<~生~信~交~流~与~合~作~请~关~注~公~众~号@生信探索>
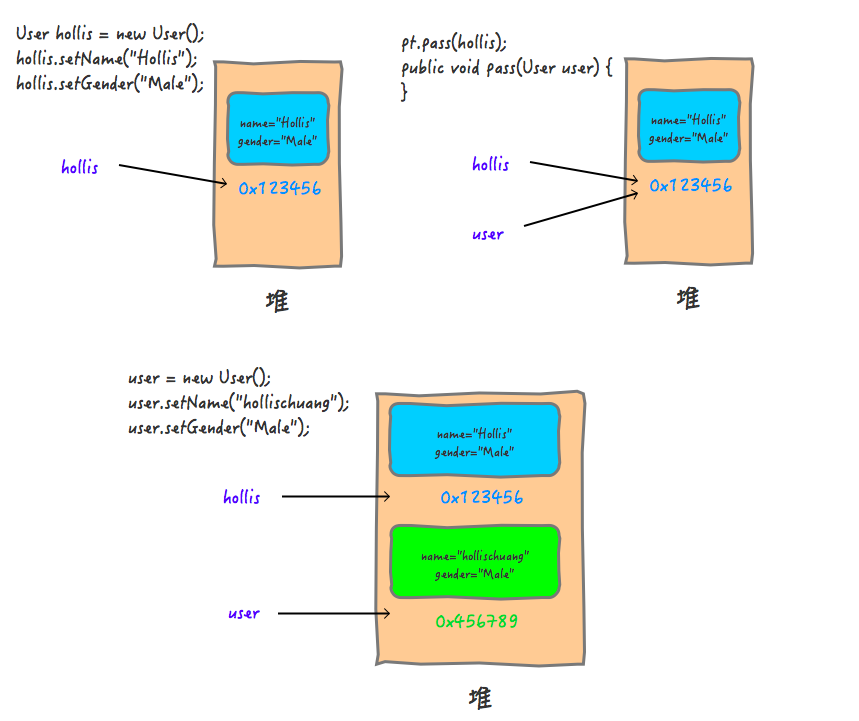
中心极限定律
中心极限定律:当样本样足够大时(n≥30),样本的mean等于总体的mean
例如,对学校的学生身高抽样,100组每组30人,每组的身高均值分别为 ,那么可以画出 的频数图,应该是正态分布的。
一般性结论,即使整体服从不同的分布他们的means也服从正态分布。
For samples of size 30 or more, the sample mean is approximately normally distributed
正态分布
正态分布(Normal distribution),也称“常态分布”,又名高斯分布(Gaussian distribution)。若随机变量X服从一个数学期望为μ、方差为σ2的正态分布,记为N(μ,σ2)。其概率密度函数为正态分布的期望值μ决定了其位置,其标准差σ决定了分布的幅度。当μ = 0,σ = 1时的正态分布是标准正态分布。
Z分布,即标准正态分布,z=(x−μ)/σ,Z值可以查表。
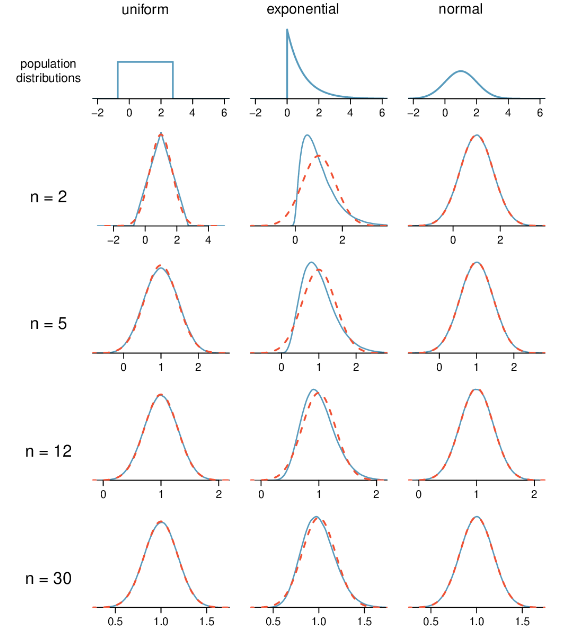
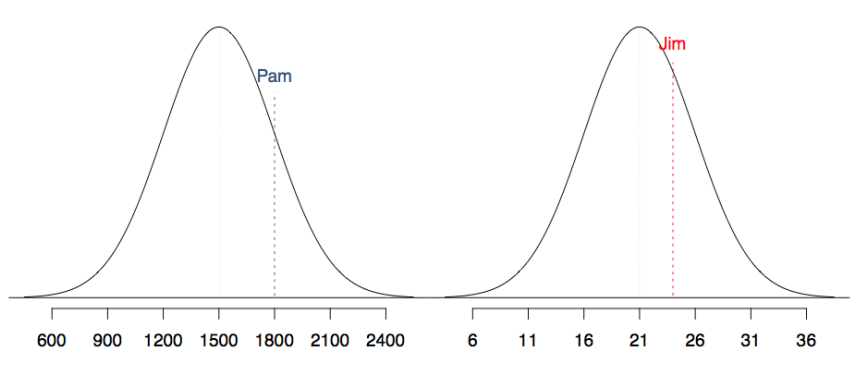
例题:SAT scores are distributed nearly normally with mean 1500 and standard deviation 300. ACT scores are distributed nearly normally with mean 21 and standard deviation 5. A college admissions officer wants to determine which of the two applicants scored better on their standardized test with respect to the other test takers: Pam, who earned an 1800 on her SAT, or Jim, who scored a 24 on his ACT?
解:
Standardizing with Z scores
Since we cannot just compare these two raw scores, we instead compare how many standard deviations beyond the mean each observation is.
-
Pam's score is (1800 - 1500) / 300 = 1 standard deviation above the mean. -
Jim's score is (24 - 21) / 5 = 0.6 standard deviations above the mean.
So Pam is better.
z-score
z-scores are the signed number of standard deviations above the mean that an observation lies, z=(x−μ)/σ
即把数据转换为z分布(标准正态分布)。
-
python
axis=0时对列z-score处理
ddof=1的意思是(自由度)计算标准差中分母上是n-1,默认是n-0,n就是样本数;当axis=0时,n=5
