你好,欢迎来到我的博客!作为一名程序员,我经常刷LeetCode题目来提升自己的编程能力。在我的博客里,我会分享一些我自己做过的题目和解题思路,希望能够帮助到大家。今天,我想和大家分享一道挑战性较高的题目,让我们一起来挑战一下吧!作者也是在学习的过程中刷到有意思的题目就会选择与大家分享,并且提供较优解,关于力扣的文章全部放在博客,如果大家喜欢记得支持作者。🤓
题目难度:简单
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
- void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
- int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
- int top() 返回栈顶元素。
- boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
注意:
你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
示例:
输入:
[“MyStack”, “push”, “push”, “top”, “pop”, “empty”]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 2, 2, false]解释:
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.top(); // 返回 2
myStack.pop(); // 返回 2
myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
提示:
- 1 <= x <= 9
- 最多调用100 次 push、pop、top 和 empty
- 每次调用 pop 和 top 都保证栈不为空
解题思路💡
如果用两个队列实现栈,首先实现一个功能完全的队列,队列的特点是先进先出,栈的特点是先进后出,要用两个队列来实现一个栈,我们可以围绕这个特点来思考此题,我的栈结构体里面定义两个队列指针,将两个指针分别成为Node1和Node2,首先将数据入到Node1中,如果入了n个,出数据的时候,将Node1中的n-1个数据出队到Node2中,此时Node1中的数据就是最后进来的数据,将他给出队,这样就形成了先进后出,后进先出,接下来每次入数据只需要入到非空的队列中,出数据将非空的队列出队到空的队列中且保留下一个将其抛出即可。
- 本题需要先写一个功能完全的队列,然后对队列进行调用。
示例
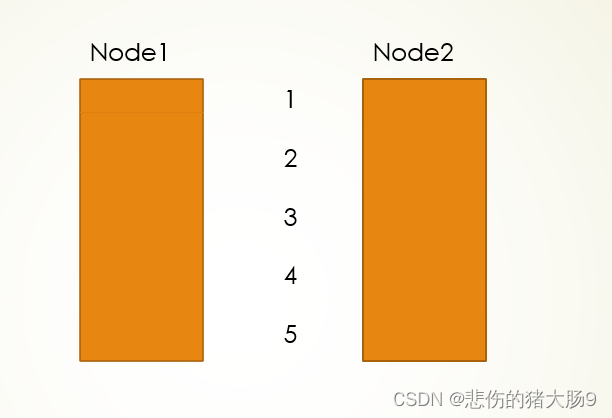
解题分析
我们需要实现的函数:
typedef struct {} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {}
(第一步)
- 写出一个
队列,有基本的初始化、入队、出队、销毁等功能。
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QListNode
{
struct QlistNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* front;
QNode* tail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
q->front = NULL;
q->tail = NULL;
q->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
QNode* cur = q->front;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
q->front = NULL;
q->tail = NULL;
q->size = 0;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{
return q->front == NULL;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType data)
{
assert(q);
QNode *temp = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc error");
return;
}
QNode* Newnode = temp;
Newnode->data = data;
Newnode->next = NULL;
if (QueueEmpty(q))
{
q->front = q->tail = Newnode;
}
else
{
q->tail->next = Newnode;
q->tail = q->tail->next;
}
q->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
QNode* next = q->front->next;
free(q->front);
q->front = next;
if (next == NULL)
q->tail == NULL;
q->size--;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->size;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->front->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->tail->data;
}
(第二步)实现结构体
使用两个队列来实现所以我们的栈结构体里面肯定是要有两个队列指针。
typedef struct {
Queue QNode1;
Queue QNode2;
} MyStack;
(第三步)结构体初始化
上面写好了队列初始化等功能智利之间将其进行调用。
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* ret= (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&ret->QNode1);
QueueInit(&ret->QNode2);
return ret;
}
(第四步)入栈功能
如果队列为空,入队到另一个队列。
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
return QueueEmpty(&(obj->QNode1))&&QueueEmpty(&(obj->QNode2));
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
if (QueueEmpty(&obj->QNode1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->QNode2, x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->QNode1, x);
}
}
(第五步)出栈函数
如果为空,则交换指针,保持Node1是不为空的一个队列,将Node1中的数据保留一个其余全部入队到Node2,然后将剩余的一个存储起来,抛出,再返回。
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
assert(!myStackEmpty(obj));
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->QNode1))
{
Queue temp = obj->QNode2;
