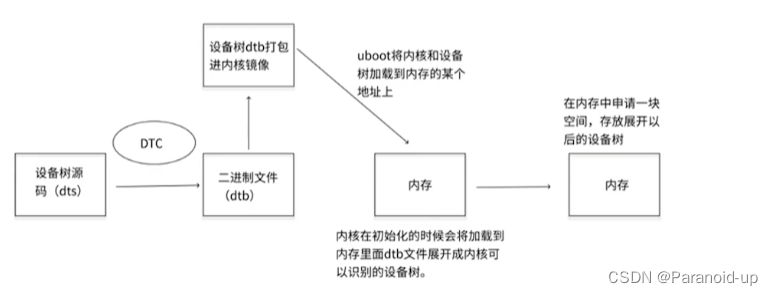
dtb展开成device_node
文章目录
- dtb展开成device_node
- 设备树是如何传递给内核的?
- 设备树相关结构体
- 举例
- of操作函数
- 与查找节点有关的 OF 函数
- 1、of_find_node_by_name 函数
- 2、of_find_node_by_type 函数
- 3、of_find_compatible_node 函数
- 4、of_find_matching_node_and_match 函数
- 5、of_find_node_by_path 函数
- 查找父/子节点的 OF 函数
- 1、of_get_parent 函数
- 2、of_get_next_child 函数
- 提取属性值的 OF 函数
- 1、of_find_property 函数
- 2、of_property_count_elems_of_size 函数
- 3、of_property_read_u32_index 函数
- 4、 of_property_read_u8_array 函数
- 5、of_property_read_u8 函数 of_property_read_u16 函数 of_property_read_u32 函数 of_property_read_u64 函数
- 6、 of_property_read_string 函数
- 7、of_n_addr_cells 函数
- 8、of_n_size_cells 函数
- 其他常用的 OF 函数
- 1、of_device_is_compatible 函数
- 2、of_get_address 函数
- 3、of_translate_address 函数
- 4、 of_address_to_resource 函数
- 5、of_iomap 函数
- IMX6ULL内核是如何展开设备树为内核可以识别的device_node
- setup_arch(&command_line);
- boot_command_line
- setup_machine_fdt
- early_fixmap_init
- unflatten_device_tree
设备树是如何传递给内核的?
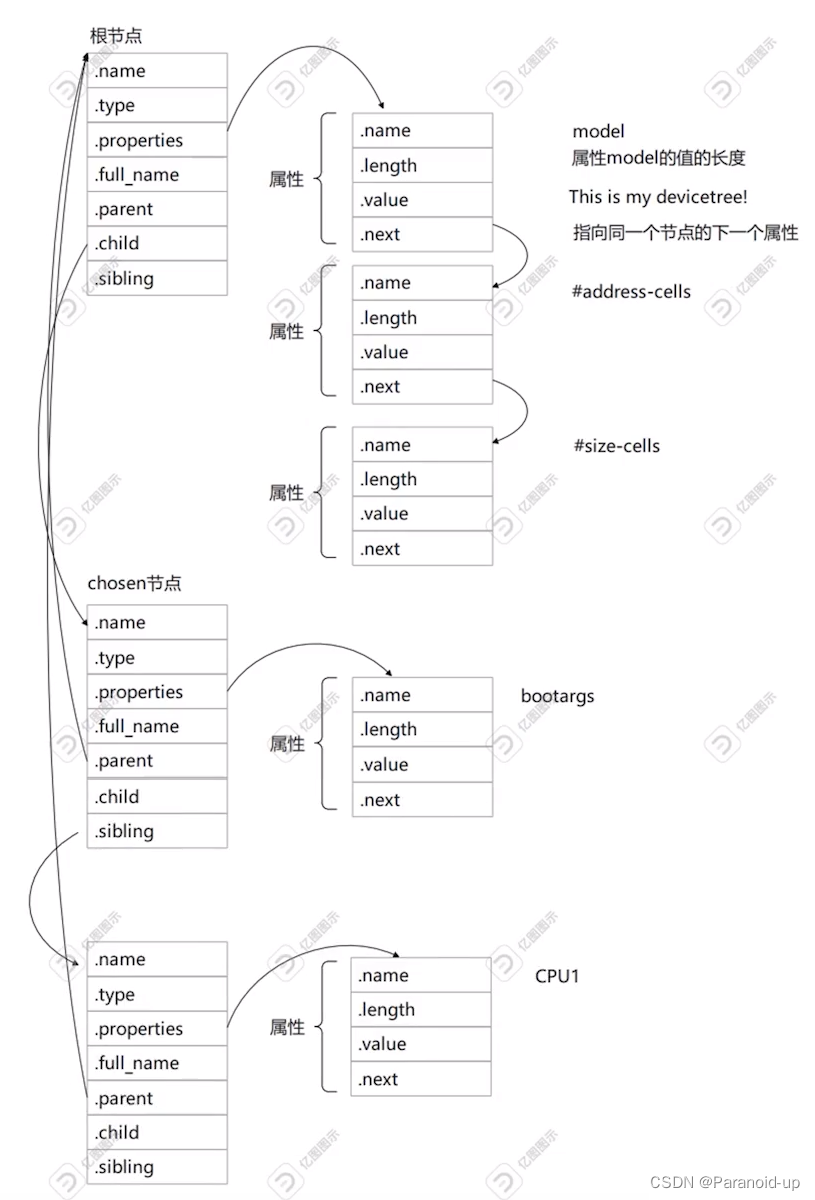
设备树相关结构体
device_node结构体
device_node结构体定义在include/linux/of.h头文件当中。
struct device_node {
const char *name; // 节点名称
const char *type; // 节点类型
phandle phandle; // 节点句柄
const char *full_name; // 节点全名
struct fwnode_handle fwnode;
struct property *properties; // 属性
struct property *deadprops; /* removed properties */
struct device_node *parent; // 父节点
struct device_node *child; // 子节点
struct device_node *sibling; // 兄弟节点
struct kobject kobj; // 内核对象
unsigned long _flags; // 节点标志
void *data; // 数据
#if defined(CONFIG_SPARC)
const char *path_component_name; // 路径组件名称
unsigned int unique_id; // 唯一ID
struct of_irq_controller *irq_trans; // 中断控制器
#endif
};
property结构体
property结构体定义在include/linux/of.h头文件当中。
struct property {
char *name; // 属性名称
int length; // 属性长度
void *value; // 属性值
struct property *next; // 下一个属性
unsigned long _flags; // 属性标志
unsigned int unique_id; // 属性唯一ID
struct bin_attribute attr; // 二进制属性
};
举例
下面设备树内置展开后如下
/ {
model = "this is my devicethree!";
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
chosen {
bootargs = "root=/dev/nfs rw nfsroot=192.168.1.1 console=ttyS0,115200";
};
cpu: cpu@1 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a35","arm,armv8";
reg = <0x0 0x1>;
};
of操作函数
与查找节点有关的 OF 函数
1、of_find_node_by_name 函数
