前言
由于大部分基础知识都已经学过了,这里只把觉得应该记录一下的知识点做个笔记。然后以下笔记和sql均来自书籍(MYSQL必会知识)
LIKE模糊查询
- 通配符%
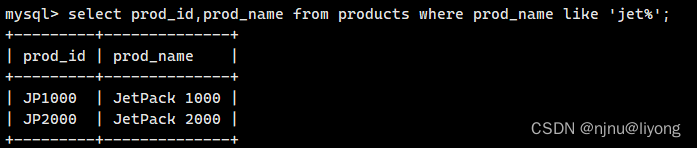
相当于是查询一jet开头后面任意的数据
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name like 'jet%';
查询jet结尾的数据,这里要注意空格的问题,有时候数据库数据后面存了空格(jet )可能导致查询不成功,这个时候需要用空格函数去除空格
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name like '%jet';
查询前:
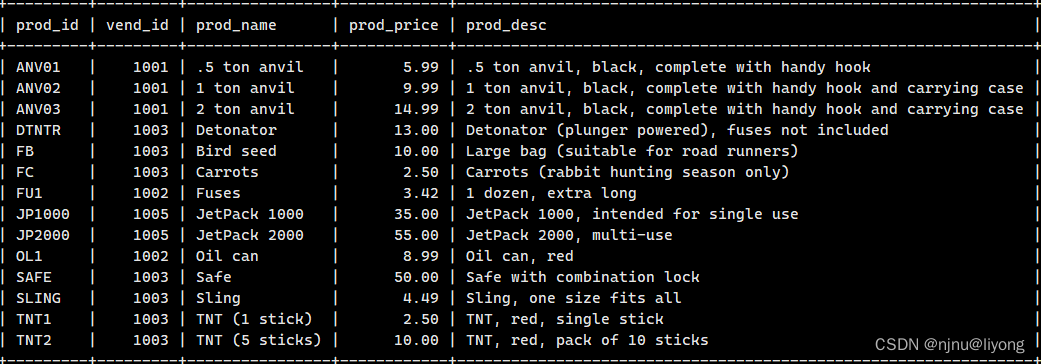
查询后:
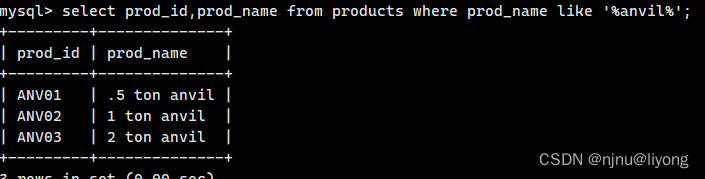
这个是查询包含anvil的数据
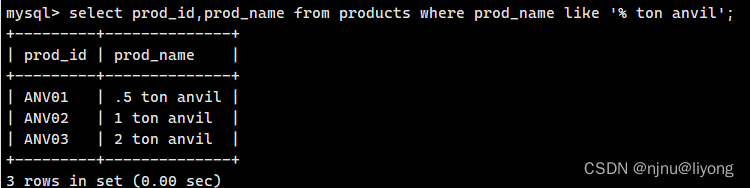
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name like '%anvil%';
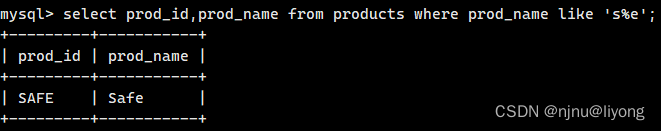
查询以s开头e结尾的数据
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name like 's%e';
- 通配符_
_下划线匹配一个字符
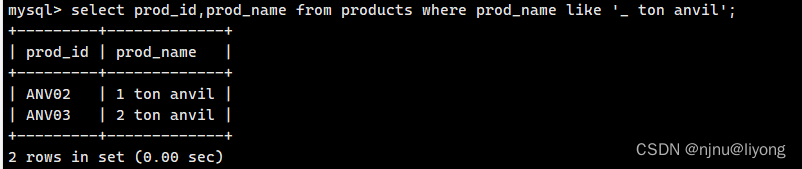
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name like '_ ton anvil';
对比%,匹配多个字符:
正则表达式
基本使用
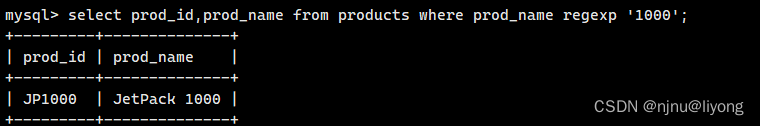
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '1000';
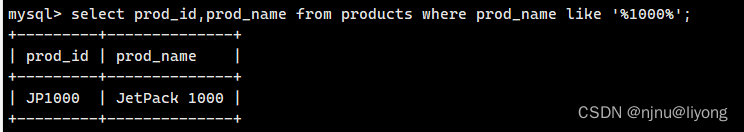
这个其实相当于like这样写
注意前后都有通配符
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name like '%1000%';
如果你这样写返回的是一个空集合,因为like会匹配整个列,如果文本在列中出现不会找到它也不会返回(mysql必会知识原话)
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name like '1000';

