1 属性服务
属性服务的启动在init进程中,init进程初始化的第二阶段初始化中启动了属性服务。
system/core/init/init.cpp
int SecondStageMain(int argc, char** argv) {
...
PropertyInit();
...
StartPropertyService(&property_fd);
...
2 启动属性服务
system/core/init/property_service.cpp
void PropertyInit() {
selinux_callback cb;
cb.func_audit = PropertyAuditCallback;
selinux_set_callback(SELINUX_CB_AUDIT, cb);
mkdir("/dev/__properties__", S_IRWXU | S_IXGRP | S_IXOTH);
CreateSerializedPropertyInfo();
if (__system_property_area_init()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to initialize property area";
}
if (!property_info_area.LoadDefaultPath()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to load serialized property info file";
}
// If arguments are passed both on the command line and in DT,
// properties set in DT always have priority over the command-line ones.
ProcessKernelDt();
ProcessKernelCmdline();
ProcessBootconfig();
// Propagate the kernel variables to internal variables
// used by init as well as the current required properties.
ExportKernelBootProps();
PropertyLoadBootDefaults();
}
接下来分析一下这个函数
mkdir("/dev/__properties__", S_IRWXU | S_IXGRP | S_IXOTH);
首先创建属性服务的存储目录,位于/dev/properties,权限为711,即rwx–x–x
2.1 写入序列化属性上下文信息
system/core/init/property_service.cpp
void CreateSerializedPropertyInfo() {
//创建一个vector用于存储selinux中属性相关
auto property_infos = std::vector<PropertyInfoEntry>();
if (access("/system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) {
if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts", //这个函数的具体作用就是从文件中解析属性相关的,写到vector中
&property_infos)) {
return;
}
// Don't check for failure here, since we don't always have all of these partitions.
// E.g. In case of recovery, the vendor partition will not have mounted and we
// still need the system / platform properties to function.
if (access("/dev/selinux/apex_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) {
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/dev/selinux/apex_property_contexts", &property_infos);
}
if (access("/system_ext/etc/selinux/system_ext_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) {
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/system_ext/etc/selinux/system_ext_property_contexts",
&property_infos);
}
if (access("/vendor/etc/selinux/vendor_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) {
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/vendor/etc/selinux/vendor_property_contexts",
&property_infos);
}
if (access("/product/etc/selinux/product_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) {
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/product/etc/selinux/product_property_contexts",
&property_infos);
}
if (access("/odm/etc/selinux/odm_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) {
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/odm/etc/selinux/odm_property_contexts", &property_infos);
}
} else {
if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/plat_property_contexts", &property_infos)) {
return;
}
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/system_ext_property_contexts", &property_infos);
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/vendor_property_contexts", &property_infos);
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/product_property_contexts", &property_infos);
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/odm_property_contexts", &property_infos);
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/dev/selinux/apex_property_contexts", &property_infos);
}
auto serialized_contexts = std::string();
auto error = std::string();
if (!BuildTrie(property_infos, "u:object_r:default_prop:s0", "string", &serialized_contexts,
&error)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to serialize property contexts: " << error;
return;
}
//上面解析的数据都写到了property_info中
constexpr static const char kPropertyInfosPath[] = "/dev/__properties__/property_info";
if (!WriteStringToFile(serialized_contexts, kPropertyInfosPath, 0444, 0, 0, false)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Unable to write serialized property infos to file";
}
selinux_android_restorecon(kPropertyInfosPath, 0);
}
创建一个存储属性服务的vector——property_infos,存储的是PropertyInfoEntry,是一个结构体
struct PropertyInfoEntry {
PropertyInfoEntry() {}
template <typename T, typename U, typename V>
PropertyInfoEntry(T&& name, U&& context, V&& type, bool exact_match)
: name(std::forward<T>(name)),
context(std::forward<U>(context)),
type(std::forward<V>(type)),
exact_match(exact_match) {}
std::string name;
std::string context;
std::string type;
bool exact_match;
};
包含一些函数和一些字段。
if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts", &property_infos)) {
return;
}
然后就是调用LoadPropertyInfoFromFile加载各个镜像中能够的属性上下文到property_infos这个结构体中。
bool LoadPropertyInfoFromFile(const std::string& filename,
std::vector<PropertyInfoEntry>* property_infos) {
auto file_contents = std::string();
if (!ReadFileToString(filename, &file_contents)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Could not read properties from '" << filename << "'";
return false;
}
auto errors = std::vector<std::string>{};
bool require_prefix_or_exact = SelinuxGetVendorAndroidVersion() >= __ANDROID_API_R__;
ParsePropertyInfoFile(file_contents, require_prefix_or_exact, property_infos, &errors);
// Individual parsing errors are reported but do not cause a failed boot, which is what
// returning false would do here.