struct device_node *of_find_node_by_name(struct device_node *from,
const char *name);
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
of_find_node_by_name 函数通过节点名字查找指定的节点,函数原型如下:
from:开始查找的节点,如果为 NULL 表示从根节点开始查找整个设备树。
name:要查找的节点名字。
返回值:找到的节点,如果为NULL 表示查找失败。
2、of_find_node_by_type 函数
of_find_node_by_type 函数通过 device_type 属性查找指定的节点,函数原型如下:
struct device_node *of_find_node_by_type(struct device_node *from, const char *type)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
from:开始查找的节点,如果为 NULL 表示从根节点开始查找整个设备树。
type:要查找的节点对应的 type 字符串,也就是 device_type 属性值。
返回值:找到的节点,如果为NULL 表示查找失败。
3、of_find_compatible_node 函数
of_find_compatible_node 函数根据 device_type 和 compatible 这两个属性查找指定的节点,
函数原型如下:
struct device_node *of_find_compatible_node(struct device_node *from,
const char *type,
const char *compatible)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
from:开始查找的节点,如果为 NULL 表示从根节点开始查找整个设备树。
type:要查找的节点对应的 type 字符串,也就是 device_type 属性值,可以为NULL,表示
忽略掉 device_type 属性。
compatible:要查找的节点所对应的 compatible 属性列表。
返回值:找到的节点,如果为NULL 表示查找失败
4、of_find_matching_node_and_match 函数
of_find_matching_node_and_match 函数通过 of_device_id 匹配表来查找指定的节点,函数原
型如下:
struct device_node *of_find_matching_node_and_match(struct device_node *from,
const struct of_device_id *matches, const struct of_device_id **match)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
from:开始查找的节点,如果为 NULL 表示从根节点开始查找整个设备树。
matches:of_device_id 匹配表,也就是在此匹配表里面查找节点。
match:找到的匹配的 of_device_id。
返回值:找到的节点,如果为NULL 表示查找失败
5、of_find_node_by_path 函数
of_find_node_by_path 函数通过路径来查找指定的节点,函数原型如下:
inline struct device_node *of_find_node_by_path(const char *path)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
path:带有全路径的节点名,可以使用节点的别名,比如“/backlight”就是 backlight 这个节点的全路径。
返回值:找到的节点,如果为NULL 表示查找失败
查找父/子节点的 OF 函数
1、of_get_parent 函数
of_get_parent 函数用于获取指定节点的父节点(如果有父节点的话),函数原型如下:
struct device_node *of_get_parent(const struct device_node *node)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
node:父节点。
返回值:找到的父节点。
2、of_get_next_child 函数
of_get_next_child 函数用迭代的方式查找子节点,函数原型如下:
struct device_node *of_get_next_child(const struct device_node *node,
struct device_node *prev)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
node:要查找的父节点的节点。
prev:前一个子节点,也就是从哪一个子节点开始迭代的查找下一个子节点。可以设置为
NULL,表示从第一个子节点开始。
返回值:找到的下一个子节点。
提取属性值的 OF 函数