点号匹配任意一个字符
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '.000';
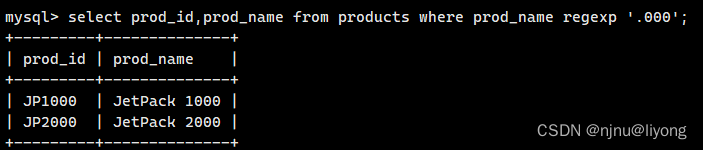
正则表达式在匹配的时候是区分大小写的如果要区分大小写用关键字binary
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name regexp binary 'JetPack .000';
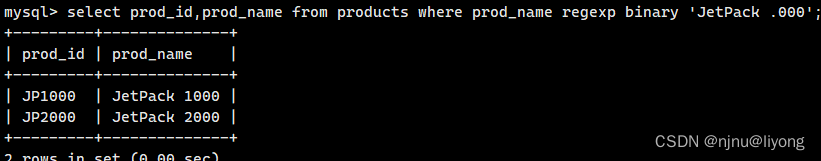
这个时候由于指定小写所以没有匹配的数据
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name regexp binary 'jetpack .000';

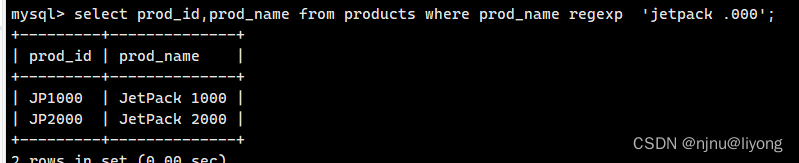
不区分大小写所以能返回所以匹配的结果
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name regexp 'jetpack .000';
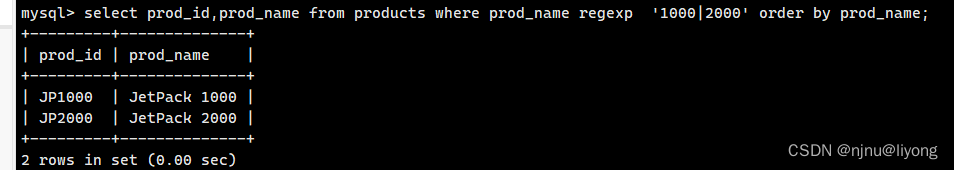
or匹配 这里匹配的就是名字包含1000或者2000的数据
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '1000|2000' order by prod_name;
集合的符号的使用
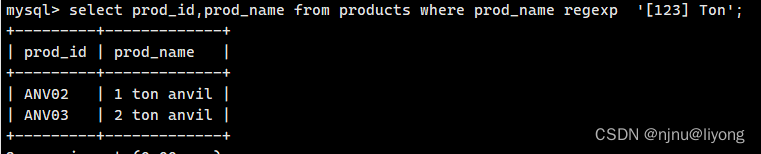
匹配几个字符之一 下面语句的意思就是匹配1 Ton 2 Ton 3 Ton
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '[123] Ton';
#上面这条语句等价于
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '1|2|3 Ton';
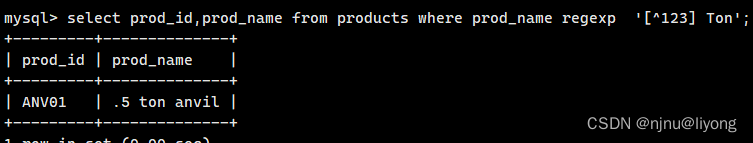
集合取反
#取几何的反集 这个的意思就是除了1 Ton 2 Ton 3 Ton 任意 * Ton都会被返回 *代表任意字符
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '[^123] Ton';
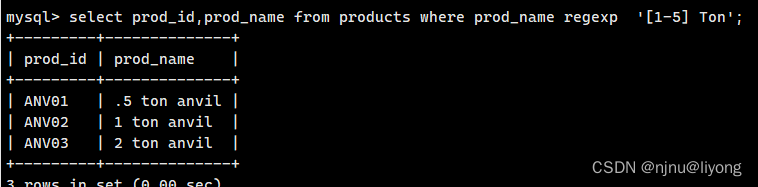
上面如果我们要比如26个子母我们可以全写到里面,但是这样会很长而且也很难写,所以我们采用范围的方式,就是在中括号里加短线标识1到5
