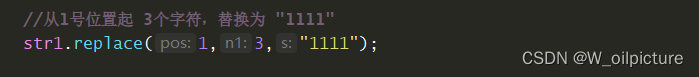
本文结合实例讲解表创建执行流程 [CREATE TABLE wp_shy(id int primary key, name carchar(20))],相关知识回顾见:
postgres源码解析38 表创建执行全流程梳理–1
postgres源码解析38 表创建执行全流程梳理–2
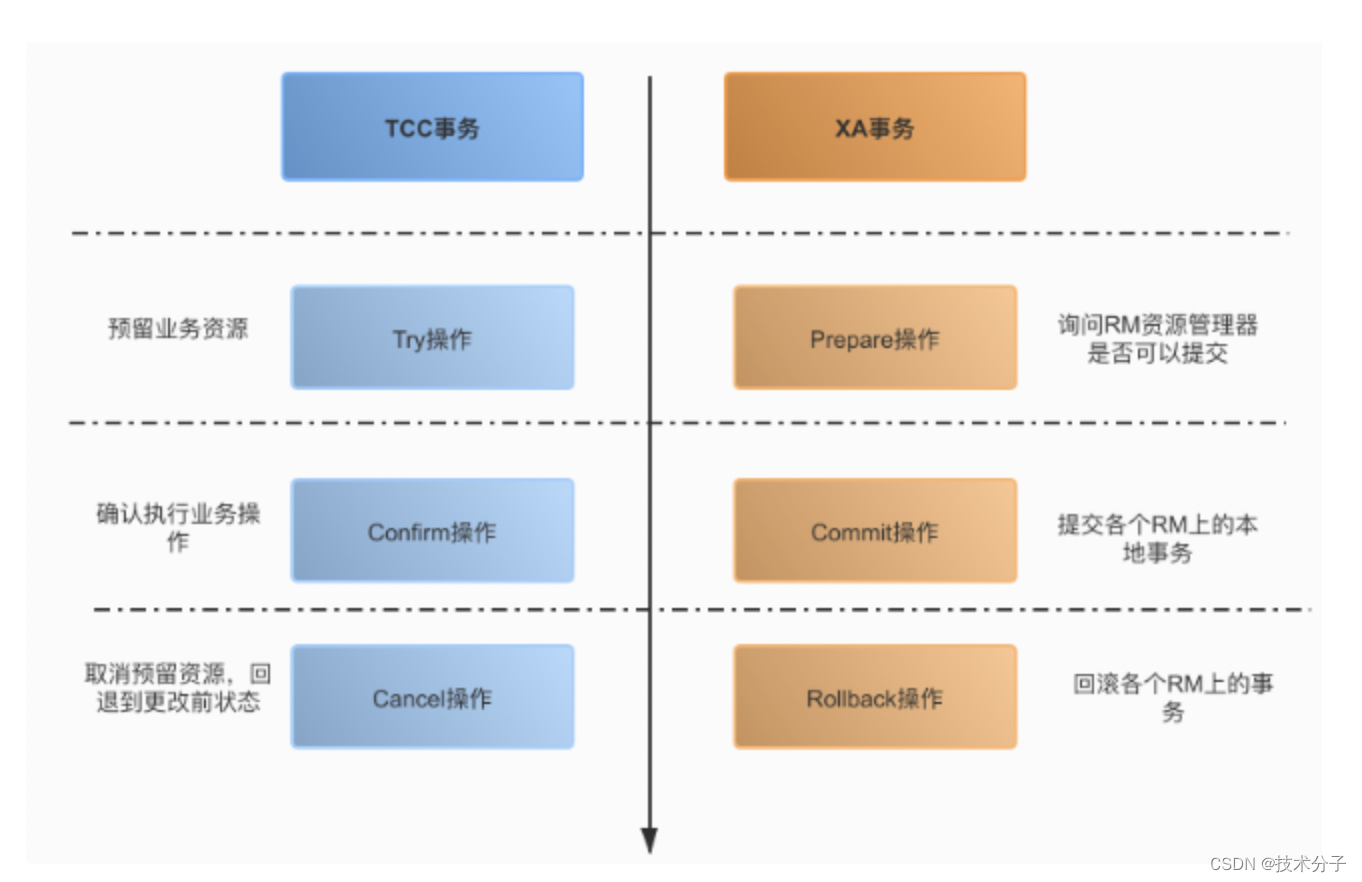
执行流程图

transformCreateStmt函数是表创建真正的入口函数,其执行流程如下:

物理文件的创建以及系统表元数据等更新由DefineRelation函数实现:

执行流程
1 transformCreateStmt
该函数对生成的计划树解析分析,返回操作节点链表,实例所生成的操作节点链表<T_CreateStmt, T_IndexsStmt>如下:
(gdb) p *stmts
$49 = {type = T_List, length = 2, max_length = 5, elements = 0x55db4d6bc5a0, initial_elements = 0x55db4d6bc5a0}
(gdb) p *(Node*)stmts->elements[0]->ptr_value
$50 = {type = T_CreateStmt}
(gdb) p *(Node*)stmts->elements[1]->ptr_value
$51 = {type = T_IndexStmt}
(gdb) p *(CreateStmt*)stmts->elements[0]->ptr_value
$52 = {type = T_CreateStmt, relation = 0x55db4d59e138, tableElts = 0x55db4d6af048, inhRelations = 0x0, partbound = 0x0, partspec = 0x0, ofTypename = 0x0, constraints = 0x0, options = 0x0, oncommit = ONCOMMIT_NOOP, tablespacename = 0x0,
accessMethod = 0x0, if_not_exists = false}
(gdb) p *(CreateStmt*)stmts->elements[1]->ptr_value
$53 = {type = T_IndexStmt, relation = 0x0, tableElts = 0x55db4d59e138, inhRelations = 0x55db4cf71355, partbound = 0x0, partspec = 0x55db4d6bc448, ofTypename = 0x0, constraints = 0x0, options = 0x0, oncommit = ONCOMMIT_NOOP,
tablespacename = 0x0, accessMethod = 0x0, if_not_exists = false}
执行流程:
1)获取并检查命名空间权限;
2)构建并初始化CreateStmtContext上下文,在后续执行过程中进一步更新relation、约束、列属性等信息。
3)遍历表中所有的列,调用相应的处理函数获取列的属性、约束等信息,填充CreateStmtContext对应字段信息<普通列调用 transformColumnDefinition, 含有约束的调用 transformTableConstraint >。
4)后续进行预处理,检查约束合理性,最后返回 utility命令的操作节点链表。
/*
* transformCreateStmt -
* parse analysis for CREATE TABLE
*
* Returns a List of utility commands to be done in sequence. One of these
* will be the transformed CreateStmt, but there may be additional actions
* to be done before and after the actual DefineRelation() call.
* In addition to normal utility commands such as AlterTableStmt and
* IndexStmt, the result list may contain TableLikeClause(s), representing
* the need to perform additional parse analysis after DefineRelation().
// 对Utility节点进行解析生成操作节点链表,其中一个为CreateStmt,其余的会在DefineRelation()调用
// 前后生成,常见的utility命令还有 AlterTableStmt、IndexStmt、 TableLikeClause(s)等
* SQL allows constraints to be scattered all over, so thumb through
* the columns and collect all constraints into one place.
* If there are any implied indices (e.g. UNIQUE or PRIMARY KEY)
* then expand those into multiple IndexStmt blocks.
// 在此过程收集所有的索引(唯一约束 + 主键),最终会将其至于 IndexStmt 块中
*/
List *
transformCreateStmt(CreateStmt *stmt, const char *queryString)
{
ParseState *pstate;
CreateStmtContext cxt;
List *result;
