今日内容
零、 复习昨日
一、数据库连接池
二、反射
三、封装DBUtil
零、 复习昨日
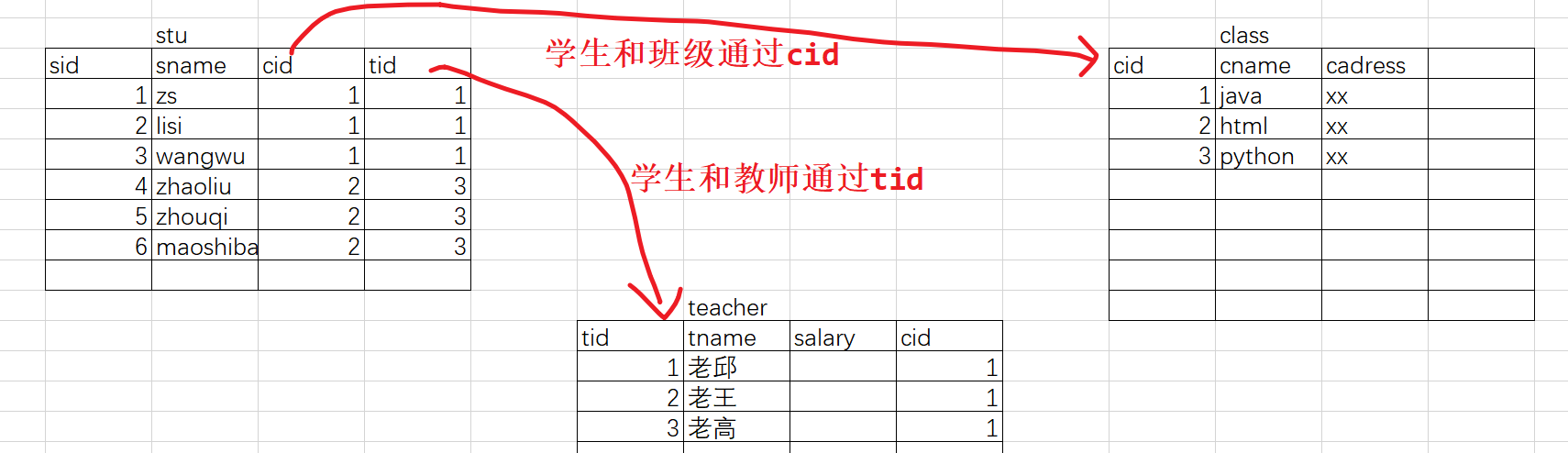
三表关联
create table teacher ( tid int, tname varchar(10) ) insert into teacher values(1,'老邱'); insert into teacher values(2,'老王'); -- 三表关联 -- 查询学生以及班级信息 select * from stu s left join class c on s.cid = c.cid -- 查询学生以及班级,以及对应教室信息 select * from stu s left join class c on s.cid = c.cid left join teacher t on s.tid = t.tid -- 内连接 select * from stu s,class c,teacher t where s.cid = c.cid and s.tid = t.tid
一、数据库连接池
目前数据库连接是使用是建立连接,用完直接关闭连接.即需要不断创建和销毁连接.就会消耗系统资源.借鉴线程池的思想,设计出
数据库连接池.在程序初始时,预先创建好指定数量的数据库连接对象,存储连接池。需要用时就去取,用完就放回去即可。就会不会频繁创建和销毁,从而节省系统资源。
使用上的线程池有很多
- druid (德鲁伊)
- c3p0
- dbcp
- …
1.1 Druid数据库连接池
Druid是阿里开源技术,性能很好
使用步骤
导入依赖druid.jar包
创建一个db.properties
# 必须是driverClass,不是jdbc.driverClass,否则创建DataSource失败 driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/database?useSSL=false username=root password=123456 # ----- 加入druid的一些连接配置 #<!-- 初始化连接 --> initialSize=10 #最大连接数量 maxActive=50 #<!-- 最小空闲连接 --> minIdle=5 #<!-- 超时等待时间以毫秒为单位 60000毫秒/1000等于60秒 --> maxWait=5000修改之前的DBUtil
public class DBUtil { // 创建Properties类对象,专用于操作properties文件 private static final Properties properties = new Properties(); // 声明Druid连接池的连接池对象 // 数据连接,一般称作数据源 dataSource private static DruidDataSource dataSource;static { try { InputStream inputStream = DBUtil.class.getResourceAsStream("/db.properties"); properties.load(inputStream); // 不需要由我们加载驱动 // 需要给dataSource赋值 dataSource = (DruidDataSource) DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("加载驱动异常!!" ); e.printStackTrace( ); } } public static Connection getConnection() { Connection conn = null; try{ // 不需要我们获得连接 // 而是通过Druid获得 conn = dataSource.getConnection(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("获得连接出异常!!!" ); e.printStackTrace(); } return conn; } // 后续正常...跟之前一样}
开始使用
跟之前一样使用
二、反射
JAVA反射(reflect)机制是在
运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法,对于任意一个对 象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性这种
动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为java 语言的反射机制。反射是在程序运行过程中拿到
类的字节码文件,进而获得类中的属性,方法等.