#匹配范围 就是匹配 1 2 3 4 5 Ton(五次匹配)
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '[1-5] Ton';
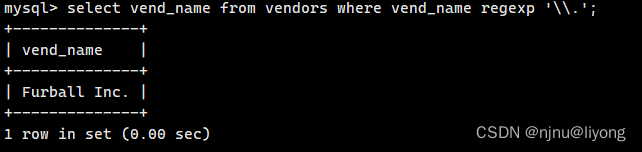
特殊字符的配配
#匹配特殊字符 注意是两个\\ 如果匹配\本身 则需要 \\\
select vend_name from vendors where vend_name regexp '\\.';
其它特殊字符:

然后mysql里面内置了一些常用的字符集

提供指定多个字符匹配的表达式:

下面再看几个例子:
#由于( )都是特殊字符所以前面有\\
select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '\\([0-9] sticks?\\)';
#等价于下面的这条语句,需要注意的是这里外面还需要包裹一对[]
select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '\\([[:digit:]] sticks?\\)';
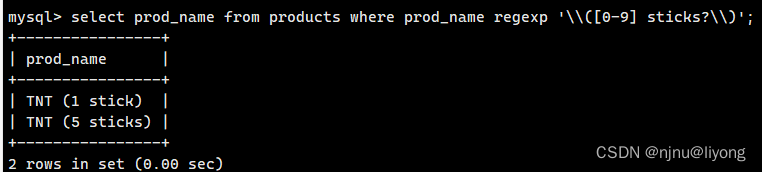
#{}里面内容限制了匹配的数量 []里限制了匹配的模式 这个正则的意思是匹配包含四个(或四个以上)数字的数据
select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '[[:digit:]]{4,}';
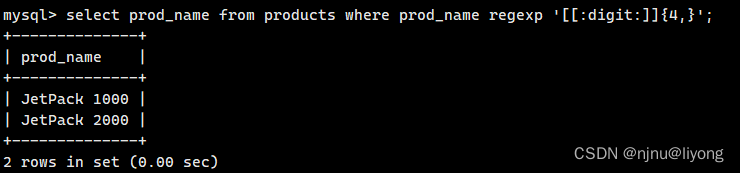
#这条sql的语句是匹配以数字或.开始的数据
select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '^[0-9\\.]';
#否定某个集合
[^123]
注:在正则表达式这块^这个符号有两种用法,第一种是否定某个集合,这个在前面我们提到过;第二种用法标志开始。
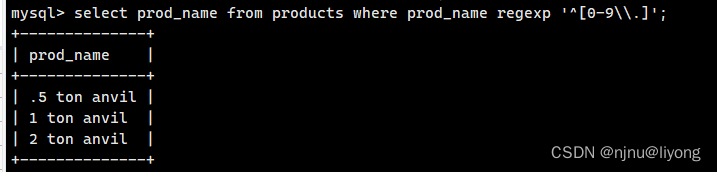
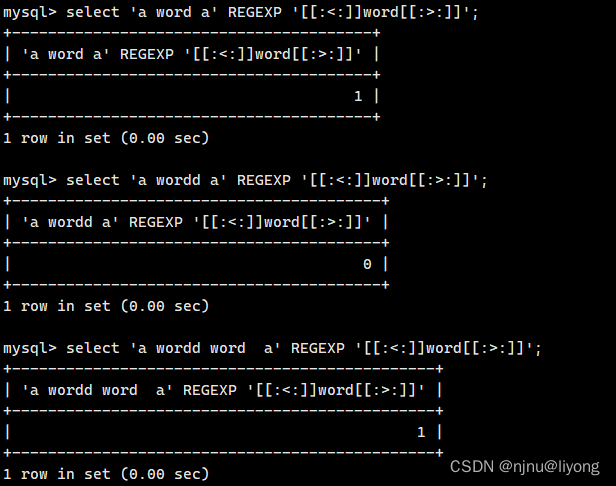
# 1 表示成功 0表示失败 这个匹配有点想找这个里面是否存在word这个词
select 'a word a' REGEXP '[[:<:]]word[[:>:]]';
select 'a wordd a' REGEXP '[[:<:]]word[[:>:]]';
select 'a wordd word a' REGEXP '[[:<:]]word[[:>:]]';
计算字段
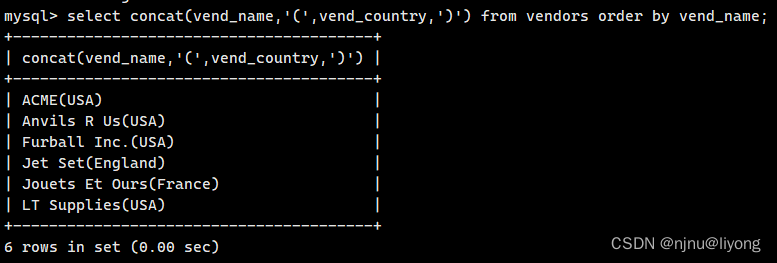
#拼接两个字段