for (const auto& error : errors) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not read line from '" << filename << "': " << error;
}
return true;
}
读取文件中的属性上下文,并生成string字符串file_contents。require_prefix_or_exact用于判断属性是不是分离存放在各个镜像中,如果版本大于R,安卓11,则为true。
system/core/property_service/libpropertyinfoserializer/property_info_file.cpp
void ParsePropertyInfoFile(const std::string& file_contents, bool require_prefix_or_exact,
std::vector<PropertyInfoEntry>* property_infos,
std::vector<std::string>* errors) {
// Do not clear property_infos to allow this function to be called on multiple files, with
// their results concatenated.
errors->clear();
for (const auto& line : Split(file_contents, "\n")) {
auto trimmed_line = Trim(line);
if (trimmed_line.empty() || StartsWith(trimmed_line, "#")) {
continue;
}
auto property_info_entry = PropertyInfoEntry{};
auto parse_error = std::string{};
if (!ParsePropertyInfoLine(trimmed_line, require_prefix_or_exact, &property_info_entry,
&parse_error)) {
errors->emplace_back(parse_error);
continue;
}
property_infos->emplace_back(property_info_entry);
}
}
然后解析文件中的属性,以行\n为分割,然后在ParsePropertyInfoLine中解析。
bool ParsePropertyInfoLine(const std::string& line, bool require_prefix_or_exact,
PropertyInfoEntry* out, std::string* error) {
auto tokenizer = SpaceTokenizer(line);
auto property = tokenizer.GetNext();
if (property.empty()) {const std::string kDefaultAndroidDtDir("/proc/device-tree/firmware/android/");
*error = "Did not find a property entry in '" + line + "'";
return false;
}
auto context = tokenizer.GetNext();
if (context.empty()) {
*error = "Did not find a context entry in '" + line + "'";
return false;
}
// It is not an error to not find exact_match or a type, as older files will not contain them.
auto match_operation = tokenizer.GetNext();
// We reformat type to be space deliminated regardless of the input whitespace for easier storage
// and subsequent parsing.
auto type_strings = std::vector<std::string>{};
auto type = tokenizer.GetNext();
while (!type.empty()) {
type_strings.emplace_back(type);
type = tokenizer.GetNext();
}
bool exact_match = false;
if (match_operation == "exact") {
exact_match = true;
} else if (match_operation != "prefix" && match_operation != "" && require_prefix_or_exact) {
*error = "Match operation '" + match_operation +
"' is not valid: must be either 'prefix' or 'exact'";
return false;
}
if (!type_strings.empty() && !IsTypeValid(type_strings)) {
*error = "Type '" + Join(type_strings, " ") + "' is not valid";
return false;
}
*out = {property, context, Join(type_strings, " "), exact_match};
return true;
}
这个函数的作用应该是把属性进行封装,封装成结构体对象。
property_infos->emplace_back(property_info_entry);
封装完成之后,放入存储的vector中。
返回到CreateSerializedPropertyInfo函数中。
auto serialized_contexts = std::string();
auto error = std::string();
if (!BuildTrie(property_infos, "u:object_r:default_prop:s0", "string", &serialized_contexts,
&error)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to serialize property contexts: " << error;
