文章目录
- 6.单元测试:JUnit
- 6.1整合JUnit5
- 6.1.1搭建子模块
- 6.1.2引入依赖
- 6.1.3添加配置文件
- 6.1.4添加java类
- 6.1.5测试
- 6.2整合JUnit4
- 6.2.添加依赖
- 6.2.2测试
- 7.事务
- 7.1JdbcTemplate
- 7.1.1简介
- 7.1.2准备工作
- 7.1.3实现CURD
- ①装配 JdbcTemplate
- ②测试增删改功能
- ③查询数据返回对象
- ④查询数据返回list集合
- ⑤查询返回单个的值
- 7.2声明式事务概念
- 7.2.1事务基本概念
- ①什么是事务
- ②事务的特性
- 7.2.2编程式事务
- 7.2.3声明式事务
- 7.3基于注解的声明式事务
- 7.3.1准备工作
- 7.3.2测试无事务情况
- 7.3.3加入事务
- ①添加事务配置
- ②添加事务注解
- ③观察结果
- 7.3.4@Transactional注解标识的位置
- 7.3.5事务属性:只读
- 7.3.6事务属性:超时
- 7.3.7事务属性:回滚策略
- 7.3.8事务属性:隔离级别
- 7.3.9事务属性:传播行为
- 7.3.10全注解配置事务
- 7.4基于XML的声明式事务
- 7.4.1场景模拟
- 7.4.2修改Spring配置文件
- 8.资源操作:Resources
- 8.1Spring Resources概述
- 8.2Resource接口
- 8.3Resource的实现类
- 8.3.1UrlResource访问网络资源
- 8.3.2ClassPathResource 访问类路径下资源
- 8.3.3FileSystemResource 访问文件系统资源
- 8.3.4ServletContextResource
- 8.3.5InputStreamResource
- 8.3.6ByteArrayResource
- 8.4Resource类图
- 8.5ResourceLoader 接口
- 8.5.1ResourceLoader 概述
- 8.5.2使用演示
- 8.5.3ResourceLoader 总结
- 8.6ResourceLoaderAware 接口
- 8.7使用Resource 作为属性
- 8.8应用程序上下文和资源路径
- 8.8.1概述
- 8.8.2ApplicationContext实现类指定访问策略
- 8.8.3使用前缀指定访问策略
- 9.国际化:i18n
- 9.1i18n概述
- 9.2Java国际化
- 9.3 Spring6国际化
- 9.3.1MessageSource接口
- 9.3.2使用Spring6国际化
- 10.数据校验:Validation
- 10.1Spring Validation概述
- 10.2实验一:通过Validator接口实现
- 10.3实验二:Bean Validation注解实现
- 10.4实验三:基于方法实现校验
- 10.5实验四:实现自定义校验
- 11.提前编译:AOT
- 11.1AOT概述
- 11.1.1JIT与AOT的区别
- 11.1.2Graalvm
- 11.1.3Native Image
学习视频: 尚硅谷Spring教程
6.单元测试:JUnit
在之前的测试方法中,几乎都能看到以下的两行代码:
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("xxx.xml");
Xxxx xxx = context.getBean(Xxxx.class);
这两行代码的作用是创建Spring容器,最终获取到对象,但是每次测试都需要重复编写。针对上述问题,我们需要的是程序能自动帮我们创建容器。我们都知道JUnit无法知晓我们是否使用了 Spring 框架,更不用说帮我们创建 Spring 容器了。Spring提供了一个运行器,可以读取配置文件(或注解)来创建容器。我们只需要告诉它配置文件位置就可以了。这样一来,我们通过Spring整合JUnit可以使程序创建spring容器了
6.1整合JUnit5
6.1.1搭建子模块
搭建spring-junit模块
6.1.2引入依赖
<dependencies>
<!--spring context依赖-->
<!--当你引入Spring Context依赖之后,表示将Spring的基础依赖引入了-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring对junit的支持相关依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>6.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit5测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--log4j2的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j2-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
6.1.3添加配置文件
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--开启组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring6.bean"/>
</beans>
copy日志文件:log4j2.xml
6.1.4添加java类
package com.atguigu.spring6.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class User {
public User() {
System.out.println("run user");
}
}
6.1.5测试
import com.atguigu.spring6.bean.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringJUnitConfig;
//两种方式均可
//方式一
//@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
//@ContextConfiguration("classpath:beans.xml")
//方式二
//加载配置文件
@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = "classpath:beans.xml")
public class SpringJUnit5Test {
//注入
@Autowired
private User user;
//测试方法
@Test
public void testUser(){
System.out.println(user);
}
}
6.2整合JUnit4
6.2.添加依赖
<!-- junit测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
6.2.2测试
import com.atguigu.spring6.bean.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:beans.xml")
public class SpringJUnit4Test {
@Autowired
private User user;
@Test
public void testUser(){
System.out.println(user);
}
}
7.事务
7.1JdbcTemplate
7.1.1简介

Spring 框架对 JDBC 进行封装,使用 JdbcTemplate 方便实现对数据库操作
7.1.2准备工作
①搭建子模块
搭建子模块:spring-jdbc-tx
②加入依赖
<dependencies>
<!--spring jdbc Spring 持久化层支持jar包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
③创建jdbc.properties
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=root
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
④配置Spring的配置文件
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 导入外部属性文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties" />
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置 JdbcTemplate -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 装配数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
⑤准备数据库与测试表
CREATE DATABASE `spring`;
use `spring`;
CREATE TABLE `t_emp` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
`sex` varchar(2) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '性别',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
7.1.3实现CURD
①装配 JdbcTemplate
创建测试类,整合JUnit,注入JdbcTemplate
package com.atguigu.spring6;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringJUnitConfig;
@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = "classpath:beans.xml")
public class JDBCTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
}
②测试增删改功能
@Test
//测试增删改功能
public void testUpdate(){
//添加功能
//编写sql语句
String sql = "insert into t_emp values(null,?,?,?)";
//调用jdbcTemplate的方法,传入相关参数
int result = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "张三", 23, "男");
//修改功能
//String sql = "update t_emp set name=? where id=?";
//int result = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "张三atguigu", 1);
//删除功能
//String sql = "delete from t_emp where id=?";
//int result = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, 1);
}
③查询数据返回对象
public class Emp {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
//生成get和set方法
//......