List *save_alist;
ListCell *elements;
Oid namespaceid;
Oid existing_relid;
ParseCallbackState pcbstate;
/* Set up pstate */
pstate = make_parsestate(NULL);
pstate->p_sourcetext = queryString;
/*
* Look up the creation namespace. This also checks permissions on the
* target namespace, locks it against concurrent drops, checks for a
* preexisting relation in that namespace with the same name, and updates
* stmt->relation->relpersistence if the selected namespace is temporary.
*/
setup_parser_errposition_callback(&pcbstate, pstate,
stmt->relation->location);
namespaceid =
RangeVarGetAndCheckCreationNamespace(stmt->relation, NoLock,
&existing_relid);
cancel_parser_errposition_callback(&pcbstate);
/*
* If the relation already exists and the user specified "IF NOT EXISTS",
* bail out with a NOTICE.
*/
if (stmt->if_not_exists && OidIsValid(existing_relid))
{
ereport(NOTICE,
(errcode(ERRCODE_DUPLICATE_TABLE),
errmsg("relation \"%s\" already exists, skipping",
stmt->relation->relname)));
return NIL;
}
/*
* If the target relation name isn't schema-qualified, make it so. This
* prevents some corner cases in which added-on rewritten commands might
* think they should apply to other relations that have the same name and
* are earlier in the search path. But a local temp table is effectively
* specified to be in pg_temp, so no need for anything extra in that case.
*/
if (stmt->relation->schemaname == NULL
&& stmt->relation->relpersistence != RELPERSISTENCE_TEMP)
stmt->relation->schemaname = get_namespace_name(namespaceid);
/* Set up CreateStmtContext */
cxt.pstate = pstate;
if (IsA(stmt, CreateForeignTableStmt))
{
cxt.stmtType = "CREATE FOREIGN TABLE";
cxt.isforeign = true;
}
else
{
cxt.stmtType = "CREATE TABLE";
cxt.isforeign = false;
}
cxt.relation = stmt->relation;
cxt.rel = NULL;
cxt.inhRelations = stmt->inhRelations;
cxt.isalter = false;
cxt.columns = NIL;
cxt.ckconstraints = NIL;
cxt.fkconstraints = NIL;
cxt.ixconstraints = NIL;
cxt.likeclauses = NIL;
cxt.extstats = NIL;
cxt.blist = NIL;
cxt.alist = NIL;
cxt.pkey = NULL;
cxt.ispartitioned = stmt->partspec != NULL;
cxt.partbound = stmt->partbound;
cxt.ofType = (stmt->ofTypename != NULL);
Assert(!stmt->ofTypename || !stmt->inhRelations); /* grammar enforces */
if (stmt->ofTypename)
transformOfType(&cxt, stmt->ofTypename);
if (stmt->partspec)
{
if (stmt->inhRelations && !stmt->partbound)
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_OBJECT_DEFINITION),
errmsg("cannot create partitioned table as inheritance child")));
}
/*
* Run through each primary element in the table creation clause. Separate
* column defs from constraints, and do preliminary analysis.
