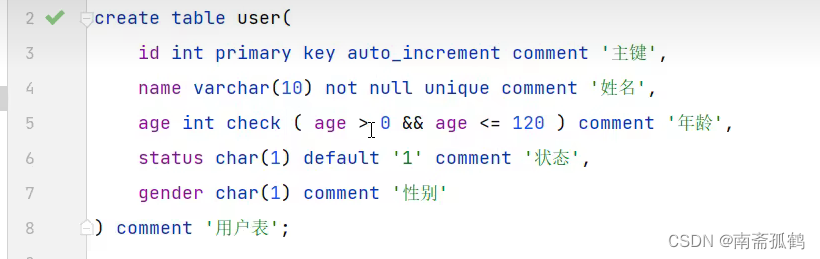
1. TCP连接
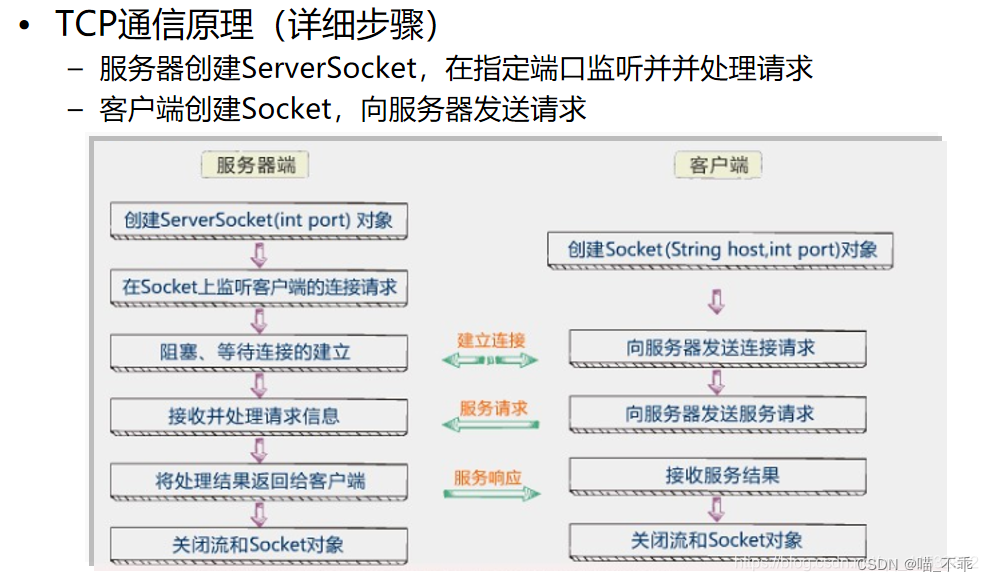
服务器创建ServerSocket,并指定端口进行监听;
ServerSocket通过accept()接受用户请求并返回Socket,否则一直处于监听状态,线程阻塞;
客户端创建Socket,需要指定服务器的ip和端口,向服务器发送连接请求。
连接建立以后,客户端发送数据需要输出流,接受数据需要输入流,服务器也一样。
客户端
连接服务器Socket
发送消息
//客户端
public class TcpClientDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//1.我要知道服务器的地址,端口号
InetAddress serverIP = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 9999;
//2.创建一个socket连接
Socket socket = new Socket(serverIP, port);
//3.发送消息IO流
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("你好,欢迎学习java".getBytes());
os.close();
socket.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
服务器
建立服务器端口ServerSocket
等待用户连接
接收用户消息
//服务端
public class TcpServerDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//1.我要有一个地址
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
//2.等待客户端连接
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
//3.读取客户端消息
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
//管道流,用来输出客户端传来的东西
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
if ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
baos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
baos.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2. UDP
发短信:不用连接,需要知道对方的地址!
发送方
//发送方
public class UdpSendDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.建立一个数据socket
DatagramSocket socket=new DatagramSocket();
//2.要发给谁
InetAddress localhost=InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
int port=9090;
//3.建一个包
String str="你好啊,服务器~";
//数据,数据的开始,结束,要发给谁
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(str.getBytes(),0,str.getBytes().length,localhost,port);
//4.发送
socket.send(packet);
//5.关闭
socket.close();
}
}
接收方
//接收方,还是要等待别人给发送!随时都在线监听
public class UdpReceiverDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//开放端口
DatagramSocket socket=new DatagramSocket(9090);
//接收数据包
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer, 0, buffer.length);//接收
//接收
socket.receive(packet);
System.out.println(packet.getAddress().getHostAddress());
System.out.println(new String(packet.getData(),0,packet.getData().length));
//关闭
socket.close();
}
}
循环发送消息
public class UdpSenderDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(8888);
//准备数据:读取控制台输入
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while (true) {
String data = reader.readLine();
byte[] bts = data.getBytes();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bts, 0, bts.length, new InetSocketAddress("localhost",6666));
socket.send(packet);
if (data.equals("bye")){
break;
}
}
socket.close();
}
}
循环接收消息
public class UdpReceiverDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(6666);
while (true) {
//准备接收包
byte[] bts = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bts, 0, bts.length);
socket.receive(packet);
//断开连接
byte[] data=packet.getData();
String receivedata = new String(data, 0, data.length);
System.out.println(receivedata);
if (receivedata.equals("bye")){
break;
}
}
socket.close();
}
}
3. 在线咨询:两个人都可以是发送方或者接收方!
先创建两个工具类,一个用来发送消息,一个用来接收消息,并且都是单独的线程(实现线程接口)
创建两个聊天的人,这两个人都有发送和接收功能。
发送线程
public class TalkSend implements Runnable { //实现线程接口
DatagramSocket socket = null;
BufferedReader reader = null;
private int fromPort;
private String toIP;
private int toPort;
public TalkSend(int fromPort, String toIP, int toPort) {
this.fromPort = fromPort;
this.toIP = toIP;
this.toPort = toPort;
try {
socket = new DatagramSocket(fromPort);
//准备数据:读取控制台输入
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
} catch (SocketException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
String data = reader.readLine();
byte[] bts = data.getBytes();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bts, 0, bts.length, new InetSocketAddress(this.toIP, this.toPort));
socket.send(packet);
if (data.equals("bye")) {
break;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
socket.close();
}
}
接收线程
public class TalkReceive implements Runnable {
DatagramSocket socket = null;
private int port;
private String msgFrom;
public TalkReceive(int port, String msgFrom) {
this.port = port;
this.msgFrom = msgFrom;
try {
socket = new DatagramSocket(port);
} catch (SocketException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
//准备接收包
byte[] bts = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bts, 0, bts.length);
socket.receive(packet);
//断开连接
byte[] data = packet.getData();
String receivedata = new String(data, 0, data.length);
System.out.println(msgFrom + ":" + receivedata);
if (receivedata.equals("bye")) {
break;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
socket.close();
}
}
学生端
public class TalkStudent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//开启两个线程
//执行发送
new Thread(new TalkSend(7777,"localhost",9099)).start();
//接收
new Thread(new TalkReceive(8888,"老师")).start();
}
}
老师端
public class TalkTeacher {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//执行发送
new Thread(new TalkSend(5555,"localhost",8888)).start();
//接收
new Thread(new TalkReceive(9099,"学生")).start();
}
}
来源:https://www.kuangstudy.com/bbs/1451008930120585218
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41532872/article/details/85786214