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
//查询:返回对象
@Test
public void testSelectObject() {
//写法一
//编写sql语句
// String sql = "select * from t_emp where id=?";
// Emp empResult = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,
// (rs, rowNum) -> {
// Emp emp = new Emp();
// emp.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
// emp.setName(rs.getString("name"));
// emp.setAge(rs.getInt("age"));
// emp.setSex(rs.getString("sex"));
// return emp;
// }, 1);
// System.out.println(empResult);
//写法二
String sql = "select * from t_emp where id=?";
Emp emp = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Emp.class),1);
System.out.println(emp);
}
④查询数据返回list集合
@Test
//查询多条数据为一个list集合
public void testSelectList(){
String sql = "select * from t_emp";
List<Emp> list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Emp.class));
System.out.println(list);
}
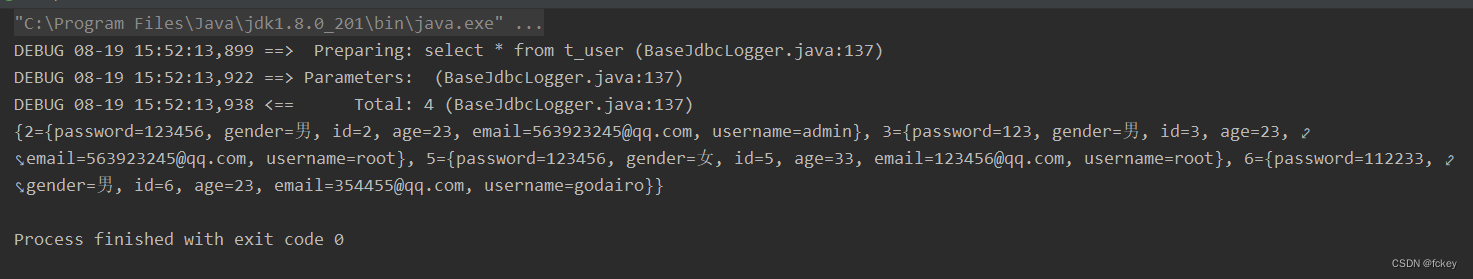
⑤查询返回单个的值
@Test
//查询单行单列的值
public void selectCount(){
String sql = "select count(id) from t_emp";
Integer count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class);
System.out.println(count);
}
7.2声明式事务概念
7.2.1事务基本概念
①什么是事务
数据库事务( transaction)是访问并可能操作各种数据项的一个数据库操作序列,这些操作要么全部执行,要么全部不执行,是一个不可分割的工作单位。事务由事务开始与事务结束之间执行的全部数据库操作组成。
②事务的特性
A:原子性(Atomicity)
一个事务(transaction)中的所有操作,要么全部完成,要么全部不完成,不会结束在中间某个环节。事务在执行过程中发生错误,会被回滚(Rollback)到事务开始前的状态,就像这个事务从来没有执行过一样。
C:一致性(Consistency)
事务的一致性指的是在一个事务执行之前和执行之后数据库都必须处于一致性状态。
如果事务成功地完成,那么系统中所有变化将正确地应用,系统处于有效状态。
如果在事务中出现错误,那么系统中的所有变化将自动地回滚,系统返回到原始状态。
I:隔离性(Isolation)
指的是在并发环境中,当不同的事务同时操纵相同的数据时,每个事务都有各自的完整数据空间。由并发事务所做的修改必须与任何其他并发事务所做的修改隔离。事务查看数据更新时,数据所处的状态要么是另一事务修改它之前的状态,要么是另一事务修改它之后的状态,事务不会查看到中间状态的数据。
D:持久性(Durability)
指的是只要事务成功结束,它对数据库所做的更新就必须保存下来。即使发生系统崩溃,重新启动数据库系统后,数据库还能恢复到事务成功结束时的状态。
7.2.2编程式事务
事务功能的相关操作全部通过自己编写代码来实现:
Connection conn = ...;
try {
// 开启事务:关闭事务的自动提交
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
// 核心操作
// 提交事务
conn.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
// 回滚事务
conn.rollBack();
}finally{
// 释放数据库连接
conn.close();
}
编程式的实现方式存在缺陷:
- 细节没有被屏蔽:具体操作过程中,所有细节都需要程序员自己来完成,比较繁琐。
- 代码复用性不高:如果没有有效抽取出来,每次实现功能都需要自己编写代码,代码就没有得到复用。
7.2.3声明式事务
既然事务控制的代码有规律可循,代码的结构基本是确定的,所以框架就可以将固定模式的代码抽取出来,进行相关的封装。
封装起来后,我们只需要在配置文件中进行简单的配置即可完成操作。
- 好处1:提高开发效率
- 好处2:消除了冗余的代码
- 好处3:框架会综合考虑相关领域中在实际开发环境下有可能遇到的各种问题,进行了健壮性、性能等各个方面的优化
所以,我们可以总结下面两个概念:
- 编程式:自己写代码实现功能
- 声明式:通过配置让框架实现功能
7.3基于注解的声明式事务
案例场景:
7.3.1准备工作
①添加配置
在beans.xml添加配置
<!--扫描组件-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring6"></context:component-scan>
②创建表
CREATE TABLE `t_book` (
`book_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`book_name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '图书名称',
`price` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '价格',
`stock` int(10) unsigned DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '库存(无符号)',
PRIMARY KEY (`book_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into `t_book`(`book_id`,`book_name`,`price`,`stock`) values (1,'斗破苍穹',80,100),(2,'斗罗大陆',50,100);
CREATE TABLE `t_user` (
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`username` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户名',
`balance` int(10) unsigned DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '余额(无符号)',
PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into `t_user`(`user_id`,`username`,`balance`) values (1,'admin',50);
③创建组件
- 创建BookController:
package com.atguigu.spring6.controller;
@Controller
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
//买书操作
public void buyBook(Integer bookId, Integer userId){
bookService.buyBook(bookId, userId);
}
}
- 创建接口BookService:
package com.atguigu.spring6.service;
public interface BookService {
void buyBook(Integer bookId, Integer userId);
}
- 创建实现类BookServiceImpl:
package com.atguigu.spring6.service.impl;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Override
public void buyBook(Integer bookId, Integer userId) {
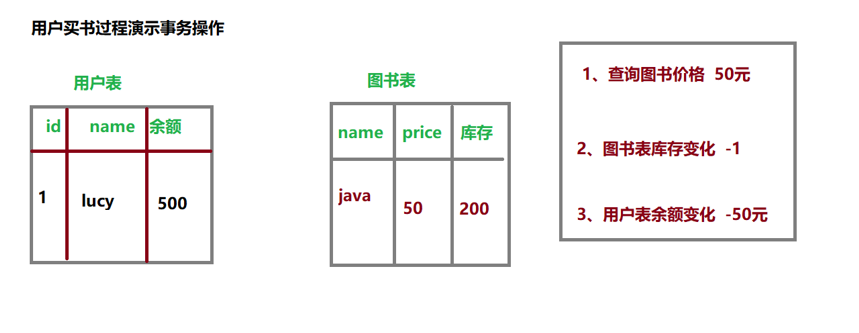
//查询图书的价格
Integer price = bookDao.getPriceByBookId(bookId);
//更新图书的库存
bookDao.updateStock(bookId);
//更新用户的余额
bookDao.updateBalance(userId, price);
}
}
- 创建接口BookDao:
package com.atguigu.spring6.dao;
public interface BookDao {
Integer getPriceByBookId(Integer bookId);
void updateStock(Integer bookId);
void updateBalance(Integer userId, Integer price);
}
- 创建实现类BookDaoImpl:
package com.atguigu.spring6.dao.impl;
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//根据图书id查询图书价格
@Override
public Integer getPriceByBookId(Integer bookId) {
String sql = "select price from t_book where book_id = ?";
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class, bookId);
}
//更新图书表库存量-1
@Override
public void updateStock(Integer bookId) {
String sql = "update t_book set stock = stock - 1 where book_id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, bookId);
}
//更新用户表用户余额-图书价格
@Override
public void updateBalance(Integer userId, Integer price) {
String sql = "update t_user set balance = balance - ? where user_id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, price, userId);
}
}
7.3.2测试无事务情况
①创建测试类
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringJUnitConfig;
@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = "classpath:beans.xml")
public class TxByAnnotationTest {
@Autowired
private BookController bookController;
@Test
