行该命令后,将删除本地存储的身份验证令牌。
加密登录
/root/.docker/config.json文件是Docker客户端的配置文件,用于存储凭据和其他相关信息。要添加内容,您可以按照以下格式将私有Harbor源的登录凭据添加到该文件中:
{
"auths": {
"your.harbor.registry": {
"auth": "base64-encoded-credentials"
}
}
}
将your.harbor.registry替换为您私有Harbor Registry的URL,并将base64-encoded-credentials替换为经过Base64编码的用户名和密码组合。您可以使用以下命令将用户名和密码进行Base64编码:
echo -n 'username:password' | base64
请确保将实际的用户名和密码替换为username和password。
例如,如果您的私有Harbor Registry的URL是https://harbor.test.com,并且您的用户名是myuser,密码是mypassword,则添加的内容如下:
{
"auths": {
"harbor.test.com": {
"auth": "bXl1c2VyOm15cGFzc3dvcmQ="
}
}
}
添加完内容后,保存文件即可。之后,您可以使用crictl 客户端进行登录,并且不会再出现密码以明文形式存储的警告。
打标签并推送与拉取
要将镜像标记(tag)并推送到Harbor仓库,您可以执行以下步骤:
-
确保您已经安装了containerd,并且已经登录到您的Harbor仓库。您可以使用前面提到的方法登录到Harbor仓库。
-
使用
crictl或者nerdctl命令来标记您的镜像。命令的基本格式如下:crictl images该命令将显示您本地的镜像列表。找到要标记的镜像的ID或名称。
-
使用
crictl tag命令来标记镜像。命令的格式如下:crictl tag <image-id-or-name> <harbor-registry-url>/<repository>/<image-name>:<tag>将以下内容替换为实际值:
<image-id-or-name>: 要标记的镜像的ID或名称。<harbor-registry-url>: 您私有Harbor Registry的URL。<repository>: 要推送到的Harbor仓库的名称。<image-name>: 标记后的镜像名称。<tag>: 标记后的镜像标签。
例如,如果要将名为
myimage的镜像标记为harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest,则命令如下:crictl tag myimage harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest -
等待镜像标记成功。
-
使用
crictl push命令将标记后的镜像推送到Harbor仓库。命令的格式如下:crictl push <harbor-registry-url>/<repository>/<image-name>:<tag>将以下内容替换为实际值:
