一 管道初级测试
写两个小程序,一个负责向管道发数据,一个从管道接收数据;
pipe.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "hello world" << endl;
return 0;
}pipe2.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#define DEBUG_INFO(format, ...) printf("%s:%d -- " format "\n", __func__, __LINE__,##__VA_ARGS__)
int main()
{
string str;
while(1){
str.clear();
cin >> str;
if(str.length() == 0)break;
DEBUG_INFO("%s",str.c_str());
}
return 0;
}编译生成pipe和pipe2两个可执行文件:
$ls -lsh pipe*
12K -rwxrwxr-x 1 lkmao lkmao 9.1K 5月 6 15:52 pipe
16K -rwxrwxr-x 1 lkmao lkmao 14K 5月 6 15:52 pipe2执行如下指令:
$ ./pipe | ./pipe2
main:14 -- hello
main:14 -- world第二个程序接收到数据了,那么问题来了,代码中怎么没有管道。执行程序那根竖线就是管道。
strace命令跟踪
strace ./pipe | ./pipe2
strace ./pipe
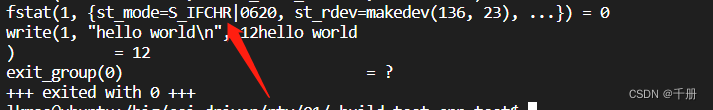
strace ./pipe | strace ./pipe2

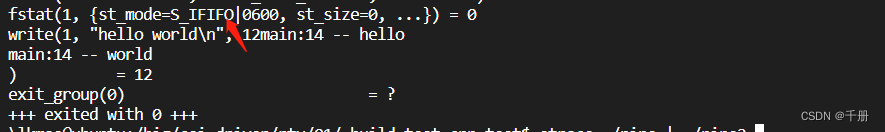
如图所示,S_IFIFO和S_IFCHR不一样,这两个宏的含义如下所示
S_IFCHR:文件是一个特殊的字符设备
S_IFIFO:文件是一个FIFO设备
也就是说,如果是S_IFIFO,那么文件描述符1表示,它对应的打开的文件是个管道。如果是S_IFCHR,则表示对应的文件是个字符设备,也就是终端,终端也是个字符设备,所以没毛病,就是常说的标准输出。
在命令./pipe | ./pipe2 中,pipe程序向管道输出"hello world" pipe2从管道中读取数据。

二 pipe函数创建匿名管道
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe(int pipefd[2]);
#define _GNU_SOURCE /* See feature_test_macros(7) */
#include <fcntl.h> /* Obtain O_* constant definitions */
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe2(int pipefd[2], int flags);测试,使用pipe创建管道,使用fork创建一个子进程,进程中向向1 写入数据,父进程从0读出数据
测试代码1:传递一个字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define DEBUG_INFO(format, ...) printf("%s:%d -- " format "\n", __func__, __LINE__,##__VA_ARGS__)
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int fds[2];
pid_t pid;
int ret = pipe(fds);
if(ret != 0){
perror("pipe");
exit(0);
}
char send_buf[100];
char read_buf[100];
memset(read_buf, 0, sizeof(read_buf));
memset(send_buf, 0, sizeof(send_buf));
DEBUG_INFO("%d %d",fds[0],fds[1]);
cout << "create pipe ok" << endl;
pid = fork();
if(pid == -1){
perror("fork");
exit(-1);
}
if(pid == 0){
int send_len = snprintf(send_buf, sizeof(send_buf),"wo shi child %u",getpid());
DEBUG_INFO("write:send_len = %d,buf = %s",send_len,send_buf);
int ret = write(fds[1], send_buf,send_len);
if(ret == -1){
perror("write");
exit(-1);
}
DEBUG_INFO("child write finish:ret = %d,buf = %s",ret,send_buf);
sleep(1);
}else{
int read_len = read(fds[0],read_buf,sizeof(read_buf));
DEBUG_INFO("parent read finish:len = %d,buf = %s",read_len,read_buf);
sleep(1);
}
DEBUG_INFO("bye bye %d",getpid());
return 0;
}测试结果:
main:23 -- 3 4
create pipe ok
main:35 -- write:send_len = 18,buf = wo shi child 46834
main:41 -- child write finish:ret = 18,buf = wo shi child 46834
main:47 -- parent read finish:len = 18,buf = wo shi child 46834
main:50 -- bye bye 46834
main:50 -- bye bye 46833测试代码2:传递一个结构体:
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#define DEBUG_INFO(format, ...) printf("%s:%d -- " format "\n", __func__, __LINE__,##__VA_ARGS__)
using namespace std;