1、of_find_property 函数
of_find_property 函数用于查找指定的属性,函数原型如下:
property *of_find_property(const struct device_node *np,
const char *name,
int *lenp)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
np:设备节点。
name: 属性名字。
lenp:属性值的字节数
返回值:找到的属性。
2、of_property_count_elems_of_size 函数
of_property_count_elems_of_size 函数用于获取属性中元素的数量,比如 reg 属性值是一个
数组,那么使用此函数可以获取到这个数组的大小,此函数原型如下:
int of_property_count_elems_of_size(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
int elem_size)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
np:设备节点。
proname: 需要统计元素数量的属性名字。
elem_size:元素长度。
返回值:得到的属性元素数量。
3、of_property_read_u32_index 函数
of_property_read_u32_index 函数用于从属性中获取指定标号的 u32 类型数据值(无符号 32
位),比如某个属性有多个 u32 类型的值,那么就可以使用此函数来获取指定标号的数据值,此
函数原型如下:
int of_property_read_u32_index(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u32 index,
u32 *out_value)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
np:设备节点。
proname: 要读取的属性名字。
index:要读取的值标号。
out_value:读取到的值
返回值:0 读取成功,负值,读取失败,-EINVAL 表示属性不存在,-ENODATA 表示没有
要读取的数据,-EOVERFLOW 表示属性值列表太小。
4、 of_property_read_u8_array 函数
of_property_read_u16_array 函数
of_property_read_u32_array 函数
of_property_read_u64_array 函数
这 4 个函数分别是读取属性中 u8、u16、u32 和 u64 类型的数组数据,比如大多数的 reg 属
性都是数组数据,可以使用这 4 个函数一次读取出 reg 属性中的所有数据。这四个函数的原型
如下:
int of_property_read_u8_array(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u8 *out_values,
size_t sz)
int of_property_read_u16_array(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u16 *out_values,
size_t sz)
int of_property_read_u32_array(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u32 *out_values,
size_t sz)
int of_property_read_u64_array(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u64 *out_values,
size_t sz)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
np:设备节点。
proname: 要读取的属性名字。
out_value:读取到的数组值,分别为 u8、u16、u32 和 u64。
sz:要读取的数组元素数量。
返回值:0,读取成功,负值,读取失败,-EINVAL 表示属性不存在,-ENODATA 表示没
有要读取的数据,-EOVERFLOW 表示属性值列表太小。
5、of_property_read_u8 函数 of_property_read_u16 函数 of_property_read_u32 函数 of_property_read_u64 函数
有些属性只有一个整形值,这四个函数就是用于读取这种只有一个整形值的属性,分别用
于读取 u8、u16、u32 和u64 类型属性值,函数原型如下:
int of_property_read_u8(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u8 *out_value)
int of_property_read_u16(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u16 *out_value)