<harbor-registry-url>: 您私有Harbor Registry的URL。<repository>: 要推送到的Harbor仓库的名称。<image-name>: 标记后的镜像名称。<tag>: 标记后的镜像标签。
例如,如果要推送标记后的镜像
harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest,则命令如下:crictl push harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest -
等待镜像推送完成。一旦完成,您的镜像就会被推送到Harbor仓库中。
请确保您已经正确配置了containerd与Harbor的集成,并且具备适当的权限来标记和推送镜像。
以下是测试使用:

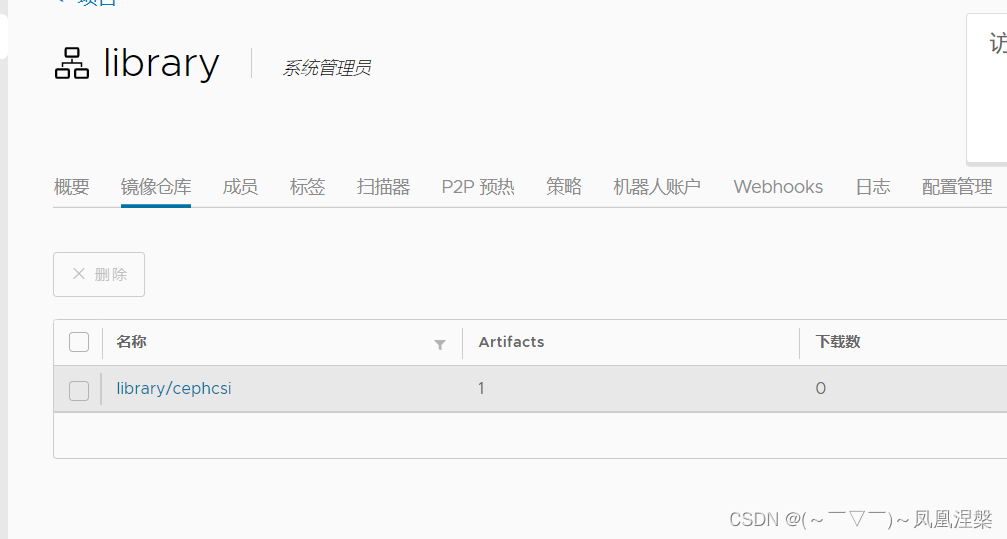
这里能看到已经推送成功了,当然,点击推送按钮,可以查看相关指令
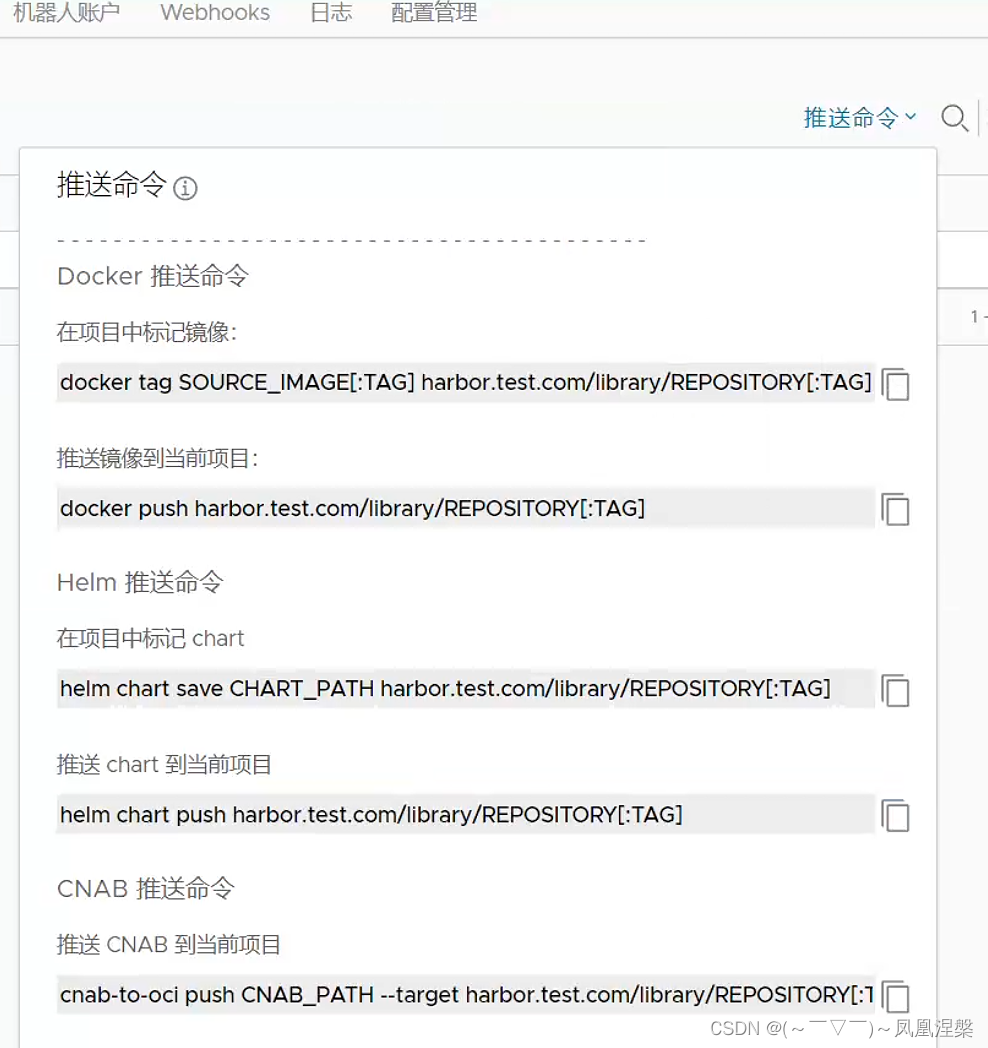
拉取镜像比较简单,就不详细介绍了,比如我刚刚推送的harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest镜像,直接使用以下命令拉取
crictl pull harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest
或者
nerdctl pull harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest
docker 配置私有仓库
创建或编辑Docker配置文件
vim /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"insecure-registries": ["your.harbor.registry"]
}
将your.harbor.registry替换为您私有Harbor仓库的URL。
分发证书(如上文)
cp yourdomain.com.cert /etc/docker/certs.d/yourdomain.com/
cp yourdomain.com.key /etc/docker/certs.d/yourdomain.com/
cp ca.crt /etc/docker/certs.d/yourdomain.com/
your.harbor.registry替换为您私有Harbor Registry的URL
重启docker
systemctl restart docker
登录
docker login yourdomain.com
your.harbor.registry替换为您私有Harbor Registry的URL,如下:
# docker login harbor.test.com
Username: admin
Password:
WARNING! Your password will be stored unencrypted in /root/.docker/config.json.