struct mystruct{
int type;
int len;
int frame_size;
int frame_index;
int frame_count;
int offset;
int length;
char buf[128];
uint32_t crc;
};
int main()
{
int fds[2];
pid_t pid;
int ret = pipe(fds);
if(ret != 0){
perror("pipe");
exit(0);
}
struct mystruct *ms1 = (struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
struct mystruct *ms2 = (struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
char send_buf[100];
char read_buf[100];
memset(read_buf, 0, sizeof(read_buf));
memset(send_buf, 0, sizeof(send_buf));
DEBUG_INFO("%d %d",fds[0],fds[1]);
cout << "create pipe ok" << endl;
pid = fork();
if(pid == -1){
perror("fork");
exit(-1);
}
if(pid == 0){
ms1->type = 1001;
ms1->crc = 0x1001;
ms2->type = 1002;
ms2->crc = 0x1002;
ret = write(fds[1], ms1,sizeof(struct mystruct));
if(ret == -1){
perror("write");
exit(-1);
}
ret = write(fds[1], ms2,sizeof(struct mystruct));
if(ret == -1){
perror("write");
exit(-1);
}
DEBUG_INFO("child %u write finish",getpid());
sleep(1);
}else{
sleep(2);
int read_len_1 = read(fds[0],ms1,sizeof(struct mystruct));
int read_len_2 = read(fds[0],ms2,sizeof(struct mystruct));
DEBUG_INFO("parent read finish:len = %d,crc = %04x",read_len_1,ms1->crc);
DEBUG_INFO("parent read finish:len = %d,crc = %04x",read_len_2,ms2->crc);
sleep(1);
}
DEBUG_INFO("bye bye %d",getpid());
return 0;
}在父进程中睡眠两秒,是为了保证让子进程先写完两次。
测试结果:
main:37 -- 3 4
create pipe ok
main:62 -- child 47519 write finish
main:75 -- bye bye 47519
main:71 -- parent read finish:len = 160,crc = 1001
main:72 -- parent read finish:len = 160,crc = 1002
main:75 -- bye bye 47518从测试结果可知:
1 管道可以用于传输结构体
2 管道中的传输的数据先写先到达,先被读
例如这些特点,和管道队列满的特点,就可以实现管道的双向通信了。
测试一下PIPE_BUF
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <linux/limits.h>
#define DEBUG_INFO(format, ...) printf("%s:%d -- " format "\n", __func__, __LINE__,##__VA_ARGS__)
using namespace std;
struct mystruct{
int type;
int len;
int frame_size;
int frame_index;
int frame_count;
int offset;
int length;
char buf[PIPE_BUF];
uint32_t crc;
};
int main()
{
int fds[2];
pid_t pid;
int ret = pipe(fds);
if(ret != 0){
perror("pipe");
exit(0);
}
DEBUG_INFO("PIPE_BUF = %d",PIPE_BUF);
struct mystruct *ms1 = (struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
struct mystruct *ms2 = (struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
char send_buf[100];
char read_buf[100];
memset(read_buf, 0, sizeof(read_buf));
memset(send_buf, 0, sizeof(send_buf));
DEBUG_INFO("%d %d",fds[0],fds[1]);
cout << "create pipe ok" << endl;
pid = fork();
if(pid == -1){
perror("fork");
exit(-1);
}
if(pid == 0){
ms1->type = 1001;
ms1->crc = 0x1001;
ms2->type = 1002;
ms2->crc = 0x1002;
ret = write(fds[1], ms1,sizeof(struct mystruct));
if(ret == -1){
perror("write");
exit(-1);
}
DEBUG_INFO("ret = %d",ret);
ret = write(fds[1], ms2,sizeof(struct mystruct));
if(ret == -1){
perror("write");
exit(-1);
}
DEBUG_INFO("ret = %d",ret);
DEBUG_INFO("child %u write finish",getpid());