2.1 获得类的字节码文件
- Object类的方法 getClass()
- 类的静态属性 Xxx.class
- Class类的静态方法Class.forName(“xxx”)
/**
* 演示获取字节码文件
*/
public static void getClassFile() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 方式1
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.qf.model.User");
// 方式2
Class<User> clazz2 = User.class;
// 方式3
User user = new User( );
Class<? extends User> clazz3 = user.getClass( );
if (clazz.equals(clazz2) && clazz2.equals(clazz3)) {
System.out.println("是同一个字节码文件" );
} else {
System.out.println("不是" );
}
}
2.2 获得并设置属性(Field)
| API |
|---|
 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Class<User> clazz = User.class;
/**
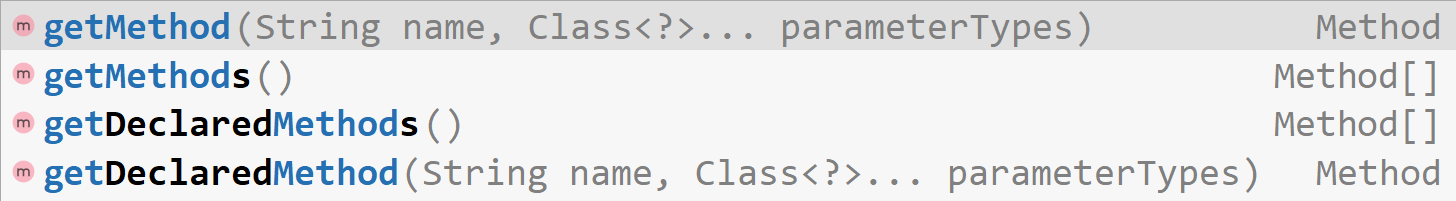
* getField(String name) 只能获得公开public的字段
* getDeclaredField(String name) 能获得声明的字段
*/
Field id = clazz.getField("id");
Field id2 = clazz.getDeclaredField("id");
/**
* getFields() 只能获得公开public的所有字段
* getDeclaredFields() 能获得声明的所有字段
*/
Field[] fields = clazz.getFields( );
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(fields ) );
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields( );
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(declaredFields ) );
/**
* 同Field属性对象,可以对象属性做各种操作
*/
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("username");
// 获得访问修饰符
System.out.println(field.getModifiers( ));
// 获得数据类型
System.out.println(field.getType() );
// 获得属性名
System.out.println(field.getName() );
// 对于私有属性/方法不能直接操作,需要设置访问权限
field.setAccessible(true);
// 获得属性值
User user = new User( );
user.setUsername("zs");
// get(对象) 获得指定对象该属性的值
Object value = field.get(user);
System.out.println(value );
// 设置属性值,参数1是指定对象 参数2是属性值
// 给指定对象的该属性设置指定值
field.set(user,"ls");
System.out.println(user );
}
2.3 获得并设置方法(Method)
| API |
|---|
 |
/**
* 获得字节码中的方法
*/
public static void getAndSeMethod() throws Exception {
Class<User> clazz = User.class;
// 方法有重载,需要通过参数来确定获得哪个方法
Method m1 = clazz.getMethod("m1"); // 获得无参的m1方法
Method m1_ = clazz.getMethod("m1",int.class); // 获得有参的m1(int)方法
// 获得关于方法的所有信息
int count = m1.getParameterCount( );// 参数个数
int count_ = m1_.getParameterCount( );// 参数个数
// 操作方法,让方法执行
// 参数1: 哪个对象的该方法执行
// 参数2: 该方法执行时的参数
Object ret = m1.invoke(new User( ));
System.out.println("m1()执行后的返回值:" + ret );
m1_.invoke(new User(),222);
}
2.4 获得并设置构造方法(Constructor)
| API |
|---|
 |
/**
* 获得字节码中的构造方法
*/
public static void getAndSeConstructor() throws Exception {
Class<User> clazz = User.class;
// 通过参数来获得有参还是无参构造
Constructor<User> constructor = clazz.getConstructor( );
// 构造方法执行,创建对象
User user = constructor.newInstance( );
System.out.println(user );
// 创建字节码的对象,还有另外方法
// 可以通过字节码,直接创建
User user1 = clazz.newInstance( );
}
三、使用反射封装DBUtil
能利用反射封装DBUtil的前提是,一定是完全按照ORM设计的类.
