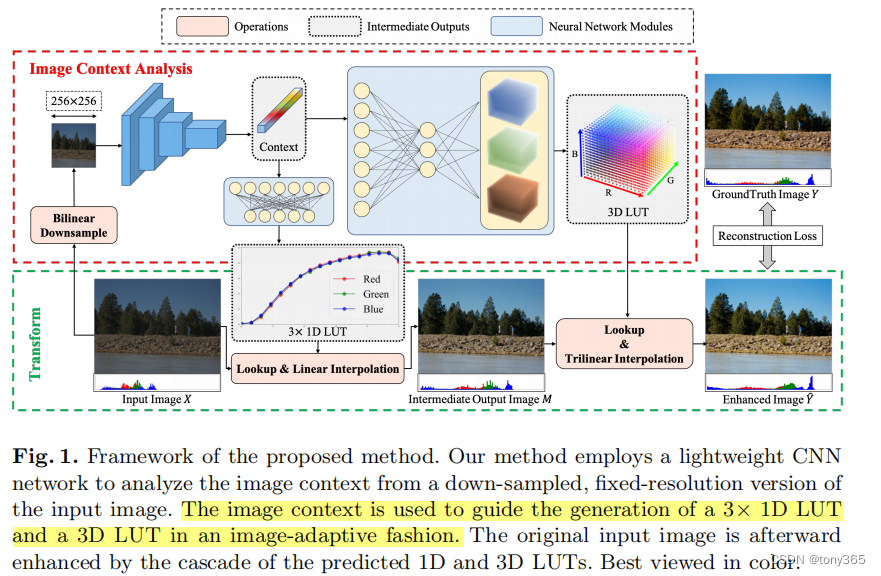
树中每个节点都有一个值,用下标从 0 开始、长度为 n 的整数数组 cost 表示,其中 cost[i] 是第 i + 1 个节点的值。每次操作,你可以将树中 任意 节点的值 增加 1 。你可以执行操作 任意 次。
你的目标是让根到每一个 叶子结点 的路径值相等。请你返回 最少 需要执行增加操作多少次。
注意:
- 满二叉树 指的是一棵树,它满足树中除了叶子节点外每个节点都恰好有 2 个节点,且所有叶子节点距离根节点距离相同。
- 路径值 指的是路径上所有节点的值之和。
示例 1:
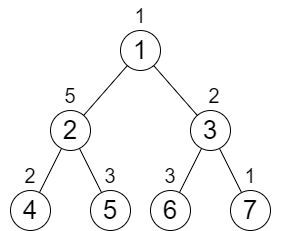
输入:n = 7, cost = [1,5,2,2,3,3,1] 输出:6 解释:我们执行以下的增加操作: - 将节点 4 的值增加一次。 - 将节点 3 的值增加三次。 - 将节点 7 的值增加两次。 从根到叶子的每一条路径值都为 9 。 总共增加次数为 1 + 3 + 2 = 6 。 这是最小的答案。
示例 2:
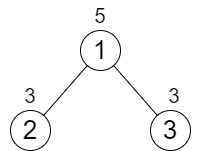
输入:n = 3, cost = [5,3,3] 输出:0 解释:两条路径已经有相等的路径值,所以不需要执行任何增加操作。
提示:
3 <= n <= 105n + 1是2的幂cost.length == n1 <= cost[i] <= 104
通过次数
3,343
提交次数
5,075
请问您在哪类招聘中遇到此题?
社招
校招
实习
未遇到
贡献者
相关企业
相关标签
隐藏提示1
The path from the root to a leaf that has the maximum cost should not be modified.
隐藏提示2
The optimal way is to increase all other paths to make their costs equal to the path with maximum cost.
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxSum;
int maxPathSum(int root, int n, vector<int>& cost) {
if (root * 2 > n) {
maxSum[root -1] = cost[root -1];
return cost[root -1];
}
if (maxSum[root - 1] != 0) return maxSum[root - 1];
int maxLeft = maxPathSum(root * 2, n, cost);
int maxRight = maxPathSum(root * 2 + 1, n, cost);
maxSum[root -1] = cost[root - 1] + max(maxLeft, maxRight);
return maxSum[root -1];
}
int minIncrements(int n, vector<int>& cost) {
maxSum.resize(n, 0);
maxSum[0] = maxPathSum(1, n, cost);
queue<vector<int>> q;
q.push({1, cost[0]});
int maxV = maxSum[0];
int ans = 0;
while(!q.empty()) {
auto top = q.front(); q.pop();
int idx = top[0];
int curSum = top[1];
if (2 * idx > n) continue;
if (curSum + maxSum[2 * idx - 1] == maxV) {
q.push({2 * idx, curSum + cost[2 * idx -1]});
}
else {
int tmp = (maxV - curSum - maxSum[2 * idx - 1]);
ans += tmp;
q.push({2 * idx, curSum + cost[2 * idx -1] + tmp});
}
if (curSum + maxSum[2 * idx] == maxV) {
q.push({2 * idx + 1, curSum + cost[2 * idx]});
}
else {
int tmp2 = (maxV - curSum - maxSum[2 * idx]);
ans += tmp2;
q.push({2 * idx + 1, curSum + cost[2 * idx] + tmp2});
}
}
return ans;
}
};