sleep(1);
}else{
sleep(2);
int read_len_1 = read(fds[0],ms1,sizeof(struct mystruct));
int read_len_2 = read(fds[0],ms2,sizeof(struct mystruct));
DEBUG_INFO("parent read finish:len = %d,crc = %04x",read_len_1,ms1->crc);
DEBUG_INFO("parent read finish:len = %d,crc = %04x",read_len_2,ms2->crc);
sleep(1);
}
DEBUG_INFO("bye bye %d",getpid());
return 0;
}测试结果:
main:33 -- PIPE_BUF = 4096
main:40 -- 3 4
create pipe ok
main:60 -- ret = 4128
main:66 -- ret = 4128
main:67 -- child 47924 write finish
main:79 -- bye bye 47924
main:75 -- parent read finish:len = 4128,crc = 1001
main:76 -- parent read finish:len = 4128,crc = 1002
main:79 -- bye bye 47923PIPE_BUF的值是4096
写一个测试程序,
测试看看写入多少时,会写满出错。在此例中,将管道描述符设置为非阻塞模式:
1 子进程循环向管道写数据,直到出错返回-1
2 父进程循环从管道读数据,直到出错返回-1
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <linux/limits.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define DEBUG_INFO(format, ...) printf("%s:%d -- " format "\n", __func__, __LINE__,##__VA_ARGS__)
using namespace std;
struct mystruct{
int type;
int len;
int frame_size;
int frame_index;
int frame_count;
int offset;
int length;
char buf[PIPE_BUF];
uint32_t crc;
};
int main()
{
int fds[2];
pid_t pid;
int ret = pipe(fds);
if(ret != 0){
perror("pipe");
exit(0);
}
DEBUG_INFO("PIPE_BUF = %d",PIPE_BUF);
struct mystruct *ms1 = (struct mystruct *)malloc(sizeof(struct mystruct));
char send_buf[100];
char read_buf[100];
memset(read_buf, 0, sizeof(read_buf));
memset(send_buf, 0, sizeof(send_buf));
DEBUG_INFO("%d %d",fds[0],fds[1]);
cout << "create pipe ok" << endl;
pid = fork();
if(pid == -1){
perror("fork");
exit(-1);
}
if(pid == 0){
int flag = fcntl(fds[1], F_GETFL, 0);
flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(fds[1], F_SETFL, flag);
int count = 0;
while(1){
ms1->type = 1001 + count;
ms1->crc = 0x1001 + count;
ret = write(fds[1], ms1,sizeof(struct mystruct));
if(ret == -1){
perror("write");
break;
}
DEBUG_INFO("ret = %d",ret);
count++;
}
DEBUG_INFO("write %d cuccess",count * sizeof(struct mystruct));
DEBUG_INFO("child %u write finish",getpid());
sleep(1);
}else{
sleep(20);
int flag = fcntl(fds[0], F_GETFL, 0);
flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(fds[0], F_SETFL, flag);
while(1){
ret = read(fds[0],ms1,sizeof(struct mystruct));
if(ret == -1){
perror("read");
break;
}
DEBUG_INFO("ret = %d,%d,%04x",ret,ms1->type,ms1->crc);
}
DEBUG_INFO("parent");
}
DEBUG_INFO("bye bye %d",getpid());
return 0;
}测试结果:
main:34 -- PIPE_BUF = 4096
main:40 -- 3 4
create pipe ok
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4096
write: Resource temporarily unavailable
main:66 -- write 45408 cuccess
main:67 -- child 48554 write finish
main:86 -- bye bye 48554
main:81 -- ret = 4128,1001,1001
main:81 -- ret = 4128,1002,1002
main:81 -- ret = 4128,1003,1003
main:81 -- ret = 4128,1004,1004
main:81 -- ret = 4128,1005,1005
main:81 -- ret = 4128,1006,1006
main:81 -- ret = 4128,1007,1007
