参考文档
模板处理
基础使用
安装过程省略,首先加载模板:
$templateProcessor = new TemplateProcessor(ROOT_PATH . 'uploads/template/自动生成模板.docx');
完整保存流程
首先,要进行测试,起码能够写一个完整的demo,以下是我测试时用的demo
$templateProcessor = new TemplateProcessor(ROOT_PATH . 'public/static/自动生成模板.docx');
(new \app\index\model\MyUse())->fillIpAndAddress($templateProcessor); // 这一行内部就是对word进行填充,所有测试代码都可以写在这里
$filename = "test.doc";
$templateProcessor->saveAs($filename); //另存为新word文档,根据模板和变量生成了新的文档
$file = fopen($filename, "rb");//以只读和二进制模式打开文件
Header("Content-type: application/octet-stream"); //告诉浏览器这是一个文件流格式的文件
Header("Accept-Ranges: bytes"); //请求范围的度量单位
Header("Accept-Length: " . filesize($filename)); //Content-Length是指定包含于请求或响应中数据的字节长度
//用来告诉浏览器,文件是可以当做附件被下载,下载后的文件名称为$file_name该变量的值。
Header("Content-Disposition: attachment; filename=$filename");
echo fread($file, filesize($filename)); //读取文件内容并直接输出到浏览器
fclose($file);
exit ();
最基础的替换
模板加载好后,一般的数据,只需要在模板中设置变量名即可替换,如:
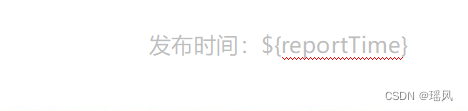
就相当于一个萝卜一个坑,xxx xxx ${firstname},使用时$templateProcessor->setValue('firstname', 'John');即可,非常简单
表格数据替换
首先是保留表头的数据替换:假设无表数据,保留表头,但是数据为空
| 姓名 | 年龄 |
|---|---|
| ${name} | ${age} |
若无数据,保留表头,但是数据为空
其实只需要计算数量,设置数量为0即可:
$templateProcessor->cloneRow('terminalNumber',0);
若有数据,填充
首先是计算数据量,然后按照数据量填充:
$count = count($userInfo);
$templateProcessor->cloneRow('name',$count);
if (is_array($userInfo) && count($userInfo) > 0) {
if (!empty($userInfo)) {
foreach ($userInfoas $key => $value) {
$id = $key + 1;
$templateProcessor->setValue("name#${id}", $value["name"]);
$templateProcessor->setValue("age#${id}", $value["age"]);
}
}
}
循环表格替换
表格替换比较简单,即使是这种类型的表格,也只是往空格里填充数据而已,cloneRow依旧很容易做到
| 用户id | 用户信息 |
| ${userId} | ${userName} |
| ${userAddress} |
但实际需求中,很可能有多个表,如根据查询的用户结果生成多个用户表数据,其中每个用户表数据包含这个用户所选的课程(即不唯一),这样的表结构设计在官方文档中没有找到。
首先确定要用克隆块,
${USER_CLASS}
用户的id为:${userId}
| 所选课程 | 课程类型 |
|---|---|
${class${key}} | ${type${key}} |
${/USER_CLASS}
按照以上模式将word中需要生成多个表格的地方做好标记,稍微解释下为什么要这么做:
(1)使用克隆块,可以根据自己需要生成多个数据,这些数据包含表格,以及表格的额外信息
(2) ${class${key}} 这种方式来作为表中的key,是因为会生成多个表格,如果不再嵌套一个唯一key,那么最终数据每个表都会是一样的
代码如下:
foreach ($userClass as $key => $value) {
$id = $key +1;
$replacements[$id] = ["userId" => $value, "key" => $id];
$classRet = [];// 作用是拼凑最终的二维数组
if (!empty($userClassInfo)) {
foreach ($userClassInfo as $classKey => $class) {
$addressCount++;
$classRet[$key][$classKey ] = [
"class" => $class["class"],
"type" => $class["type"],
];
}
} else {
$templateProcessor->setValue('userId', " ");
}
}
实际上,就是构造一个二维数组:
{
"101":[
{
"1":{
"class":"数学",
"type":"normal"
},
"2":{
"class":"语文",
"type":"normal"
}
}
],
"102":[
{
"1":{
"class":"数学",
"type":"normal"
},
"2":{
"class":"语文",
"type":"normal"
}
}
]
}
这个数组需要包含两层的id,然后就是填充数据:
if (!empty($classRet)) {
foreach ($classRetas $key => $value) {
$id = $key + 1;
$templateProcessor->cloneRow("class" . $id, $locationCount);
foreach ($value as $ipKey => $ipValue) {
$ipId = $ipKey + 1;
$templateProcessor->setValue("class${id}#${ipId}", $ipValue["class"]);
$templateProcessor->setValue("type${id}#${ipId}", $ipValue["type"]);
}
}
}
这样就可以填充了。
注意:
(1)我写的示例都是从我自己的代码修改而来,改后没有测试,主要是表达原理
(2)如果不要代码块,deleteBlock可能不生效,我是用的cloneBlock,数量设置为0,cloneRow设置空数据同理,如果不设置,当无数据时可能变量名会保留在最终生成的word中