*/
foreach(elements, stmt->tableElts)
{
Node *element = lfirst(elements);
switch (nodeTag(element))
{
case T_ColumnDef:
transformColumnDefinition(&cxt, (ColumnDef *) element);
break;
case T_Constraint:
transformTableConstraint(&cxt, (Constraint *) element);
break;
case T_TableLikeClause:
transformTableLikeClause(&cxt, (TableLikeClause *) element);
break;
default:
elog(ERROR, "unrecognized node type: %d",
(int) nodeTag(element));
break;
}
}
/*
* Transfer anything we already have in cxt.alist into save_alist, to keep
* it separate from the output of transformIndexConstraints. (This may
* not be necessary anymore, but we'll keep doing it to preserve the
* historical order of execution of the alist commands.)
*/
save_alist = cxt.alist;
cxt.alist = NIL;
Assert(stmt->constraints == NIL);
/*
* Postprocess constraints that give rise to index definitions.
*/
transformIndexConstraints(&cxt);
/*
* Re-consideration of LIKE clauses should happen after creation of
* indexes, but before creation of foreign keys. This order is critical
* because a LIKE clause may attempt to create a primary key. If there's
* also a pkey in the main CREATE TABLE list, creation of that will not
* check for a duplicate at runtime (since index_check_primary_key()
* expects that we rejected dups here). Creation of the LIKE-generated
* pkey behaves like ALTER TABLE ADD, so it will check, but obviously that
* only works if it happens second. On the other hand, we want to make
* pkeys before foreign key constraints, in case the user tries to make a
* self-referential FK.
*/
cxt.alist = list_concat(cxt.alist, cxt.likeclauses);
/*
* Postprocess foreign-key constraints.
*/
transformFKConstraints(&cxt, true, false);
/*
* Postprocess check constraints.
*
* For regular tables all constraints can be marked valid immediately,
* because the table is new therefore empty. Not so for foreign tables.
*/
transformCheckConstraints(&cxt, !cxt.isforeign);
/*
* Postprocess extended statistics.
*/
transformExtendedStatistics(&cxt);
/*
* Output results.
*/
stmt->tableElts = cxt.columns;
stmt->constraints = cxt.ckconstraints;
result = lappend(cxt.blist, stmt);
result = list_concat(result, cxt.alist);
result = list_concat(result, save_alist);
return result;
}
2 DefineRelation
该函数的功能是创建新的relation,包括物理文件、相应的内存relcache Entry和系统表元数据的更新
1)首先进行权限检查,确定当前用户是否有权限创建表;
2)对创建表语句中的WITH子句进行解析(transformRelOptions);
3)调用heap_reloptions对参数进行合法验证。
4)调用 MergeAttributes 将继承的属性合并到表属性定义中;
5)根据表列信息调用 BuildDescForRelation函数生成元组描述符TupleDesc,该结构体记录了元组每列字段的详细信息(pg_attribute)
6)遍历定义链表中的每一个属性查看是否有默认值、压缩等信息;
7)在上述条件准备完善下调用 heap_create_with_catalog创建物理文件并在系统表中注册;
8)调用 AddRelationNewConstraints 处理表中新增的约束与默认值
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------
* DefineRelation
* Creates a new relation.
*
* stmt carries parsetree information from an ordinary CREATE TABLE statement.
* The other arguments are used to extend the behavior for other cases:
* relkind: relkind to assign to the new relation
* ownerId: if not InvalidOid, use this as the new relation's owner.
* typaddress: if not null, it's set to the pg_type entry's address.
* queryString: for error reporting
*
* Note that permissions checks are done against current user regardless of
* ownerId. A nonzero ownerId is used when someone is creating a relation
* "on behalf of" someone else, so we still want to see that the current user
* has permissions to do it.
*
* If successful, returns the address of the new relation.
* ----------------------------------------------------------------
*/
ObjectAddress
DefineRelation(CreateStmt *stmt, char relkind, Oid ownerId,
ObjectAddress *typaddress, const char *queryString)
{
char relname[NAMEDATALEN];
Oid namespaceId;
Oid relationId;
Oid tablespaceId;
Relation rel;
TupleDesc descriptor;
List *inheritOids;
List *old_constraints;
List *rawDefaults;
List *cookedDefaults;
Datum reloptions;
ListCell *listptr;
AttrNumber attnum;
bool partitioned;
static char *validnsps[] = HEAP_RELOPT_NAMESPACES;
Oid ofTypeId;
ObjectAddress address;
LOCKMODE parentLockmode;
const char *accessMethod = NULL;
Oid accessMethodId = InvalidOid;
/*
* Truncate relname to appropriate length (probably a waste of time, as
* parser should have done this already).