int of_property_read_u32(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u32 *out_value)
int of_property_read_u64(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u64 *out_value)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
np:设备节点。
proname: 要读取的属性名字。
out_value:读取到的数组值。
返回值:0,读取成功,负值,读取失败,-EINVAL 表示属性不存在,-ENODATA 表示没
有要读取的数据,-EOVERFLOW 表示属性值列表太小。
6、 of_property_read_string 函数
of_property_read_string 函数用于读取属性中字符串值,函数原型如下:
int of_property_read_string(struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
const char **out_string)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
np:设备节点。
proname: 要读取的属性名字。
out_string:读取到的字符串值。
返回值:0,读取成功,负值,读取失败。
7、of_n_addr_cells 函数
of_n_addr_cells 函数用于获取#address-cells 属性值,函数原型如下:
int of_n_addr_cells(struct device_node *np)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
np:设备节点。
返回值:获取到的#address-cells 属性值。
8、of_n_size_cells 函数
of_size_cells 函数用于获取#size-cells 属性值,函数原型如下:
int of_n_size_cells(struct device_node *np)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
np:设备节点。
返回值:获取到的#size-cells 属性值。
其他常用的 OF 函数
1、of_device_is_compatible 函数
of_device_is_compatible 函数用于查看节点的 compatible 属性是否有包含 compat 指定的字
符串,也就是检查设备节点的兼容性,函数原型如下:
int of_device_is_compatible(const struct device_node *device,
const char *compat)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
device:设备节点。
compat:要查看的字符串。
返回值:0,节点的 compatible 属性中不包含 compat 指定的字符串;正数,节点的 compatible
属性中包含compat 指定的字符串。
2、of_get_address 函数
of_get_address 函数用于获取地址相关属性,主要是“reg”或者“assigned-addresses”属性
值,函数原型如下:
const be32 *of_get_address(struct device_node *dev,
int index,
u64 *size,
unsigned int *flags)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
dev:设备节点。
index:要读取的地址标号。
size:地址长度。
flags:参数,比如 IORESOURCE_IO、IORESOURCE_MEM 等
返回值:读取到的地址数据首地址,为NULL 的话表示读取失败。
3、of_translate_address 函数
of_translate_address 函数负责将从设备树读取到的地址转换为物理地址,函数原型如下:
u64 of_translate_address(struct device_node *dev,
const be32 *in_addr)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
dev:设备节点。
in_addr:要转换的地址。
返回值:得到的物理地址,如果为OF_BAD_ADDR 的话表示转换失败。
4、 of_address_to_resource 函数
函数看名字像是从设备树里面提取资源值,但是本质上就是将 reg 属性值,然后将其转换为 resource 结构体类型,函数原型如下所示
int of_address_to_resource(struct device_node *dev,
int index,
struct resource *r)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
dev:设备节点。
