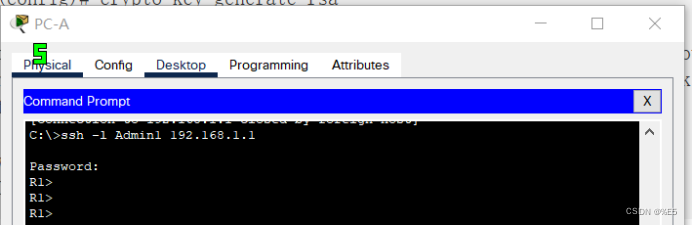
四、Composition API 的优势
1. Options API 存在的问题
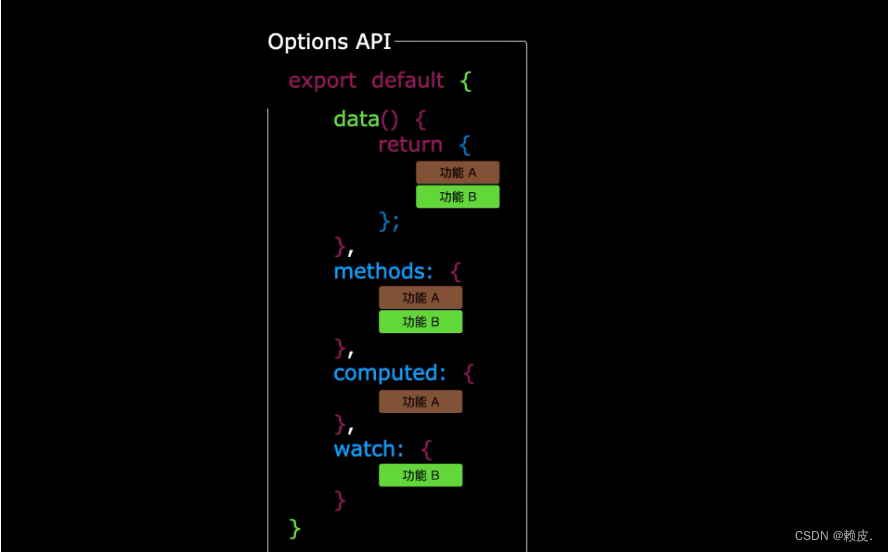
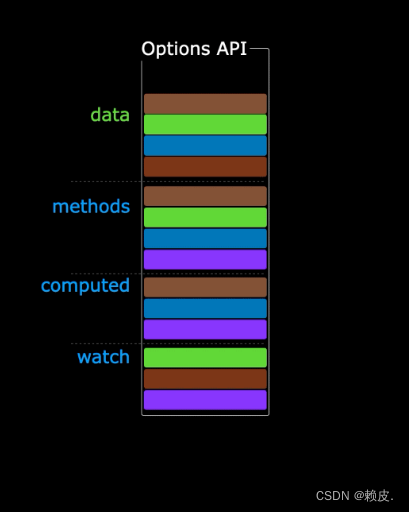
使用传统OptionsAPI中,新增或者修改一个需求,就需要分别在data,methods,computed里修改。
2. Composition API 的优势
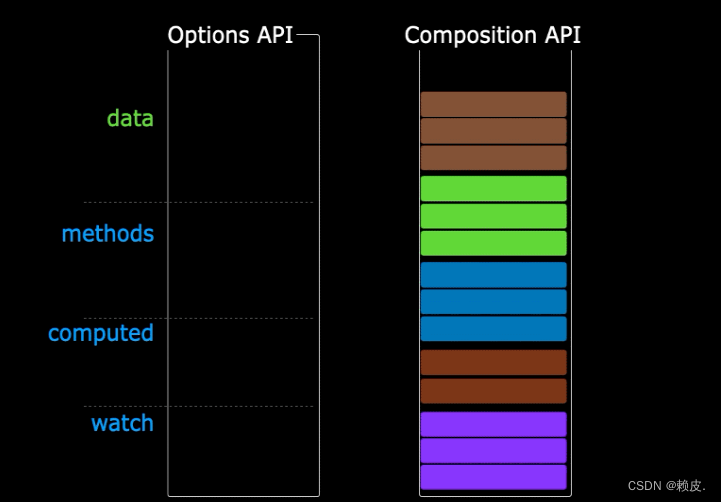
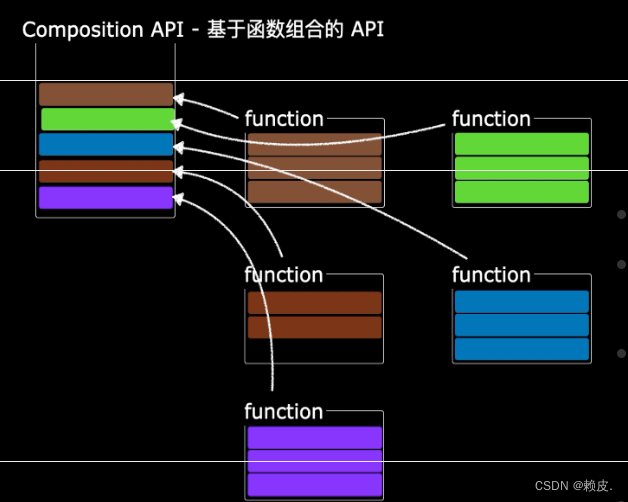
我们可以更加优雅的组织我们的代码,函数。让相关功能的代码更加有序的组织在一起。
五、新的组件
1. Fragment
- 在Vue2中:组件必须有一个根标签
- 在Vue3中:组件可以没有根标签,内部会将多个标签包含在一个Fragment虚拟元素中
- 好处:减少标签层级,减小内存占用
2. Teleport
- 什么是Teleport?