*/
strlcpy(relname, stmt->relation->relname, NAMEDATALEN);
/*
* Check consistency of arguments
*/
if (stmt->oncommit != ONCOMMIT_NOOP
&& stmt->relation->relpersistence != RELPERSISTENCE_TEMP)
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_TABLE_DEFINITION),
errmsg("ON COMMIT can only be used on temporary tables")));
if (stmt->partspec != NULL)
{
if (relkind != RELKIND_RELATION)
elog(ERROR, "unexpected relkind: %d", (int) relkind);
relkind = RELKIND_PARTITIONED_TABLE;
partitioned = true;
}
else
partitioned = false;
/*
* Look up the namespace in which we are supposed to create the relation,
* check we have permission to create there, lock it against concurrent
* drop, and mark stmt->relation as RELPERSISTENCE_TEMP if a temporary
* namespace is selected.
*/
namespaceId =
RangeVarGetAndCheckCreationNamespace(stmt->relation, NoLock, NULL);
/*
* Security check: disallow creating temp tables from security-restricted
* code. This is needed because calling code might not expect untrusted
* tables to appear in pg_temp at the front of its search path.
*/
if (stmt->relation->relpersistence == RELPERSISTENCE_TEMP
&& InSecurityRestrictedOperation())
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_INSUFFICIENT_PRIVILEGE),
errmsg("cannot create temporary table within security-restricted operation")));
/*
* Determine the lockmode to use when scanning parents. A self-exclusive
* lock is needed here.
*
* For regular inheritance, if two backends attempt to add children to the
* same parent simultaneously, and that parent has no pre-existing
* children, then both will attempt to update the parent's relhassubclass
* field, leading to a "tuple concurrently updated" error. Also, this
* interlocks against a concurrent ANALYZE on the parent table, which
* might otherwise be attempting to clear the parent's relhassubclass
* field, if its previous children were recently dropped.
*
* If the child table is a partition, then we instead grab an exclusive
* lock on the parent because its partition descriptor will be changed by
* addition of the new partition.
*/
parentLockmode = (stmt->partbound != NULL ? AccessExclusiveLock :
ShareUpdateExclusiveLock);
/* Determine the list of OIDs of the parents. */
inheritOids = NIL;
foreach(listptr, stmt->inhRelations)
{
RangeVar *rv = (RangeVar *) lfirst(listptr);
Oid parentOid;
parentOid = RangeVarGetRelid(rv, parentLockmode, false);
/*
* Reject duplications in the list of parents.
*/
if (list_member_oid(inheritOids, parentOid))
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_DUPLICATE_TABLE),
errmsg("relation \"%s\" would be inherited from more than once",
get_rel_name(parentOid))));
inheritOids = lappend_oid(inheritOids, parentOid);
}
/*
* Select tablespace to use: an explicitly indicated one, or (in the case
* of a partitioned table) the parent's, if it has one.
*/
if (stmt->tablespacename)
{
tablespaceId = get_tablespace_oid(stmt->tablespacename, false);
if (partitioned && tablespaceId == MyDatabaseTableSpace)
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),
errmsg("cannot specify default tablespace for partitioned relations")));
}
else if (stmt->partbound)
{
/*
* For partitions, when no other tablespace is specified, we default
* the tablespace to the parent partitioned table's.
*/
Assert(list_length(inheritOids) == 1);
tablespaceId = get_rel_tablespace(linitial_oid(inheritOids));
}
else
tablespaceId = InvalidOid;
/* still nothing? use the default */
if (!OidIsValid(tablespaceId))
tablespaceId = GetDefaultTablespace(stmt->relation->relpersistence,
partitioned);
/* Check permissions except when using database's default */
if (OidIsValid(tablespaceId) && tablespaceId != MyDatabaseTableSpace)
{
AclResult aclresult;
aclresult = pg_tablespace_aclcheck(tablespaceId, GetUserId(),
ACL_CREATE);
if (aclresult != ACLCHECK_OK)
aclcheck_error(aclresult, OBJECT_TABLESPACE,
get_tablespace_name(tablespaceId));
}
/* In all cases disallow placing user relations in pg_global */
if (tablespaceId == GLOBALTABLESPACE_OID)
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE),
errmsg("only shared relations can be placed in pg_global tablespace")));
/* Identify user ID that will own the table */
if (!OidIsValid(ownerId))
ownerId = GetUserId();
/*
* Parse and validate reloptions, if any.
*/
reloptions = transformRelOptions((Datum) 0, stmt->options, NULL, validnsps,
true, false);
switch (relkind)
{
case RELKIND_VIEW:
(void) view_reloptions(reloptions, true);
break;
case RELKIND_PARTITIONED_TABLE:
(void) partitioned_table_reloptions(reloptions, true);
break;
default:
(void) heap_reloptions(relkind, reloptions, true);
}
if (stmt->ofTypename)
{
AclResult aclresult;
ofTypeId = typenameTypeId(NULL, stmt->ofTypename);
aclresult = pg_type_aclcheck(ofTypeId, GetUserId(), ACL_USAGE);
if (aclresult != ACLCHECK_OK)
aclcheck_error_type(aclresult, ofTypeId);
}
else
ofTypeId = InvalidOid;
/*
* Look up inheritance ancestors and generate relation schema, including
* inherited attributes. (Note that stmt->tableElts is destructively
* modified by MergeAttributes.)