Configure a credential helper to remove this warning. See
https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/login/#credentials-store
加密登录(同上文)
/root/.docker/config.json文件是Docker客户端的配置文件,用于存储凭据和其他相关信息。要添加内容,您可以按照以下格式将私有Harbor源的登录凭据添加到该文件中:
{
"auths": {
"your.harbor.registry": {
"auth": "base64-encoded-credentials"
}
}
}
将your.harbor.registry替换为您私有Harbor Registry的URL,并将base64-encoded-credentials替换为经过Base64编码的用户名和密码组合。您可以使用以下命令将用户名和密码进行Base64编码:
echo -n 'username:password' | base64
请确保将实际的用户名和密码替换为username和password。
例如,如果您的私有Harbor Registry的URL是https://harbor.test.com,并且您的用户名是myuser,密码是mypassword,则添加的内容如下:
{
"auths": {
"harbor.test.com": {
"auth": "bXl1c2VyOm15cGFzc3dvcmQ="
}
}
}
添加完内容后,保存文件即可。之后,您可以使用Docker客户端进行登录,并且不会再出现密码以明文形式存储的警告。
打标签并推送与拉取
要将Docker镜像标记(tag)并推送到Harbor仓库,您可以按照以下步骤进行操作:
-
确保您已经安装了Docker,并且已经登录到您的Harbor仓库。如果还没有登录,请使用以下命令登录到Harbor仓库:
shellCopy code docker login <harbor-registry-url>将
<harbor-registry-url>替换为您私有Harbor仓库的URL,并按照提示输入用户名和密码。 -
使用
docker images命令查看本地已有的镜像列表,找到要标记的镜像的镜像ID或名称。 -
使用
docker tag命令来标记您的镜像。命令的格式如下:shellCopy code docker tag <image-id-or-name> <harbor-registry-url>/<repository>/<image-name>:<tag>将以下内容替换为实际值:
<image-id-or-name>: 要标记的镜像的ID或名称。<harbor-registry-url>: 您私有Harbor仓库的URL。<repository>: 要推送到的Harbor仓库的名称。<image-name>: 标记后的镜像名称。<tag>: 标记后的镜像标签。
例如,如果要将名为
myimage的镜像标记为harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest,则命令如下:shellCopy code docker tag myimage harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest -
等待镜像标记成功。
-
使用
docker push命令将标记后的镜像推送到Harbor仓库。命令的格式如下:shellCopy code docker push <harbor-registry-url>/<repository>/<image-name>:<tag>将以下内容替换为实际值:
<harbor-registry-url>: 您私有Harbor仓库的URL。<repository>: 要推送到的Harbor仓库的名称。<image-name>: 标记后的镜像名称。<tag>: 标记后的镜像标签。
例如,如果要推送标记后的镜像
harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest,则命令如下:shellCopy code docker push harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest -
等待镜像推送完成。一旦完成,您的镜像就会被推送到Harbor仓库中。
请确保您已经正确配置了Docker与Harbor仓库的集成,并且具备适当的权限来标记和推送镜像。
总结
本文提供了关于使用Harbor上传和管理容器镜像的完整指南。通过使用Harbor,您可以搭建自己的私有容器镜像仓库,实现镜像的安全存储、版本管理和访问控制。我们将涵盖Harbor的安装过程,以及使用containerd和Docker两种常见容器运行时登录和上传镜像到Harbor的方法。
harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest
4. 等待镜像标记成功。
5. 使用`docker push`命令将标记后的镜像推送到Harbor仓库。命令的格式如下:
shellCopy code
docker push //:
将以下内容替换为实际值:
- `<harbor-registry-url>`: 您私有Harbor仓库的URL。
- `<repository>`: 要推送到的Harbor仓库的名称。
- `<image-name>`: 标记后的镜像名称。
- `<tag>`: 标记后的镜像标签。
例如,如果要推送标记后的镜像`harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest`,则命令如下:
shellCopy code
docker push harbor.test.com/myrepository/myimage:latest
6. 等待镜像推送完成。一旦完成,您的镜像就会被推送到Harbor仓库中。
请确保您已经正确配置了Docker与Harbor仓库的集成,并且具备适当的权限来标记和推送镜像。
## 总结
本文提供了关于使用Harbor上传和管理容器镜像的完整指南。通过使用Harbor,您可以搭建自己的私有容器镜像仓库,实现镜像的安全存储、版本管理和访问控制。我们将涵盖Harbor的安装过程,以及使用containerd和Docker两种常见容器运行时登录和上传镜像到Harbor的方法。





![DataNode启动报错Failed to add storage directory [DISK]file:【已解决】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/50abfce494904acdafd827b1a8d91282.png)