public void testBuyBook(){
bookController.buyBook(1, 1);
}
}
②模拟场景
用户购买图书,先查询图书的价格,再更新图书的库存和用户的余额
假设用户id为1的用户,购买id为1的图书
用户余额为50,而图书价格为80
购买图书之后,用户的余额为-30,数据库中余额字段设置了无符号,因此无法将-30插入到余额字段
此时执行sql语句会抛出SQLException
③观察结果
因为没有添加事务,图书的库存更新了,但是用户的余额没有更新
显然这样的结果是错误的,购买图书是一个完整的功能,更新库存和更新余额要么都成功要么都失败
7.3.3加入事务
①添加事务配置
在spring配置文件中引入tx命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
在Spring的配置文件中添加配置:
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--
开启事务的注解驱动
通过注解@Transactional所标识的方法或标识的类中所有的方法,都会被事务管理器管理事务
-->
<!-- transaction-manager属性的默认值是transactionManager,如果事务管理器bean的id正好就是这个默认值,则可以省略这个属性 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
②添加事务注解
因为service层表示业务逻辑层,一个方法表示一个完成的功能,因此处理事务一般在service层处理
在BookServiceImpl的buybook()添加注解@Transactional
③观察结果
由于使用了Spring的声明式事务,更新库存和更新余额都没有执行
7.3.4@Transactional注解标识的位置
@Transactional标识在方法上,则只会影响该方法
@Transactional标识的类上,则会影响类中所有的方法
7.3.5事务属性:只读
①介绍
对一个查询操作来说,如果我们把它设置成只读,就能够明确告诉数据库,这个操作不涉及写操作。这样数据库就能够针对查询操作来进行优化。
②使用方式
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public void buyBook(Integer bookId, Integer userId) {
//查询图书的价格
Integer price = bookDao.getPriceByBookId(bookId);
//更新图书的库存
bookDao.updateStock(bookId);
//更新用户的余额
bookDao.updateBalance(userId, price);
//System.out.println(1/0);
}
③注意
对增删改操作设置只读会抛出下面异常:
Caused by: java.sql.SQLException: Connection is read-only. Queries leading to data modification are not allowed
7.3.6事务属性:超时
①介绍
事务在执行过程中,有可能因为遇到某些问题,导致程序卡住,从而长时间占用数据库资源。而长时间占用资源,大概率是因为程序运行出现了问题(可能是Java程序或MySQL数据库或网络连接等等)。此时这个很可能出问题的程序应该被回滚,撤销它已做的操作,事务结束,把资源让出来,让其他正常程序可以执行。
概括来说就是一句话:超时回滚,释放资源。
②使用方式
//超时时间单位秒
@Transactional(timeout = 3)
public void buyBook(Integer bookId, Integer userId) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//查询图书的价格
Integer price = bookDao.getPriceByBookId(bookId);
//更新图书的库存
bookDao.updateStock(bookId);
//更新用户的余额
bookDao.updateBalance(userId, price);
//System.out.println(1/0);
}
③观察结果
执行过程中抛出异常:
org.springframework.transaction.TransactionTimedOutException: Transaction timed out: deadline was Fri Jun 04 16:25:39 CST 2022
7.3.7事务属性:回滚策略
①介绍
声明式事务默认只针对运行时异常回滚,编译时异常不回滚。
可以通过@Transactional中相关属性设置回滚策略
-
rollbackFor属性:需要设置一个Class类型的对象
-
rollbackForClassName属性:需要设置一个字符串类型的全类名
-
noRollbackFor属性:需要设置一个Class类型的对象
-
rollbackFor属性:需要设置一个字符串类型的全类名
②使用方式
@Transactional(noRollbackFor = ArithmeticException.class)
//@Transactional(noRollbackForClassName = "java.lang.ArithmeticException")
public void buyBook(Integer bookId, Integer userId) {
//查询图书的价格
Integer price = bookDao.getPriceByBookId(bookId);
//更新图书的库存
bookDao.updateStock(bookId);
//更新用户的余额
bookDao.updateBalance(userId, price);
System.out.println(1/0);
}
③观察结果
虽然购买图书功能中出现了数学运算异常(ArithmeticException),但是我们设置的回滚策略是,当出现ArithmeticException不发生回滚,因此购买图书的操作正常执行
7.3.8事务属性:隔离级别
①介绍
数据库系统必须具有隔离并发运行各个事务的能力,使它们不会相互影响,避免各种并发问题。一个事务与其他事务隔离的程度称为隔离级别。SQL标准中规定了多种事务隔离级别,不同隔离级别对应不同的干扰程度,隔离级别越高,数据一致性就越好,但并发性越弱。
隔离级别一共有四种:
-
读未提交:READ UNCOMMITTED
允许Transaction01读取Transaction02未提交的修改。
-
读已提交:READ COMMITTED、
要求Transaction01只能读取Transaction02已提交的修改。
-
可重复读:REPEATABLE READ
确保Transaction01可以多次从一个字段中读取到相同的值,即Transaction01执行期间禁止其它事务对这个字段进行更新。
-
串行化:SERIALIZABLE
确保Transaction01可以多次从一个表中读取到相同的行,在Transaction01执行期间,禁止其它事务对这个表进行添加、更新、删除操作。可以避免任何并发问题,但性能十分低下。
各个隔离级别解决并发问题的能力见下表:
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|
| READ UNCOMMITTED | 有 | 有 | 有 |
| READ COMMITTED | 无 | 有 | 有 |
| REPEATABLE READ | 无 | 无 | 有 |
| SERIALIZABLE | 无 | 无 | 无 |
各种数据库产品对事务隔离级别的支持程度:
| 隔离级别 | Oracle | MySQL |
|---|---|---|
| READ UNCOMMITTED | × | √ |
| READ COMMITTED | √(默认) | √ |
| REPEATABLE READ | × | √(默认) |
| SERIALIZABLE | √ | √ |
②使用方式
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT)//使用数据库默认的隔离级别
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_UNCOMMITTED)//读未提交
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED)//读已提交
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ)//可重复读
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.SERIALIZABLE)//串行化
7.3.9事务属性:传播行为
①介绍
什么是事务的传播行为?
在service类中有a()方法和b()方法,a()方法上有事务,b()方法上也有事务,当a()方法执行过程中调用了b()方法,事务是如何传递的?合并到一个事务里?还是开启一个新的事务?这就是事务传播行为。
一共有七种传播行为:
- REQUIRED:支持当前事务,如果不存在就新建一个(默认)【没有就新建,有就加入】
- SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行**【有就加入,没有就不管了】**
- MANDATORY:必须运行在一个事务中,如果当前没有事务正在发生,将抛出一个异常**【有就加入,没有就抛异常】**
- REQUIRES_NEW:开启一个新的事务,如果一个事务已经存在,则将这个存在的事务挂起**【不管有没有,直接开启一个新事务,开启的新事务和之前的事务不存在嵌套关系,之前事务被挂起】**
- NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,挂起当前事务**【不支持事务,存在就挂起】**
- NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,抛出异常**【不支持事务,存在就抛异常】**
- NESTED:如果当前正有一个事务在进行中,则该方法应当运行在一个嵌套式事务中。被嵌套的事务可以独立于外层事务进行提交或回滚。如果外层事务不存在,行为就像REQUIRED一样。【有事务的话,就在这个事务里再嵌套一个完全独立的事务,嵌套的事务可以独立的提交和回滚。没有事务就和REQUIRED一样。】
②测试
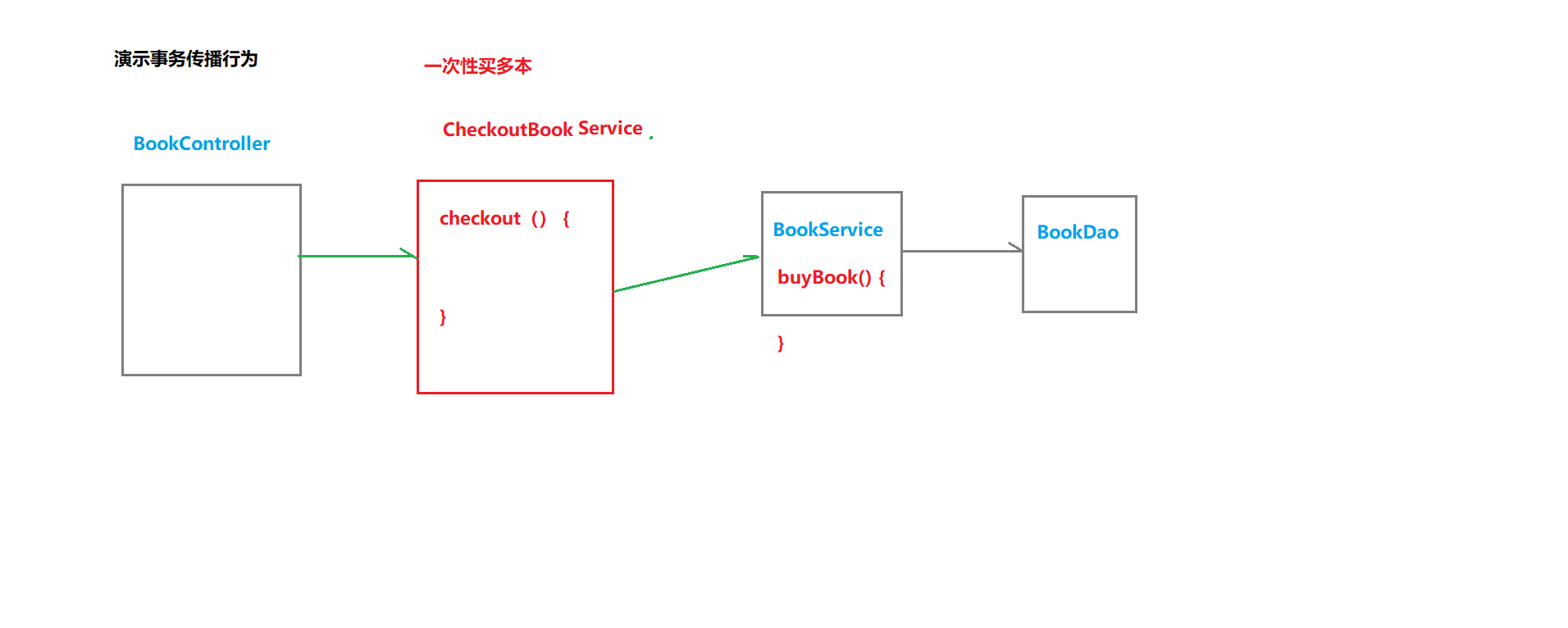
checkout()与buyBook()都是事务方法
创建接口CheckoutService:
package com.atguigu.spring6.service;
public interface CheckoutService {
void checkout(Integer[] bookIds, Integer userId);
}
创建实现类CheckoutServiceImpl:
package com.atguigu.spring6.service.impl;
@Service
public class CheckoutServiceImpl implements CheckoutService {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@Override
@Transactional
//一次购买多本图书
public void checkout(Integer[] bookIds, Integer userId) {
for (Integer bookId : bookIds) {
bookService.buyBook(bookId, userId);
}
}
}
在BookController中添加方法:
@Autowired
