文章目录
- 前言
- 一、SearchAPI
- 1.1 URL 后接参数检索
- 1.2 URL 加请求体检索
- 二、Query DSL
- 2.1 基本语法格式
- 2.2 匹配查询 match
- 2.3 短语匹配 match_phase
- 2.4 多字段匹配 multi_match
- 2.5 复合查询 bool
- 2.6 过滤 filter
- 2.7 查询 term
- 2.8 聚合 aggregations
- 三、Mapping
- 3.1 待完成
- 3.2 待完成
前言
本文记录谷粒商城高级篇的 Elasticsearch 进阶检索部分,续上之前记录的 Elasticsearch入门篇。
一、SearchAPI
ES 支持两种基本方式检索 :
- 一个是通过使用 REST request URI 发送搜索参数(uri + 检索参数)
- 另一个是通过使用 REST request body 来发送它们(uri + 请求体)
1.1 URL 后接参数检索
GET bank/_search 检索 bank 下所有信息,包括 type 和 docs
GET bank/_search?q=*&sort=account_number:asc 请求参数方式检索

响应结果解释:
took - Elasticsearch 执行搜索的时间(毫秒)
time_out - 告诉我们搜索是否超时
_shards - 告诉我们多少个分片被搜索了,以及统计了成功/失败的搜索分片
hits - 搜索结果
hits.total - 搜索结果
hits.hits - 实际的搜索结果数组(默认为前 10 的文档)
sort - 结果的排序 key(键)(没有则按 score 排序)
score 和 max_score - 相关性得分和最高得分(全文检索用)
1.2 URL 加请求体检索
请求体中写查询条件,语法:
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"account_number": "asc"
},
{
"balance": "desc"
}
]
}
示例:查询出所有,先按照 accout_number 升序排序,再按照 balance 降序排序

二、Query DSL
2.1 基本语法格式
Elasticsearch 提供了一个可以执行查询的 Json 风格的 DSL(domain-specific language 领域特定语言)。这个被称为 Query DSL。该查询语言非常全面,并且刚开始的时候感觉有点复杂,真正学好它的方法是从一些基础的示例开始的。
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"balance": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
"from": 10,
"size": 10,
"_source": ["balance", "firstname"]
}
示例:查询所有记录,按照 balance 降序排序,只返回第 11 条记录到第 20 条记录,只显示 balance 和 firstname 字段。

