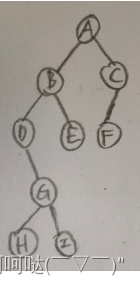
(一)递归实现:

完整代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxSize 100
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct BiNode {
ElemType data;
BiNode* lchild;
BiNode* rchild;
}BiNode, * BiTree;
//构建二叉树
BiNode* Create(BiNode* bt) {
static int i = 0;
char ch;
//string str = "AB#D##C##";
//string str = "124##56##7##3##";
//string str = "ABD#G##E##CF###";
string str = "ABD#GH##I##E##CF###";
ch = str[i++];
if (ch == '#')bt = NULL;//建立一棵空树
else {
bt = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode)); bt->data = ch;//生成一个结点,数据域为ch
bt->lchild = Create(bt->lchild);//递归建立左子树
bt->rchild = Create(bt->rchild);//递归建立右子树
}
return bt;
}
typedef struct {
ElemType data[MaxSize];//存放栈中元素
int top;//栈顶指针
}SqStack;
//(1)初始化
void InitStack(SqStack& S) {
S.top = -1;//初始化栈顶指针
}
//(2)判栈空
bool IsEmpty(SqStack& S) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空
return true;
}
else {//不空
return false;
}
}
//(3)进栈
bool Push(SqStack& S, ElemType data) {
if (S.top == MaxSize - 1) {//栈满,报错
return false;
}
S.data[++S.top] = data;//指针先加1,再加入栈
return true;
}
//(4)出栈
bool Pop(SqStack& S, ElemType &data) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空,报错
return false;
}
data = S.data[S.top--];//先出栈,指针再减1
return true;
}
//(5)读栈顶元素
bool GetTop(SqStack& S, ElemType data) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空,报错
return false;
}
data = S.data[S.top];//先出栈,指针再减1
return true;
}
bool Ancestors(BiNode* root,ElemType x, SqStack &S) {
if (!root) return false;
if (root->data == x) return true;
if (Ancestors(root->lchild, x,S) || Ancestors(root->rchild, x, S)) {
//printf("%c ", root->data);//G D B A
Push(S, root->data);
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main() {
//创建一棵二叉树
BiTree T = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));//创建一颗二叉树
T = Create(T);
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
Ancestors(T, 'I',S);
ElemType ch;
while (!IsEmpty(S)) {
Pop(S, ch);
printf("%c ", ch); // A B D G
}
}
(二)非递归实现:

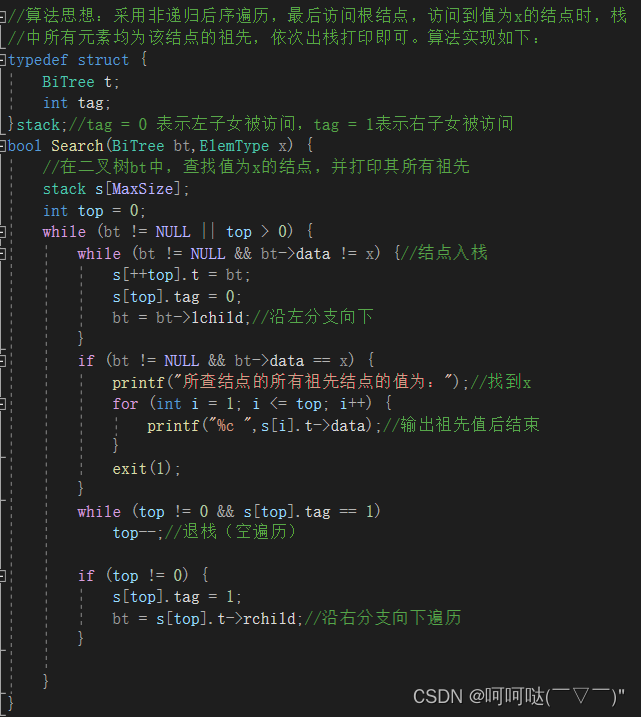
因为查找的过程就是后序遍历的过程,因此使用的栈的深度不超过树的深度
完整的代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxSize 100
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct BiNode {
ElemType data;
BiNode* lchild;
BiNode* rchild;
}BiNode, * BiTree;
//构建二叉树
BiNode* Create(BiNode* bt) {
static int i = 0;
char ch;
//string str = "AB#D##C##";
//string str = "124##56##7##3##";
//string str = "ABD#G##E##CF###";
string str = "ABD#GH##I##E##CF###";
ch = str[i++];
if (ch == '#')bt = NULL;//建立一棵空树
else {
bt = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode)); bt->data = ch;//生成一个结点,数据域为ch
bt->lchild = Create(bt->lchild);//递归建立左子树
bt->rchild = Create(bt->rchild);//递归建立右子树
}
return bt;
}
//算法思想:采用非递归后序遍历,最后访问根结点,访问到值为x的结点时,栈
//中所有元素均为该结点的祖先,依次出栈打印即可。算法实现如下:
typedef struct {
BiTree t;
int tag;
}stack;//tag = 0 表示左子女被访问,tag = 1表示右子女被访问
bool Search(BiTree bt,ElemType x) {
//在二叉树bt中,查找值为x的结点,并打印其所有祖先
stack s[MaxSize];
int top = 0;
while (bt != NULL || top > 0) {
while (bt != NULL && bt->data != x) {//结点入栈
s[++top].t = bt;
s[top].tag = 0;
bt = bt->lchild;//沿左分支向下
}
if (bt != NULL && bt->data == x) {
printf("所查结点的所有祖先结点的值为:\n");//找到x
for (int i = 1; i <= top; i++) {
printf("%c ",s[i].t->data);//输出祖先值后结束
}
exit(1);
}
while (top != 0 && s[top].tag == 1)
top--;//退栈(空遍历)
if (top != 0) {
s[top].tag = 1;
bt = s[top].t->rchild;//沿右分支向下遍历
}
}
}
int main() {
//创建一棵二叉树
BiTree bt = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));//创建一颗二叉树
bt = Create(bt);
Search(bt, 'I');
}



![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django高校车辆管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/24fe2d14d93847bebb84d2cc2a1b075a.png)