问题
今天有个小伙伴给我出了一个难题:在 SpringBoot 中如何让自己的某个指定的 Bean 在其他 Bean 前完成被 Spring 加载?我听到这个问题的第一反应是,为什么会有这样奇怪的需求?
Talk is cheap,show me the code,这里列出了那个想做最先加载的“天选 Bean” 的代码,我们来分析一下:
/**
* 系统属性服务
**/
@Service
public class SystemConfigService {
// 访问 db 的 mapper
private final SystemConfigMapper systemConfigMapper;
// 存放一些系统配置的缓存 map
private static Map<String, String>> SYS_CONF_CACHE = new HashMap<>()
// 使用构造方法完成依赖注入
public SystemConfigServiceImpl(SystemConfigMapper systemConfigMapper) {
this.systemConfigMapper = systemConfigMapper;
}
// Bean 的初始化方法,捞取数据库中的数据,放入缓存的 map 中
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
// systemConfigMapper 访问 DB,捞取数据放入缓存的 map 中
// SYS_CONF_CACHE.put(key, value);
// ...
}
// 对外提供获得系统配置的 static 工具方法
public static String getSystemConfig(String key) {
return SYS_CONF_CACHE.get(key);
}
// 省略了从 DB 更新缓存的代码
// ...
}
看过了上面的代码后,很容易就理解了为什么会标题中的需求了。
SystemConfigService 是一个提供了查询系统属性的服务,系统属性存放在 DB 中并且读多写少,在 Bean 创建的时候,通过 @PostConstruct 注解的 init() 方法完成了数据加载到缓存中,最关键的是,由于是系统属性,所以需要在很多地方都想使用,尤其需要在很多 bean 启动的时候使用,为了方便就提供了 static 方法来方便调用,这样其他的 bean 不需要依赖注入就可以直接调用,但问题是系统属性是存在 db 里面的,这就导致了不能把 SystemConfigService做成一个纯「工具类」,它必须要被 Spring 托管起来,完成 mapper 的注入才能正常工作。因此这样一来就比较麻烦,其他的类或者 Bean 如果想安全的使用 SystemConfigService#getSystemConfig 中的获取配置的静态方法,就必须等 SystemConfigService 先被 Spring 创建加载起来,完成 init() 方法后才可以。
所以才有了最开头提到的问题,如何让这个 Bean 在其他的 Bean 之前加载。
SpringBoot 官方文档推荐做法
这里引用了一段 Spring Framework 官方文档的原文:
Constructor-based or setter-based DI?
Since you can mix constructor-based and setter-based DI, it is a good rule of thumb to use constructors for mandatory dependencies and setter methods or configuration methods for optional dependencies. Note that use of the @Autowired annotation on a setter method can be used to make the property be a required dependency; however, constructor injection with programmatic validation of arguments is preferable.
可以看到 Spring 对于依赖注入更推荐(is preferable)使用构造函数来注入必须的依赖,用 setter 方法来注入可选的依赖。至于我们平时工作中更多采用的 @Autowired 注解 + 属性的注入方式是不推荐的,这也是为什么你用 Idea 集成开发环境的时候会给你一个警告。
按照 Spring 的文档,我们应该直接去掉 getSystemConfig 的 static 修饰,让 getSystemConfig 变成一个实例方法,让每个需要依赖的 SystemConfigService 的 Bean 通过构造函数完成依赖注入,这样 Spring 会保证每个 Bean 在创建之前会先把它所有的依赖创建并初始化完成。
看来我们还是要想一些其他的方法来达成我们的目的。
尝试解决问题的一些方法
@Order 注解或者实现 org.springframework.core.Ordered
最先想到的就是 Spring 提供的 Order 相关的注解和接口,实际上测试下来不可行。Order 相关的方法一般用来控制 Spring 自身组件相关 Bean 的顺序,比如 ApplicationListener,RegistrationBean 等,对于我们自己使用 @Service @Compont 注解注册的业务相关的 bean 没有排序的效果。
@AutoConfigureOrder/@AutoConfigureAfter/@AutoConfigureBefore 注解
测试下来这些注解也是不可行,它们和 Ordered 一样都是针对 Spring 自身组件 Bean 的顺序。
@DependsOn 注解
接下来是尝试加上 @DependsOn 注解:
@Service
@DependsOn({"systemConfigService"})
public class BizService {
public BizService() {
String xxValue = SystemConfigService.getSystemConfig("xxKey");
// 可行
}
}
这样测试下来是可以是可以的,就是操作起来也太麻烦了,需要让每个每个依赖 SystemConfigService的 Bean 都改代码加上注解,那有没有一种默认就让 SystemConfigService 提前的方法?
