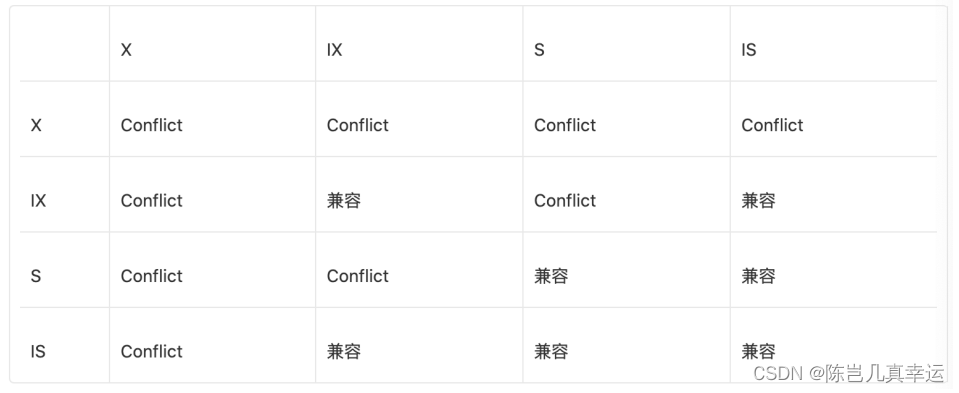
手搓决策树:用决策树将其应用于分类蘑菇是可食用还是有毒的任务
温馨提示:下面为不完全代码,只是每个步骤代码的实现,需要完整跑通代码的同学不建议花时间看;适合了解决策树各个流程及代码实现的同学复习使用。
1 数据
1.1 one-hot编码数据集

1.2数据集:
X_train = np.array([[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,0,0],[1,0,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1],[0,1,0],[1,0,0]])
y_train = np.array([1,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,0])The shape of X_train is: (10, 3) The shape of y_train is: (10,)
10条数据,3个特征xi+1个目标y
2 计算熵
- 计算𝑝1,这是可食用示例的一部分(即具有 value =
1iny) - 然后计算熵:
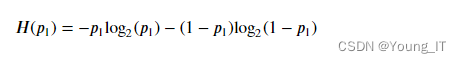
代码:
def compute_entropy(y):
"""
Computes the entropy for
Args:
y (ndarray): Numpy array indicating whether each example at a node is
edible (`1`) or poisonous (`0`)
Returns:
entropy (float): Entropy at that node
"""
# You need to return the following variables correctly
entropy = 0.
### START CODE HERE ###
if len(y) != 0:
p1 = np.count_nonzero(y == 1)/len(y)
if p1 != 0 and p1 != 1:
entropy = -p1*np.log2(p1) - (1-p1)*np.log2(1-p1)
### END CODE HERE ###
return entropy3 拆分数据集(分裂)
- 该函数接收训练数据、该节点的数据点索引列表以及要拆分的特征。
- 它拆分数据并返回左右分支的索引子集。
- 例如,假设我们从根节点 (so
node_indices = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]) 开始,我们选择在特征上进行拆分0,即示例是否有棕色帽。left_indices = [0,1,2,3,4,7,9]然后函数的输出是right_indices = [5,6,8]
split_dataset()下图所示的功能
- 对于中的每个索引
node_indicesX如果该特征在该索引处的值为1,则将该索引添加到left_indicesX如果该特征在该索引处的值为0,则将该索引添加到right_indices
def split_dataset(X, node_indices, feature):
"""
Splits the data at the given node into
left and right branches
Args:
X (ndarray): Data matrix of shape(n_samples, n_features)
node_indices (ndarray): List containing the active indices. I.e, the samples being considered at this step.
feature (int): Index of feature to split on
Returns:
left_indices (ndarray): Indices with feature value == 1
right_indices (ndarray): Indices with feature value == 0
"""
# You need to return the following variables correctly
left_indices = []
right_indices = []
### START CODE HERE ###
X_f = X[:,feature]
for i in node_indices:
if X_f[i] == 1:
left_indices.append(i)
elif X_f[i] == 0:
right_indices.append(i)
### END CODE HERE ###
return left_indices, right_indices4 计算信息增益
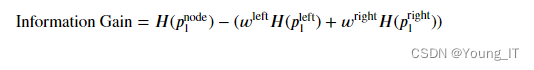
- 𝐻(𝑝node1)是节点处的熵
- 𝐻(𝑝left1) 和𝐻(𝑝right1)是由分裂产生的左分支和右分支的熵
- 𝑤分别是左右分支的示例比例
def compute_information_gain(X, y, node_indices, feature):
"""
Compute the information of splitting the node on a given feature
Args:
X (ndarray): Data matrix of shape(n_samples, n_features)
y (array like): list or ndarray with n_samples containing the target variable
node_indices (ndarray): List containing the active indices. I.e, the samples being considered in this step.