private CheckoutService checkoutService;
public void checkout(Integer[] bookIds, Integer userId){
checkoutService.checkout(bookIds, userId);
}
在数据库中将用户的余额修改为100元
③观察结果
可以通过@Transactional中的propagation属性设置事务传播行为
修改BookServiceImpl中buyBook()上,注解@Transactional的propagation属性
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED),默认情况,表示如果当前线程上有已经开启的事务可用,那么就在这个事务中运行。经过观察,购买图书的方法buyBook()在checkout()中被调用,checkout()上有事务注解,因此在此事务中执行。所购买的两本图书的价格为80和50,而用户的余额为100,因此在购买第二本图书时余额不足失败,导致整个checkout()回滚,即只要有一本书买不了,就都买不了
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW),表示不管当前线程上是否有已经开启的事务,都要开启新事务。同样的场景,每次购买图书都是在buyBook()的事务中执行,因此第一本图书购买成功,事务结束,第二本图书购买失败,只在第二次的buyBook()中回滚,购买第一本图书不受影响,即能买几本就买几本。
7.3.10全注解配置事务
创建配置类替代配置文件
①添加配置类
package com.atguigu.spring6.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.spring6")
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource getDataSource(){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
return dataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "jdbcTemplate")
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
dataSourceTransactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return dataSourceTransactionManager;
}
}
②测试
import com.atguigu.spring6.config.SpringConfig;
import com.atguigu.spring6.controller.BookController;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringJUnitConfig;
public class TxByAllAnnotationTest {
@Test
public void testTxAllAnnotation(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
BookController accountService = applicationContext.getBean("bookController", BookController.class);
accountService.buyBook(1, 1);
}
}
7.4基于XML的声明式事务
1)环境准备
2)创建Spring配置文件
- 开启组件扫描
- 创建数据源
- 创建JdbcTemplate,注入数据源
- 创建事务管理器,注入数据源
- 配置事务通知,设置事务相关属性
- 配置切入点表达式,把事务通知添加到方法上
7.4.1场景模拟
参考基于注解的声明式事务
7.4.2修改Spring配置文件
将Spring配置文件中去掉tx:annotation-driven 标签,并添加配置:
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置事务通知和切入点表达式 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* com.atguigu.spring.tx.xml.service.impl.*.*(..))"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
<!-- tx:advice标签:配置事务通知 -->
<!-- id属性:给事务通知标签设置唯一标识,便于引用 -->
<!-- transaction-manager属性:关联事务管理器 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!-- tx:method标签:配置具体的事务方法 -->
<!-- name属性:指定方法名,可以使用星号代表多个字符 -->
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="query*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
<!-- read-only属性:设置只读属性 -->
<!-- rollback-for属性:设置回滚的异常 -->
<!-- no-rollback-for属性:设置不回滚的异常 -->
<!-- isolation属性:设置事务的隔离级别 -->
<!-- timeout属性:设置事务的超时属性 -->
<!-- propagation属性:设置事务的传播行为 -->
<tx:method name="save*" read-only="false" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" propagation="REQUIRES_NEW"/>
<tx:method name="update*" read-only="false" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" propagation="REQUIRES_NEW"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" read-only="false" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" propagation="REQUIRES_NEW"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
注意:基于xml实现的声明式事务,必须引入aspectJ的依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId> <version>6.0.2</version> </dependency>
8.资源操作:Resources
8.1Spring Resources概述


Java的标准java.net.URL类和各种URL前缀的标准处理程序无法满足所有对low-level资源的访问,比如:没有标准化的 URL 实现可用于访问需要从类路径或相对于 ServletContext 获取的资源。并且缺少某些Spring所需要的功能,例如检测某资源是否存在等。而Spring的Resource声明了访问low-level资源的能力。
8.2Resource接口
Spring 的 Resource 接口位于 org.springframework.core.io 中。 旨在成为一个更强大的接口,用于抽象对低级资源的访问。以下显示了Resource接口定义的方法
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
boolean exists();
boolean isReadable();
boolean isOpen();
boolean isFile();
URL getURL() throws IOException;
URI getURI() throws IOException;
File getFile() throws IOException;
ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException;
long contentLength() throws IOException;
long lastModified() throws IOException;
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
String getFilename();
String getDescription();
}
Resource接口继承了InputStreamSource接口,提供了很多InputStreamSource所没有的方法。InputStreamSource接口,只有一个方法:
public interface InputStreamSource {
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
其中一些重要的方法:
getInputStream(): 找到并打开资源,返回一个InputStream以从资源中读取。预计每次调用都会返回一个新的InputStream(),调用者有责任关闭每个流
exists(): 返回一个布尔值,表明某个资源是否以物理形式存在
isOpen: 返回一个布尔值,指示此资源是否具有开放流的句柄。如果为true,InputStream就不能够多次读取,只能够读取一次并且及时关闭以避免内存泄漏。对于所有常规资源实现,返回false,但是InputStreamResource除外。
getDescription(): 返回资源的描述,用来输出错误的日志。这通常是完全限定的文件名或资源的实际URL。
其他方法:
isReadable(): 表明资源的目录读取是否通过getInputStream()进行读取。
isFile(): 表明这个资源是否代表了一个文件系统的文件。
getURL(): 返回一个URL句柄,如果资源不能够被解析为URL,将抛出IOException
getURI(): 返回一个资源的URI句柄
getFile(): 返回某个文件,如果资源不能够被解析称为绝对路径,将会抛出FileNotFoundException
lastModified(): 资源最后一次修改的时间戳
createRelative(): 创建此资源的相关资源
getFilename(): 资源的文件名是什么 例如:最后一部分的文件名 myfile.txt
8.3Resource的实现类
Resource 接口是 Spring 资源访问策略的抽象,它本身并不提供任何资源访问实现,具体的资源访问由该接口的实现类完成——每个实现类代表一种资源访问策略。Resource一般包括这些实现类:UrlResource、ClassPathResource、FileSystemResource、ServletContextResource、InputStreamResource、ByteArrayResource
8.3.1UrlResource访问网络资源
Resource的一个实现类,用来访问网络资源,它支持URL的绝对路径。
http:------该前缀用于访问基于HTTP协议的网络资源。
ftp:------该前缀用于访问基于FTP协议的网络资源
file: ------该前缀用于从文件系统中读取资源
实验:访问基于HTTP协议的网络资源
创建一个maven子模块spring6-resources,配置Spring依赖(参考前面)
package com.atguigu.spring6.resources;
