文章目录
- 8.1 基本类型原子类
- 8.1.1 常用API简介
- 8.1.2 Case
- 8.2 数组类型原子类
- 8.2.1 常用API简介
- 8.2.2 Case
- 8.3 引用类型原子类
- 8.4 对象的属性修改原子类
- 8.4.1 使用目的
- 8.4.2 使用要求
- 8.4.3 Case
- 8.5 原子操作增强类原理深度解析
- 8.5.1 常用API
- 8.5.2 面试题
- 8.5.3 点赞计数器
- 8.5.4 源码、原理分析
- 8.5.5 总结
Atomic 翻译成中文是原子的意思。在化学上,我们知道原子是构成一般物质的最小单位,在化学反应中是不可分割的。在我们这里 Atomic 是指一个操作是不可中断的。即使是在多个线程一起执行的时候,一个操作一旦开始,就不会被其他线程干扰。
8.1 基本类型原子类
AtomicInteger:整型原子类AtomicBoolean:布尔型原子类AtomicLong:长整型原子类
8.1.1 常用API简介
public final int get() //获取当前的值
public final int getAndSet(int newValue)//获取当前的值,并设置新的值
public final int getAndIncrement()//获取当前的值,并自增
public final int getAndDecrement() //获取当前的值,并自减
public final int getAndAdd(int delta) //获取当前的值,并加上预期的值
boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) //如果输入的数值等于预期值,则以原子方式将该值设置为输入值(update)
public final void lazySet(int newValue)//最终设置为newValue,使用 lazySet 设置之后可能导致其他线程在之后的一小段时间内还是可以读到旧的值。
8.1.2 Case
class MyNumber {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
public void addPlusPlus() {
atomicInteger.getAndIncrement();
}
}
public class AtomicIntegerDemo {
public static final int SIZE = 50;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyNumber myNumber = new MyNumber();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(SIZE);
for (int i = 1; i <= SIZE; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 10; j++) {
myNumber.addPlusPlus();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "result: " + myNumber.atomicInteger.get());//main result: 500
}
}
8.2 数组类型原子类
AtomicIntegerArray:整型数组原子类AtomicLongrArray:长整型数组原子类AtomicReferenceArray:用类型数组原子类
8.2.1 常用API简介
public final int get(int i) //获取 index=i 位置元素的值
public final int getAndSet(int i, int newValue)//返回 index=i 位置的当前的值,并将其设置为新值:newValue
public final int getAndIncrement(int i)//获取 index=i 位置元素的值,并让该位置的元素自增
public final int getAndDecrement(int i) //获取 index=i 位置元素的值,并让该位置的元素自减
public final int getAndAdd(int i, int delta) //获取 index=i 位置元素的值,并加上预期的值
boolean compareAndSet(int i, int expect, int update) //如果输入的数值等于预期值,则以原子方式将 index=i 位置的元素值设置为输入值(update)
public final void lazySet(int i, int newValue)//最终 将index=i 位置的元素设置为newValue,使用 lazySet 设置之后可能导致其他线程在之后的一小段时间内还是可以读到旧的值。
8.2.2 Case
public class AtomicIntegerArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntegerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5});
AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntegerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[5]);
for (int i = 0; i < atomicIntegerArray.length(); i++) {
System.out.println(atomicIntegerArray.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
int tempInt = 0;
tempInt = atomicIntegerArray.getAndSet(0, 1122);
System.out.println(tempInt + "\t" + atomicIntegerArray.get(0));
tempInt = atomicIntegerArray.getAndIncrement(0);
System.out.println(tempInt + "\t" + atomicIntegerArray.get(0));
}
}
8.3 引用类型原子类
AtomicReference:引用类型原子类AtomicStampedReference:原子更新带有版本号的引用类型。该类将整数值与引用关联起来,可用于解决原子的更新数据和数据的版本号,可以解决使用 CAS 进行原子更新时可能出现的 ABA 问题。- 解决修改过几次
AtomicMarkableReference:原子更新带有标记的引用类型。该类将 boolean 标记与引用关联起来- 解决是否修改过,它的定义就是将标记戳简化为true/false,类似于一次性筷子
public class AtomicMarkableReferenceDemo {
static AtomicMarkableReference markableReference = new AtomicMarkableReference(100, false);
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
boolean marked = markableReference.isMarked();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "默认标识: " + marked);//t1 默认标识: false
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
markableReference.compareAndSet(100, 1000, marked, !marked);//t2 默认标识: false
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
boolean marked = markableReference.isMarked();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "默认标识: " + marked);//t2 t2线程CASResult:false
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean b = markableReference.compareAndSet(100, 2000, marked, !marked);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "t2线程CASResult:" + b);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + markableReference.isMarked());//t2 true
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + markableReference.getReference());//t2 1000
}, "t2").start();
}
}
8.4 对象的属性修改原子类
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater:原子更新对象中int类型字段的值AtomicLongFieldUpdater:原子更新对象中Long类型字段的值AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater:原子更新对象中引用类型字段的值
8.4.1 使用目的
以一种线程安全的方式操作非线程安全对象内的某些字段
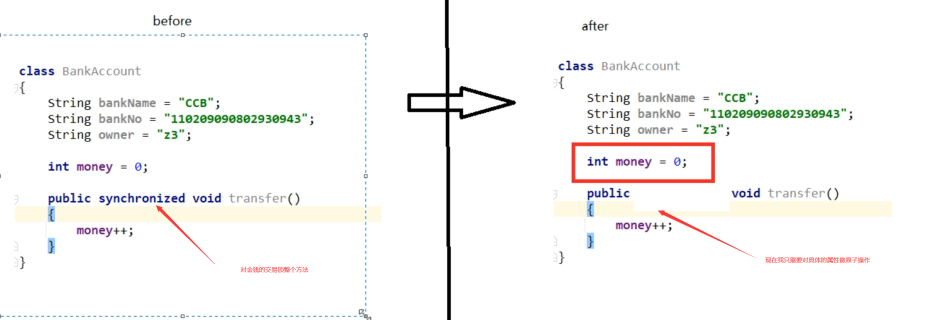
8.4.2 使用要求
- 更新的对象属性必须使用public volatile修饰符
- 因为对象的属性修改类型原子类都是抽象类,所以每次使用都必须使用静态方法newUpdater()创建一个更新器,并且需要设置想要更新的类和属性
8.4.3 Case
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater使用案例
/**
* 需求:10个线程各自转账1000