上面提到的方法都不好用,那我们只能利用 spring 给我们提供的扩展点来做文章了。
Spring 中 Bean 创建的相关知识
首先要明白一点,Bean 创建的顺序是怎么来的,如果你对 Spring 的源码比较熟悉,你会知道在 AbstractApplicationContext 里面有个 refresh 方法, Bean 创建的大部分逻辑都在 refresh 方法里面,在 refresh 末尾的 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory) 方法调用中,会调用 beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(),在这里对所有的 beanDefinitionNames 一一遍历,进行 bean 实例化和组装:
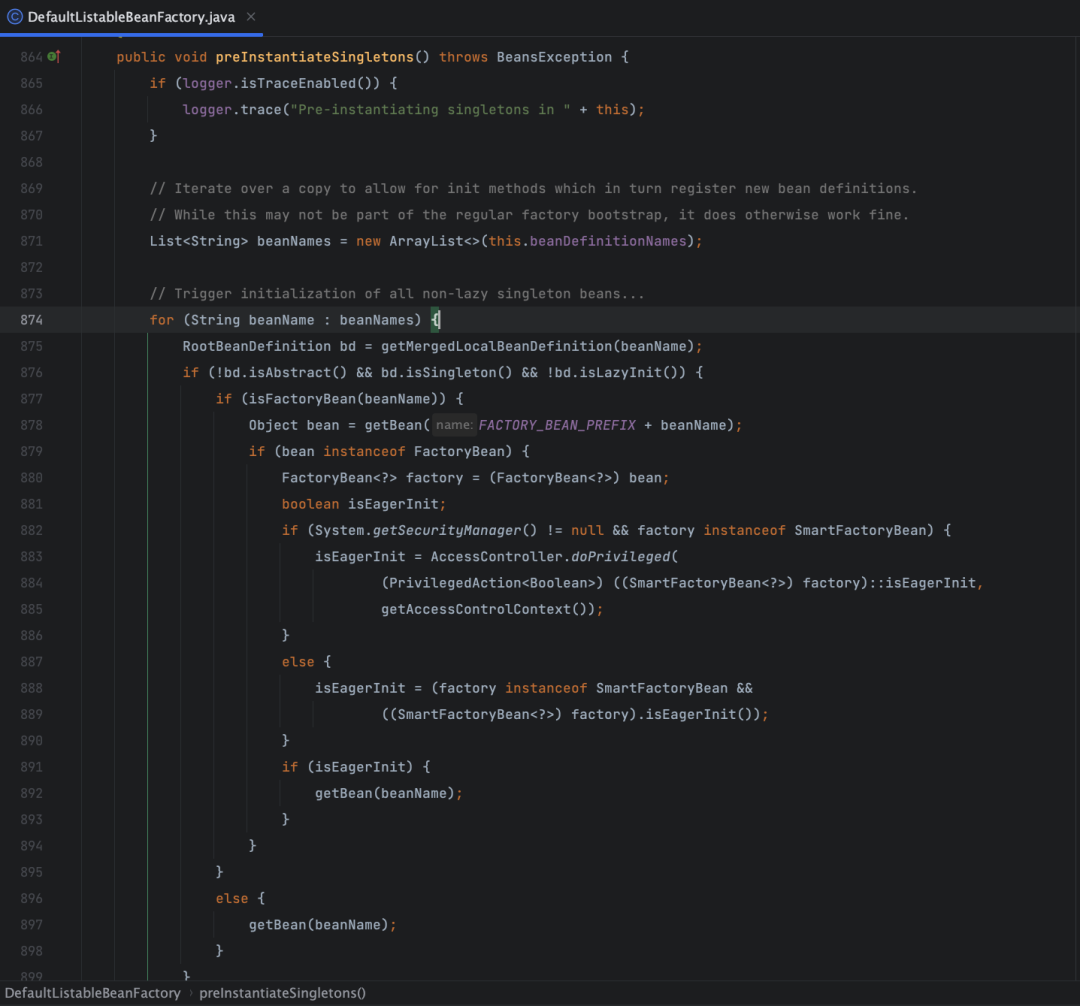
这个 beanDefinitionNames 列表的顺序就决定了 Bean 的创建顺序,那么这个 beanDefinitionNames 列表又是怎么来的?答案是 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 通过扫描你的代码和注解生成的,将 Bean 扫描解析成 Bean 定义(BeanDefinition),同时将 Bean 定义(BeanDefinition)注册到 BeanDefinitionRegistry 中,才有了 beanDefinitionNames 列表。
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 的介绍
这里提到了 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口。它是一个非常非常重要的类,甚至可以说它是 Spring boot 提供的扫描你的注解并解析成 BeanDefinition 最重要的组件。我们在使用 SpringBoot 过程中用到的 @Configuration、@ComponentScan、@Import、@Bean 这些注解的功能都是通过 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 注解实现的,这里找了一篇文件介绍,就不多说了。https://juejin.cn/post/6844903944146124808
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 相关接口的介绍
接下来还要介绍 Spring 中提供的一些扩展,它们在 Bean 的创建过程中起到非常重要的作用。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 它的作用:
- 在 BeanFactory 初始化之后调用,来定制和修改 BeanFactory 的内容
- 所有的 Bean 定义(BeanDefinition)已经保存加载到 beanFactory,但是 Bean 的实例还未创建
- 方法的入参是 ConfigurrableListableBeanFactory,意思是你可以调整 ConfigurrableListableBeanFactory 的配置
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 它的作用:
- 是 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的子接口
- 在所有 Bean 定义(BeanDefinition)信息将要被加载,Bean 实例还未创建的时候加载
- 优先于 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 执行,利用 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 可以给 Spring 容器中自定义添加 Bean