index:地址资源标号。
r:得到的 resource 类型的资源值。
返回值:0,成功;负值,失败。
5、of_iomap 函数
of_iomap 函数用于直接内存映射,以前我们会通过 ioremap 函数来完成物理地址到虚拟地
址的映射,采用设备树以后就可以直接通过 of_iomap 函数来获取内存地址所对应的虚拟地址,
不需要使用 ioremap 函数了。当然了,你也可以使用 ioremap 函数来完成物理地址到虚拟地址
的内存映射,只是在采用设备树以后,大部分的驱动都使用 of_iomap 函数了。of_iomap 函数本
质上也是将reg 属性中地址信息转换为虚拟地址,如果 reg 属性有多段的话,可以通过 index 参
数指定要完成内存映射的是哪一段,of_iomap 函数原型如下:
void iomem *of_iomap(struct device_node *np,
int index)
函数参数和返回值含义如下:
np:设备节点。
index:reg 属性中要完成内存映射的段,如果 reg 属性只有一段的话index 就设置为 0。
返回值:经过内存映射后的虚拟内存首地址,如果为 NULL 的话表示内存映射失败。
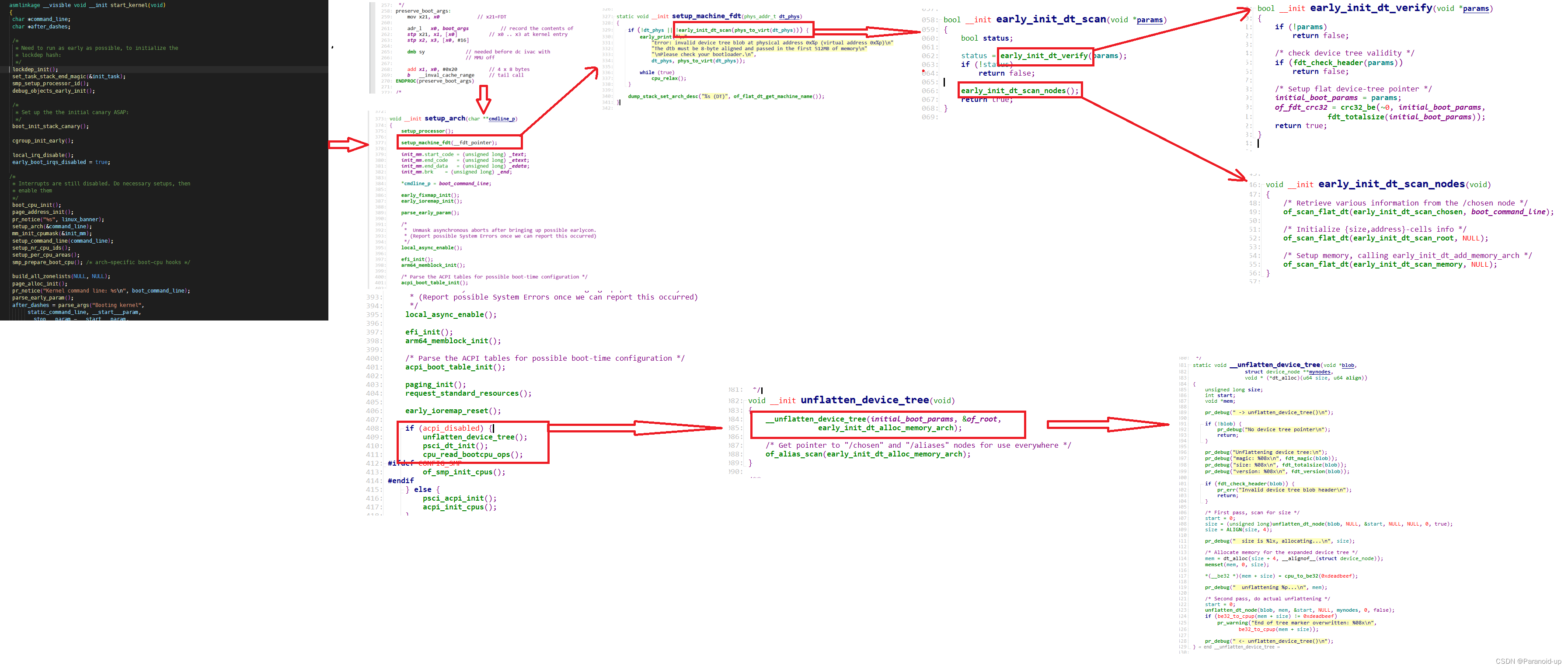
IMX6ULL内核是如何展开设备树为内核可以识别的device_node
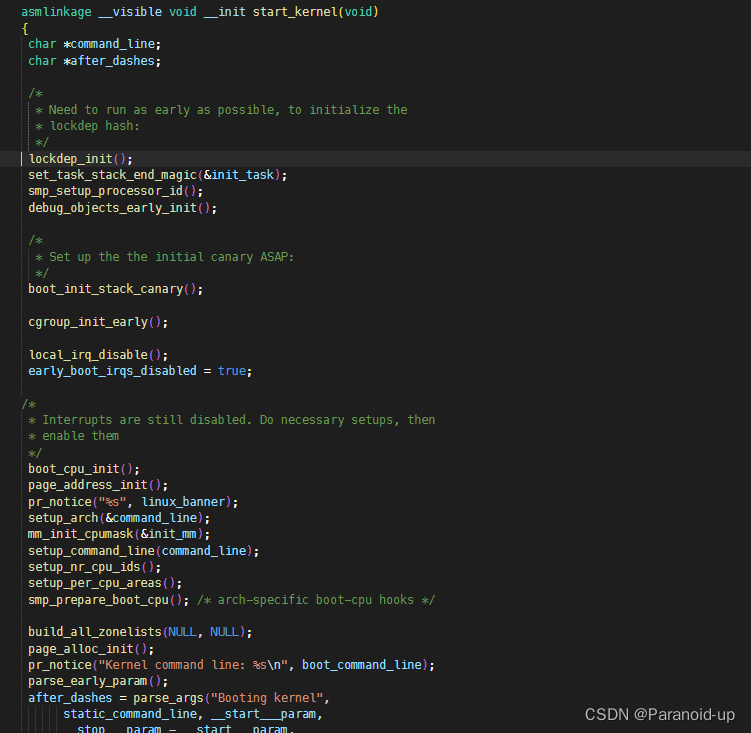
打开内核源码init/main.c,找到start_kernel函数
asmlinkage __visible void __init start_kernel(void)
{
char *command_line;
char *after_dashes;
/*
* Need to run as early as possible, to initialize the
* lockdep hash:
*/
/*
* 初始化锁定机制
* 设置初始任务的栈结束标志
* 设置处理器ID
* 初始化调试对象
* 设置初始栈金丝雀
* 初始化cgroup
* 禁用中断
* 启动CPU
* 初始化页地址
* 打印内核版本信息
* 设置内核命令行
* 设置CPU掩码
* 设置每个CPU的区域
* 准备启动CPU
* 构建所有可用的空闲页列表
* 初始化页分配器
*/
lockdep_init();
set_task_stack_end_magic(&init_task);
smp_setup_processor_id();
debug_objects_early_init();
/*
* Set up the the initial canary ASAP:
*/
boot_init_stack_canary();
cgroup_init_early();
local_irq_disable();
early_boot_irqs_disabled = true;
/*
* Interrupts are still disabled. Do necessary setups, then
* enable them
*/
boot_cpu_init();
page_address_init();
pr_notice("%s", linux_banner);
setup_arch(&command_line);
mm_init_cpumask(&init_mm);
setup_command_line(command_line);
setup_nr_cpu_ids();
setup_per_cpu_areas();
smp_prepare_boot_cpu(); /* arch-specific boot-cpu hooks */
build_all_zonelists(NULL, NULL);
page_alloc_init();
为什么要从start_kernel函数入手?
start_kernel函数是内核启动阶段的入囗,类似于main函数。
在start_kernel函数里面有非常多的子函数,这些子函数都是完成Linux内核初始化的函数,这里我们只关心和dtb展开有关的函数。
setup_arch(&command_line);
/arch/arm64/kernel/setup.c
start_kernel
setup_arch
void __init setup_arch(char **cmdline_p)
{
setup_processor();
setup_machine_fdt(__fdt_pointer);
init_mm.start_code = (unsigned long) _text;
init_mm.end_code = (unsigned long) _etext;
init_mm.end_data = (unsigned long) _edata;
init_mm.brk = (unsigned long) _end;
*cmdline_p = boot_command_line;
early_fixmap_init();
early_ioremap_init();
parse_early_param();
/*
* Unmask asynchronous aborts after bringing up possible earlycon.