import org.springframework.core.io.UrlResource;
//演示UrlResource访问网络资源
public class UrlResourceDemo {
//访问前缀http、file
public static void loadAndReadUrlResource(String path){
// 创建一个 Resource 对象
UrlResource url = null;
try {
url = new UrlResource(path);
// 获取资源名
System.out.println(url.getFilename());
System.out.println(url.getURI());
// 获取资源描述
System.out.println(url.getDescription());
//获取资源内容
System.out.println(url.getInputStream().read());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//访问网络资源
loadAndReadUrlResource("http://www.baidu.com");
}
}
实验二:在项目根路径下创建文件,从文件系统中读取资源
方法不变,修改调用传递路径
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1 访问网络资源
//loadAndReadUrlResource("http://www.atguigu.com");
//2 访问文件系统资源
loadAndReadUrlResource("file:atguigu.txt");
}
8.3.2ClassPathResource 访问类路径下资源
ClassPathResource 用来访问类加载路径下的资源,相对于其他的 Resource 实现类,其主要优势是方便访问类加载路径里的资源,尤其对于 Web 应用,ClassPathResource 可自动搜索位于 classes 下的资源文件,无须使用绝对路径访问。
实验:在类路径下创建文件atguigu.txt,使用ClassPathResource 访问
package com.atguigu.spring6.resources;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class ClassPathResourceDemo {
public static void loadAndReadUrlResource(String path) throws Exception{
// 创建一个 Resource 对象
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(path);
// 获取文件名
System.out.println("resource.getFileName = " + resource.getFilename());
// 获取文件描述
System.out.println("resource.getDescription = "+ resource.getDescription());
//获取文件内容
InputStream in = resource.getInputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
while(in.read(b)!=-1) {
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
loadAndReadUrlResource("atguigu.txt");
}
}
ClassPathResource实例可使用ClassPathResource构造器显式地创建,但更多的时候它都是隐式地创建的。当执行Spring的某个方法时,该方法接受一个代表资源路径的字符串参数,当Spring识别该字符串参数中包含classpath:前缀后,系统会自动创建ClassPathResource对象。
8.3.3FileSystemResource 访问文件系统资源
Spring 提供的 FileSystemResource 类用于访问文件系统资源,使用 FileSystemResource 来访问文件系统资源并没有太大的优势,因为 Java 提供的 File 类也可用于访问文件系统资源。
实验:使用FileSystemResource 访问文件系统资源
package com.atguigu.spring6.resources;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class FileSystemResourceDemo {
public static void loadAndReadUrlResource(String path) throws Exception{
//相对路径
FileSystemResource resource = new FileSystemResource("atguigu.txt");
//绝对路径
//FileSystemResource resource = new FileSystemResource("C:\\atguigu.txt");
// 获取文件名
System.out.println("resource.getFileName = " + resource.getFilename());
// 获取文件描述
System.out.println("resource.getDescription = "+ resource.getDescription());
//获取文件内容
InputStream in = resource.getInputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
while(in.read(b)!=-1) {
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
loadAndReadUrlResource("atguigu.txt");
}
}
FileSystemResource实例可使用FileSystemResource构造器显示地创建,但更多的时候它都是隐式创建。执行Spring的某个方法时,该方法接受一个代表资源路径的字符串参数,当Spring识别该字符串参数中包含file:前缀后,系统将会自动创建FileSystemResource对象。
8.3.4ServletContextResource
这是ServletContext资源的Resource实现,它解释相关Web应用程序根目录中的相对路径。它始终支持流(stream)访问和URL访问,但只有在扩展Web应用程序存档且资源实际位于文件系统上时才允许java.io.File访问。无论它是在文件系统上扩展还是直接从JAR或其他地方(如数据库)访问,实际上都依赖于Servlet容器。
8.3.5InputStreamResource
InputStreamResource 是给定的输入流(InputStream)的Resource实现。它的使用场景在没有特定的资源实现的时候使用(感觉和@Component 的适用场景很相似)。与其他Resource实现相比,这是已打开资源的描述符。 因此,它的isOpen()方法返回true。如果需要将资源描述符保留在某处或者需要多次读取流,请不要使用它。
8.3.6ByteArrayResource
字节数组的Resource实现类。通过给定的数组创建了一个ByteArrayInputStream。它对于从任何给定的字节数组加载内容非常有用,而无需求助于单次使用的InputStreamResource。
8.4Resource类图
上述Resource实现类与Resource顶级接口之间的关系可以用下面的UML关系模型来表示
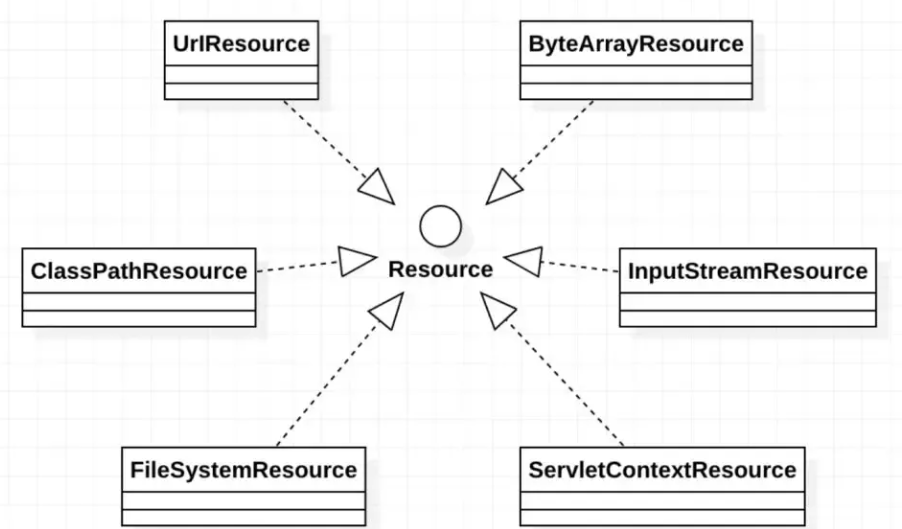
8.5ResourceLoader 接口
8.5.1ResourceLoader 概述
Spring 提供如下两个标志性接口:
(1)ResourceLoader : 该接口实现类的实例可以获得一个Resource实例。
(2) ResourceLoaderAware : 该接口实现类的实例将获得一个ResourceLoader的引用。
在ResourceLoader接口里有如下方法:
(1)Resource getResource(String location) : 该接口仅有这个方法,用于返回一个Resource实例。ApplicationContext实现类都实现ResourceLoader接口,因此ApplicationContext可直接获取Resource实例。
8.5.2使用演示
实验一:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext获取Resource实例
package com.atguigu.spring6.resouceloader;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
// 通过ApplicationContext访问资源
// ApplicationContext实例获取Resource实例时,
// 默认采用与ApplicationContext相同的资源访问策略
Resource res = ctx.getResource("atguigu.txt");
System.out.println(res.getFilename());
}
}
实验二:FileSystemApplicationContext获取Resource实例
package com.atguigu.spring6.resouceloader;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext();
Resource res = ctx.getResource("atguigu.txt");
System.out.println(res.getFilename());
}
}
8.5.3ResourceLoader 总结
Spring将采用和ApplicationContext相同的策略来访问资源。也就是说,如果ApplicationContext是FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,res就是FileSystemResource实例;如果ApplicationContext是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,res就是ClassPathResource实例
当Spring应用需要进行资源访问时,实际上并不需要直接使用Resource实现类,而是调用ResourceLoader实例的getResource()方法来获得资源,ReosurceLoader将会负责选择Reosurce实现类,也就是确定具体的资源访问策略,从而将应用程序和具体的资源访问策略分离开来
另外,使用ApplicationContext访问资源时,可通过不同前缀指定强制使用指定的ClassPathResource、FileSystemResource等实现类
Resource res = ctx.getResource("calsspath:bean.xml");
Resrouce res = ctx.getResource("file:bean.xml");
Resource res = ctx.getResource("http://localhost:8080/beans.xml");
8.6ResourceLoaderAware 接口
ResourceLoaderAware接口实现类的实例将获得一个ResourceLoader的引用,ResourceLoaderAware接口也提供了一个setResourceLoader()方法,该方法将由Spring容器负责调用,Spring容器会将一个ResourceLoader对象作为该方法的参数传入。