- 方法入参是 BeanDefinitionRegistry,意思是你可以调整 BeanDefinitionRegistry 的配置
还有一个类似的 BeanPostProcessor 它的作用:
- 在 Bean 实例化之后执行的
- 执行顺序在 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 之后
- 方法入参是 Object bean,意思是你可以调整 bean 的配置
搞明白了以上的内容,下面我们可以直接动手写代码了。
最终答案
第一步:通过 spring.factories 扩展来注册一个 ApplicationContextInitializer:
# 注册 ApplicationContextInitializer
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=com.antbank.demo.bootstrap.MyApplicationContextInitializer
注册 ApplicationContextInitializer 的目的其实是为了接下来注册 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 到 Spring 中,我没有找到直接使用 spring.factories 来注册 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的方式,猜测是不支持的:
public class MyApplicationContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// 注意,如果你同时还使用了 spring cloud,这里需要做个判断,要不要在 spring cloud applicationContext 中做这个事
// 通常 spring cloud 中的 bean 都和业务没关系,是需要跳过的
applicationContext.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor());
}
}
除了使用 spring 提供的 SPI 来注册 ApplicationContextInitializer,你也可以用 SpringApplication.addInitializers 的方式直接在 main 方法中直接注册一个 ApplicationContextInitializer 结果都是可以的:
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(SpringBootDemoApplication.class);
// 通过 SpringApplication 注册 ApplicationContextInitializer
application.addInitializers(new MyApplicationContextInitializer());
application.run(args);
}
}
当然了,通过 Spring 的事件机制也可以做到注册 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,选择实现合适的 ApplicationListener 事件,可以通过 ApplicationContextEvent 获得 ApplicationContext,即可注册 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,这里就不多展开了。
这里需要注意一点,为什么需要用 ApplicationContextInitializer 来注册 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,能不能用 @Component 或者其他的注解的方式注册?