* (Report possible System Errors once we can report this occurred)
*/
local_async_enable();
efi_init();
arm64_memblock_init();
/* Parse the ACPI tables for possible boot-time configuration */
acpi_boot_table_init();
paging_init();
request_standard_resources();
early_ioremap_reset();
if (acpi_disabled) {
unflatten_device_tree();
psci_dt_init();
cpu_read_bootcpu_ops();
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
of_smp_init_cpus();
#endif
} else {
psci_acpi_init();
acpi_init_cpus();
}
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
smp_build_mpidr_hash();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_VT
#if defined(CONFIG_VGA_CONSOLE)
conswitchp = &vga_con;
#elif defined(CONFIG_DUMMY_CONSOLE)
conswitchp = &dummy_con;
#endif
#endif
if (boot_args[1] || boot_args[2] || boot_args[3]) {
pr_err("WARNING: x1-x3 nonzero in violation of boot protocol:\n"
"\tx1: %016llx\n\tx2: %016llx\n\tx3: %016llx\n"
"This indicates a broken bootloader or old kernel\n",
boot_args[1], boot_args[2], boot_args[3]);
}
}
boot_command_line
*cmdline_p = boot_command_line;
char __initdata boot_command_line[COMMAND_LINE_SIZE];
#define COMMAND_LINE_SIZE 1024
记录了uboot传递给内核的boot_command_line,大小是4096.。如果uboot传递给boot_command_line的大小超过4096,就要修改这个数组的大小。
setup_machine_fdt
setup_machine_fdt(__fdt_pointer);
参数__fdt_pointer是dtb位于内存的地址
打开arch/arm64/head.S,找到下列内容
/*
* Preserve the arguments passed by the bootloader in x0 .. x3
*/
preserve_boot_args:
mov x21, x0 // x21=FDT
adr_l x0, boot_args // record the contents of
stp x21, x1, [x0] // x0 .. x3 at kernel entry
stp x2, x3, [x0, #16]
dmb sy // needed before dc ivac with
// MMU off
add x1, x0, #0x20 // 4 x 8 bytes
b __inval_cache_range // tail call
ENDPROC(preserve_boot_args)

可以看到dtb位于内存的地址是x0传递过来的,x0里面存放的地址是规定的。
1: cmp x6, x7
b.hs 2f
str xzr, [x6], #8 // Clear BSS
b 1b
2:
adr_l sp, initial_sp, x4
str_l x21, __fdt_pointer, x5 // Save FDT pointer
str_l x24, memstart_addr, x6 // Save PHYS_OFFSET
mov x29, #0
b start_kernel
ENDPROC(__mmap_switched)

str_l x21, __fdt_pointer, x5将设备位于内存的地址保存到__fdt_pointer。
setup_machine_fdt函数
此时mmu已经开启,需要将dtb位于内存物理地址映射成虚拟地址
start_kernel
setup_arch
setup_machine_fdt
static void __init setup_machine_fdt(phys_addr_t dt_phys)
{
if (!dt_phys || !early_init_dt_scan(phys_to_virt(dt_phys))) {
early_print("\n"
"Error: invalid device tree blob at physical address 0x%p (virtual address 0x%p)\n"
"The dtb must be 8-byte aligned and passed in the first 512MB of memory\n"
"\nPlease check your bootloader.\n",
dt_phys, phys_to_virt(dt_phys));
while (true)
cpu_relax();
}
dump_stack_set_arch_desc("%s (DT)", of_flat_dt_get_machine_name());
}
phys_to_virt(dt_phys)将dtb位于内存物理地址映射成虚拟地址
of_flat_dt_get_machine_name获取model和compatible属性的值
early_init_dt_scan函数中调用early_init_dt_scan(phys_to_virt(dt_phys)),用于扫描设备树(Device Tree)
start_kernel
setup_arch
setup_machine_fdt
early_init_dt_scan
bool __init early_init_dt_scan(void *params)
{
bool status;
status = early_init_dt_verify(params);
if (!status)
return false;
early_init_dt_scan_nodes();
return true;
}
early_init_dt_scan调用early_init_dt_verify(params);检查设备树头部是否满足要求。将内存中dtb的虚拟地址保存到了initial_boot_params
start_kernel
setup_arch
setup_machine_fdt
early_init_dt_scan
early_init_dt_verify
bool __init early_init_dt_verify(void *params)
{
if (!params)
return false;
/* check device tree validity */
if (fdt_check_header(params))
return false;
/* Setup flat device-tree pointer */
initial_boot_params = params;
of_fdt_crc32 = crc32_be(~0, initial_boot_params,
fdt_totalsize(initial_boot_params));
return true;
}
start_kernel
setup_arch
setup_machine_fdt
early_init_dt_scan
early_init_dt_scan_nodes
void __init early_init_dt_scan_nodes(void)
{
/* Retrieve various information from the /chosen node */
of_scan_flat_dt(early_init_dt_scan_chosen, boot_command_line);
/* Initialize {size,address}-cells info */
of_scan_flat_dt(early_init_dt_scan_root, NULL);
/* Setup memory, calling early_init_dt_add_memory_arch */
of_scan_flat_dt(early_init_dt_scan_memory, NULL);
}
early_init_dt_scan
early_init_dt_verify(params);
initial_boot_params //将内存中dtb的虚拟地址保存到了initial_boot_params
early_init_dt_scan_nodes
early_fixmap_init
start_kernel