*/
class BankAccount {
public volatile int money = 0;
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<BankAccount> atomicIntegerFieldUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(BankAccount.class, "money");
public void transferMoney(BankAccount bankAccount) {
atomicIntegerFieldUpdater.getAndIncrement(bankAccount);
}
}
public class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BankAccount bankAccount = new BankAccount();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(10);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 1000; j++) {
bankAccount.transferMoney(bankAccount);
}
} finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + '\t' + "result: " + bankAccount.money); //main result: 10000
}
}
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater案例演示
/**
* 需求:多线程并发调用一个类的初始化方法,如果未被初始化过,将执行初始化工作
* 要求只能被初始化一次,只有一个线程操作成功
*/
class MyVar {
public volatile Boolean isInit = Boolean.FALSE;
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<MyVar, Boolean> referenceFieldUpdater = AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(MyVar.class, Boolean.class, "isInit");
public void init(MyVar myVar) {
if (referenceFieldUpdater.compareAndSet(myVar, Boolean.FALSE, Boolean.TRUE)) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "--------------start init ,need 2 secondes");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "--------------over init");
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "--------------已经有线程进行初始化工作了。。。。。");
}
}
}
public class AtomicReferenceFieldUpdaterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyVar myVar = new MyVar();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
myVar.init(myVar);
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
/**
* 1 --------------start init ,need 2 secondes
* 5 --------------已经有线程进行初始化工作了。。。。。
* 2 --------------已经有线程进行初始化工作了。。。。。
* 4 --------------已经有线程进行初始化工作了。。。。。
* 3 --------------已经有线程进行初始化工作了。。。。。
* 1 --------------over init
*/
8.5 原子操作增强类原理深度解析
DoubleAccumulator:一个或多个变量,它们一起保持运行double使用所提供的功能更新值DoubleAdder:一个或多个变量一起保持初始为零double总和LongAccumulator:一个或多个变量,一起保持使用提供的功能更新运行的值long ,提供了自定义的函数操作LongAdder:一个或多个变量一起维持初始为零long总和(重点),只能用来计算加法,且从0开始计算
8.5.1 常用API
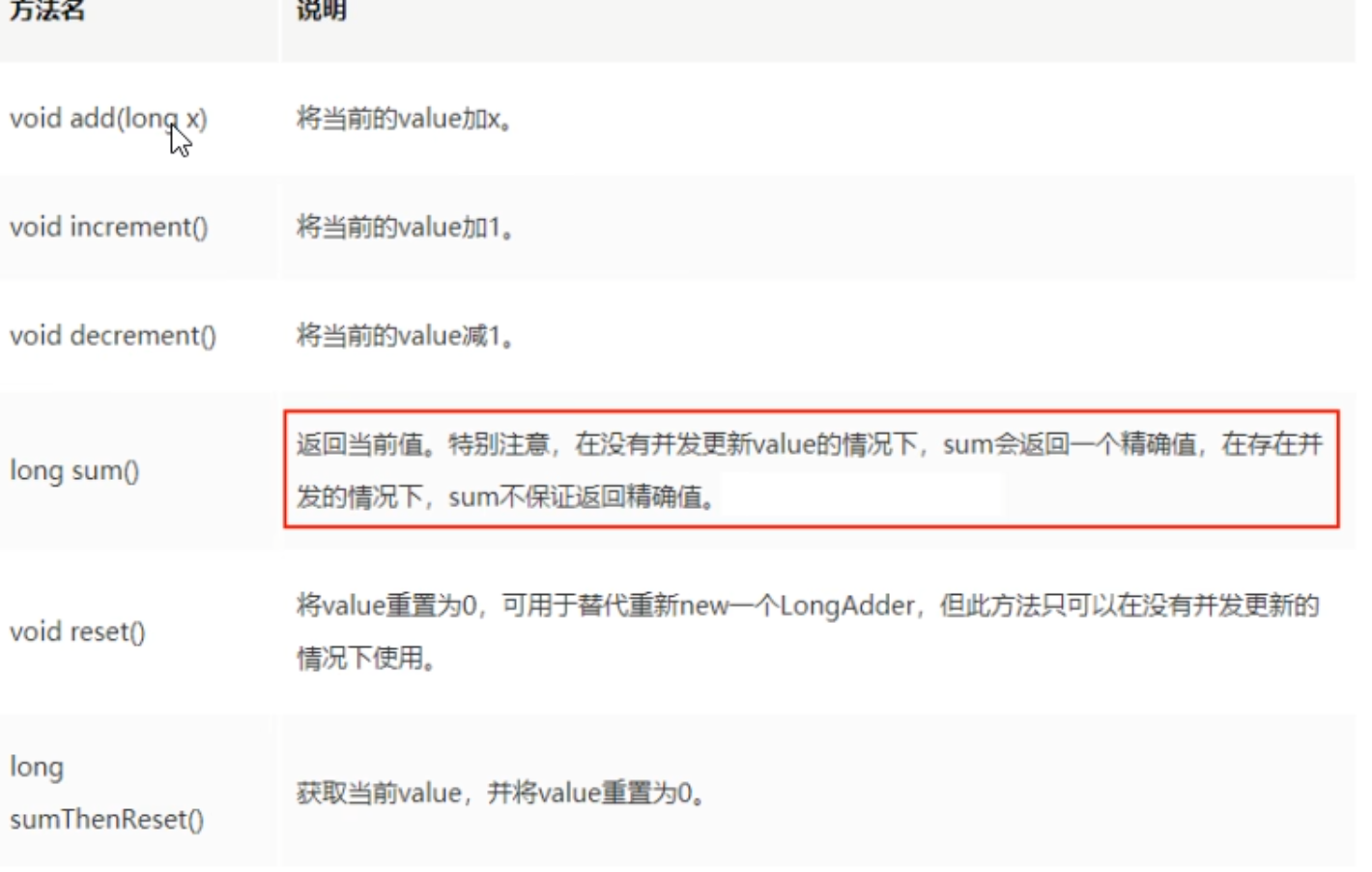
8.5.2 面试题
- 热点商品点赞计算器,点赞数加加统计,不要求实时精确
- 一个很大的list,里面都是int类型,如何实现加加,思路?