答案是不能的。@Component 注解的方式注册能注册上的前提是能被 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 扫描到,也就是说用 @Component 注解的方式来注册,注册出来的 Bean 一定不可能排在 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 前面,而我们的目的就是在所有的 Bean 扫描前注册你需要的 Bean,这样才能排在其他所有 Bean 前面,所以这里的场景下是不能用注解注册的,这点需要额外注意。
第二步:实现 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,注册目标 bean:
用 MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 在 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 扫描前注册你需要的目标 bean 的 BeanDefinition 即可。
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
// 手动注册一个 BeanDefinition
registry.registerBeanDefinition("systemConfigService", new RootBeanDefinition(SystemConfigService.class));
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {}
}
当然你也可以使用一个类同时实现 ApplicationContextInitializer 和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
通过 applicationContext#addBeanFactoryPostProcessor 注册的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,比 Spring 自带的优先级要高,所以这里就不需要再实现 Ordered 接口提升优先级就可以排在 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 前面:
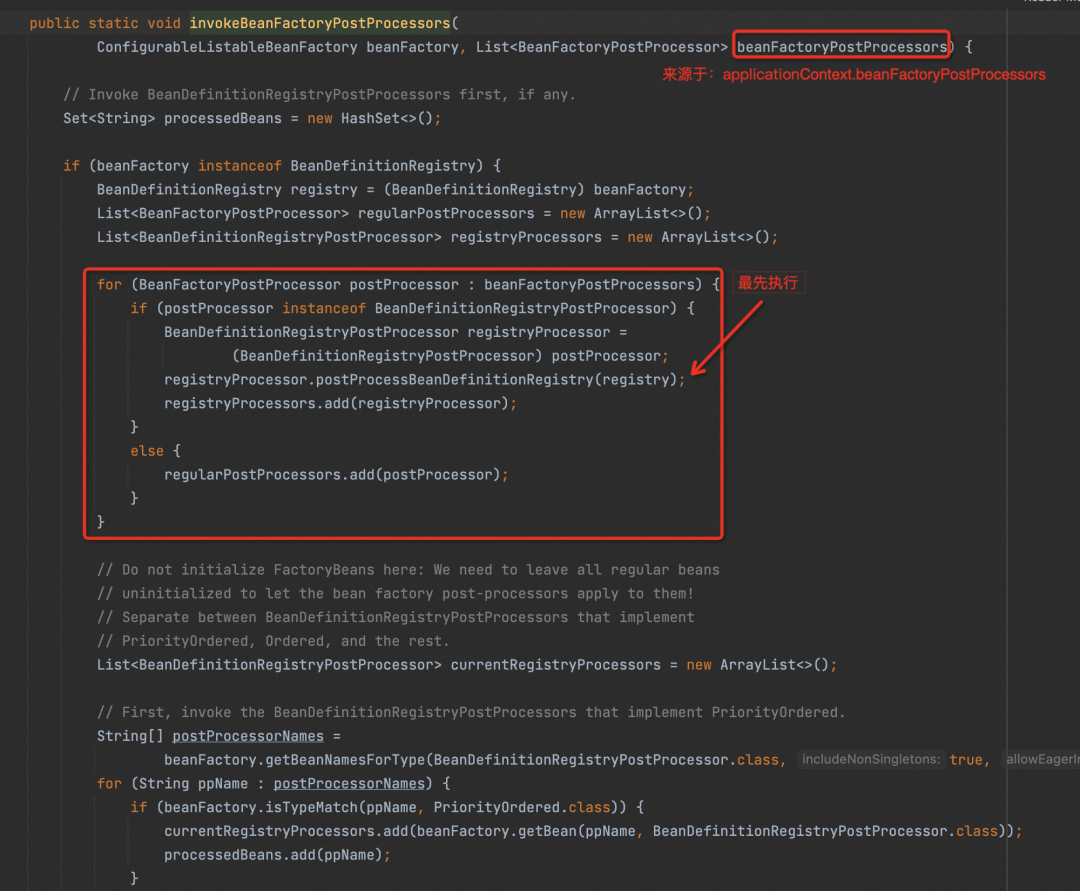
经过测试发现,上面的方式可行的,SystemConfigService 被排在第五个 Bean 进行实例化,排在前面的四个都是 Spring 自己内部的 Bean 了,也没有必要再提前了。
本文提供的方式并不是唯一的,如果你有更好的方法,欢迎在评论区留言交流。