main:81 -- ret = 4128,1008,1008
main:81 -- ret = 4128,1009,1009
main:81 -- ret = 4128,1010,100a
main:81 -- ret = 4096,1011,100a
read: Resource temporarily unavailable
main:84 -- parent
main:86 -- bye bye 48553从结果可知,write返回结果的前一次,返回结果是4096,小于结构体的大小。这里需要判断,这个返回的4096,是不是表示写了4096个字节。正式项目时,这里还要剩下的没写成功的数据写完。
父进程读数据,最后读回了4096个字节,也是要判断数据的完整性。防止误判。
至少,管道中到底能存多少数据。这个要不同的操作系统,在使用之前测试一下。大部分情况下,只要满足需要就可以了。
测试代码修改为阻塞模式:就是注释掉下图中的两段代码
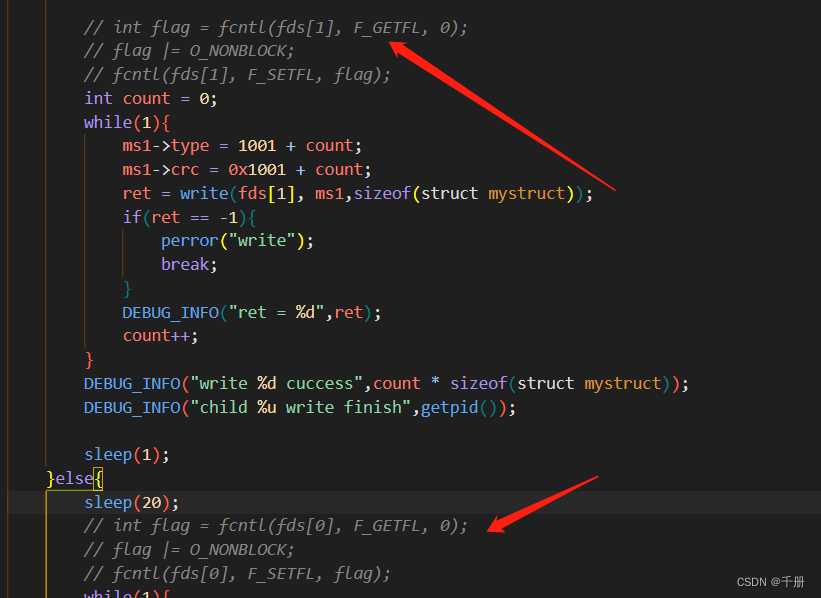
一不小心,就出来了一大堆,总之阻塞模式下是不会出现写一半的情况的。
main:81 -- ret = 4128,75163,131b3
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:81 -- ret = 4128,75164,131b4
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:81 -- ret = 4128,75165,131b5
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:81 -- ret = 4128,75166,131b6
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:81 -- ret = 4128,75167,131b7
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:81 -- ret = 4128,75168,131b8
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:81 -- ret = 4128,75169,131b9
main:81 -- ret = 4128,75170,131ba
main:81 -- ret = 4128,75171,131bb
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:63 -- ret = 4128
main:81 -- ret = 4128,75172,131b所以,如果代码相对简单,设置为阻塞模式。就会使代码更简单。减少出错的机会。尽量不要为了使用IO多路复用而使用IO多路复用。
三 命名管道
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mkfifoat(int dirfd, const char *pathname, mode_t mode);删除一个命名管道:
#include <unistd.h>
int unlink(const char *pathname);测试一:创建一个命名管道:子进程写,父进程读
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <linux/limits.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define DEBUG_INFO(format, ...) printf("%s:%d -- " format "\n", __func__, __LINE__,##__VA_ARGS__)
using namespace std;
#define FIFO_NAME "myfifo"
void create_fifo(const char *file_name){
int ret = unlink(file_name);
if(ret == -1){
perror("unlink");
}
ret = mkfifo(file_name,0666);
if(ret < 0){
perror("mkfifo");
exit(1);
}
DEBUG_INFO("mkfifo ok ret = %d",ret);
system("ls -lsh myfifo");
}
int main(int argc, char** argv){
create_fifo(FIFO_NAME);
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == 0){
int fd = open(FIFO_NAME,O_WRONLY);
if(fd < 0){
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
write(fd, "hello world",sizeof("hello world"));
close(fd);
sleep(1);
}
if(pid > 0){
char buf[100] = {0};
int fd = open(FIFO_NAME,O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0){
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
int len = read(fd, buf,sizeof(buf));
DEBUG_INFO("read len = %d,buf = %s",len,buf);
close(fd);
}
if(pid == -1){
perror("fork");
exit(-1);
}
sleep(10);
return 0;
}测试结果:
create_fifo:28 -- mkfifo ok ret = 0
0 prw-rw-r-- 1 lkmao lkmao 0 5月 8 12:49 myfifo
main:53 -- read len = 12,buf = hello world代码中设置的mode是0666,但是文件实际上是664,为什么呢,这个和系统本身的掩码mask有关:
执行umask:
umask 0002所以设置的真正值是(mode & ~umask) = 0666 &~0002 = 0664
小结
更多细节还需根据具体情况严谨测试,切记相当然的认为,它一定会使这样的,以事实为依据,以理论为准绳。