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import zscore
m = np.array([[ 0.3148, 0.0478, 0.6243, 0.4608],
[ 0.7149, 0.0775, 0.6072, 0.9656],
[ 0.6341, 0.1403, 0.9759, 0.4064],
[ 0.5918, 0.6948, 0.904 , 0.3721],
[ 0.0921, 0.2481, 0.1188, 0.1366]])
zscore(m, axis=1, ddof=0)
-
julia
默认对行z-score处理,std计算时默认的分母是n-1,默认对行zscore处理,所以对m转制
using StatsBase
m = [0.3148 0.0478 0.6243 0.4608
0.7149 0.0775 0.6072 0.9656
0.6341 0.1403 0.9759 0.4064
0.5918 0.6948 0.904 0.3721
0.0921 0.2481 0.1188 0.1366]
μ = mean.(eachrow(m'))
σ = std.(eachrow(m'))
z=zscore(m', μ, σ)
z'
-
R
默认对列z-score处理,std计算时默认的分母是n-1
m = matrix(c(0.3148, 0.0478, 0.6243, 0.4608,
0.7149, 0.0775, 0.6072, 0.9656,
0.6341, 0.1403, 0.9759, 0.4064,
0.5918, 0.6948, 0.904 , 0.3721,
0.0921, 0.2481, 0.1188, 0.1366)
,ncol=4,byrow=T)
scale(m)
Reference
https://spot.pcc.edu/math/ahss/ed2/distributionofxbar.html
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1CA411P7bL
https://stats.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_Statistics/Introductory_Statistics_(Shafer_and_Zhang)/06%3A_Sampling_Distributions/6.02%3A_The_Sampling_Distribution_of_the_Sample_Mean
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/141732064
https://baike.baidu.com/item/Z%E5%88%86%E6%95%B0/8268473
https://people.umass.edu/biep540w/pdf/Open%20Intro%20Slides%20-%20Normal%20Distribution.pdf#:~:text=SAT%20scores%20are%20distributed%20nearly%20normally%20with%20mean,Jim%2C%20who%20scored%20a%2024%20on%20his%20ACT%3F
本文由 mdnice 多平台发布