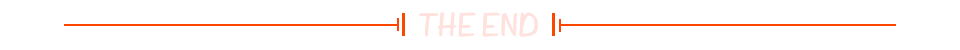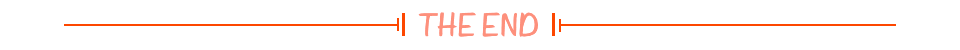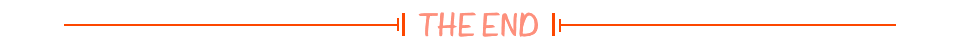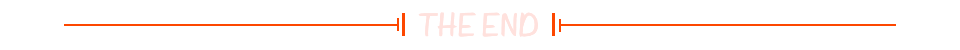lambda表达式是在C++11中引入的,它们可以嵌套在其它函数甚至函数调用语句中,C++11中lambda表达式的使用参考:https://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/52653313
lambda表达式语法如下:除capture和body是必须的,其它均是可选的
[capture] (params) mutable exception attribute -> return-type { body }这里介绍下C++14中对lambda表达式新增加的features:
1.generic lambda:lambda表达式与auto关键字组合,将auto用作参数类型,以下为测试代码:
namespace {
//void print_elements(auto& C) // windows need to c++20
template<typename T>
void print_elements(const T& C)
{
for (const auto& e : C)
std::cout << e << " ";
std::cout << "\n";
}
}
int test_lambda_14_1()
{
// reference: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/generalized-lambda-expressions-c14/
/* Under the hood, the C++ implementation uses the closure type’s operator() to overload a template function
struct sum {
template<typename T1, typename T2>
auto operator()(T1 a, T2 b) const { return (a + b); }
};
*/
auto sum = [](auto a, auto b) {
return (a + b);
};
std::cout << "int sum:" << sum(10, 20) << "\n";
std::cout << "float sum:" << sum(1.2f, 2.3f) << "\n";
std::cout << "float sum:" << sum(10, 1.5f) << "\n";
std::cout << "string sum:" << sum(std::string("csdn addr:"), std::string("https://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun")) << "\n";
auto greater = [](auto a, auto b) -> bool {
return (a > b);
};
std::vector<int> vi = { 1, 4, 2, 6 };
std::vector<float> vf = { 4.62f, 161.3f, 62.26f, 13.4f };
std::vector<std::string> vs = { "Tom", "Harry", "Ram", "Shyam" };
std::sort(vi.begin(), vi.end(), greater);
std::sort(vf.begin(), vf.end(), greater);