return;
}
这里对读取到的属性的上下文,做字典排序,得到一个序列化后的属性上下文字符串
constexpr static const char kPropertyInfosPath[] = "/dev/__properties__/property_info";
if (!WriteStringToFile(serialized_contexts, kPropertyInfosPath, 0444, 0, 0, false)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Unable to write serialized property infos to file";
}
然后把序列化后的属性上下文字符串写入到"/dev/__properties__/property_info"文件中
总结:CreateSerializedPropertyInfo函数的左右就是创建序列化的属性上下文信息,并写入property_info文件中。
2.2 初始化属性域
if (__system_property_area_init()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to initialize property area";
}
bionic/libc/bionic/system_property_api.cpp
int __system_property_area_init() {
bool fsetxattr_failed = false;
return system_properties.AreaInit(PROP_FILENAME, &fsetxattr_failed) && !fsetxattr_failed ? 0 : -1;
}
bionic/libc/system_properties/system_properties.cpp
bool SystemProperties::AreaInit(const char* filename, bool* fsetxattr_failed) {
if (strlen(filename) >= PROP_FILENAME_MAX) {
return false;
}
strcpy(property_filename_, filename);
contexts_ = new (contexts_data_) ContextsSerialized();
if (!contexts_->Initialize(true, property_filename_, fsetxattr_failed)) {
return false;
}
initialized_ = true;
return true;
}
bionic/libc/system_properties/contexts_serialized.cpp
bool ContextsSerialized::Initialize(bool writable, const char* filename, bool* fsetxattr_failed) {
filename_ = filename;
if (!InitializeProperties()) {
return false;
}
if (writable) {
mkdir(filename_, S_IRWXU | S_IXGRP | S_IXOTH);
bool open_failed = false;
if (fsetxattr_failed) {
*fsetxattr_failed = false;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < num_context_nodes_; ++i) {
if (!context_nodes_[i].Open(true, fsetxattr_failed)) {
open_failed = true;
}
}
if (open_failed || !MapSerialPropertyArea(true, fsetxattr_failed)) {
FreeAndUnmap();
return false;
}
} else {
if (!MapSerialPropertyArea(false, nullptr)) {
FreeAndUnmap();
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
这是整个调用流程,最终调到ContextsSerialized::Initialize中。首先看InitializeProperties函数
bool ContextsSerialized::InitializeProperties() {
if (!property_info_area_file_.LoadDefaultPath()) {
return false;
}
if (!InitializeContextNodes()) {
FreeAndUnmap();
return false;
}
return true;
}
system/core/property_service/libpropertyinfoparser/property_info_parser.cpp
bool PropertyInfoAreaFile::LoadDefaultPath() {
return LoadPath("/dev/__properties__/property_info");
}
加载property_info这个文件,这个文件就是上一小节中序列化后的属性上下文信息。
Initialize的第一个参数是true,所以会创建filename_代表的文件。该文件之前已经创建过了,可能是为了保证目录存在吧,这里的权限也是给的711
#define PROP_FILENAME "/dev/__properties__"
num_context_nodes_和context_nodes_[i]是在InitializeContextNodes中初始化的
bool ContextsSerialized::InitializeContextNodes() {
auto num_context_nodes = property_info_area_file_->num_contexts();
auto context_nodes_mmap_size = sizeof(ContextNode) * num_context_nodes;
// We want to avoid malloc in system properties, so we take an anonymous map instead (b/31659220).