select concat(vend_name,'(',vend_country,')') from vendors order by vend_name;
#可以在函数中再使用函数
select concat(vend_name,'(',rtrim(vend_country),')') from vendors order by vend_name;
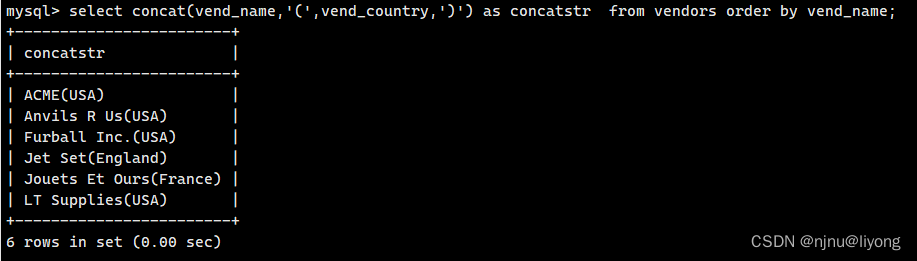
#可以取别名
select concat(vend_name,'(',vend_country,')') as concatstr from vendors order by vend_name;
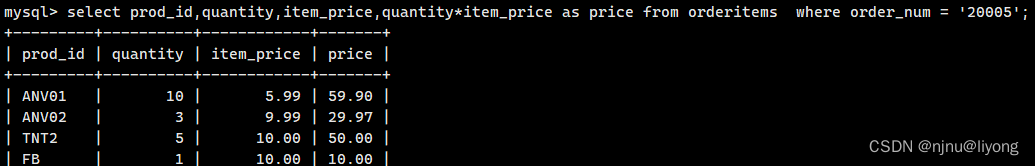
#执行算术运算
select prod_id,quantity,item_price,quantity*item_price as price from orderitems where order_num = '20005';
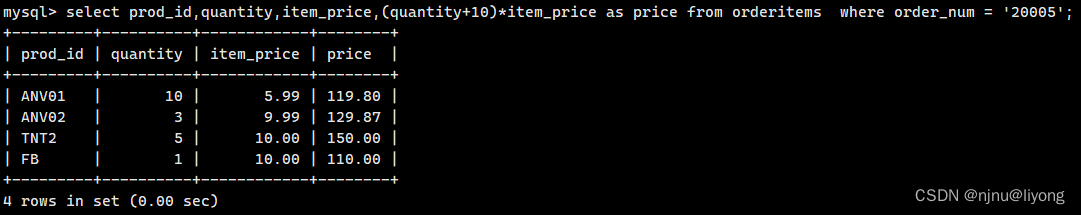
支持四则运算和()指定优先级
例如:
select prod_id,quantity,item_price,(quantity+10)*item_price as price from orderitems where order_num = '20005';
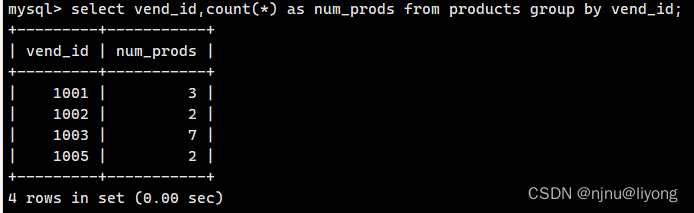
数据分组
select vend_id,count(*) as num_prods from products group by vend_id;
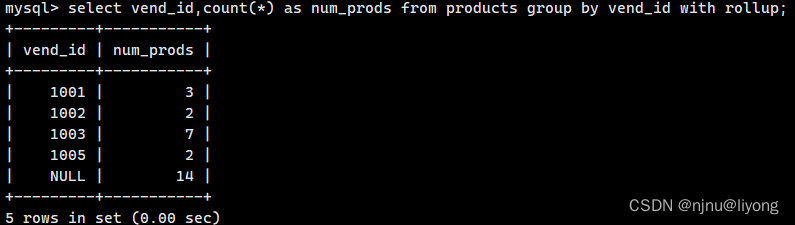
#使用WITH ROLLUP关键字,可以得到每个分组以及每个分组汇总级别(针对每个分组)的值,可以看到其实有这个关键字
#它会对分组的结果进行再统计也就是就一个和
select vend_id,count(*) as num_prods from products group by vend_id with rollup;
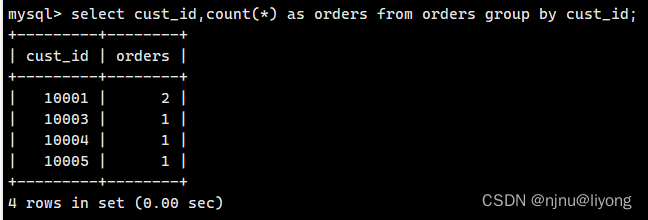
select cust_id,count(*) as orders from orders group by cust_id;
#可以看到having分组后的结果进行了过滤
select cust_id,count(*) as orders from orders group by cust_id having count(*) >=2;
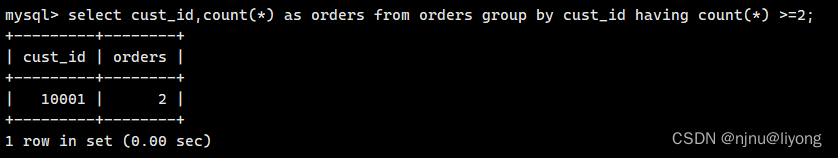
