Shell脚本快速入门
- 1 Hello World
- 2 Shell 变量
- 3 Shell 传递参数
- 4 Shell 基本运算符
- 5 Shell echo命令
- 5 Shell printf 命令
- 6 Shell test 命令
- 7 Shell 流程控制
- 8 Shell 函数
- 9 Shell 输入/输出重定向
- 10 Shell 文件包含
- 参考
1 Hello World
编写脚本文件 test.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello World !"
#! 是一个约定的标记,它告诉系统这个脚本需要什么解释器来执行,即使用哪一种 Shell。
chmod +x ./test.sh #使脚本具有执行权限
./test.sh #执行脚本
2 Shell 变量
注意,变量名和等号之间不能有空格,这可能和你熟悉的所有编程语言都不一样。
your_name="runoob.com"
除了显式地直接赋值,还可以用语句给变量赋值,如:
for file in `ls /etc`
或
for file in $(ls /etc)
使用一个定义过的变量,只要在变量名前面加美元符号即可,如:
your_name="qinjx"
echo $your_name
echo ${your_name}
推荐给所有变量加上花括号,这是个好的编程习惯。
使用 readonly 命令可以将变量定义为只读变量,只读变量的值不能被改变。
#!/bin/bash
myUrl="https://www.google.com"
myUrl2="https://www.google.com"
readonly myUrl #将变量定义为只读变量
unset myUrl2 #删除变量,unset 命令不能删除只读变量
运行shell时,会同时存在三种变量:
- 局部变量 局部变量在脚本或命令中定义,仅在当前shell实例中有效,其他shell启动的程序不能访问局部变量。
- 环境变量 所有的程序,包括shell启动的程序,都能访问环境变量,有些程序需要环境变量来保证其正常运行。必要的时候shell脚本也可以定义环境变量。
- shell变量 shell变量是由shell程序设置的特殊变量。shell变量中有一部分是环境变量,有一部分是局部变量,这些变量保证了shell的正常运行
字符串:
your_name="runoob"
str="Hello, I know you are \"$your_name\"! \n"
echo -e $str
Shell 数组
bash支持一维数组(不支持多维数组),并且没有限定数组的大小。类似于 C 语言,数组元素的下标由 0 开始编号。
数组名=(值1 值2 ... 值n)
array_name=(value0 value1 value2 value3)
${数组名[下标]} #读取数组
echo ${array_name[@]} #@ 符号可以获取数组中的所有元素
# 取得数组元素的个数
length=${#array_name[@]}
# 或者
length=${#array_name[*]}
# 取得数组单个元素的长度
lengthn=${#array_name[n]}
# 关联数组,Bash 支持关联数组,可以使用任意的字符串、或者整数作为下标来访问数组元素。
declare -A site
site["google"]="www.google.com"
site["runoob"]="www.runoob.com"
site["taobao"]="www.taobao.com"
echo ${site["runoob"]}
3 Shell 传递参数
我们可以在执行 Shell 脚本时,向脚本传递参数,脚本内获取参数的格式为:$n。n 代表一个数字,1 为执行脚本的第一个参数,2 为执行脚本的第二个参数,以此类推……
#!/bin/bash
echo "Shell 传递参数实例!";
echo "执行的文件名:$0"; # $0 为执行的文件名(包含文件路径)
echo "第一个参数为:$1";
echo "第二个参数为:$2";
echo "第三个参数为:$3";
echo "参数个数为:$#";
echo "传递的参数作为一个字符串显示:$*";
$ chmod +x test.sh
$ ./test.sh 1 2 3
Shell 传递参数实例!