void* const map_result = mmap(nullptr, context_nodes_mmap_size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE,
MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0);
if (map_result == MAP_FAILED) {
return false;
}
prctl(PR_SET_VMA, PR_SET_VMA_ANON_NAME, map_result, context_nodes_mmap_size,
"System property context nodes");
context_nodes_ = reinterpret_cast<ContextNode*>(map_result);
num_context_nodes_ = num_context_nodes;
context_nodes_mmap_size_ = context_nodes_mmap_size;
for (size_t i = 0; i < num_context_nodes; ++i) {
new (&context_nodes_[i]) ContextNode(property_info_area_file_->context(i), filename_);
}
return true;
}
property_info_area_file_是一个PropertyInfoAreaFile对象,在上面的时候通过property_info_area_file_.LoadDefaultPath()加载了属性的上下文信息,之前说的是加载的是存储于/dev/__properties__/property_info中的序列化属性上下文对象数据。
这个首先获取对象的个数num_context_nodes,然后使用mmp映射一个对应大小的内存空间,首地址为map_result,接下来使用reinterpret_cast<ContextNode*>(map_result)将这块空间强转为ContextNode数组类型,然后就是遍历property_info中存储的PropertyInfoArea并将其封装到context_nodes_数组中。
实际的流程就是将上节中的序列化属性上下文数据获取出来,然后封装成context_nodes_数组。
for (size_t i = 0; i < num_context_nodes_; ++i) {
if (!context_nodes_[i].Open(true, fsetxattr_failed)) {
open_failed = true;
}
}
接下来就是调用Open函数
bool ContextNode::Open(bool access_rw, bool* fsetxattr_failed) {
lock_.lock();
if (pa_) {
lock_.unlock();
return true;
}
char filename[PROP_FILENAME_MAX];
int len = async_safe_format_buffer(filename, sizeof(filename), "%s/%s", filename_, context_);
if (len < 0 || len >= PROP_FILENAME_MAX) {
lock_.unlock();
return false;
}
if (access_rw) {
pa_ = prop_area::map_prop_area_rw(filename, context_, fsetxattr_failed);
} else {
pa_ = prop_area::map_prop_area(filename);
}
lock_.unlock();
return pa_;
}
async_safe_format_buffer将filename_和context_拼接,filename_是/dev/__properties__,context_是读取的属性上下文信息。所以在dev/__properties__目录下有很多selinux定义文件。
prop_area* prop_area::map_prop_area_rw(const char* filename, const char* context,
bool* fsetxattr_failed) {
/* dev is a tmpfs that we can use to carve a shared workspace
* out of, so let's do that...
*/
const int fd = open(filename, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_NOFOLLOW | O_CLOEXEC | O_EXCL, 0444);
if (fd < 0) {
if (errno == EACCES) {
/* for consistency with the case where the process has already
* mapped the page in and segfaults when trying to write to it
*/
abort();
}
return nullptr;
}
if (context) {
if (fsetxattr(fd, XATTR_NAME_SELINUX, context, strlen(context) + 1, 0) != 0) {
async_safe_format_log(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR, "libc",
"fsetxattr failed to set context (%s) for \"%s\"", context, filename);
/*
* fsetxattr() will fail during system properties tests due to selinux policy.
* We do not want to create a custom policy for the tester, so we will continue in
* this function but set a flag that an error has occurred.
* Init, which is the only daemon that should ever call this function will abort
* when this error occurs.
* Otherwise, the tester will ignore it and continue, albeit without any selinux
* property separation.
*/
if (fsetxattr_failed) {
*fsetxattr_failed = true;
}
}
}
if (ftruncate(fd, PA_SIZE) < 0) {
close(fd);
return nullptr;
}
pa_size_ = PA_SIZE;
pa_data_size_ = pa_size_ - sizeof(prop_area);
void* const memory_area = mmap(nullptr, pa_size_, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if (memory_area == MAP_FAILED) {
close(fd);
return nullptr;
}
prop_area* pa = new (memory_area) prop_area(PROP_AREA_MAGIC, PROP_AREA_VERSION);
close(fd);
return pa;
}
这里的O_CREAT表示文件不存在则创建,刚开始启动,肯定是不存在的,所以会创建。
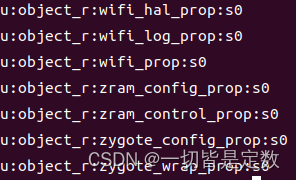
创建了这些文件。
接下来就是通过mmap去映射这些文件,并创建prop_area类型数据。
总结:初始化属性域的左右就是创建并设置属性的selinux上下文,生成对应的文件。
if (!property_info_area.LoadDefaultPath()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to load serialized property info file";
}
bool PropertyInfoAreaFile::LoadDefaultPath() {
return LoadPath("/dev/__properties__/property_info");
}
返回PropertyInit函数,这里读取了属性服务上下文信息
2.3 读取设备树中的属性
const std::string kDefaultAndroidDtDir("/proc/device-tree/firmware/android/");