#where 和 having的组合使用 where 用于分组前 having用于分组后 同时order by一定是在group by后面
select vend_id,count(*) as num_prods from products where prod_price >= 10 group by vend_id having count(*) >= 2;

子查询
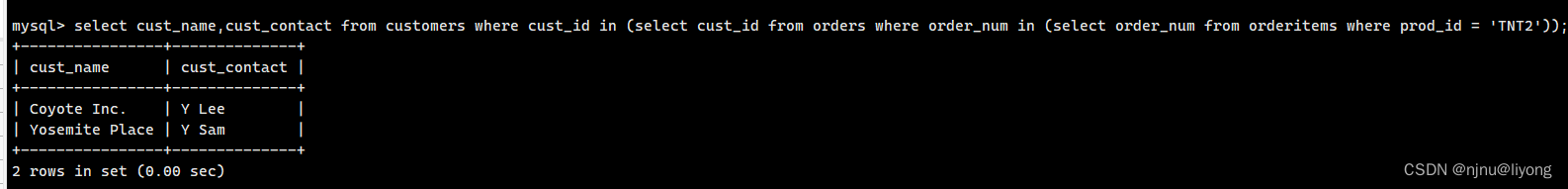
select cust_name,cust_contact from customers where cust_id in (select cust_id from orders where order_num in (select order_num from orderitems where prod_id = 'TNT2'));
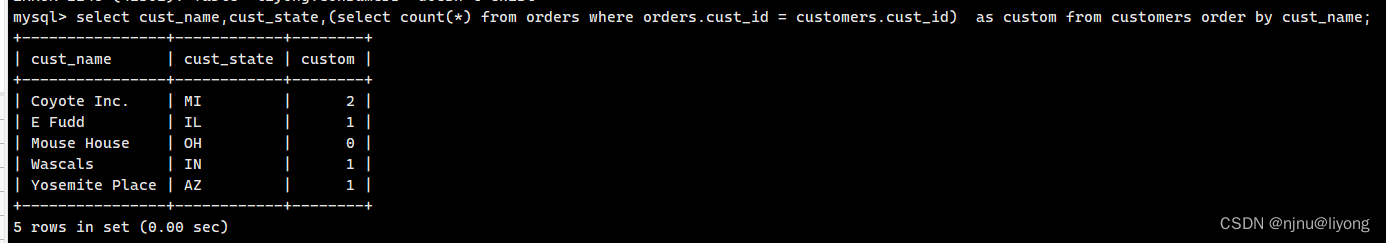
#子查询作为计算字段
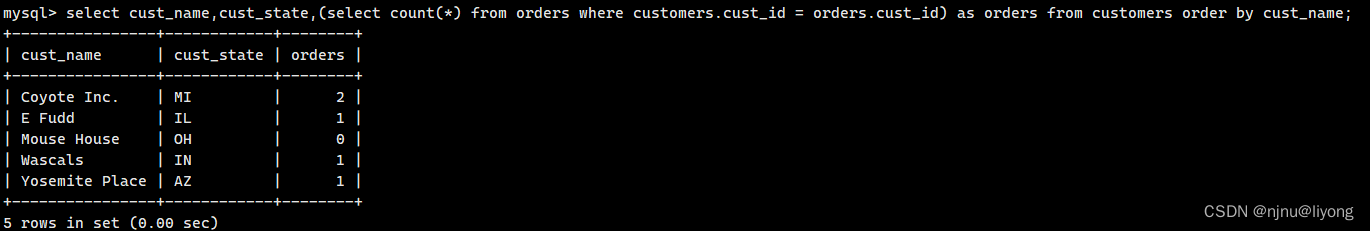
select cust_name,cust_state,(select count(*) from orders where orders.cust_id = customers.cust_id) as custom from customers order by cust_name;
注:这里有一个概念就是相关子查询也就是子查询涉及引用外部的表
#子查询涉及了外部表customers
select cust_name,cust_state,(select count(*) from orders where customers.ct_idust_id = orders.cust_id) as orders from customers order by cust_name;
连接
注:没有加条件的连接返回的是一个笛卡尔积
#返回笛卡尔积
select vend_name,prod_name,prod_price from vendors,products order by vend_
name,prod_name;
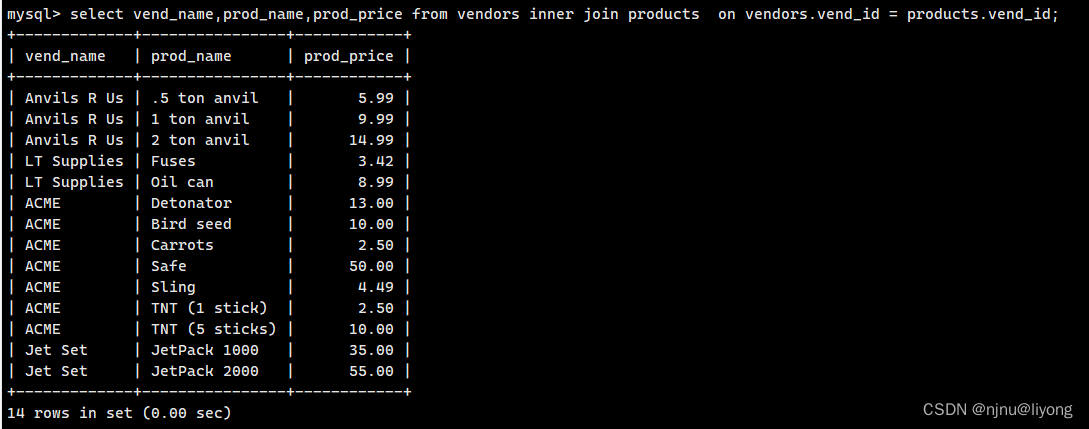
#内连接 等值连接 不保存没有匹配上的值
select vend_name,prod_name,prod_price from vendors inner join products on vendors.vend_id = products.vend_id;
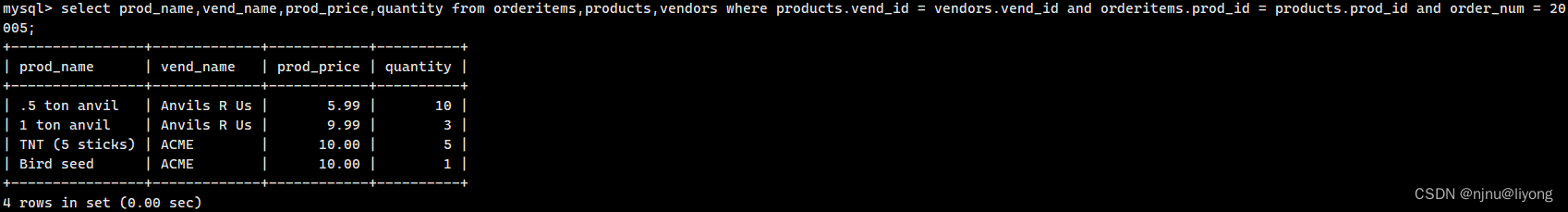
#连接多个表