如果把实现ResourceLoaderAware接口的Bean类部署在Spring容器中,Spring容器会将自身当成ResourceLoader作为setResourceLoader()方法的参数传入。由于ApplicationContext的实现类都实现了ResourceLoader接口,Spring容器自身完全可作为ResorceLoader使用。
实验:演示ResourceLoaderAware使用
第一步 创建类,实现ResourceLoaderAware接口
package com.atguigu.spring6.resouceloader;
import org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
public class TestBean implements ResourceLoaderAware {
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
//实现ResourceLoaderAware接口必须实现的方法
//如果把该Bean部署在Spring容器中,该方法将会有Spring容器负责调用。
//SPring容器调用该方法时,Spring会将自身作为参数传给该方法。
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
//返回ResourceLoader对象的应用
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader(){
return this.resourceLoader;
}
}
第二步 创建bean.xml文件,配置TestBean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="testBean" class="com.atguigu.spring6.resouceloader.TestBean"></bean>
</beans>
第三步 测试
package com.atguigu.spring6.resouceloader;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Spring容器会将一个ResourceLoader对象作为该方法的参数传入
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
TestBean testBean = ctx.getBean("testBean",TestBean.class);
//获取ResourceLoader对象
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = testBean.getResourceLoader();
System.out.println("Spring容器将自身注入到ResourceLoaderAware Bean 中 ? :" + (resourceLoader == ctx));
//加载其他资源
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource("atguigu.txt");
System.out.println(resource.getFilename());
System.out.println(resource.getDescription());
}
}
8.7使用Resource 作为属性
前面介绍了 Spring 提供的资源访问策略,但这些依赖访问策略要么需要使用 Resource 实现类,要么需要使用 ApplicationContext 来获取资源。实际上,当应用程序中的 Bean 实例需要访问资源时,Spring 有更好的解决方法:直接利用依赖注入。从这个意义上来看,Spring 框架不仅充分利用了策略模式来简化资源访问,而且还将策略模式和 IoC 进行充分地结合,最大程度地简化了 Spring 资源访问。
归纳起来,如果 Bean 实例需要访问资源,有如下两种解决方案:
- 代码中获取 Resource 实例。
- 使用依赖注入。
对于第一种方式,当程序获取 Resource 实例时,总需要提供 Resource 所在的位置,不管通过 FileSystemResource 创建实例,还是通过 ClassPathResource 创建实例,或者通过 ApplicationContext 的 getResource() 方法获取实例,都需要提供资源位置。这意味着:资源所在的物理位置将被耦合到代码中,如果资源位置发生改变,则必须改写程序。因此,通常建议采用第二种方法,让 Spring 为 Bean 实例依赖注入资源。
实验:让Spring为Bean实例依赖注入资源
第一步 创建依赖注入类,定义属性和方法
package com.atguigu.spring6.resouceloader;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
public class ResourceBean {
private Resource res;
public void setRes(Resource res) {
this.res = res;
}
public Resource getRes() {
return res;
}
public void parse(){
System.out.println(res.getFilename());
System.out.println(res.getDescription());
}
}
第二步 创建spring配置文件,配置依赖注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="resourceBean" class="com.atguigu.spring6.resouceloader.ResourceBean" >
<!-- 可以使用file:、http:、ftp:等前缀强制Spring采用对应的资源访问策略 -->
<!-- 如果不采用任何前缀,则Spring将采用与该ApplicationContext相同的资源访问策略来访问资源 -->
<property name="res" value="classpath:atguigu.txt"/>
</bean>
</beans>
第三步 测试
package com.atguigu.spring6.resouceloader;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
ResourceBean resourceBean = ctx.getBean("resourceBean",ResourceBean.class);
resourceBean.parse();
}
}
8.8应用程序上下文和资源路径
8.8.1概述
不管以怎样的方式创建ApplicationContext实例,都需要为ApplicationContext指定配置文件,Spring允许使用一份或多分XML配置文件。当程序创建ApplicationContext实例时,通常也是以Resource的方式来访问配置文件的,所以ApplicationContext完全支持ClassPathResource、FileSystemResource、ServletContextResource等资源访问方式。
ApplicationContext确定资源访问策略通常有两种方法:
(1)使用ApplicationContext实现类指定访问策略。
(2)使用前缀指定访问策略。
8.8.2ApplicationContext实现类指定访问策略
创建ApplicationContext对象时,通常可以使用如下实现类:
(1) ClassPathXMLApplicationContext : 对应使用ClassPathResource进行资源访问。
(2)FileSystemXmlApplicationContext : 对应使用FileSystemResource进行资源访问。
(3)XmlWebApplicationContext : 对应使用ServletContextResource进行资源访问。
当使用ApplicationContext的不同实现类时,就意味着Spring使用响应的资源访问策略。
效果前面已经演示
8.8.3使用前缀指定访问策略
实验一:classpath前缀使用
package com.atguigu.spring6.context;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 通过搜索文件系统路径下的xml文件创建ApplicationContext,
* 但通过指定classpath:前缀强制搜索类加载路径
* classpath:bean.xml
* */
ApplicationContext ctx =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean.xml");
System.out.println(ctx);
Resource resource = ctx.getResource("atguigu.txt");
System.out.println(resource.getFilename());
System.out.println(resource.getDescription());
}
}
实验二:classpath通配符使用
classpath * :前缀提供了加载多个XML配置文件的能力,当使用classpath*:前缀来指定XML配置文件时,系统将搜索类加载路径,找到所有与文件名匹配的文件,分别加载文件中的配置定义,最后合并成一个ApplicationContext。
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath*:bean.xml");
System.out.println(ctx);
当使用classpath * :前缀时,Spring将会搜索类加载路径下所有满足该规则的配置文件。
如果不是采用classpath * :前缀,而是改为使用classpath:前缀,Spring则只加载第一个符合条件的XML文件
注意 :
classpath * : 前缀仅对ApplicationContext有效。实际情况是,创建ApplicationContext时,分别访问多个配置文件(通过ClassLoader的getResource方法实现)。因此,classpath * :前缀不可用于Resource。
使用三:通配符其他使用
一次性加载多个配置文件的方式:指定配置文件时使用通配符
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean*.xml");
Spring允许将classpath*:前缀和通配符结合使用:
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath*:bean*.xml");
9.国际化:i18n

9.1i18n概述
国际化也称作i18n,其来源是英文单词 internationalization的首末字符i和n,18为中间的字符数。由于软件发行可能面向多个国家,对于不同国家的用户,软件显示不同语言的过程就是国际化。通常来讲,软件中的国际化是通过配置文件来实现的,假设要支撑两种语言,那么就需要两个版本的配置文件。
9.2Java国际化
(1)Java自身是支持国际化的,java.util.Locale用于指定当前用户所属的语言环境等信息,java.util.ResourceBundle用于查找绑定对应的资源文件。Locale包含了language信息和country信息,Locale创建默认locale对象时使用的静态方法:
/**
* This method must be called only for creating the Locale.*
* constants due to making shortcuts.