setup_arch
early_fixmap_init //保存dtb位于内存的地址,并设置为只读,不可修改
void __init early_fixmap_init(void)
{
pgd_t *pgd;
pud_t *pud;
pmd_t *pmd;
unsigned long addr = FIXADDR_START;
pgd = pgd_offset_k(addr);
pgd_populate(&init_mm, pgd, bm_pud);
pud = pud_offset(pgd, addr);
pud_populate(&init_mm, pud, bm_pmd);
pmd = pmd_offset(pud, addr);
pmd_populate_kernel(&init_mm, pmd, bm_pte);
/*
* The boot-ioremap range spans multiple pmds, for which
* we are not preparted:
*/
BUILD_BUG_ON((__fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN) >> PMD_SHIFT)
!= (__fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_END) >> PMD_SHIFT));
if ((pmd != fixmap_pmd(fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN)))
|| pmd != fixmap_pmd(fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_END))) {
WARN_ON(1);
pr_warn("pmd %p != %p, %p\n",
pmd, fixmap_pmd(fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN)),
fixmap_pmd(fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_END)));
pr_warn("fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN): %08lx\n",
fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN));
pr_warn("fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_END): %08lx\n",
fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_END));
pr_warn("FIX_BTMAP_END: %d\n", FIX_BTMAP_END);
pr_warn("FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN: %d\n", FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN);
}
}
unflatten_device_tree
unflatten_device_tree是dtb转换为device的核心函数
void __init unflatten_device_tree(void)
{
__unflatten_device_tree(initial_boot_params, &of_root,
early_init_dt_alloc_memory_arch);
/* Get pointer to "/chosen" and "/aliases" nodes for use everywhere */
of_alias_scan(early_init_dt_alloc_memory_arch);
}
start_kernel
setup_arch
unflatten_device_tree
__unflatten_device_tree
static void __unflatten_device_tree(void *blob,
struct device_node **mynodes,
void * (*dt_alloc)(u64 size, u64 align))
{
unsigned long size;
int start;
void *mem;
pr_debug(" -> unflatten_device_tree()\n");
if (!blob) {
pr_debug("No device tree pointer\n");
return;
}
pr_debug("Unflattening device tree:\n");
pr_debug("magic: %08x\n", fdt_magic(blob));
pr_debug("size: %08x\n", fdt_totalsize(blob));
pr_debug("version: %08x\n", fdt_version(blob));
if (fdt_check_header(blob)) {
pr_err("Invalid device tree blob header\n");
return;
}
/* First pass, scan for size */
start = 0;
size = (unsigned long)unflatten_dt_node(blob, NULL, &start, NULL, NULL, 0, true);
size = ALIGN(size, 4);
pr_debug(" size is %lx, allocating...\n", size);
/* Allocate memory for the expanded device tree */
mem = dt_alloc(size + 4, __alignof__(struct device_node));
memset(mem, 0, size);
*(__be32 *)(mem + size) = cpu_to_be32(0xdeadbeef);
pr_debug(" unflattening %p...\n", mem);
/* Second pass, do actual unflattening */
start = 0;
unflatten_dt_node(blob, mem, &start, NULL, mynodes, 0, false);
if (be32_to_cpup(mem + size) != 0xdeadbeef)
pr_warning("End of tree marker overwritten: %08x\n",
be32_to_cpup(mem + size));
pr_debug(" <- unflatten_device_tree()\n");
}
size = (unsigned long)unflatten_dt_node(blob, NULL, &start, NULL, NULL, 0, true);
第一次扫描,统计设备树需要的内存大小,第二个参数是NULL,说明只统计大小,不做其他的事。
mem = dt_alloc(size + 4, __alignof__(struct device_node));
一次就把需要的空间分配出来
unflatten_dt_node(blob, mem, &start, NULL, mynodes, 0, false);
第二次扫描,应为第二个参数不是NULL,所以会执行核心函数中的某几个函数构造device_node树
start_kernel
setup_arch
unflatten_device_tree
__unflatten_device_tree
unflatten_dt_node //解析dtb文件中的各个节点
static void * unflatten_dt_node(void *blob,
void *mem,
int *poffset,
struct device_node *dad,
struct device_node **nodepp,
unsigned long fpsize,
bool dryrun)
{
const __be32 *p;
struct device_node *np;
struct property *pp, **prev_pp = NULL;
const char *pathp;
unsigned int l, allocl;
static int depth = 0;
int old_depth;
int offset;
int has_name = 0;
int new_format = 0;
pathp = fdt_get_name(blob, *poffset, &l);
if (!pathp)
return mem;
allocl = ++l;
/* version 0x10 has a more compact unit name here instead of the full
* path. we accumulate the full path size using "fpsize", we'll rebuild
* it later. We detect this because the first character of the name is
* not '/'.