select prod_name,vend_name,prod_price,quantity from orderitems,products,vendors where products.vend_id = vendors.vend_id and orderitems.prod_id = products.prod_id and order_num = 20005;
#使用别名缩短查询语句 这条查询语句和我们之前子查询的效果是一样的
select cust_name,cust_contact from customers as c,orders as o,orderitems as oi where c.cust_id=o.cust_id and o.order_num = oi.order_num and prod_id = 'TNT2
';
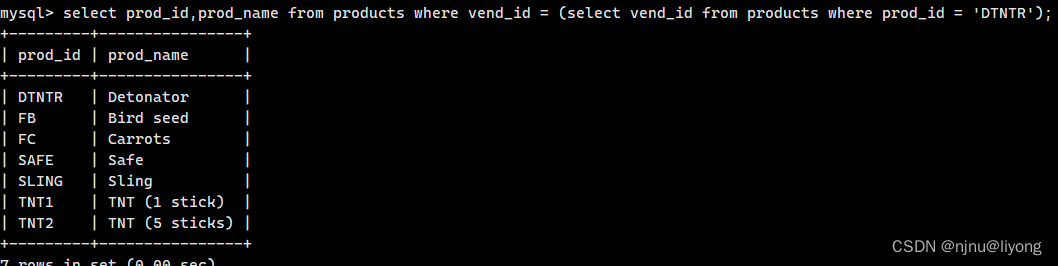
#这一条语句我们两次使用了当前表
select prod_id,prod_name from products where vend_id = (select vend_id from products where prod_id = 'DTNTR');
#我们可用自连接,达到相同的效果
select p1.prod_id,p1.prod_name from products as p1, products as p2 where p1.vend_id = p2.vend_id and p2.prod_id = 'DTNTR';
注:通常使用自连接代替子查询嵌套,通常情况前者的效率更高,但是实际情况需要进行测试,那种效率高用那种并不绝对。
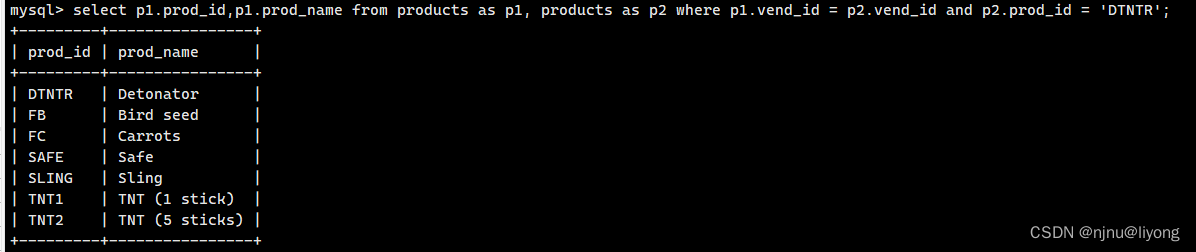
#外连接所谓的外连接只是保留没有匹配上的数据 如果保留左边的数据就是左连接 否则是有连接
select customers.cust_id,orders.order_num from customers left outer join orders on customers.cust_id = orders.cust_id;
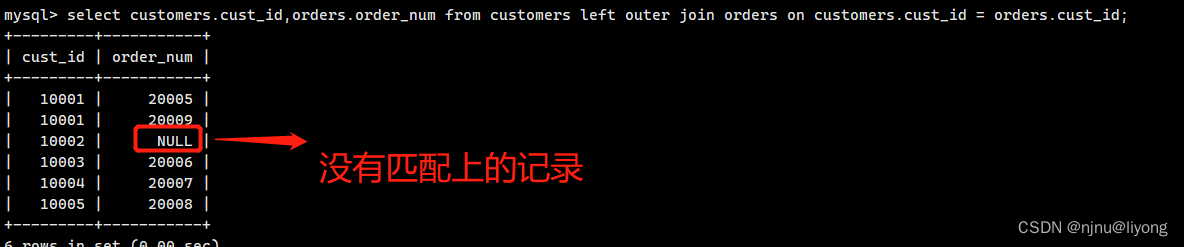
组合查询
组合查询是把具有相同结构的数据组合到一起,数据里面的列的次序可以不一致。
用UNION 默认会去掉重复的行,如果你需要保留重复的行用UNION ALL
select vend_id,prod_id,prod_price from products where prod_price <= 5 unionon all select vend_id,prod_id,prod_price from products where vend_id in (1001,10002);
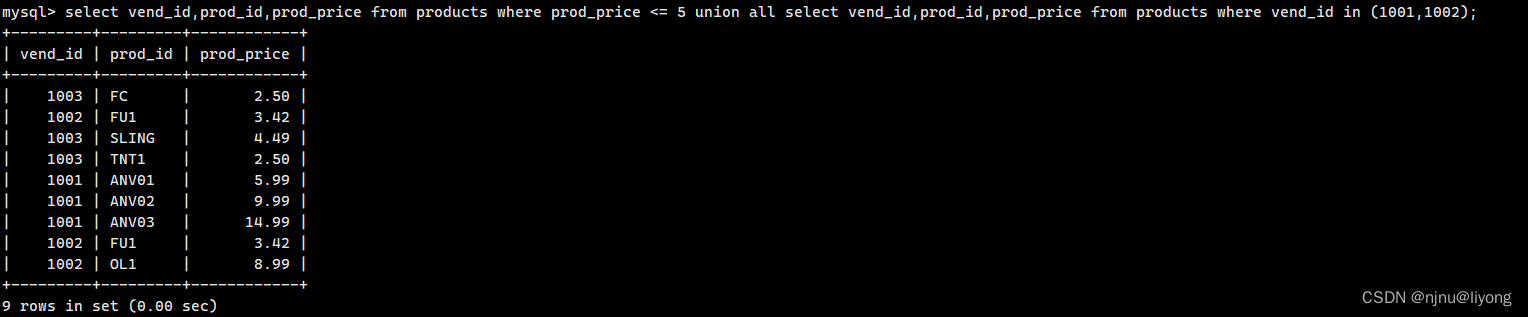