std::sort(vs.begin(), vs.end(), greater);
print_elements(vi);
print_elements(vf);
print_elements(vs);
std::vector<std::vector<int>> v = { {7, 8}, {1, 2}, {3, 7}, {4, 5} };
std::sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [](std::vector<int>& a, std::vector<int>& b) {
return (a[1] < b[1]);
});
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < v[0].size(); ++j) {
std::cout << v[i][j] << " ";
}
std::cout << "\n";
}
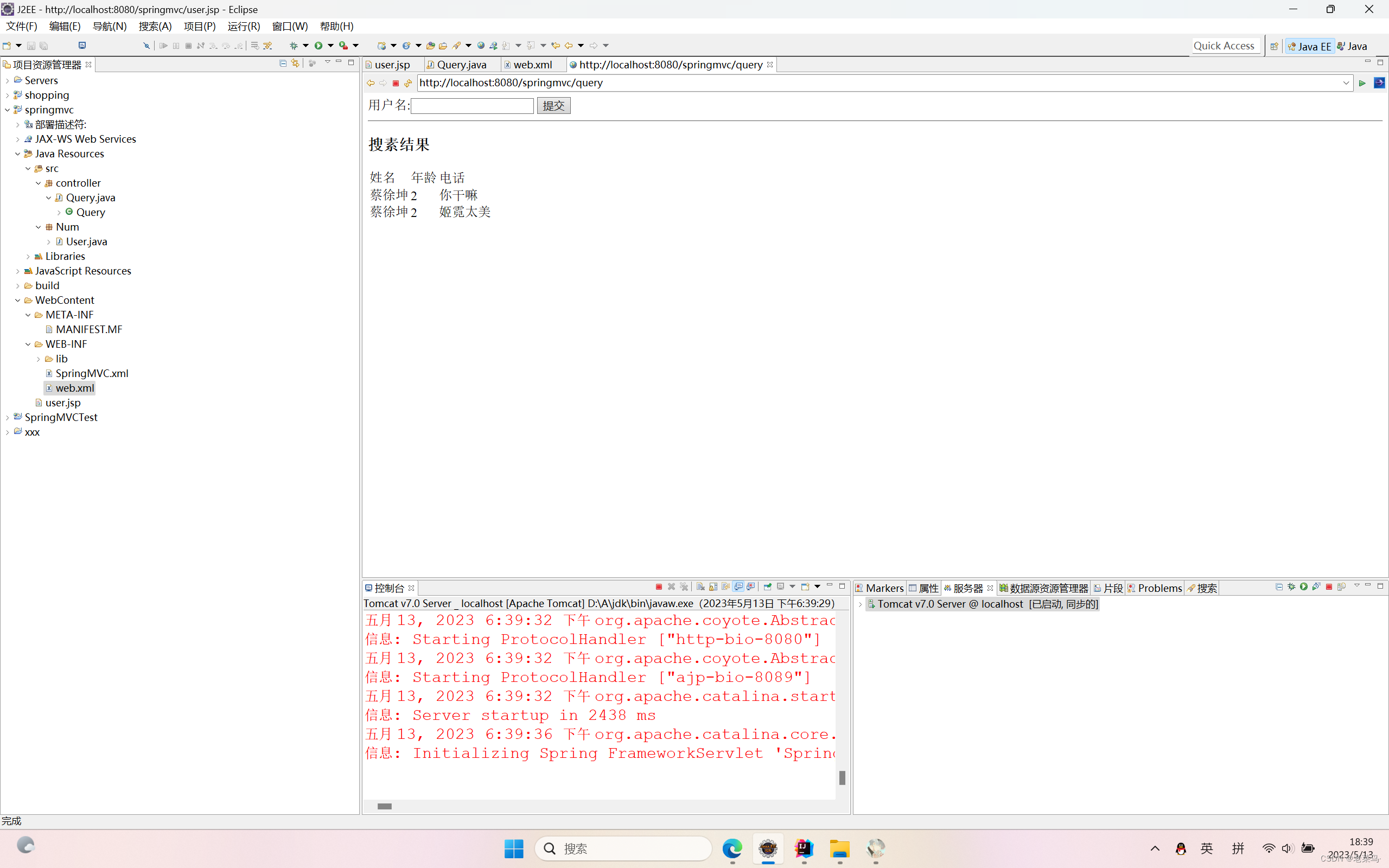
return 0;
}执行结果如下图所示:
2.capture initializers:允许创建使用任意表达式初始化captures。初始化表达式在创建lambda时计算,而不是在调用时,以下为测试代码:
namespace { int factory(int i) { return i * 10; } }
int test_lambda_14_2()
{
// reference: https://github.com/AnthonyCalandra/modern-cpp-features#lambda-capture-initializers
auto f = [x = factory(2)] { return x; };
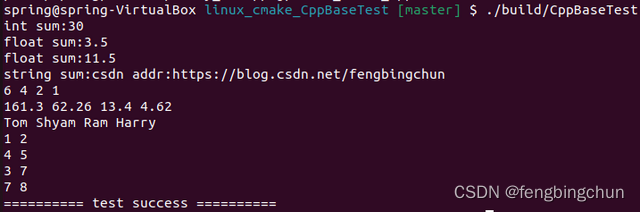
std::cout << "f:" << f() << "\n";
auto generator = [x = 0]() mutable {
// this would not compile without 'mutable' as we are modifying x on each call
return x++;
};
auto a = generator();
auto b = generator();
auto c = generator();
std::cout << "a:" << a << ",b:" << b << ",c:" << c << "\n";
auto p = std::make_unique<int>(1);
//auto task1 = [=] { *p = 5; }; // ERROR: std::unique_ptr cannot be copied
auto task2 = [p = std::move(p)] { *p = 5; return *p; }; // OK: p is move-constructed into the closure object
// the original p is empty after task2 is created
if (!p)
std::cout << "p is empty" << "\n";
std::cout << "task2:" << task2() << "\n";
auto x = 2;
auto f2 = [&r = x, x = x * 10] {
++r;
return r + x;
};
std::cout << "f2:" << f2() << ",x:" << x << "\n";
return 0;
}执行结果如下图所示:
GitHub:https://github.com/fengbingchun/Messy_Test