*/
private static Locale createConstant(String lang, String country) {
BaseLocale base = BaseLocale.createInstance(lang, country);
return getInstance(base, null);
}
(2)配置文件命名规则:
basename_language_country.properties
必须遵循以上的命名规则,java才会识别。其中,basename是必须的,语言和国家是可选的。这里存在一个优先级概念,如果同时提供了messages.properties和messages_zh_CN.propertes两个配置文件,如果提供的locale符合en_CN,那么优先查找messages_en_CN.propertes配置文件,如果没查找到,再查找messages.properties配置文件。最后,提示下,所有的配置文件必须放在classpath中,一般放在resources目录下
(3)实验:演示Java国际化
第一步 创建子模块spring6-i18n,引入spring依赖
第二步 在resource目录下创建两个配置文件:messages_zh_CN.propertes和messages_en_GB.propertes

第三步 测试
package com.atguigu.spring6.javai18n;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(ResourceBundle.getBundle("messages",
new Locale("en","GB")).getString("test"));
System.out.println(ResourceBundle.getBundle("messages",
new Locale("zh","CN")).getString("test"));
}
}
9.3 Spring6国际化
9.3.1MessageSource接口
spring中国际化是通过MessageSource这个接口来支持的
常见实现类
ResourceBundleMessageSource
这个是基于Java的ResourceBundle基础类实现,允许仅通过资源名加载国际化资源
ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource
这个功能和第一个类的功能类似,多了定时刷新功能,允许在不重启系统的情况下,更新资源的信息
StaticMessageSource
它允许通过编程的方式提供国际化信息,一会我们可以通过这个来实现db中存储国际化信息的功能。
9.3.2使用Spring6国际化
第一步 创建资源文件
国际化文件命名格式:基本名称 _ 语言 _ 国家.properties
{0},{1}这样内容,就是动态参数

(1)创建atguigu_en_US.properties
www.atguigu.com=welcome {0},时间:{1}
(2)创建atguigu_zh_CN.properties
www.atguigu.com=欢迎 {0},时间:{1}
第二步 创建spring配置文件,配置MessageSource
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basenames">
<list>
<value>atguigu</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="defaultEncoding">
<value>utf-8</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
第三步 创建测试类
package com.atguigu.spring6.javai18n;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Locale;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
//传递动态参数,使用数组形式对应{0} {1}顺序
Object[] objs = new Object[]{"atguigu",new Date().toString()};
//www.atguigu.com为资源文件的key值,
//objs为资源文件value值所需要的参数,Local.CHINA为国际化为语言
String str=context.getMessage("www.atguigu.com", objs, Locale.CHINA);
System.out.println(str);
}
}
10.数据校验:Validation

10.1Spring Validation概述

在开发中,我们经常遇到参数校验的需求,比如用户注册的时候,要校验用户名不能为空、用户名长度不超过20个字符、手机号是合法的手机号格式等等。如果使用普通方式,我们会把校验的代码和真正的业务处理逻辑耦合在一起,而且如果未来要新增一种校验逻辑也需要在修改多个地方。而spring validation允许通过注解的方式来定义对象校验规则,把校验和业务逻辑分离开,让代码编写更加方便。Spring Validation其实就是对Hibernate Validator进一步的封装,方便在Spring中使用。
在Spring中有多种校验的方式
第一种是通过实现org.springframework.validation.Validator接口,然后在代码中调用这个类
第二种是按照Bean Validation方式来进行校验,即通过注解的方式。
第三种是基于方法实现校验
除此之外,还可以实现自定义校验
10.2实验一:通过Validator接口实现
第一步 创建子模块 spring6-validator
第二步 引入相关依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>7.0.5.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.glassfish</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.el</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
第三步 创建实体类,定义属性和方法
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method1;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
第四步 创建类实现Validator接口,实现接口方法指定校验规则
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method1;
import org.springframework.validation.Errors;
import org.springframework.validation.ValidationUtils;
import org.springframework.validation.Validator;
public class PersonValidator implements Validator {
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return Person.class.equals(clazz);
}
@Override
public void validate(Object object, Errors errors) {
//name不能为空
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmpty(errors, "name", "name.empty");
//age不能小于0,不能大于200
Person p = (Person) object;
if (p.getAge() < 0) {
errors.rejectValue("age", "error value < 0");
} else if (p.getAge() > 110) {
errors.rejectValue("age", "error value too old");
}
}
}
上面定义的类,其实就是实现接口中对应的方法,
supports方法用来表示此校验用在哪个类型上,
validate是设置校验逻辑的地点,其中ValidationUtils,是Spring封装的校验工具类,帮助快速实现校验。
第五步 使用上述Validator进行测试
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method1;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.DataBinder;
public class TestMethod1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建person对象
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("lucy");
person.setAge(-1);
// 创建Person对应的DataBinder
DataBinder binder = new DataBinder(person);
// 设置校验
binder.setValidator(new PersonValidator());
// 由于Person对象中的属性为空,所以校验不通过
binder.validate();
//输出结果
BindingResult results = binder.getBindingResult();
System.out.println(results.getAllErrors());
}
}
10.3实验二:Bean Validation注解实现
使用Bean Validation校验方式,就是如何将Bean Validation需要使用的javax.validation.ValidatorFactory 和javax.validation.Validator注入到容器中。spring默认有一个实现类LocalValidatorFactoryBean,它实现了上面Bean Validation中的接口,并且也实现了org.springframework.validation.Validator接口。
第一步 创建配置类,配置LocalValidatorFactoryBean
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method2")
public class ValidationConfig {
@Bean
public LocalValidatorFactoryBean validator() {
return new LocalValidatorFactoryBean();
}
}
第二步 创建实体类,使用注解定义校验规则
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method2;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.Max;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.Min;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.NotNull;
public class User {
@NotNull
private String name;
@Min(0)
@Max(120)
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
常用注解说明
@NotNull 限制必须不为null
@NotEmpty 只作用于字符串类型,字符串不为空,并且长度不为0
@NotBlank 只作用于字符串类型,字符串不为空,并且trim()后不为空串
@DecimalMax(value) 限制必须为一个不大于指定值的数字
@DecimalMin(value) 限制必须为一个不小于指定值的数字
@Max(value) 限制必须为一个不大于指定值的数字
@Min(value) 限制必须为一个不小于指定值的数字
@Pattern(value) 限制必须符合指定的正则表达式
@Size(max,min) 限制字符长度必须在min到max之间
@Email 验证注解的元素值是Email,也可以通过正则表达式和flag指定自定义的email格式
第三步 使用两种不同的校验器实现
(1)使用jakarta.validation.Validator校验
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method2;
import jakarta.validation.ConstraintViolation;
import jakarta.validation.Validator;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Set;
@Service
public class MyService1 {
@Autowired
private Validator validator;
public boolean validator(User user){
Set<ConstraintViolation<User>> sets = validator.validate(user);
return sets.isEmpty();
}
}
(2)使用org.springframework.validation.Validator校验
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method2;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.validation.BindException;
import org.springframework.validation.Validator;
@Service