static void ProcessKernelDt() {
if (!is_android_dt_value_expected("compatible", "android,firmware")) {
return;
}
std::unique_ptr<DIR, int (*)(DIR*)> dir(opendir(get_android_dt_dir().c_str()), closedir);
if (!dir) return;
std::string dt_file;
struct dirent* dp;
while ((dp = readdir(dir.get())) != NULL) {
if (dp->d_type != DT_REG || !strcmp(dp->d_name, "compatible") ||
!strcmp(dp->d_name, "name")) {
continue;
}
std::string file_name = get_android_dt_dir() + dp->d_name;
android::base::ReadFileToString(file_name, &dt_file);
std::replace(dt_file.begin(), dt_file.end(), ',', '.');
InitPropertySet("ro.boot."s + dp->d_name, dt_file);
}
}
ProcessKernelDt函数中的get_android_dt_dir获取到的是上面的kDefaultAndroidDtDir这个string。即这个函数就是遍历/proc/device-tree/firmware/android/目录,将其加上ro.boot前缀后调用InitPropertySet。InitPropertySet后面走的就是属性设置的流程,属性设置的流程后面分析。
2.4 读取cmdline中的属性
constexpr auto ANDROIDBOOT_PREFIX = "androidboot."sv;
static void ProcessKernelCmdline() {
ImportKernelCmdline([&](const std::string& key, const std::string& value) {
if (StartsWith(key, ANDROIDBOOT_PREFIX)) {
InitPropertySet("ro.boot." + key.substr(ANDROIDBOOT_PREFIX.size()), value);
}
});
}
这个函数的左右就是读取cmdline传递的属性,如果是以androidboot.开头的,将其转化为ro.boot.开头,并设置属性。
2.5 读取bootconfig中的属性
static void ProcessBootconfig() {
ImportBootconfig([&](const std::string& key, const std::string& value) {
if (StartsWith(key, ANDROIDBOOT_PREFIX)) {
InitPropertySet("ro.boot." + key.substr(ANDROIDBOOT_PREFIX.size()), value);
}
});
}
读取bootconfig中以androidboot.开头的,将其转化为ro.boot.开头,并设置属性。
2.6 读取内核启动参数
static void ExportKernelBootProps() {
constexpr const char* UNSET = "";
struct {
const char* src_prop;
const char* dst_prop;
const char* default_value;
} prop_map[] = {
// clang-format off
{ "ro.boot.serialno", "ro.serialno", UNSET, },
{ "ro.boot.mode", "ro.bootmode", "unknown", },
{ "ro.boot.baseband", "ro.baseband", "unknown", },
{ "ro.boot.bootloader", "ro.bootloader", "unknown", },
{ "ro.boot.hardware", "ro.hardware", "unknown", },
{ "ro.boot.revision", "ro.revision", "0", },
// clang-format on
};
for (const auto& prop : prop_map) {
std::string value = GetProperty(prop.src_prop, prop.default_value);
if (value != UNSET) InitPropertySet(prop.dst_prop, value);
}
}
将内核启动参数做一个转换,并设置属性。
void PropertyLoadBootDefaults() {
// We read the properties and their values into a map, in order to always allow properties
// loaded in the later property files to override the properties in loaded in the earlier
// property files, regardless of if they are "ro." properties or not.
//将属性读取后存入map中,后面读取的可以覆盖前面文件读取的属性,如果是不是ro开头的。ro开头表示为read only,只读属性。
std::map<std::string, std::string> properties;
if (IsRecoveryMode()) {
load_properties_from_file("/prop.default", nullptr, &properties);
}
// /<part>/etc/build.prop is the canonical location of the build-time properties since S.
// Falling back to /<part>/defalt.prop and /<part>/build.prop only when legacy path has to
// be supported, which is controlled by the support_legacy_path_until argument.
const auto load_properties_from_partition = [&properties](const std::string& partition,
int support_legacy_path_until) {
auto path = "/" + partition + "/etc/build.prop";
if (load_properties_from_file(path.c_str(), nullptr, &properties)) {
return;
}
// To read ro.<partition>.build.version.sdk, temporarily load the legacy paths into a
// separate map. Then by comparing its value with legacy_version, we know that if the
// partition is old enough so that we need to respect the legacy paths.
std::map<std::string, std::string> temp;
auto legacy_path1 = "/" + partition + "/default.prop";
auto legacy_path2 = "/" + partition + "/build.prop";
load_properties_from_file(legacy_path1.c_str(), nullptr, &temp);
load_properties_from_file(legacy_path2.c_str(), nullptr, &temp);
bool support_legacy_path = false;
auto version_prop_name = "ro." + partition + ".build.version.sdk";
auto it = temp.find(version_prop_name);
if (it == temp.end()) {
// This is embarassing. Without the prop, we can't determine how old the partition is.