Returns:
cost (float): Cost computed
"""
# Split dataset
left_indices, right_indices = split_dataset(X, node_indices, feature)
# Some useful variables
X_node, y_node = X[node_indices], y[node_indices]
X_left, y_left = X[left_indices], y[left_indices]
X_right, y_right = X[right_indices], y[right_indices]
# You need to return the following variables correctly
information_gain = 0
### START CODE HERE ###
# Weights
wl = len(X_left)/len(X_node)
wr = len(X_right)/len(X_node)
#Weighted entropy
Hn = compute_entropy(y_node)
Hl = compute_entropy(y_left)
Hr = compute_entropy(y_right)
#Information gain
information_gain = Hn-(wl*Hl+wr*Hr)
### END CODE HERE ###
return information_gain5 获得最佳划分(分裂)
get_best_split()如下所示的功能。
- 该函数接收训练数据以及该节点的数据点索引
- 函数的输出给出最大信息增益的特征
- 您可以使用该
compute_information_gain()函数迭代特征并计算每个特征的信息
- 您可以使用该
def get_best_split(X, y, node_indices):
"""
Returns the optimal feature and threshold value
to split the node data
Args:
X (ndarray): Data matrix of shape(n_samples, n_features)
y (array like): list or ndarray with n_samples containing the target variable
node_indices (ndarray): List containing the active indices. I.e, the samples being considered in this step.
Returns:
best_feature (int): The index of the best feature to split
"""
# Some useful variables
num_features = X.shape[1]
# You need to return the following variables correctly
best_feature = -1
gain_max = 0
### START CODE HERE ###
for i in range(num_features):
gain_ = compute_information_gain(X, y, node_indices, i)
if gain_ > gain_max:
gain_max = gain_
best_feature = i
### END CODE HERE ##
return best_feature6 构建树
在上面实现的函数来生成决策树,方法是连续选择最佳特征进行拆分,直到达到停止条件(最大深度为 2)。
tree = []
def build_tree_recursive(X, y, node_indices, branch_name, max_depth, current_depth):
"""
Build a tree using the recursive algorithm that split the dataset into 2 subgroups at each node.
This function just prints the tree.
Args:
X (ndarray): Data matrix of shape(n_samples, n_features)
y (array like): list or ndarray with n_samples containing the target variable
node_indices (ndarray): List containing the active indices. I.e, the samples being considered in this step.
branch_name (string): Name of the branch. ['Root', 'Left', 'Right']
max_depth (int): Max depth of the resulting tree.
current_depth (int): Current depth. Parameter used during recursive call.
"""
# Maximum depth reached - stop splitting
if current_depth == max_depth:
formatting = " "*current_depth + "-"*current_depth
print(formatting, "%s leaf node with indices" % branch_name, node_indices)
return
# Otherwise, get best split and split the data
# Get the best feature and threshold at this node
best_feature = get_best_split(X, y, node_indices)
tree.append((current_depth, branch_name, best_feature, node_indices))
formatting = "-"*current_depth
print("%s Depth %d, %s: Split on feature: %d" % (formatting, current_depth, branch_name, best_feature))
# Split the dataset at the best feature
left_indices, right_indices = split_dataset(X, node_indices, best_feature)
# continue splitting the left and the right child. Increment current depth
build_tree_recursive(X, y, left_indices, "Left", max_depth, current_depth+1)
build_tree_recursive(X, y, right_indices, "Right", max_depth, current_depth+1)build_tree_recursive(X_train, y_train, root_indices, "Root", max_depth=2, current_depth=0)(本示例问题来源Andrew NG 机器学习公开课)