文章目录
- 前言
- 1.需求分析
- 1.1 场景
- 1.2 解决方案
- 2. 代码
- 2.1 提取特征
- 2.2 构建分类器
- 2.4 集成模型
- 2.5 总的训练代码
- 3.fast api 封装
- 4.总结
前言
深度学习崛起后,好像机器学习就没落了,但在固定场景下,还是很好用的。下面就是展厅项目的识别任务。老规矩,集成学习的基础知识点少讲,或者不讲,因为这种文章已经很多了。主要是基于场景的业务问题解决。
1.需求分析
1.1 场景

画框的这几个小人会移动,移动到左边靠近水的地方,要报警。目标检测比如yolov之类的是可以实现的,但现在想学习一下sklearn的集成学习。所以采用了这个方式。
挑战,灯光的变化
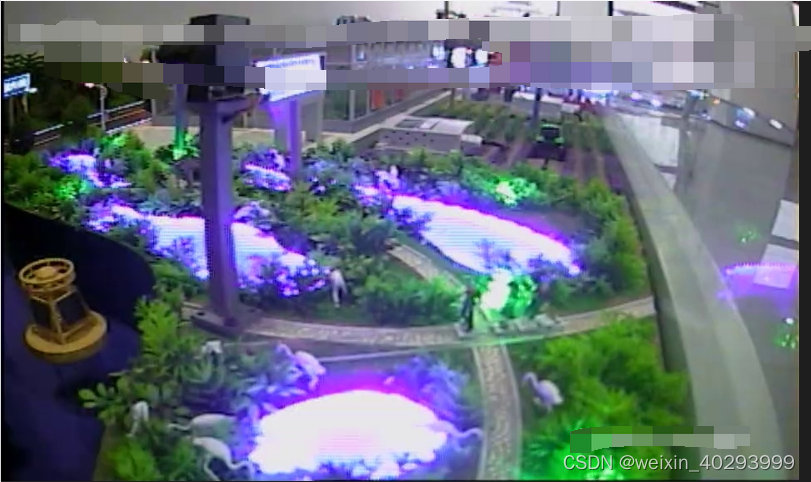

1.2 解决方案
摄像头是不动的,所以用opencv把这部分切割出来做分类。有人和没人两类 0 表示有人, 1表示没人。

2. 代码
2.1 提取特征
提取图像特征的方式有很多种,这里介绍两张haar和lbp
# 提取Haar特征
def extract_haar_features(images):
features = []
for image in images:
# a = 1
# feature = cv2.HOGDescriptor().compute(image)
feature = cv2.HOGDescriptor().compute(image).flatten()
features.append(feature)
return np.array(features)
# 提取lbp特征
def extract_lbp_features(images):
features = []
for image in images:
# a = 1
feature = local_binary_pattern(image, 8, 1, method='uniform').flatten()
features.append(feature)
return np.array(features)
2.2 构建分类器
我这里用了决策树、随机森林、KNN、SVM四个分类器,因为是sklearn封装的,调用起来很简单。
# 构建决策树分类器
def build_decision_tree_classifier(X_train, y_train):
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
return clf
# 构建随机森林分类器
def build_random_forest_classifier(X_train, y_train):
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=50, max_depth=3)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
return clf
# 构建KNN分类器
def build_knn_classifier(X_train, y_train):
clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=10,algorithm='kd_tree')
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
return clf
# 构建SVM分类器
def build_svm_classifier(X_train, y_train):
clf = SVC(kernel='linear', C=0.025)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
return clf
2.4 集成模型
构建集成模型并保存权重,clf最终的预测是由几个分类器投票形成的。
# 构建集成模型
def build_ensemble_model(X_train, y_train):
clfs = []
clf1 = build_decision_tree_classifier(X_train, y_train)
clfs.append(('dt', clf1))
clf2 = build_random_forest_classifier(X_train, y_train)
clfs.append(('rf', clf2))
clf3 = build_knn_classifier(X_train, y_train)
clfs.append(('knn', clf3))
clf4 = build_svm_classifier(X_train, y_train)
clfs.append(('svm', clf4))
eclf = VotingClassifier(estimators=clfs, voting='hard')
# 输出训练过程
for clf in [clf1,clf2,clf3,clf4, eclf]:
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f'{clf.__class__.__name__} Accuracy: {acc}')
eclf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 保存模型权重
joblib.dump(eclf, target_weight_path)
return eclf
2.5 总的训练代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, VotingClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
import joblib
from util_help import read_images
import os
import pickle
from skimage.feature import local_binary_pattern
model_name = "people_drown"
weight_name = model_name + ".joblib"
save_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)),"weight",model_name)
os.makedirs(save_dir,exist_ok=True)
target_weight_path = os.path.join(save_dir,weight_name)
# 提取Haar特征
def extract_haar_features(images):
features = []
for image in images:
# a = 1
# feature = cv2.HOGDescriptor().compute(image)
feature = cv2.HOGDescriptor().compute(image).flatten()
features.append(feature)
return np.array(features)
# 提取Haar特征
def extract_lbp_features(images):
features = []
for image in images:
# a = 1
feature = local_binary_pattern(image, 8, 1, method='uniform').flatten()
features.append(feature)
return np.array(features)
# 构建决策树分类器
def build_decision_tree_classifier(X_train, y_train):
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
return clf
# 构建随机森林分类器
def build_random_forest_classifier(X_train, y_train):
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=50, max_depth=3)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
return clf
# 构建KNN分类器
def build_knn_classifier(X_train, y_train):
clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=10,algorithm='kd_tree')
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
return clf
# 构建SVM分类器
def build_svm_classifier(X_train, y_train):
clf = SVC(kernel='linear', C=0.025)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
return clf
# 构建集成模型
def build_ensemble_model(X_train, y_train):
clfs = []
clf1 = build_decision_tree_classifier(X_train, y_train)
clfs.append(('dt', clf1))
clf2 = build_random_forest_classifier(X_train, y_train)
clfs.append(('rf', clf2))
clf3 = build_knn_classifier(X_train, y_train)
clfs.append(('knn', clf3))
clf4 = build_svm_classifier(X_train, y_train)
clfs.append(('svm', clf4))
eclf = VotingClassifier(estimators=clfs, voting='hard')
# 输出训练过程
for clf in [clf1,clf2,clf3,clf4, eclf]:
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f'{clf.__class__.__name__} Accuracy: {acc}')
eclf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 保存模型权重
joblib.dump(eclf, target_weight_path)
return eclf
# 对测试集进行预测
def predict(model, test_features):
preds = model.predict(test_features)
return preds
# 评估模型准确率
def evaluate(y_true, y_pred):
acc = accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)
print(f'Accuracy: {acc}')
# 加载模型权重
clf = joblib.load(target_weight_path) if os.path.exists(target_weight_path) else None
image_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)),"data","handle",model_name)
# 读取数据集
images, labels = read_images(image_dir)
print(len(images))
# 提取特征
# features = extract_haar_features(images)
features = extract_lbp_features(images)
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(features, labels, test_size=0.25, random_state=42)
# 构建或加载集成模型
if clf is None:
clf = build_ensemble_model(X_train, y_train)
# 对测试集进行预测
y_pred = predict(clf, X_test)
# 评估模型性能
evaluate(y_test, y_pred)
3.fast api 封装
待续,正在开发中。
4.总结
对于光的影响,转成灰度图是否有影响–这是一个大的话题?待续。
另外,用Haar提取特征的时候,权重文件会恐怖的达到12G,而且训练的时候内存会爆掉,这个问题耽误我小半天时间,原因未知。
后来改成lbp的方式就很小的,速度也很快。