*/
if ((*pathp) != '/') {
new_format = 1;
if (fpsize == 0) {
/* root node: special case. fpsize accounts for path
* plus terminating zero. root node only has '/', so
* fpsize should be 2, but we want to avoid the first
* level nodes to have two '/' so we use fpsize 1 here
*/
fpsize = 1;
allocl = 2;
l = 1;
pathp = "";
} else {
/* account for '/' and path size minus terminal 0
* already in 'l'
*/
fpsize += l;
allocl = fpsize;
}
}
np = unflatten_dt_alloc(&mem, sizeof(struct device_node) + allocl,
__alignof__(struct device_node));
if (!dryrun) {
char *fn;
of_node_init(np);
np->full_name = fn = ((char *)np) + sizeof(*np);
if (new_format) {
/* rebuild full path for new format */
if (dad && dad->parent) {
strcpy(fn, dad->full_name);
#ifdef DEBUG
if ((strlen(fn) + l + 1) != allocl) {
pr_debug("%s: p: %d, l: %d, a: %d\n",
pathp, (int)strlen(fn),
l, allocl);
}
#endif
fn += strlen(fn);
}
*(fn++) = '/';
}
memcpy(fn, pathp, l);
prev_pp = &np->properties;
if (dad != NULL) {
np->parent = dad;
np->sibling = dad->child;
dad->child = np;
}
}
/* process properties */
for (offset = fdt_first_property_offset(blob, *poffset);
(offset >= 0);
(offset = fdt_next_property_offset(blob, offset))) {
const char *pname;
u32 sz;
if (!(p = fdt_getprop_by_offset(blob, offset, &pname, &sz))) {
offset = -FDT_ERR_INTERNAL;
break;
}
if (pname == NULL) {
pr_info("Can't find property name in list !\n");
break;
}
if (strcmp(pname, "name") == 0)
has_name = 1;
pp = unflatten_dt_alloc(&mem, sizeof(struct property),
__alignof__(struct property));
if (!dryrun) {
/* We accept flattened tree phandles either in
* ePAPR-style "phandle" properties, or the
* legacy "linux,phandle" properties. If both
* appear and have different values, things
* will get weird. Don't do that. */
if ((strcmp(pname, "phandle") == 0) ||
(strcmp(pname, "linux,phandle") == 0)) {
if (np->phandle == 0)
np->phandle = be32_to_cpup(p);
}
/* And we process the "ibm,phandle" property
* used in pSeries dynamic device tree
* stuff */
if (strcmp(pname, "ibm,phandle") == 0)
np->phandle = be32_to_cpup(p);
pp->name = (char *)pname;
pp->length = sz;
pp->value = (__be32 *)p;
*prev_pp = pp;
prev_pp = &pp->next;
}
}
/* with version 0x10 we may not have the name property, recreate
* it here from the unit name if absent
*/
if (!has_name) {
const char *p1 = pathp, *ps = pathp, *pa = NULL;
int sz;
while (*p1) {
if ((*p1) == '@')
pa = p1;
if ((*p1) == '/')
ps = p1 + 1;
p1++;
}
if (pa < ps)
pa = p1;
sz = (pa - ps) + 1;
pp = unflatten_dt_alloc(&mem, sizeof(struct property) + sz,
__alignof__(struct property));
if (!dryrun) {
pp->name = "name";
pp->length = sz;
pp->value = pp + 1;
*prev_pp = pp;
prev_pp = &pp->next;
memcpy(pp->value, ps, sz - 1);
((char *)pp->value)[sz - 1] = 0;
pr_debug("fixed up name for %s -> %s\n", pathp,
(char *)pp->value);
}
}
if (!dryrun) {
*prev_pp = NULL;
np->name = of_get_property(np, "name", NULL);
np->type = of_get_property(np, "device_type", NULL);
if (!np->name)
np->name = "<NULL>";
if (!np->type)
np->type = "<NULL>";
}
old_depth = depth;
*poffset = fdt_next_node(blob, *poffset, &depth);
if (depth < 0)
depth = 0;
while (*poffset > 0 && depth > old_depth)
mem = unflatten_dt_node(blob, mem, poffset, np, NULL,
fpsize, dryrun);
if (*poffset < 0 && *poffset != -FDT_ERR_NOTFOUND)
pr_err("unflatten: error %d processing FDT\n", *poffset);
/*
* Reverse the child list. Some drivers assumes node order matches .dts
* node order
*/
if (!dryrun && np->child) {
struct device_node *child = np->child;
np->child = NULL;
while (child) {
struct device_node *next = child->sibling;
child->sibling = np->child;
np->child = child;
child = next;
}
}
if (nodepp)
*nodepp = np;
return mem;
}