// Let's be conservative by assuming it is very very old.
support_legacy_path = true;
} else if (int value;
ParseInt(it->second.c_str(), &value) && value <= support_legacy_path_until) {
support_legacy_path = true;
}
if (support_legacy_path) {
// We don't update temp into properties directly as it might skip any (future) logic
// for resolving duplicates implemented in load_properties_from_file. Instead, read
// the files again into the properties map.
load_properties_from_file(legacy_path1.c_str(), nullptr, &properties);
load_properties_from_file(legacy_path2.c_str(), nullptr, &properties);
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << legacy_path1 << " and " << legacy_path2 << " were not loaded "
<< "because " << version_prop_name << "(" << it->second << ") is newer "
<< "than " << support_legacy_path_until;
}
};
// Order matters here. The more the partition is specific to a product, the higher its
// precedence is.
//这里加载的顺序很重要,正如前面注释所说,如果有相同的属性,后面的会覆盖前面的,所有product中是最高的。
LoadPropertiesFromSecondStageRes(&properties);
load_properties_from_file("/system/build.prop", nullptr, &properties);
load_properties_from_partition("system_ext", /* support_legacy_path_until */ 30);
load_properties_from_file("/system_dlkm/etc/build.prop", nullptr, &properties);
// TODO(b/117892318): uncomment the following condition when vendor.imgs for aosp_* targets are
// all updated.
// if (SelinuxGetVendorAndroidVersion() <= __ANDROID_API_R__) {
load_properties_from_file("/vendor/default.prop", nullptr, &properties);
// }
load_properties_from_file("/vendor/build.prop", nullptr, &properties);
load_properties_from_file("/vendor_dlkm/etc/build.prop", nullptr, &properties);
load_properties_from_file("/odm_dlkm/etc/build.prop", nullptr, &properties);
load_properties_from_partition("odm", /* support_legacy_path_until */ 28);
load_properties_from_partition("product", /* support_legacy_path_until */ 30);
if (access(kDebugRamdiskProp, R_OK) == 0) {
//constexpr const char kDebugRamdiskProp[] = "/debug_ramdisk/adb_debug.prop";
LOG(INFO) << "Loading " << kDebugRamdiskProp;
load_properties_from_file(kDebugRamdiskProp, nullptr, &properties);
}
//将前面读取的属性,设置到属性服务中
for (const auto& [name, value] : properties) {
std::string error;
if (PropertySet(name, value, &error) != PROP_SUCCESS) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not set '" << name << "' to '" << value
<< "' while loading .prop files" << error;
}
}
//初始化一些属性,包括ro.product开头,usb相关等。
property_initialize_ro_product_props();
property_initialize_build_id();
property_derive_build_fingerprint();
property_derive_legacy_build_fingerprint();
property_initialize_ro_cpu_abilist();
property_initialize_ro_vendor_api_level();
update_sys_usb_config();
}
这个函数主要是添加特定文件中的属性
3 启动属性服务
Epoll epoll;
if (auto result = epoll.Open(); !result.ok()) {
PLOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
...