public class MyService2 {
@Autowired
private Validator validator;
public boolean validaPersonByValidator(User user) {
BindException bindException = new BindException(user, user.getName());
validator.validate(user, bindException);
return bindException.hasErrors();
}
}
第四步 测试
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method2;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class TestMethod2 {
@Test
public void testMyService1() {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ValidationConfig.class);
MyService1 myService = context.getBean(MyService1.class);
User user = new User();
user.setAge(-1);
boolean validator = myService.validator(user);
System.out.println(validator);
}
@Test
public void testMyService2() {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ValidationConfig.class);
MyService2 myService = context.getBean(MyService2.class);
User user = new User();
user.setName("lucy");
user.setAge(130);
user.setAge(-1);
boolean validator = myService.validaPersonByValidator(user);
System.out.println(validator);
}
}
10.4实验三:基于方法实现校验
第一步 创建配置类,配置MethodValidationPostProcessor
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method3;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.LocalValidatorFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.MethodValidationPostProcessor;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method3")
public class ValidationConfig {
@Bean
public MethodValidationPostProcessor validationPostProcessor() {
return new MethodValidationPostProcessor();
}
}
第二步 创建实体类,使用注解设置校验规则
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method3;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.*;
public class User {
@NotNull
private String name;
@Min(0)
@Max(120)
private int age;
@Pattern(regexp = "^1(3|4|5|7|8)\\d{9}$",message = "手机号码格式错误")
@NotBlank(message = "手机号码不能为空")
private String phone;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
}
第三步 定义Service类,通过注解操作对象
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method3;
import jakarta.validation.Valid;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
@Service
@Validated
public class MyService {
public String testParams(@NotNull @Valid User user) {
return user.toString();
}
}
第四步 测试
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method3;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class TestMethod3 {
@Test
public void testMyService1() {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ValidationConfig.class);
MyService myService = context.getBean(MyService.class);
User user = new User();
user.setAge(-1);
myService.testParams(user);
}
}
10.5实验四:实现自定义校验
第一步 自定义校验注解
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method4;
import jakarta.validation.Constraint;
import jakarta.validation.Payload;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Constraint(validatedBy = {CannotBlankValidator.class})
public @interface CannotBlank {
//默认错误消息
String message() default "不能包含空格";
//分组
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
//负载
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
//指定多个时使用
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.TYPE_USE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@interface List {
CannotBlank[] value();
}
}
第二步 编写真正的校验类
package com.atguigu.spring6.validation.method4;
import jakarta.validation.ConstraintValidator;
import jakarta.validation.ConstraintValidatorContext;
public class CannotBlankValidator implements ConstraintValidator<CannotBlank, String> {
@Override
public void initialize(CannotBlank constraintAnnotation) {
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
//null时不进行校验
if (value != null && value.contains(" ")) {
//获取默认提示信息
String defaultConstraintMessageTemplate = context.getDefaultConstraintMessageTemplate();
System.out.println("default message :" + defaultConstraintMessageTemplate);
//禁用默认提示信息
context.disableDefaultConstraintViolation();
//设置提示语
context.buildConstraintViolationWithTemplate("can not contains blank").addConstraintViolation();
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
11.提前编译:AOT

11.1AOT概述
11.1.1JIT与AOT的区别
JIT和AOT 这个名词是指两种不同的编译方式,这两种编译方式的主要区别在于是否在“运行时”进行编译
(1)JIT, Just-in-time,动态(即时)编译,边运行边编译;
在程序运行时,根据算法计算出热点代码,然后进行 JIT 实时编译,这种方式吞吐量高,有运行时性能加成,可以跑得更快,并可以做到动态生成代码等,但是相对启动速度较慢,并需要一定时间和调用频率才能触发 JIT 的分层机制。JIT 缺点就是编译需要占用运行时资源,会导致进程卡顿。
(2)AOT,Ahead Of Time,指运行前编译,预先编译。
AOT 编译能直接将源代码转化为机器码,内存占用低,启动速度快,可以无需 runtime 运行,直接将 runtime 静态链接至最终的程序中,但是无运行时性能加成,不能根据程序运行情况做进一步的优化,AOT 缺点就是在程序运行前编译会使程序安装的时间增加。
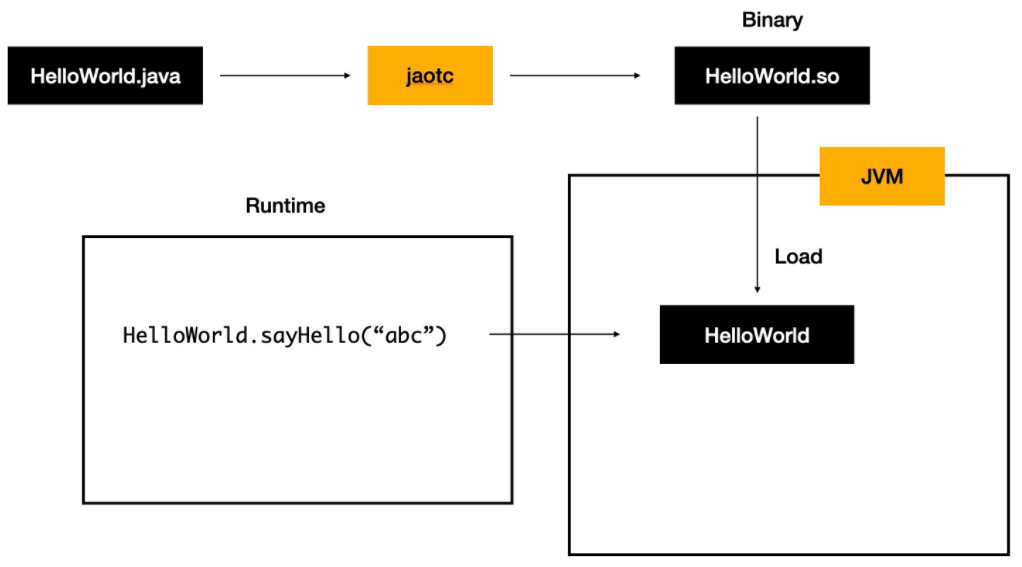
**简单来讲:**JIT即时编译指的是在程序的运行过程中,将字节码转换为可在硬件上直接运行的机器码,并部署至托管环境中的过程。而 AOT 编译指的则是,在程序运行之前,便将字节码转换为机器码的过程。
.java -> .class -> (使用jaotc编译工具) -> .so(程序函数库,即编译好的可以供其他程序使用的代码和数据)
(3)AOT的优点
**简单来讲,**Java 虚拟机加载已经预编译成二进制库,可以直接执行。不必等待及时编译器的预热,减少 Java 应用给人带来“第一次运行慢” 的不良体验。
在程序运行前编译,可以避免在运行时的编译性能消耗和内存消耗
可以在程序运行初期就达到最高性能,程序启动速度快
运行产物只有机器码,打包体积小
AOT的缺点
由于是静态提前编译,不能根据硬件情况或程序运行情况择优选择机器指令序列,理论峰值性能不如JIT
没有动态能力,同一份产物不能跨平台运行
第一种即时编译 (JIT) 是默认模式,Java Hotspot 虚拟机使用它在运行时将字节码转换为机器码。后者提前编译 (AOT)由新颖的 GraalVM 编译器支持,并允许在构建时将字节码直接静态编译为机器码。
现在正处于云原生,降本增效的时代,Java 相比于 Go、Rust 等其他编程语言非常大的弊端就是启动编译和启动进程非常慢,这对于根据实时计算资源,弹性扩缩容的云原生技术相冲突,Spring6 借助 AOT 技术在运行时内存占用低,启动速度快,逐渐的来满足 Java 在云原生时代的需求,对于大规模使用 Java 应用的商业公司可以考虑尽早调研使用 JDK17,通过云原生技术为公司实现降本增效。
11.1.2Graalvm
Spring6 支持的 AOT 技术,这个 GraalVM 就是底层的支持,Spring 也对 GraalVM 本机映像提供了一流的支持。GraalVM 是一种高性能 JDK,旨在加速用 Java 和其他 JVM 语言编写的应用程序的执行,同时还为 JavaScript、Python 和许多其他流行语言提供运行时。 GraalVM 提供两种运行 Java 应用程序的方法:在 HotSpot JVM 上使用 Graal 即时 (JIT) 编译器或作为提前 (AOT) 编译的本机可执行文件。 GraalVM 的多语言能力使得在单个应用程序中混合多种编程语言成为可能,同时消除了外语调用成本。GraalVM 向 HotSpot Java 虚拟机添加了一个用 Java 编写的高级即时 (JIT) 优化编译器。
GraalVM 具有以下特性:
(1)一种高级优化编译器,它生成更快、更精简的代码,需要更少的计算资源
(2)AOT 本机图像编译提前将 Java 应用程序编译为本机二进制文件,立即启动,无需预热即可实现最高性能
(3)Polyglot 编程在单个应用程序中利用流行语言的最佳功能和库,无需额外开销
(4)高级工具在 Java 和多种语言中调试、监视、分析和优化资源消耗
总的来说对云原生的要求不算高短期内可以继续使用 2.7.X 的版本和 JDK8,不过 Spring 官方已经对 Spring6 进行了正式版发布。
11.1.3Native Image
目前业界除了这种在JVM中进行AOT的方案,还有另外一种实现Java AOT的思路,那就是直接摒弃JVM,和C/C++一样通过编译器直接将代码编译成机器代码,然后运行。这无疑是一种直接颠覆Java语言设计的思路,那就是GraalVM Native Image。它通过C语言实现了一个超微缩的运行时组件 —— Substrate VM,基本实现了JVM的各种特性,但足够轻量、可以被轻松内嵌,这就让Java语言和工程摆脱JVM的限制,能够真正意义上实现和C/C++一样的AOT编译。这一方案在经过长时间的优化和积累后,已经拥有非常不错的效果,基本上成为Oracle官方首推的Java AOT解决方案。
Native Image 是一项创新技术,可将 Java 代码编译成独立的本机可执行文件或本机共享库。在构建本机可执行文件期间处理的 Java 字节码包括所有应用程序类、依赖项、第三方依赖库和任何所需的 JDK 类。生成的自包含本机可执行文件特定于不需要 JVM 的每个单独的操作系统和机器体系结构。