执行的文件名:./test.sh
第一个参数为:1
第二个参数为:2
第三个参数为:3
参数个数为:3
传递的参数作为一个字符串显示:1 2 3
4 Shell 基本运算符
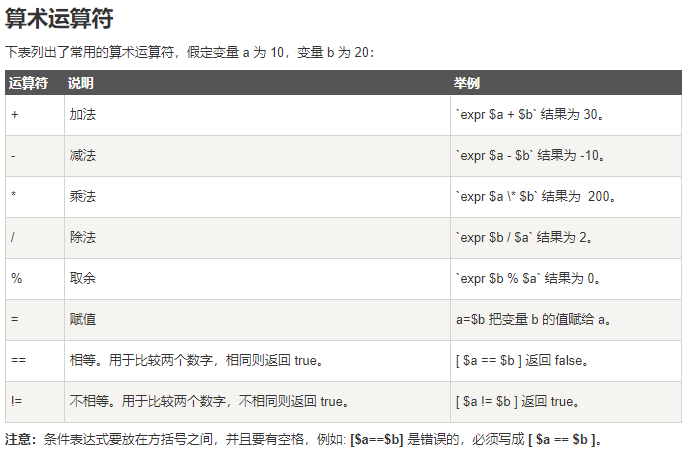
原生bash不支持简单的数学运算,但是可以通过其他命令来实现,例如 awk 和 expr,expr 最常用。
expr 是一款表达式计算工具,使用它能完成表达式的求值操作。
#!/bin/bash
val=`expr 2 + 2` #表达式和运算符之间要有空格,例如 2+2 是不对的,必须写成 2 + 2; 完整的表达式要被 ` ` 包含
echo "两数之和为 : $val"

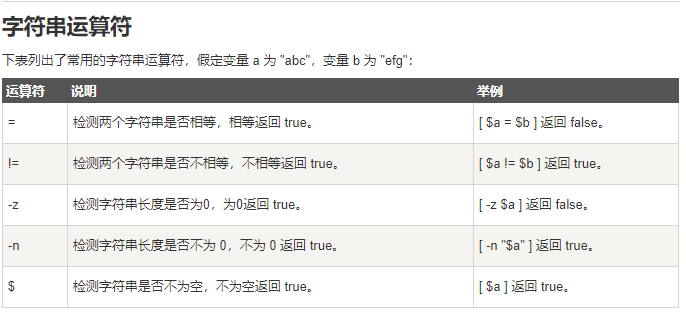
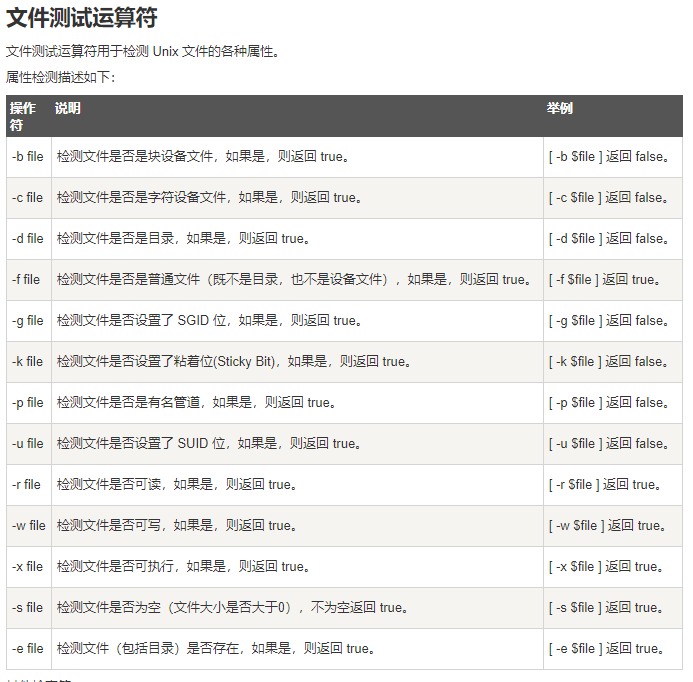
5 Shell echo命令
#!/bin/sh
read name #read 命令从标准输入中读取一行,并把输入行的每个字段的值指定给 shell 变量
echo "$name It is a test"
[root@www ~]# sh test.sh
OK #标准输入
OK It is a test #输出
echo -e "OK! \n" # -e 开启转义
echo "It is a test"
echo -e "OK! \c" # -e 开启转义 \c 不换行
echo "It is a test"
echo "It is a test" > myfile #显示结果定向至文件
echo '$name\"' #原样输出字符串,不进行转义或取变量(用单引号) 输出结果:$name\"
echo `date` #显示命令执行结果,这里使用的是反引号 `, 而不是单引号 '
5 Shell printf 命令
# 格式
printf format-string [arguments...]
printf "%d %s\n" 1 "abc"
%s %c %d %f 都是格式替代符,%s 输出一个字符串,%d 整型输出,%c 输出一个字符,%f 输出实数,以小数形式输出。
6 Shell test 命令
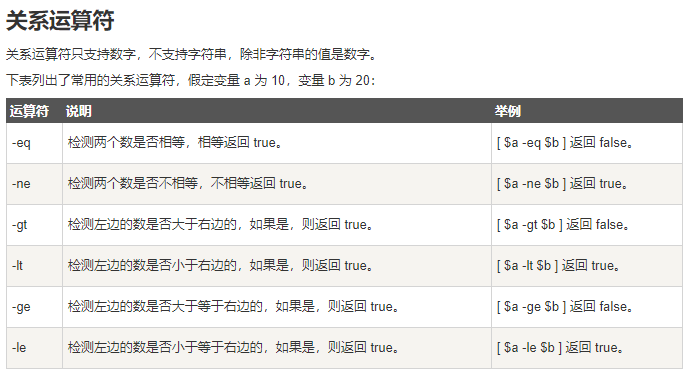
Shell中的 test 命令用于检查某个条件是否成立,它可以进行数值、字符和文件三个方面的测试。
num1=100
num2=100
if test $[num1] -eq $[num2]
then
echo '两个数相等!'