*/
stmt->tableElts =
MergeAttributes(stmt->tableElts, inheritOids,
stmt->relation->relpersistence,
stmt->partbound != NULL,
&old_constraints);
/*
* Create a tuple descriptor from the relation schema. Note that this
* deals with column names, types, and NOT NULL constraints, but not
* default values or CHECK constraints; we handle those below.
*/
descriptor = BuildDescForRelation(stmt->tableElts);
/*
* Find columns with default values and prepare for insertion of the
* defaults. Pre-cooked (that is, inherited) defaults go into a list of
* CookedConstraint structs that we'll pass to heap_create_with_catalog,
* while raw defaults go into a list of RawColumnDefault structs that will
* be processed by AddRelationNewConstraints. (We can't deal with raw
* expressions until we can do transformExpr.)
*
* We can set the atthasdef flags now in the tuple descriptor; this just
* saves StoreAttrDefault from having to do an immediate update of the
* pg_attribute rows.
*/
rawDefaults = NIL;
cookedDefaults = NIL;
attnum = 0;
foreach(listptr, stmt->tableElts)
{
ColumnDef *colDef = lfirst(listptr);
Form_pg_attribute attr;
attnum++;
attr = TupleDescAttr(descriptor, attnum - 1);
if (colDef->raw_default != NULL)
{
RawColumnDefault *rawEnt;
Assert(colDef->cooked_default == NULL);
rawEnt = (RawColumnDefault *) palloc(sizeof(RawColumnDefault));
rawEnt->attnum = attnum;
rawEnt->raw_default = colDef->raw_default;
rawEnt->missingMode = false;
rawEnt->generated = colDef->generated;
rawDefaults = lappend(rawDefaults, rawEnt);
attr->atthasdef = true;
}
else if (colDef->cooked_default != NULL)
{
CookedConstraint *cooked;
cooked = (CookedConstraint *) palloc(sizeof(CookedConstraint));
cooked->contype = CONSTR_DEFAULT;
cooked->conoid = InvalidOid; /* until created */
cooked->name = NULL;
cooked->attnum = attnum;
cooked->expr = colDef->cooked_default;
cooked->skip_validation = false;
cooked->is_local = true; /* not used for defaults */
cooked->inhcount = 0; /* ditto */
cooked->is_no_inherit = false;
cookedDefaults = lappend(cookedDefaults, cooked);
attr->atthasdef = true;
}
if (colDef->identity)
attr->attidentity = colDef->identity;
if (colDef->generated)
attr->attgenerated = colDef->generated;
if (colDef->compression)
attr->attcompression = GetAttributeCompression(attr->atttypid,
colDef->compression);
}
/*
* If the statement hasn't specified an access method, but we're defining
* a type of relation that needs one, use the default.
*/
if (stmt->accessMethod != NULL)
{
accessMethod = stmt->accessMethod;
if (partitioned)
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),
errmsg("specifying a table access method is not supported on a partitioned table")));
}
else if (relkind == RELKIND_RELATION ||
relkind == RELKIND_TOASTVALUE ||
relkind == RELKIND_MATVIEW)
accessMethod = default_table_access_method;
/* look up the access method, verify it is for a table */
if (accessMethod != NULL)
accessMethodId = get_table_am_oid(accessMethod, false);
/*
* Create the relation. Inherited defaults and constraints are passed in
* for immediate handling --- since they don't need parsing, they can be
* stored immediately.
*/
relationId = heap_create_with_catalog(relname,
namespaceId,
tablespaceId,
InvalidOid,
InvalidOid,
ofTypeId,
ownerId,
accessMethodId,
descriptor,
list_concat(cookedDefaults,
old_constraints),
relkind,
stmt->relation->relpersistence,
false,
false,
stmt->oncommit,
reloptions,
true,
allowSystemTableMods,
false,
InvalidOid,
typaddress);
/*
* We must bump the command counter to make the newly-created relation
* tuple visible for opening.
*/
CommandCounterIncrement();
/*
* Open the new relation and acquire exclusive lock on it. This isn't
* really necessary for locking out other backends (since they can't see
* the new rel anyway until we commit), but it keeps the lock manager from
* complaining about deadlock risks.
*/
rel = relation_open(relationId, AccessExclusiveLock);
/*
* Now add any newly specified column default and generation expressions
* to the new relation. These are passed to us in the form of raw
* parsetrees; we need to transform them to executable expression trees
* before they can be added. The most convenient way to do that is to
* apply the parser's transformExpr routine, but transformExpr doesn't
* work unless we have a pre-existing relation. So, the transformation has
* to be postponed to this final step of CREATE TABLE.