StartPropertyService(&property_fd);
init进程创建了一个epoll对象,property_fd是一个int类型的值,表示的是一个文件描述符。
void StartPropertyService(int* epoll_socket) {
InitPropertySet("ro.property_service.version", "2"); //设置属性服务的版本为2
int sockets[2];
//创建一对可以通信的套接字,这里创建的是UNIX域套接字。这一对socket实现双工通信,用于属性服务和init进程间通信
if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET | SOCK_CLOEXEC, 0, sockets) != 0) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "Failed to socketpair() between property_service and init";
}
*epoll_socket = from_init_socket = sockets[0];
init_socket = sockets[1];
StartSendingMessages();
//创建socket,名字为property_service
if (auto result = CreateSocket(PROP_SERVICE_NAME, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK,
false, 0666, 0, 0, {});
result.ok()) {
property_set_fd = *result;
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << "start_property_service socket creation failed: " << result.error();
}
listen(property_set_fd, 8); //开始接收消息,最大连接数为8
//创建线程执行,执行函数为PropertyServiceThread
auto new_thread = std::thread{PropertyServiceThread};
property_service_thread.swap(new_thread);
}
static void PropertyServiceThread() {
Epoll epoll;
if (auto result = epoll.Open(); !result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
if (auto result = epoll.RegisterHandler(property_set_fd, handle_property_set_fd);
!result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
if (auto result = epoll.RegisterHandler(init_socket, HandleInitSocket); !result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
while (true) {
auto pending_functions = epoll.Wait(std::nullopt);
if (!pending_functions.ok()) {
LOG(ERROR) << pending_functions.error();
} else {
for (const auto& function : *pending_functions) {
(*function)();
}
}
}
}
将socket添加到epoll中进行监控,如果有事件发生,则调用回调函数。对于property_set_fd这个fd,回调函数为handle_property_set_fd,对于init_socket,回调函数为HandleInitSocket。
4 设置属性
上面的属性服务中,创建了一个socket,并将其加入epoll进行监控,如果有socket消息,则调用handle_property_set_fd函数处理属性设置
static void handle_property_set_fd() {
static constexpr uint32_t kDefaultSocketTimeout = 2000; /* ms */
int s = accept4(property_set_fd, nullptr, nullptr, SOCK_CLOEXEC);
if (s == -1) {
return;
}
ucred cr;
socklen_t cr_size = sizeof(cr);
if (getsockopt(s, SOL_SOCKET, SO_PEERCRED, &cr, &cr_size) < 0) {
close(s);
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: unable to get SO_PEERCRED";
return;
}
SocketConnection socket(s, cr);
uint32_t timeout_ms = kDefaultSocketTimeout;
uint32_t cmd = 0;
if (!socket.RecvUint32(&cmd, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: error while reading command from the socket";
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_READ_CMD);
return;
}
switch (cmd) {
case PROP_MSG_SETPROP: {
char prop_name[PROP_NAME_MAX];
char prop_value[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
if (!socket.RecvChars(prop_name, PROP_NAME_MAX, &timeout_ms) ||
!socket.RecvChars(prop_value, PROP_VALUE_MAX, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(PROP_MSG_SETPROP): error while reading name/value from the socket";
return;
}
prop_name[PROP_NAME_MAX-1] = 0;
prop_value[PROP_VALUE_MAX-1] = 0;
std::string source_context;
if (!socket.GetSourceContext(&source_context)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Unable to set property '" << prop_name << "': getpeercon() failed";
return;
}
const auto& cr = socket.cred();
std::string error;
uint32_t result =
HandlePropertySet(prop_name, prop_value, source_context, cr, nullptr, &error);
if (result != PROP_SUCCESS) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to set property '" << prop_name << "' from uid:" << cr.uid
<< " gid:" << cr.gid << " pid:" << cr.pid << ": " << error;
}
break;
}
case PROP_MSG_SETPROP2: {
std::string name;
std::string value;
if (!socket.RecvString(&name, &timeout_ms) ||
!socket.RecvString(&value, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(PROP_MSG_SETPROP2): error while reading name/value from the socket";
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_READ_DATA);
return;
}
std::string source_context;
if (!socket.GetSourceContext(&source_context)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Unable to set property '" << name << "': getpeercon() failed";
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_PERMISSION_DENIED);
return;
}
const auto& cr = socket.cred();
std::string error;
uint32_t result = HandlePropertySet(name, value, source_context, cr, &socket, &error);
if (result != PROP_SUCCESS) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to set property '" << name << "' from uid:" << cr.uid
<< " gid:" << cr.gid << " pid:" << cr.pid << ": " << error;
}
socket.SendUint32(result);
break;
}
default:
LOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: invalid command " << cmd;
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_INVALID_CMD);
break;
}
}
PROP_MSG_SETPROP和PROP_MSG_SETPROP2感觉没啥区别,就是一个读取c风格字符串char数组,一个读取string。最终调用为HandlePropertySet函数。
uint32_t HandlePropertySet(const std::string& name, const std::string& value,
const std::string& source_context, const ucred& cr,
SocketConnection* socket, std::string* error) {
//检查权限
if (auto ret = CheckPermissions(name, value, source_context, cr, error); ret != PROP_SUCCESS) {
return ret;
}
//如果是ctl开头的,则发送控制信息
if (StartsWith(name, "ctl.")) {
return SendControlMessage(name.c_str() + 4, value, cr.pid, socket, error);
}
// sys.powerctl is a special property that is used to make the device reboot. We want to log
// any process that sets this property to be able to accurately blame the cause of a shutdown.