即 表名即类名,字段名即属性名
package com.qf.util;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* --- 天道酬勤 ---
*
* @author QiuShiju
* @desc
*/
public class DBUtil {
// 创建Properties类对象,专用于操作properties文件
private static final Properties properties = new Properties( );
// 声明Druid连接池的连接池对象
// 数据连接,一般称作数据源 dataSource
private static DruidDataSource dataSource;
static {
try {
InputStream inputStream = DBUtil.class.getResourceAsStream("/jdbc.properties");
properties.load(inputStream);
// 不需要由我们加载驱动
// 需要给dataSource赋值
dataSource = (DruidDataSource) DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("加载驱动异常!!");
e.printStackTrace( );
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() {
Connection conn = null;
try {
// 不需要我们获得连接
// 而是通过Druid获得
conn = dataSource.getConnection( );
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("获得连接出异常!!!");
e.printStackTrace( );
}
return conn;
}
/**
* 关闭所有流
*/
public static void closeAll(Connection conn, Statement s) {
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close( );
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace( );
}
}
if (s != null) {
try {
s.close( );
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace( );
}
}
}
public static void closeAll(Connection conn, Statement s, ResultSet rs) {
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close( );
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace( );
}
}
if (s != null) {
try {
s.close( );
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace( );
}
}
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close( );
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace( );
}
}
}
/**
* 封装查询方法,返回一个对象
* 参数1 执行查询的SQL,预处理的,条件用?占位
* select * from tb_user where id = ? and username = ? and password = ?
* 参数2 结果要封装的类
* 参数3 给?赋值,不定长参数,是数组
* 1,admin,123456
*/
public static <T> T selectOne(String sql, Class<T> t, Object... args) {
Connection conn = getConnection( );
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
T target = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; args != null && i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery( );
/**
* 创建对象
* 从数据库取出数据,并设置对象属性
*/
while (rs.next( )) {
target = t.newInstance( );
Field[] declaredFields = t.getDeclaredFields( );
for (int i = 0; i < declaredFields.length; i++) {
Field field = declaredFields[i];
Object value = rs.getObject(field.getName( ));
if(value == null){
continue;
}
// 破解私有
field.setAccessible(true);
// 给对象的该字段赋值
field.set(target, value);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace( );
} finally {
closeAll(conn, ps, rs);
}
return target;
}
public static <T> List<T> selectAll(String sql, Class<T> t, Object... args) {
Connection conn = getConnection( );
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
T target = null;
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<>( );
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; args != null && i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery( );
/**
* 创建对象
* 从数据库取出数据,并设置对象属性
*/
while (rs.next( )) {
target = t.newInstance( );
Field[] declaredFields = t.getDeclaredFields( );
for (int i = 0; i < declaredFields.length; i++) {
Field field = declaredFields[i];
Object value = rs.getObject(field.getName( ));
if(value == null){
continue;
}
// 破解私有
field.setAccessible(true);
// 给对象的该字段赋值
field.set(target, value);
}
list.add(target);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace( );
} finally {
closeAll(conn, ps, rs);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 增删改方法一样
*/
public static boolean update(String sql, Object... args) {
Connection conn = getConnection( );
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int num = 0;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; args != null && i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
num = ps.executeUpdate( );
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace( );
} finally {
closeAll(conn, ps);
}
return num > 0 ? true : false;
}
}
测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
User user = DBUtil.selectOne("select * from tb_user where id = ?", User.class, 3);
System.out.println(user );
// List<User> list = DBUtil.selectAll("select * from tb_user", User.class);
// for (User user : list) {
// System.out.println(user );
// }
//
// List<Goods> goods = DBUtil.selectAll("select * from tb_goods", Goods.class);
// for (Goods good : goods) {
// System.out.println(good );
// }
// int num = DBUtil.update("insert into tb_user (username,password,phone) values (?,?,?)", "666", "666", "666");
// int num2 = DBUtil.update("update tb_user set username = ? where id = ?", "六六六", 8);
// int num2 = DBUtil.update("delete from tb_user where id = ?", 8);
// System.out.println(num2);
}