*
* This needs to be before processing the partitioning clauses because
* those could refer to generated columns.
*/
if (rawDefaults)
AddRelationNewConstraints(rel, rawDefaults, NIL,
true, true, false, queryString);
/*
* Make column generation expressions visible for use by partitioning.
*/
CommandCounterIncrement();
/* Store inheritance information for new rel. */
StoreCatalogInheritance(relationId, inheritOids, stmt->partbound != NULL);
// 省略分区表处理逻辑
/*
* Now add any newly specified CHECK constraints to the new relation. Same
* as for defaults above, but these need to come after partitioning is set
* up.
*/
if (stmt->constraints)
AddRelationNewConstraints(rel, NIL, stmt->constraints,
true, true, false, queryString);
ObjectAddressSet(address, RelationRelationId, relationId);
/*
* Clean up. We keep lock on new relation (although it shouldn't be
* visible to anyone else anyway, until commit).
*/
relation_close(rel, NoLock);
return address;
}
heap_create_with_catalog执行流程
1)首先进行参数校验检查,在同一命名空间是否存在相同名、pg_type系统表是否存在相同typename等;
2)调用 GetNewRelFileNode为此表分配一个全局唯一对象标识符Oid;
3) 结合表名、命名空间、对象标识符OID以及元组描述符等信息调用 heap_create 创建一个Relation 结构放入RelCache,后续根据此信息 table_relation_set_new_filenode(Relation)/ RelationCreateStorage(Index)创建物理文件。
4)紧接着调用 AddNewRelationType向pg_type系统表中注册该表的记录;
5)AddNewRelationTuple向pg_class 系统表中插入该表的相关信息;
6)AddNewAttributeTuples 将该表每个字段信息填充值 pg_attribute系统表;
7)最后通过 StoreConstraints 将约束和默认值等信息存储至 pg_constraint和pg_attrdef系统表中。
* --------------------------------
* heap_create_with_catalog
*
* creates a new cataloged relation. see comments above.
*
* Arguments:
* relname: name to give to new rel
* relnamespace: OID of namespace it goes in
* reltablespace: OID of tablespace it goes in
* relid: OID to assign to new rel, or InvalidOid to select a new OID
* reltypeid: OID to assign to rel's rowtype, or InvalidOid to select one
* reloftypeid: if a typed table, OID of underlying type; else InvalidOid
* ownerid: OID of new rel's owner
* accessmtd: OID of new rel's access method
* tupdesc: tuple descriptor (source of column definitions)
* cooked_constraints: list of precooked check constraints and defaults
* relkind: relkind for new rel
* relpersistence: rel's persistence status (permanent, temp, or unlogged)
* shared_relation: true if it's to be a shared relation
* mapped_relation: true if the relation will use the relfilenode map
* oncommit: ON COMMIT marking (only relevant if it's a temp table)
* reloptions: reloptions in Datum form, or (Datum) 0 if none
* use_user_acl: true if should look for user-defined default permissions;
* if false, relacl is always set NULL
* allow_system_table_mods: true to allow creation in system namespaces
* is_internal: is this a system-generated catalog?
*
* Output parameters:
* typaddress: if not null, gets the object address of the new pg_type entry
* (this must be null if the relkind is one that doesn't get a pg_type entry)
*
* Returns the OID of the new relation
* --------------------------------
*/
Oid
heap_create_with_catalog(const char *relname,
Oid relnamespace,
Oid reltablespace,
Oid relid,
Oid reltypeid,
Oid reloftypeid,
Oid ownerid,
Oid accessmtd,
TupleDesc tupdesc,
List *cooked_constraints,
char relkind,
char relpersistence,
bool shared_relation,
bool mapped_relation,
OnCommitAction oncommit,
Datum reloptions,
bool use_user_acl,
bool allow_system_table_mods,
bool is_internal,
Oid relrewrite,
ObjectAddress *typaddress)
{
Relation pg_class_desc;
Relation new_rel_desc;
Acl *relacl;
Oid existing_relid;
Oid old_type_oid;
Oid new_type_oid;
TransactionId relfrozenxid;
MultiXactId relminmxid;
pg_class_desc = table_open(RelationRelationId, RowExclusiveLock);
/*
* sanity checks
*/
Assert(IsNormalProcessingMode() || IsBootstrapProcessingMode());
/*
* Validate proposed tupdesc for the desired relkind. If
* allow_system_table_mods is on, allow ANYARRAY to be used; this is a
* hack to allow creating pg_statistic and cloning it during VACUUM FULL.
*/
CheckAttributeNamesTypes(tupdesc, relkind,
allow_system_table_mods ? CHKATYPE_ANYARRAY : 0);
/*
* This would fail later on anyway, if the relation already exists. But
* by catching it here we can emit a nicer error message.
*/
existing_relid = get_relname_relid(relname, relnamespace);
if (existing_relid != InvalidOid)
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_DUPLICATE_TABLE),
errmsg("relation \"%s\" already exists", relname)));
/*
* Since we are going to create a rowtype as well, also check for
* collision with an existing type name. If there is one and it's an
* autogenerated array, we can rename it out of the way; otherwise we can
* at least give a good error message.