obj->QNode2 = obj->QNode1;
obj->QNode1 = temp;
}
while(obj->QNode1.front->next!=NULL)
{
int temp = QueueFront(&obj->QNode1);
QueuePop(&obj->QNode1);
QueuePush(&obj->QNode2,temp);
}
int ret = QueueFront(&obj->QNode1);
QueuePop(&obj->QNode1);
return ret;
}
(第六步)获取栈顶元素
获取有数据的队列指针,调用写好的获取队列队尾函数。
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
assert(!myStackEmpty(obj));
Queue SPush = obj->QNode1;
if(QueueEmpty(&SPush))
{
SPush = obj->QNode2;
}
int ret = QueueBack(&SPush);
return ret;
}
(第七步)释放栈
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
QueueDestroy(&obj->QNode1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->QNode2);
free(obj);
}
源代码分享⭐
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct STNode
{
STDataType* str;
int top;
int capacity;
}STNode;
void STInit(STNode* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->str = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
bool STEmpty(STNode* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
void STPush(STNode* pst, STDataType data)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int Newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* temp =(STDataType*)realloc(pst->str,sizeof(STDataType) * Newcapacity);
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc error");
return;
}
pst->str = temp;
pst->capacity = Newcapacity;
}
pst->str[pst->top++] = data;
}
void STPop(STNode* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
void STDestroy(STNode* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->str);
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
STDataType STTop(STNode* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
return pst->str[pst->top - 1];
}
typedef struct {
STNode* STPushStack;
STNode* STPopStack;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* mq = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
mq->STPushStack = (STNode*)malloc(sizeof(STNode));
STInit(mq->STPushStack);
mq->STPopStack = (STNode*)malloc(sizeof(STNode));
STInit(mq->STPopStack);
return mq;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
STPush(obj->STPushStack,x);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
return obj->STPushStack->top==0&&obj->STPopStack->top==0;
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
assert(!myQueueEmpty(obj));
if(obj->STPopStack->top==0)
{
while(obj->STPushStack->top!=0)
{
STDataType temp = STTop(obj->STPushStack);
STPop(obj->STPushStack);
STPush(obj->STPopStack,temp);
}
}
STDataType ret = STTop(obj->STPopStack);
STPop(obj->STPopStack);
return ret;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
assert(!myQueueEmpty(obj));
if(obj->STPopStack->top==0)
{
while(obj->STPushStack->top!=0)
{
STDataType temp = STTop(obj->STPushStack);
STPop(obj->STPushStack);
STPush(obj->STPopStack,temp);
}
}
return STTop(obj->STPopStack);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
STDestroy(obj->STPushStack);
STDestroy(obj->STPopStack);
obj->STPushStack = NULL;
obj->STPopStack = NULL;
}
/**
* Your MyQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();
* myQueuePush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myQueuePop(obj);
* int param_3 = myQueuePeek(obj);
* bool param_4 = myQueueEmpty(obj);
* myQueueFree(obj);
*/
完结
当你喜欢一篇文章时,点赞、收藏和关注是最好的支持方式。如果你喜欢我的文章,请不要吝啬你的支持,点赞👍、收藏⭐和关注都是对我最好的鼓励。感谢你们的支持!









![[Nacos] Nacos Server主要类和接口 (五)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c3a8dbdedb7e481b8e744b997a94fb2b.png)