8.5.3 点赞计数器
/**
* 需求:50个线程,每个线程100w此,总点赞数出来
*/
class ClickNumber {
int number = 0;
public synchronized void clickBySynchronized() {
number++;
}
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0);
public void clickByAtomicLong() {
atomicLong.getAndIncrement();
}
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
public void clickByLongAdder() {
longAdder.increment();
}
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x, y) -> x + y, 0);
public void clickByLongAccumulator() {
longAccumulator.accumulate(1);
}
}
public class AccumulatorCompareDemo {
public static final int _1W = 10000;
public static final int THREAD_NUMBER = 50;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ClickNumber clickNumber = new ClickNumber();
long StartTime;
long endTime;
CountDownLatch countDownLatch1 = new CountDownLatch(THREAD_NUMBER);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch2 = new CountDownLatch(THREAD_NUMBER);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch3 = new CountDownLatch(THREAD_NUMBER);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch4 = new CountDownLatch(THREAD_NUMBER);
StartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * _1W; j++) {
clickNumber.clickBySynchronized();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch1.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch1.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("------costTime: " + (endTime - StartTime) + " 毫秒" + "\t clickBySynchronized: " + clickNumber.number);
StartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * _1W; j++) {
clickNumber.clickByAtomicLong();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch2.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch2.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("------costTime: " + (endTime - StartTime) + " 毫秒" + "\t clickByAtomicLong: " + clickNumber.atomicLong.get());
StartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * _1W; j++) {
clickNumber.clickByLongAdder();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch3.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch3.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("------costTime: " + (endTime - StartTime) + " 毫秒" + "\t clickByLongAdder: " + clickNumber.longAdder.sum());
StartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * _1W; j++) {
clickNumber.clickByLongAccumulator();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch4.countDown();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch4.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("------costTime: " + (endTime - StartTime) + " 毫秒" + "\t clickByLongAccumulator: " + clickNumber.longAccumulator.get());