*/
old_type_oid = GetSysCacheOid2(TYPENAMENSP, Anum_pg_type_oid,
CStringGetDatum(relname),
ObjectIdGetDatum(relnamespace));
if (OidIsValid(old_type_oid))
{
if (!moveArrayTypeName(old_type_oid, relname, relnamespace))
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_DUPLICATE_OBJECT),
errmsg("type \"%s\" already exists", relname),
errhint("A relation has an associated type of the same name, "
"so you must use a name that doesn't conflict "
"with any existing type.")));
}
/*
* Shared relations must be in pg_global (last-ditch check)
*/
if (shared_relation && reltablespace != GLOBALTABLESPACE_OID)
elog(ERROR, "shared relations must be placed in pg_global tablespace");
/*
* Allocate an OID for the relation, unless we were told what to use.
*
* The OID will be the relfilenode as well, so make sure it doesn't
* collide with either pg_class OIDs or existing physical files.
*/
if (!OidIsValid(relid))
{
/* Use binary-upgrade override for pg_class.oid/relfilenode? */
if (IsBinaryUpgrade &&
(relkind == RELKIND_RELATION || relkind == RELKIND_SEQUENCE ||
relkind == RELKIND_VIEW || relkind == RELKIND_MATVIEW ||
relkind == RELKIND_COMPOSITE_TYPE || relkind == RELKIND_FOREIGN_TABLE ||
relkind == RELKIND_PARTITIONED_TABLE))
{
if (!OidIsValid(binary_upgrade_next_heap_pg_class_oid))
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE),
errmsg("pg_class heap OID value not set when in binary upgrade mode")));
relid = binary_upgrade_next_heap_pg_class_oid;
binary_upgrade_next_heap_pg_class_oid = InvalidOid;
}
/* There might be no TOAST table, so we have to test for it. */
else if (IsBinaryUpgrade &&
OidIsValid(binary_upgrade_next_toast_pg_class_oid) &&
relkind == RELKIND_TOASTVALUE)
{
relid = binary_upgrade_next_toast_pg_class_oid;
binary_upgrade_next_toast_pg_class_oid = InvalidOid;
}
else
relid = GetNewRelFileNode(reltablespace, pg_class_desc,
relpersistence);
}
/*
* Determine the relation's initial permissions.
*/
if (use_user_acl)
{
switch (relkind)
{
case RELKIND_RELATION:
case RELKIND_VIEW:
case RELKIND_MATVIEW:
case RELKIND_FOREIGN_TABLE:
case RELKIND_PARTITIONED_TABLE:
relacl = get_user_default_acl(OBJECT_TABLE, ownerid,
relnamespace);
break;
case RELKIND_SEQUENCE:
relacl = get_user_default_acl(OBJECT_SEQUENCE, ownerid,
relnamespace);
break;
default:
relacl = NULL;
break;
}
}
else
relacl = NULL;
/*
* Create the relcache entry (mostly dummy at this point) and the physical
* disk file. (If we fail further down, it's the smgr's responsibility to
* remove the disk file again.)
*/
new_rel_desc = heap_create(relname,
relnamespace,
reltablespace,
relid,
InvalidOid,
accessmtd,
tupdesc,
relkind,
relpersistence,
shared_relation,
mapped_relation,
allow_system_table_mods,
&relfrozenxid,
&relminmxid);
Assert(relid == RelationGetRelid(new_rel_desc));
new_rel_desc->rd_rel->relrewrite = relrewrite;
/*
* Decide whether to create a pg_type entry for the relation's rowtype.
* These types are made except where the use of a relation as such is an
* implementation detail: toast tables, sequences and indexes.
*/
if (!(relkind == RELKIND_SEQUENCE ||
relkind == RELKIND_TOASTVALUE ||
relkind == RELKIND_INDEX ||
relkind == RELKIND_PARTITIONED_INDEX))
{
Oid new_array_oid;
ObjectAddress new_type_addr;
char *relarrayname;
/*
* We'll make an array over the composite type, too. For largely
* historical reasons, the array type's OID is assigned first.
*/
new_array_oid = AssignTypeArrayOid();
/*
* Make the pg_type entry for the composite type. The OID of the
* composite type can be preselected by the caller, but if reltypeid
* is InvalidOid, we'll generate a new OID for it.
*
* NOTE: we could get a unique-index failure here, in case someone
* else is creating the same type name in parallel but hadn't
* committed yet when we checked for a duplicate name above.