——Teleport (传送)是一种能够将我们的组件html结构移动到指定位置的技术。
Dialog.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = true">点我弹窗</button>
<teleport to="body">
<div v-if="isShow" class="mask">
<div class="dialog">
<h3>我是一个弹窗</h3>
<h4>一些内容</h4>
<h4>一些内容</h4>
<h4>一些内容</h4>
<button @click="isShow = false">关闭弹窗</button>
</div>
</div>
</teleport>
</div>
</template>
<script >
import {ref} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'Dialog',
setup(){
let isShow = ref(false)
return {isShow}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.mask {
position: absolute;
top: 0;bottom: 0; left: 0; right: 0;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
}
.dialog {
position: absolute;
top: 50%; left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
text-align: center;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: green;
}
</style>
Son.vue
<template>
<div class="Son">
<h3>我是Son组件</h3>
<Dialog></Dialog>
</div>
</template>
<script >
import Dialog from './Dialog.vue'
export default {
name: 'Son',
components: {Dialog}
}
</script>
<style>
.Son {
background-color: orange;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
Child.vue
<template>
<div class="Child">
<h3>我是Child组件</h3>
<Son></Son>
</div>
</template>
<script >
import Son from './Son.vue'
export default {
name: 'Child',
components: {Son},
}
</script>
<style>
.Child {
background-color: skyblue;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
3. Suspense
- 等待异步组件时渲染一些额外内容,让应用有更好的用户体验
- 使用步骤:
- 引入异步组件
import { defineAsyncComponent } from 'vue';//静态引入
const Child = defineAsyncComponent(() => import('./components/Child.vue'))//异步引入
- 使用 Suspense 包裹组件,并配置好default 与 fallback
<template>
<div class="app">
<h3>我是App组件</h3>
<Suspense>
<template v-slot:default>
<Child></Child>
</template>
<template v-slot:fallback>
<h3>稍等,加载中...</h3>
</template>
</Suspense>
</div>
</template>
六、其他
1. 全局API的转移
- Vue2.x有许多全局API 和 配置。
- 例如:注册全局组件、注册全局指令等。
//注册全局组件
Vue.component('MyButton', {
data: () => ({
count: 0
}),
template: '<button @click="count++">Clicked {{ count }} times.</button>'
})
//注册全局指令
Vue.directive('focus', {
inserted: el => el.focus()
}
- Vue3.0 中对这些API做出了调整:
- 将全局的API,即:Vue.xxx 调整到应用实例(app)上
| 2.x全局API(vue) | 3.x 实例API(app) |
|---|---|
| Vue.config.xxxx | app.config.xxxx |
| Vue.config.production Tip | 移除 |
| Vue.component | app.component |
| Vue.directive | app.directive |
| Vue.mixin | app.mixin |
| Vue.use | app.use |
| Vue.prototype | app.config.globalProperties |
2.其他改变
- data选项应始终被声明为一个函数。
- 过度类名的更改:
- Vue2.x写法
.v-enter,
.v-leave-to {
opacity: 0;
}
.v-leave,
.v-enter-to {
opacity: 1;
}
- Vue3.x写法
.v-enter-from,
.v-leave-to {
opacity: 0;
}
.v-leave-from,
.v-enter-to {
opacity: 1;
}
- 移除keyCode作为 v-on 的修饰符,同时也不再支持
configkeyCodes - 移除
v-on.native修饰符- 父组件中绑定事件
<my-component
v-on:close="handleComponentEvent"
v-on:click="handleNativeClickEvent"
/>
- 子组件中声明自定义事件
<script>
export default {
emits: ['close']
}
</script>
- 移除过滤器(filter)
过滤器虽然这看起来很方便,但它需要一个自定义语法,打破大括号内表达式是“只是JavaScript”的假设,这不仅有学习成本,而且有实现成本!建议用方法调用或计算属性去替换过滤器。