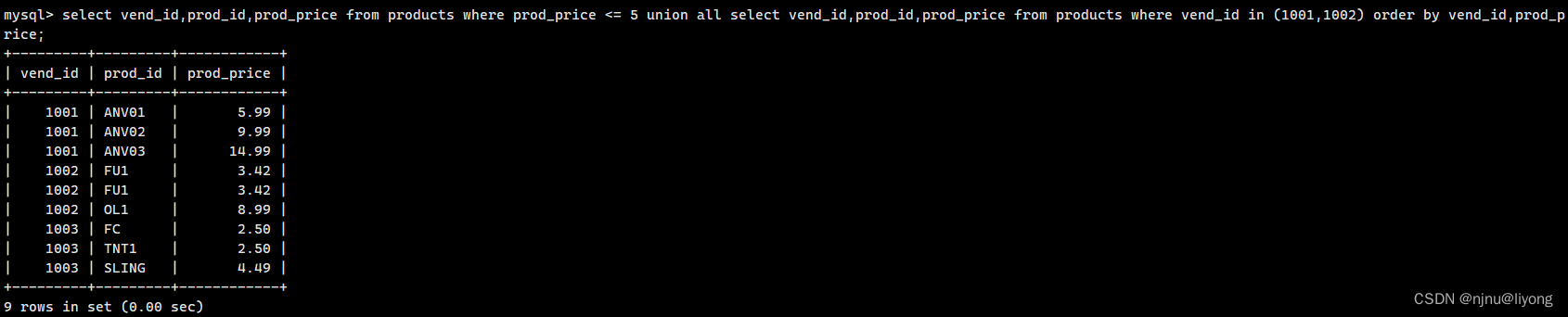
#使用了UNION后排序会针对整个结果而不是后面这条语句
select vend_id,prod_id,prod_price from products where prod_price <= 5 union all select vend_id,prod_id,prod_price from products where vend_id in (1001,1002) order by vend_id,prod_price;
全文检索
- 普通全文搜索
#注意在创建表的时候启用全文搜索
CREATE TABLE productnotes
(
note_id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
prod_id char(10) NOT NULL,
note_date datetime NOT NULL,
note_text text NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY(note_id),
FULLTEXT(note_text)
) ENGINE=MyISAM;
#使用全文搜索
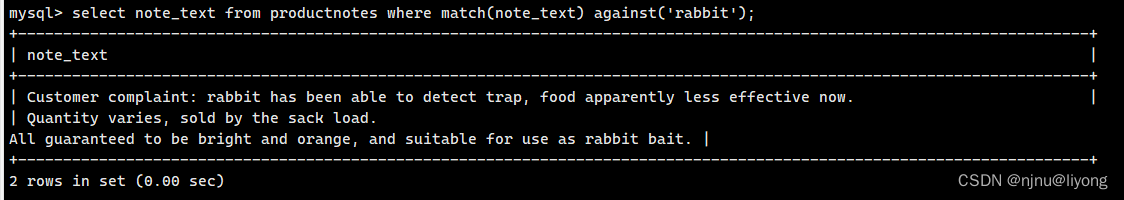
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('rabbit');
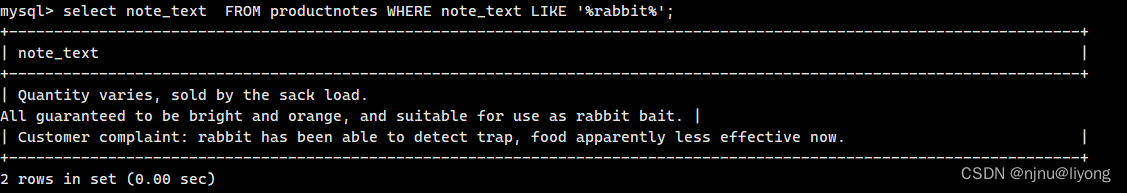
#这里可以用幕府查询但是我们对比一下结果就可以发现全文搜索是有权重的,关键字越靠前则他会在结果中的排序也更靠前
select note_text FROM productnotes WHERE note_text LIKE '%rabbit%';
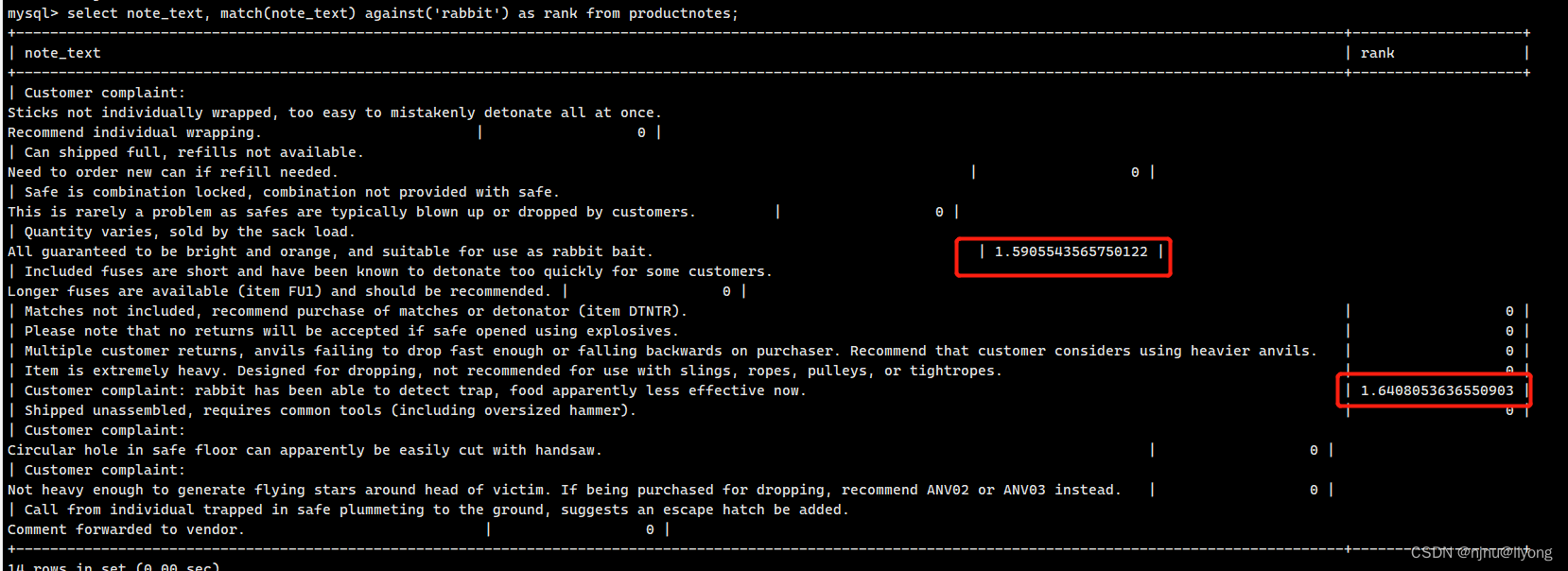
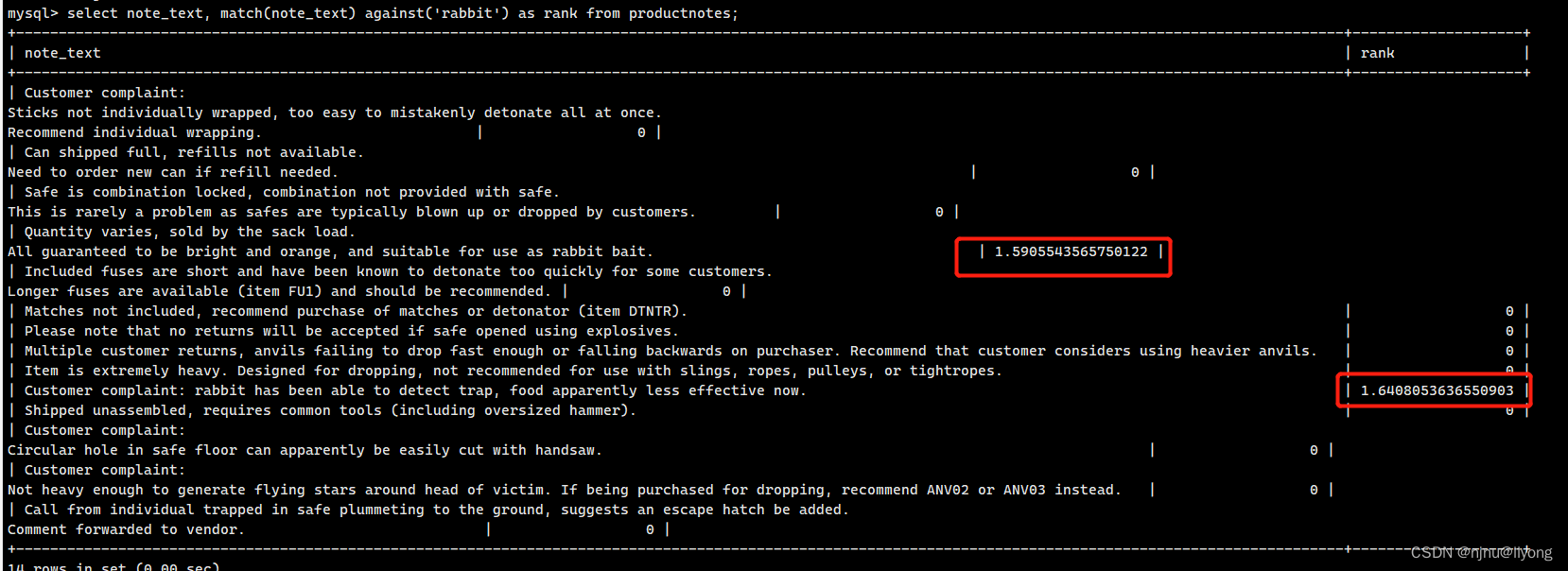
#可以看到全文搜索计算了一个数值,这个相当于是相关性打分
select note_text, match(note_text) against('rabbit') as rank from productnotes;
- 拓展搜索
1)第一条语句只是不使用拓展模式,返回一条结果
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('anvils');
2)使用拓展搜索
返回了多条结果,并且第二,三条的结果和第一条结果相关它包含第一行中的两个词(customer和recommend)。
这个就是拓展搜索的优势,返回更多具有相关性的结果。