if (name == "sys.powerctl") {
std::string cmdline_path = StringPrintf("proc/%d/cmdline", cr.pid);
std::string process_cmdline;
std::string process_log_string;
if (ReadFileToString(cmdline_path, &process_cmdline)) {
// Since cmdline is null deliminated, .c_str() conveniently gives us just the process
// path.
process_log_string = StringPrintf(" (%s)", process_cmdline.c_str());
}
LOG(INFO) << "Received sys.powerctl='" << value << "' from pid: " << cr.pid
<< process_log_string;
if (!value.empty()) {
DebugRebootLogging();
}
if (value == "reboot,userspace" && !is_userspace_reboot_supported().value_or(false)) {
*error = "Userspace reboot is not supported by this device";
return PROP_ERROR_INVALID_VALUE;
}
}
// If a process other than init is writing a non-empty value, it means that process is
// requesting that init performs a restorecon operation on the path specified by 'value'.
// We use a thread to do this restorecon operation to prevent holding up init, as it may take
// a long time to complete.
if (name == kRestoreconProperty && cr.pid != 1 && !value.empty()) {
static AsyncRestorecon async_restorecon;
async_restorecon.TriggerRestorecon(value);
return PROP_SUCCESS;
}
return PropertySet(name, value, error);
}
ctl开头的控制类属性特殊处理,sys.powerctl属性跟重启关机相关,需要记录谁来设置的。其他的属性调用PropertySet设置。
static uint32_t PropertySet(const std::string& name, const std::string& value, std::string* error) {
size_t valuelen = value.size();
if (!IsLegalPropertyName(name)) {
*error = "Illegal property name";
return PROP_ERROR_INVALID_NAME;
}
if (auto result = IsLegalPropertyValue(name, value); !result.ok()) {
*error = result.error().message();
return PROP_ERROR_INVALID_VALUE;
}
prop_info* pi = (prop_info*) __system_property_find(name.c_str());
if (pi != nullptr) {
// ro.* properties are actually "write-once".
if (StartsWith(name, "ro.")) {
*error = "Read-only property was already set";
return PROP_ERROR_READ_ONLY_PROPERTY;
}
__system_property_update(pi, value.c_str(), valuelen);
} else {
int rc = __system_property_add(name.c_str(), name.size(), value.c_str(), valuelen);
if (rc < 0) {
*error = "__system_property_add failed";
return PROP_ERROR_SET_FAILED;
}
}
// Don't write properties to disk until after we have read all default
// properties to prevent them from being overwritten by default values.
//持久化相关的属性需要写入文件,特殊处理
if (persistent_properties_loaded && StartsWith(name, "persist.")) {
WritePersistentProperty(name, value);
}
// If init hasn't started its main loop, then it won't be handling property changed messages
// anyway, so there's no need to try to send them.
auto lock = std::lock_guard{accept_messages_lock};
if (accept_messages) {
PropertyChanged(name, value);
}
return PROP_SUCCESS;
}
主要是对属性进行判断,如果已经存在,则判断是不是ro开头的,如果是则返回设置失败。如果不是则调用__system_property_update更新,如果不存在则调用__system_property_add新增一个属性。



![[医学分割比赛] ISBI2023 APIS多模态医学分割比赛总结 + top3解决方案](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6ace3d9f5eaa49bd8bda61be56bf443e.png)