query 定义如何查询,
match_all 查询类型【代表查询所有的所有】,es 中可以在 query 中组合非常多的查
询类型完成复杂查询
除了 query 参数之外,我们也可以传递其它的参数以改变查询结果。如 sort,size
from + size 限定,完成分页功能
sort 排序,多字段排序,会在前序字段相等时后续字段内部排序,否则以前序为准
_source 返回部分字段
2.2 匹配查询 match
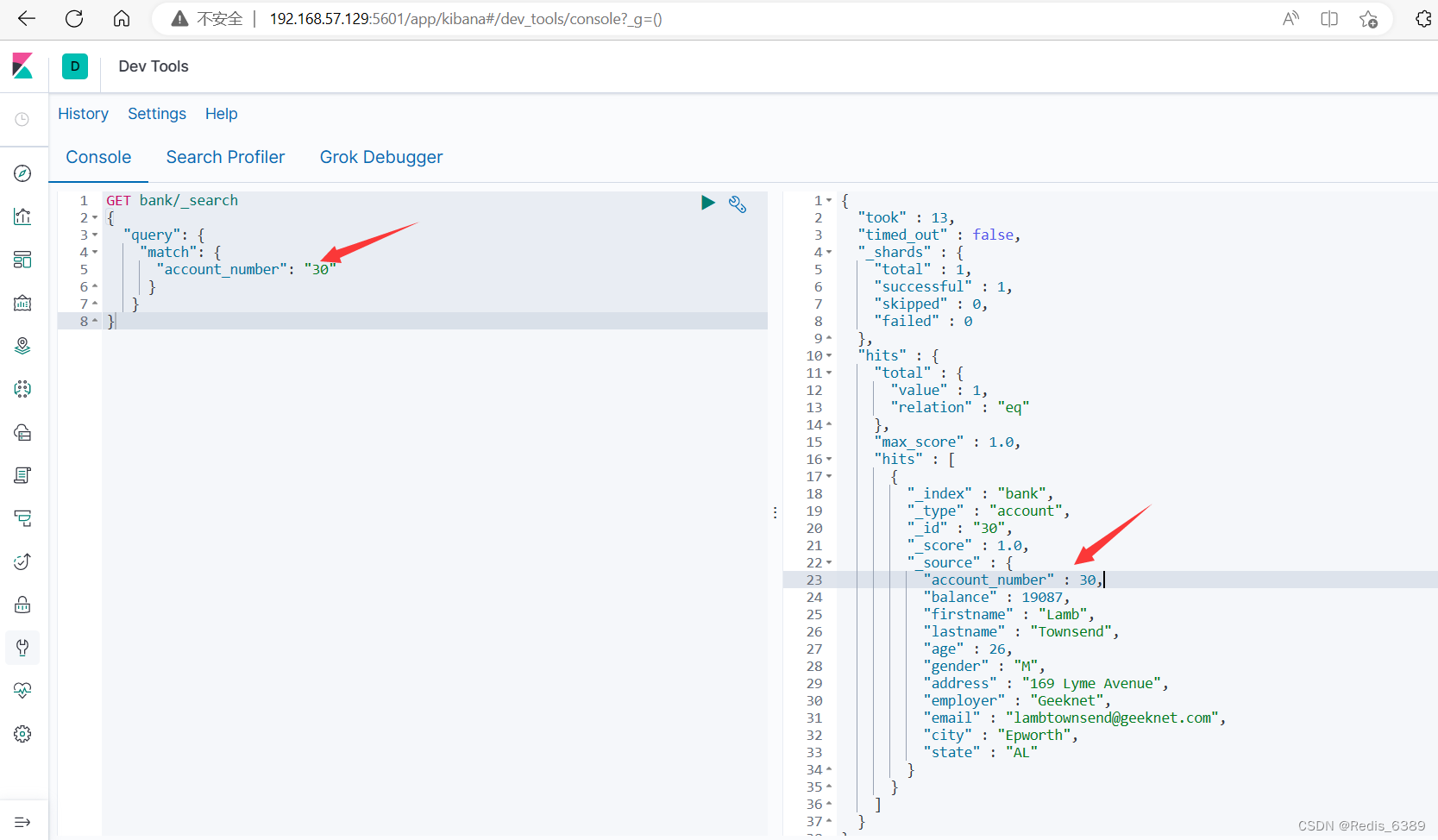
1.基本类型 ( 非字符串 ) ,精确匹配
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"account_number": "30"
}
}
}
2.字符串,全文检索
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "mill road"
}
}
}
全文检索按照评分进行排序,会对检索条件进行分词匹配。
查询 address 中包含 mill 或者 road 或者 mill road 的所有记录,并给出相关性得分。
2.3 短语匹配 match_phase
将需要匹配的值当成一个整体单词 ( 不分词 ) 进行检索
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"address": "mill road"
}
}
}
2.4 多字段匹配 multi_match
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "mill land",
"fields": [
"state",
"address"
]
}
}
}
multi_match 中的 query 也会进行分词。
查询 state 包含 mill 或 land 或者 address 包含 mill 或 land 的记录。
2.5 复合查询 bool
复合语句可以合并任何其他查询语句,包括复合语句。复合语句之间可以相互嵌套,可以表达复杂的逻辑。
搭配使用 must,must_not,should
must: 必须达到 must 指定的条件。 ( 影响相关性得分 )
must_not: 必须不满足 must_not 的条件。 ( 不影响相关性得分 )
should: 如果满足 should 条件,则可以提高得分。如果不满足,也可以查询出记录。 ( 影响相关性得分 )
示例:查询出地址包含 mill,且性别为 M,年龄不等于 28 的记录,且优先展示 firstname 包含 Winnie 的记录。
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"address": "mill"
}
},
{
"match": {
"gender": "M"
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"age": "28"
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"match": {
"firstname": "Winnie"
}
}
]
}
}
}
2.6 过滤 filter
不影响相关性得分,查询出满足 filter 条件的记录。
在 bool 中使用。
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 18,
"lte": 30
}
}
}
}
}
}
2.7 查询 term
匹配某个属性的值。
全文检索字段用 match,其他非 text 字段匹配用 term
keyword:文本精确匹配 ( 全部匹配 )
match_phase:文本短语匹配
规范:非 text 字段精确匹配使用 term
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"age": "20"
}
}
}
2.8 聚合 aggregations
聚合提供了从数据中分组和提取数据的能力。最简单的聚合方法大致等于 SQL GROUP
BY 和 SQL 聚合函数。在 Elasticsearch 中,您有执行搜索返回 hits(命中结果),并且同时返回聚合结果,把一个响应中的所有 hits(命中结果)分隔开的能力。这是非常强大且有效的,您可以执行查询和多个聚合,并且在一次使用中得到各自的(任何一个的)返回结果,使用一次简洁和简化的 API 来避免网络往返。
# 聚合语法
"aggregations" : {
"<聚合名称 1>" : {
"<聚合类型>" : {
<聚合体内容>
}
[,"元数据" : { [<meta_data_body>] }]?
[,"aggregations" : { [<sub_aggregation>]+ }]?
}
[,"聚合名称 2>" : { ... }]*
}
示例 1:搜索 address 中包含 mill 的所有人的年龄分布 ( 前 10 条 ) 以及平均年龄,以及平均薪资
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "mill"
}
},
"aggs": {
"aggAge": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 10
}
},
"ageAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "age"
}
},
"balanceAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
如果不想返回 hits 结果,可以在最后面设置 size:0
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "mill"
}
},
"aggs": {
"ageAggr": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 10
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
示例 2:按照年龄聚合,并且请求这些年龄段的这些人的平均薪资
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"age_avg": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 1000
},
"aggs": {
"banlances_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 1000
}
示例 3:查出所有年龄分布,并且这些年龄段中 M 的平均薪资和 F 的平均薪资以及这个年龄段的总体平均薪资
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"age_agg": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 100
},
"aggs": {
"gender_agg": {
"terms": {
"field": "gender.keyword",
"size": 100
},
"aggs": {
"balance_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
},
"balance_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 1000
}