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('anvils' with query expansion);
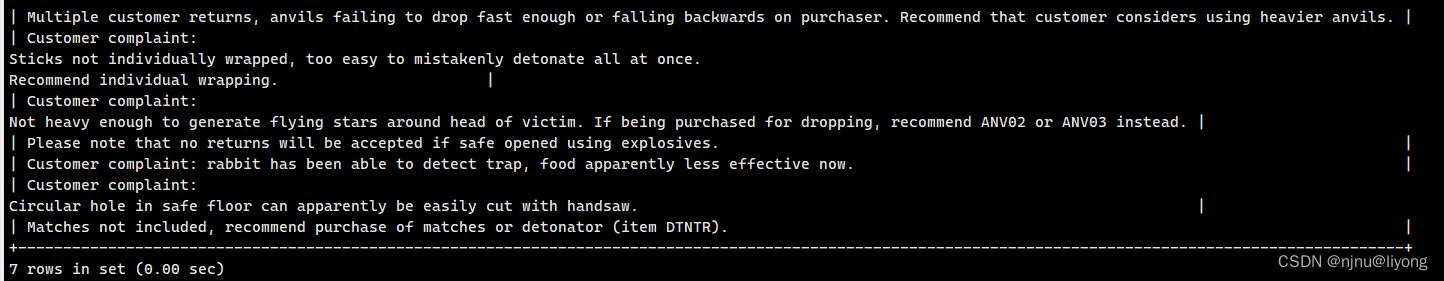
- 布尔文本搜索
在这个模式下我们可以手动的设置某个单词权重
下面这条sql的意思就是匹配heavy 并且排除包含rope开头的记录
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('heavy -rope*' in boolean mode);
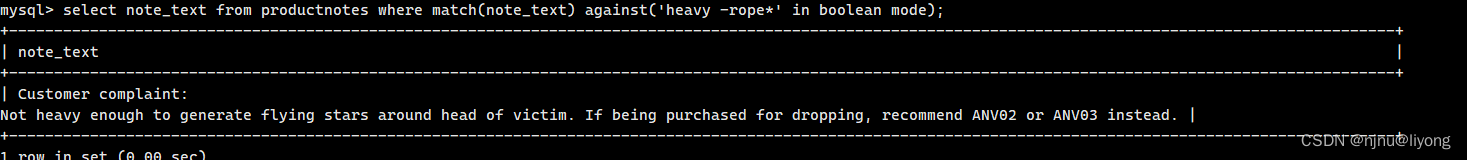
如果不写这个条件,可以对比一下结果差异:
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('heavy' in boolean mode);
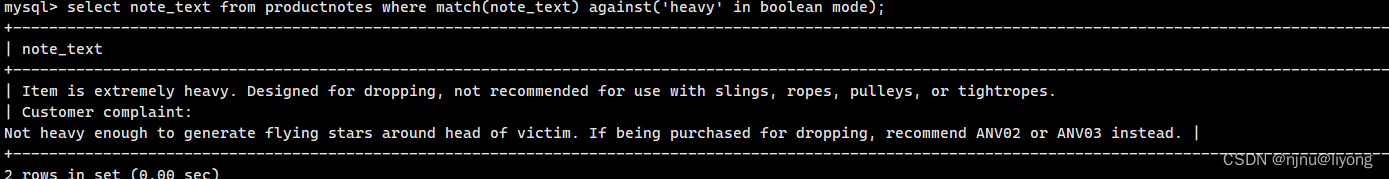
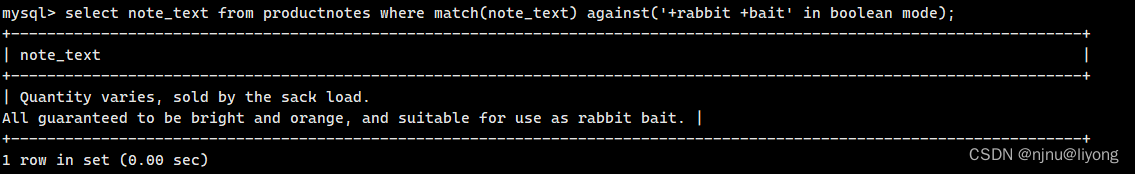
再看一个例子:
这条语句的意思是记录必须包含rabbit 和bait
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('+rabbit +bait' in boolean mode);
更多操作符号:

全文搜索的一些注意事项:
在索引全文本数据时,短词被忽略且从索引中排除。短词定义为那些具有3个或3个以下字符的词(如果需要,这个数目可以更改)。
MySQL带有一个内建的非用词(stopword)列表,这些词在索引全文本数据时总是被忽略。如果需要,可以覆盖这个列表(请参阅MySQL文档以了解如何完成此工作)。
许多词出现的频率很高,搜索它们没有用处(返回太多的结果)。因此,MySQL规定了一条50%规则,如果一个词出现在50%以上的行中,则将它作为一个非用词忽略。50%规则不用于IN BOOLEAN MODE。
如果表中的行数少于3行,则全文本搜索不返回结果(因为每个词或者不出现,或者至少出现在50%的行中)。
忽略词中的单引号。例如,don’t索引为dont。
不具有词分隔符(包括日语和汉语)的语言不能恰当地返回全文本搜索结果。
如前所述,仅在MyISAM数据库引擎中支持全文本搜索。



![[pgrx开发postgresql数据库扩展]7.返回序列的函数编写(2)表序列](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/c0f3c08d10ab46ada568f0a2994ac713.webp?x-oss-process=image/format,png)