*/
new_type_addr = AddNewRelationType(relname,
relnamespace,
relid,
relkind,
ownerid,
reltypeid,
new_array_oid);
new_type_oid = new_type_addr.objectId;
if (typaddress)
*typaddress = new_type_addr;
/* Now create the array type. */
relarrayname = makeArrayTypeName(relname, relnamespace);
TypeCreate(new_array_oid, /* force the type's OID to this */
relarrayname, /* Array type name */
relnamespace, /* Same namespace as parent */
InvalidOid, /* Not composite, no relationOid */
0, /* relkind, also N/A here */
ownerid, /* owner's ID */
-1, /* Internal size (varlena) */
TYPTYPE_BASE, /* Not composite - typelem is */
TYPCATEGORY_ARRAY, /* type-category (array) */
false, /* array types are never preferred */
DEFAULT_TYPDELIM, /* default array delimiter */
F_ARRAY_IN, /* array input proc */
F_ARRAY_OUT, /* array output proc */
F_ARRAY_RECV, /* array recv (bin) proc */
F_ARRAY_SEND, /* array send (bin) proc */
InvalidOid, /* typmodin procedure - none */
InvalidOid, /* typmodout procedure - none */
F_ARRAY_TYPANALYZE, /* array analyze procedure */
F_ARRAY_SUBSCRIPT_HANDLER, /* array subscript procedure */
new_type_oid, /* array element type - the rowtype */
true, /* yes, this is an array type */
InvalidOid, /* this has no array type */
InvalidOid, /* domain base type - irrelevant */
NULL, /* default value - none */
NULL, /* default binary representation */
false, /* passed by reference */
TYPALIGN_DOUBLE, /* alignment - must be the largest! */
TYPSTORAGE_EXTENDED, /* fully TOASTable */
-1, /* typmod */
0, /* array dimensions for typBaseType */
false, /* Type NOT NULL */
InvalidOid); /* rowtypes never have a collation */
pfree(relarrayname);
}
else
{
/* Caller should not be expecting a type to be created. */
Assert(reltypeid == InvalidOid);
Assert(typaddress == NULL);
new_type_oid = InvalidOid;
}
/*
* now create an entry in pg_class for the relation.
*
* NOTE: we could get a unique-index failure here, in case someone else is
* creating the same relation name in parallel but hadn't committed yet
* when we checked for a duplicate name above.
*/
AddNewRelationTuple(pg_class_desc,
new_rel_desc,
relid,
new_type_oid,
reloftypeid,
ownerid,
relkind,
relfrozenxid,
relminmxid,
PointerGetDatum(relacl),
reloptions);
/*
* now add tuples to pg_attribute for the attributes in our new relation.
*/
AddNewAttributeTuples(relid, new_rel_desc->rd_att, relkind);
/*
* Make a dependency link to force the relation to be deleted if its
* namespace is. Also make a dependency link to its owner, as well as
* dependencies for any roles mentioned in the default ACL.
*
* For composite types, these dependencies are tracked for the pg_type
* entry, so we needn't record them here. Likewise, TOAST tables don't
* need a namespace dependency (they live in a pinned namespace) nor an
* owner dependency (they depend indirectly through the parent table), nor
* should they have any ACL entries. The same applies for extension
* dependencies.
*
* Also, skip this in bootstrap mode, since we don't make dependencies
* while bootstrapping.
*/
if (relkind != RELKIND_COMPOSITE_TYPE &&
relkind != RELKIND_TOASTVALUE &&
!IsBootstrapProcessingMode())
{
ObjectAddress myself,
referenced;
ObjectAddresses *addrs;
ObjectAddressSet(myself, RelationRelationId, relid);
recordDependencyOnOwner(RelationRelationId, relid, ownerid);
recordDependencyOnNewAcl(RelationRelationId, relid, 0, ownerid, relacl);
recordDependencyOnCurrentExtension(&myself, false);
addrs = new_object_addresses();
ObjectAddressSet(referenced, NamespaceRelationId, relnamespace);
add_exact_object_address(&referenced, addrs);
if (reloftypeid)
{
ObjectAddressSet(referenced, TypeRelationId, reloftypeid);
add_exact_object_address(&referenced, addrs);
}
/*
* Make a dependency link to force the relation to be deleted if its
* access method is. Do this only for relation and materialized views.
*
* No need to add an explicit dependency for the toast table, as the
* main table depends on it.
*/
if (relkind == RELKIND_RELATION ||
relkind == RELKIND_MATVIEW)
{
ObjectAddressSet(referenced, AccessMethodRelationId, accessmtd);
add_exact_object_address(&referenced, addrs);
}
record_object_address_dependencies(&myself, addrs, DEPENDENCY_NORMAL);
free_object_addresses(addrs);
}
/* Post creation hook for new relation */
InvokeObjectPostCreateHookArg(RelationRelationId, relid, 0, is_internal);
/*
* Store any supplied constraints and defaults.
*
* NB: this may do a CommandCounterIncrement and rebuild the relcache
* entry, so the relation must be valid and self-consistent at this point.
* In particular, there are not yet constraints and defaults anywhere.
*/
StoreConstraints(new_rel_desc, cooked_constraints, is_internal);
/*
* If there's a special on-commit action, remember it
*/
if (oncommit != ONCOMMIT_NOOP)
register_on_commit_action(relid, oncommit);
/*
* ok, the relation has been cataloged, so close our relations and return
* the OID of the newly created relation.
*/
table_close(new_rel_desc, NoLock); /* do not unlock till end of xact */
table_close(pg_class_desc, RowExclusiveLock);
return relid;
}

![[东华杯2021] ezgadget](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/959da7f0ebb04b76ac997453a5d86579.png)