}
}
/**
* ------costTime: 1313 毫秒 clickBySynchronized: 50000000
* ------costTime: 825 毫秒 clickByAtomicLong: 50000000
* ------costTime: 92 毫秒 clickByLongAdder: 50000000
* ------costTime: 61 毫秒 clickByLongAccumulator: 50000000
*/
8.5.4 源码、原理分析
- 架构
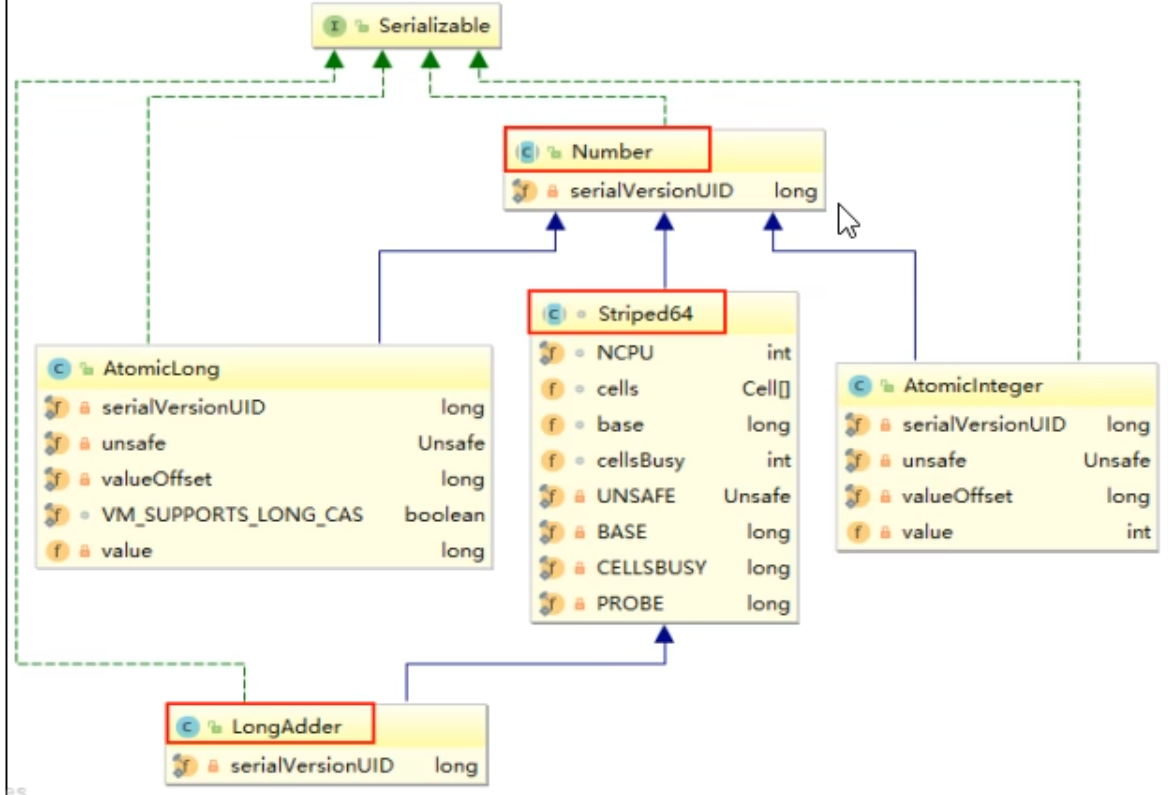
原理(LongAdder为什么这么快)
-
如果是JDK8,推荐使用LongAdder对象,比AtomicLong性能更好(减少乐观锁的重试次数)
-
LongAdder是Striped64的子类
-
Striped64的基本结构
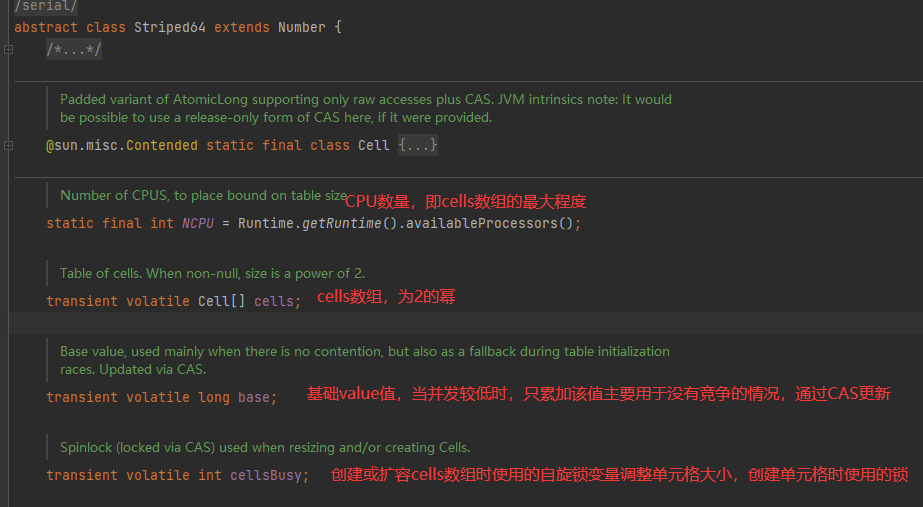

-
cell:是java.util.concurrent.atomic下Striped64的一个内部类
-
LongAdder为什么这么快
-
LongAdder的基本思路就是分散热点,将value值分散到一个Cell数组中,不同线程会命中到数组的不同槽中,各个线程只对自己槽中的那个值进行CAS操作,这样热点就被分散了,冲突的概率就小很多,如果要获取真正的long值,只要将各个槽中的变量值累加返回
-
sum()会将所有的Cell数组中的value和base累加作为返回值,核心的思想就是将之前AtomicLong一个value的更新压力分散到多个value中去,从而降级更新热点。
-
内部有一个base变量,一个Cell[]数组
- base变量:低并发,直接累加到该变量上
- Cell[]数组:高并发,累加进各个线程自己的槽Cell[i]中
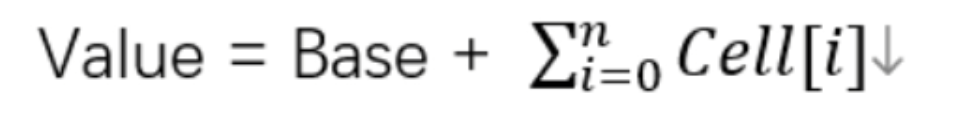
-
源码解读深度分析
-
LongAdder在无竞争的情况下,跟AtomicLong一样,对同一个base进行操作,当出现竞争关系时则是采用化整为零分散热点的做法,用空间换时间,用一个数组cells,将一个value值拆分进这个数组cells。多个线程需要同时对value进行操作的时候,可以对线程id进行hash得到hash值,再根据hash值映射到这个数组cells的某个下标,再对该下标所对应的值进行自增操作。当所有线程操作完毕,将数组cells的所有值和base都加起来作为最终结果