else
echo '两个数不相等!'
fi
7 Shell 流程控制
sh 的流程控制不可为空
if else
if condition1
then
command1
elif condition2
then
command2
else
commandN
fi
#if else 的 [...] 判断语句中大于使用 -gt,小于使用 -lt。
if [ "$a" -gt "$b" ]; then
...
fi
# 如果使用 ((...)) 作为判断语句,大于和小于可以直接使用 > 和 <
if (( a > b )); then
...
fi
for 循环
for var in item1 item2 ... itemN
do
command1
command2
...
commandN
done
for loop in 1 2 3 4 5
do
echo "The value is: $loop"
done
while 语句
while condition
do
command
done
#!/bin/bash
int=1
while(( $int<=5 ))
do
echo $int
let "int++"
done
case … esac
case 值 in
模式1)
command1
command2
...
commandN
;;
模式2)
command1
command2
...
commandN
;;
esac
跳出循环
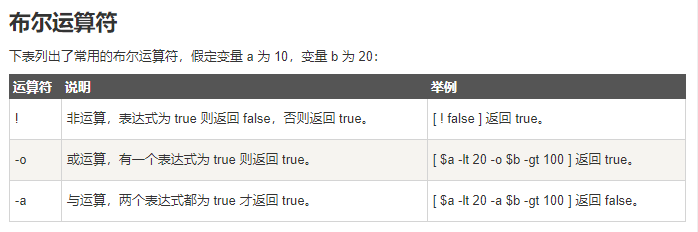
在循环过程中,有时候需要在未达到循环结束条件时强制跳出循环,Shell 使用两个命令来实现该功能:break 和 continue
8 Shell 函数
#!/bin/bash
funWithReturn(){
echo "这个函数会对输入的两个数字进行相加运算..."
echo "输入第一个数字: "
read aNum
echo "输入第二个数字: "
read anotherNum
echo "两个数字分别为 $aNum 和 $anotherNum !"
return $(($aNum+$anotherNum))
}
funWithReturn
echo "输入的两个数字之和为 $? !" #函数返回值在调用该函数后通过 $? 来获得
9 Shell 输入/输出重定向
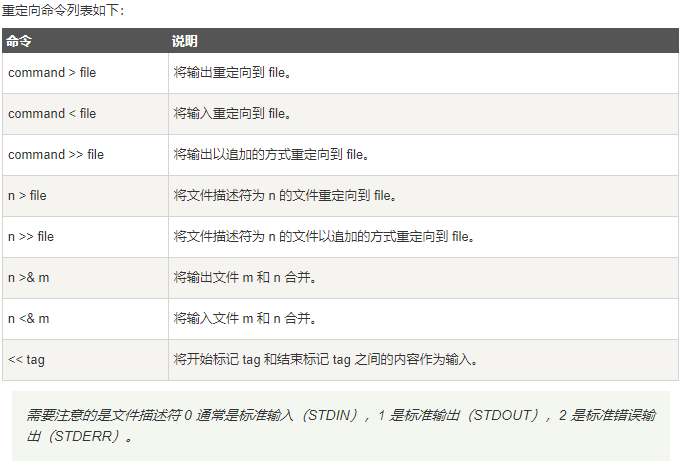
默认情况下,command > file 将 stdout 重定向到 file,command < file 将stdin 重定向到 file
如果希望 stderr 重定向到 file,可以这样写:
command 2>file
如果希望将 stdout 和 stderr 合并后重定向到 file,可以这样写:
command > file 2>&1
# 或者
command >> file 2>&1
#如果希望对 stdin 和 stdout 都重定向,command 命令将 stdin 重定向到 file1,将 stdout 重定向到 file2
command < file1 >file2
#如果希望执行某个命令,但又不希望在屏幕上显示输出结果,那么可以将输出重定向到 /dev/null:
command > /dev/null
10 Shell 文件包含
#!/bin/bash
#使用 . 号来引用test1.sh 文件
. ./test1.sh
# 或者使用以下包含文件代码
# source ./test1.sh
# url 为test1.sh 中定义的变量
echo "菜鸟教程官网地址:$url"
参考
Shell 教程