-
add(1L)
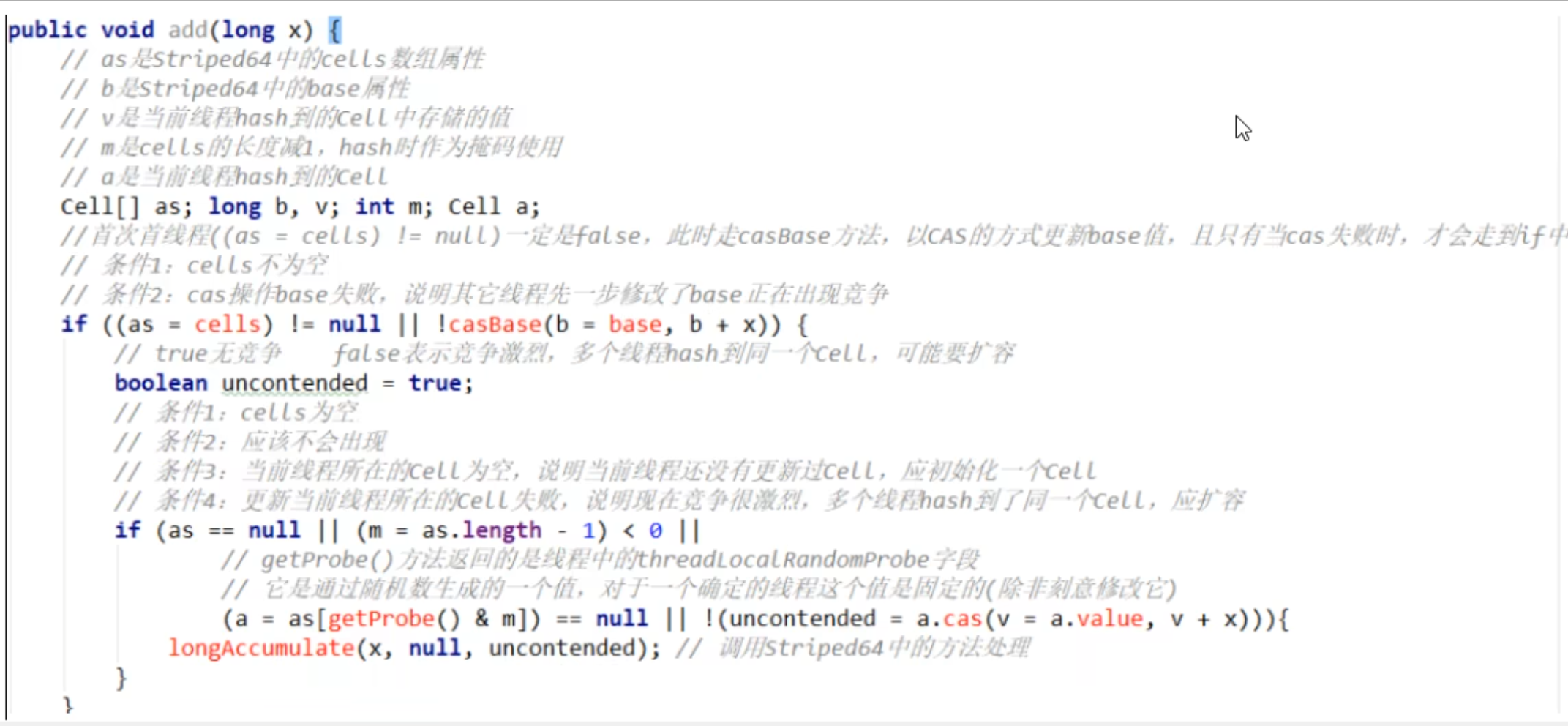
- 1 如果Cells表为空,尝试用CAS更新base字段,成功则退出
- 2 如果Cells表为空,CAS更新base字段失败,出现竞争,uncontended为true,调用longAccumulate(新建数组)
- 3 如果Cells表非空,但当前线程映射的槽为空,uncontended为true,调用longAccumulate(初始化)
- 4 如果Cells表非空,且当前线程映射的槽非空,CAS更新Cell的值,成功则返回,否则,uncontended设为false,调用longAccumulate(扩容)
-
longAccumulate
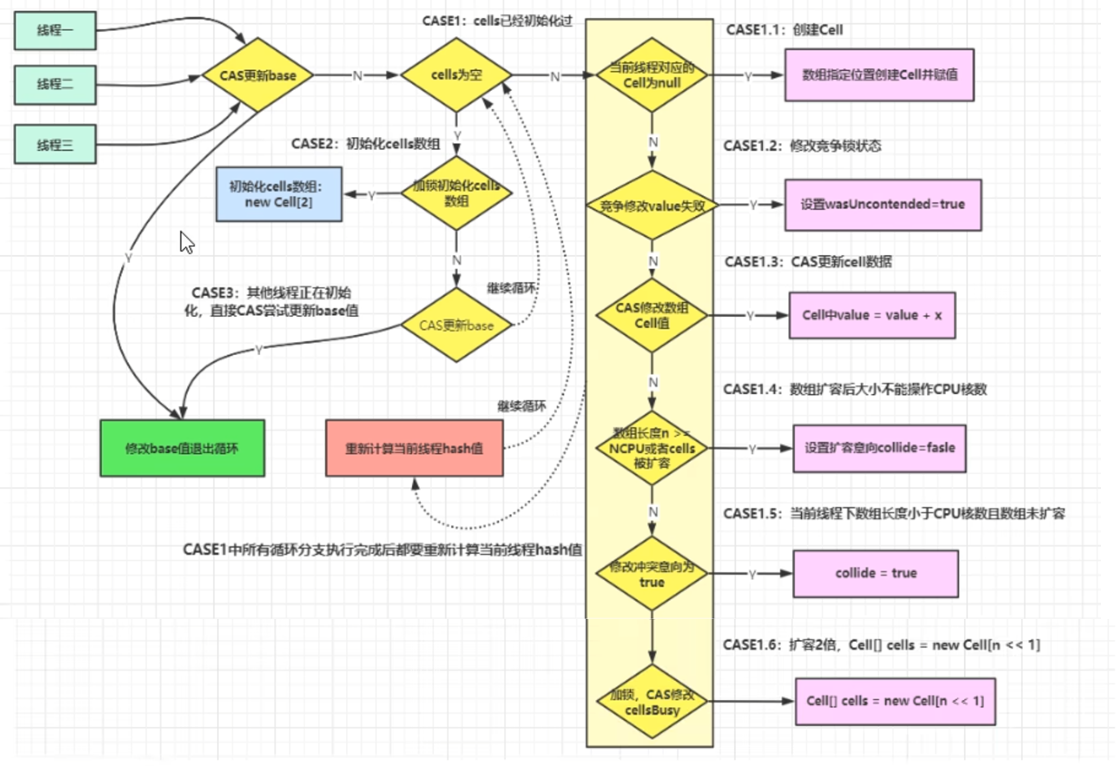
-
sum
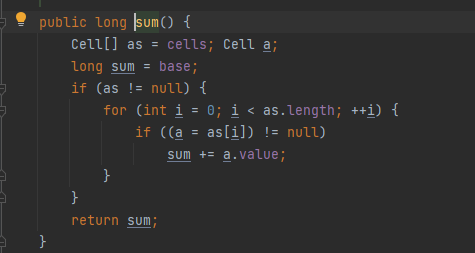
- sum()会将所有Cell数组中的value和base累加作为返回值。核心思想就是将之前AtomicLong一个value的更新压力分散到多个value中去,从而降级更新热点。
- sum执行时,并没有限制对base和cells的更新,所以LongAdder不是强一致性的,它是最终一致性的,对cell的读取无法保证是最后一次写入的值,所以在没有并发的场景下,可以获得正确的结果。
-
使用总结
- AtomicLong线程安全,可允许一些性能损耗,要求高精度时可使用,保证精度,多个线程对单个热点值value进行了原子操作-----保证精度,性能代码
- LongAdder当需要在高并发场景下有较好的性能表现,且对值得精确度要求不高时,可以使用,LongAdder时每个线程拥有自己得槽,各个线程一般只对自己槽中得那个值进行CAS操作—保证性能,精度代价
8.5.5 总结
-
AtomicLong
- 原理:CAS+自旋
- 场景:低并发下的全局计算,AtomicLong能保证并发情况下计数的准确性,其内部通过CAS来解决并发安全性问题
- 缺陷:高并发后性能急剧下降----AtomicLong的自旋会成为瓶颈(N个线程CAS操作修改线程的值,每次只有一个成功过,其他N-1失败,失败的不停自旋直至成功,这样大量失败自旋的情况,一下子cpu就打高了)
-
LongAdder
- 原理:CAS+Base+Cell数组分散-----空间换时间并分散了热点数据
- 场景:高并发下的全局计算
- 缺陷:sum求和后还有计算线程修改结果的话,最后结果不够准确
![读书笔记-《ON JAVA 中文版》-摘要15[第十五章 异常]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/23514dd52c824b8b95e44071635a1b67.png)