定义于头文件 <vector>
| template< class T, | (1) | |
| namespace pmr { template <class T> | (2) | (C++17 起) |
1) std::vector 是封装动态数组的顺序容器。
2) std::pmr::vector 是使用多态分配器的模板别名。
| 元素相继存储,这意味着不仅可通过迭代器,还能用指向元素的常规指针访问元素。这意味着指向 vector 元素的指针能传递给任何期待指向数组元素的指针的函数。 | (C++03 起) |
vector 的存储是自动管理的,按需扩张收缩。 vector 通常占用多于静态数组的空间,因为要分配更多内存以管理将来的增长。 vector 所用的方式不在每次插入元素时,而只在额外内存耗尽时重分配。分配的内存总量可用 capacity() 函数查询。额外内存可通过对 shrink_to_fit() 的调用返回给系统。 (C++11 起)
重分配通常是性能上有开销的操作。若元素数量已知,则 reserve() 函数可用于消除重分配。
vector 上的常见操作复杂度(效率)如下:
- 随机访问——常数 O(1)
- 在末尾插入或移除元素——均摊常数 O(1)
- 插入或移除元素——与到 vector 结尾的距离成线性 O(n)
std::vector (对于 bool 以外的 T )满足容器 (Container) 、具分配器容器 (AllocatorAwareContainer) 、序列容器 (SequenceContainer) 、连续容器 (ContiguousContainer) (C++17 起)及可逆容器 (ReversibleContainer) 的要求。
容量
检查容器是否为空
std::vector<T,Allocator>::empty| bool empty() const; | (C++11 前) | |
| bool empty() const noexcept; | (C++11 起) (C++20 前) | |
| [[nodiscard]] bool empty() const noexcept; | (C++20 起) |
检查容器是否无元素,即是否 begin() == end() 。
参数
(无)
返回值
若容器为空则为 true ,否则为 false
复杂度
常数。
返回容纳的元素数
std::vector<T,Allocator>::size| size_type size() const; | (C++11 前) | |
| size_type size() const noexcept; | (C++11 起) |
返回容器中的元素数,即 std::distance(begin(), end()) 。
参数
(无)
返回值
容器中的元素数量。
复杂度
常数。
返回可容纳的最大元素数
std::vector<T,Allocator>::max_size| size_type max_size() const; | (C++11 前) | |
| size_type max_size() const noexcept; | (C++11 起) |
返回根据系统或库实现限制的容器可保有的元素最大数量,即对于最大容器的 std::distance(begin(), end()) 。
参数
(无)
返回值
元素数量的最大值。
复杂度
常数。
注意
此值通常反映容器大小上的理论极限,至多为 std::numeric_limits<difference_type>::max() 。运行时,可用 RAM 总量可能会限制容器大小到小于 max_size() 的值
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <time.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Cell
{
int x;
int y;
Cell() = default;
Cell(int a, int b): x(a), y(b) {}
Cell &operator +=(const Cell &cell)
{
x += cell.x;
y += cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator +(const Cell &cell)
{
x += cell.x;
y += cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator *(const Cell &cell)
{
x *= cell.x;
y *= cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator ++()
{
x += 1;
y += 1;
return *this;
}
bool operator <(const Cell &cell) const
{
if (x == cell.x)
{
return y < cell.y;
}
else
{
return x < cell.x;
}
}
bool operator >(const Cell &cell) const
{
if (x == cell.x)
{
return y > cell.y;
}
else
{
return x > cell.x;
}
}
bool operator ==(const Cell &cell) const
{
return x == cell.x && y == cell.y;
}
};
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Cell &cell)
{
os << "{" << cell.x << "," << cell.y << "}";
return os;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::mt19937 g{std::random_device{}()};
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
auto generate = []()
{
int n = std::rand() % 10 + 110;
Cell cell{n, n};
return cell;
};
std::vector<Cell> vector1;
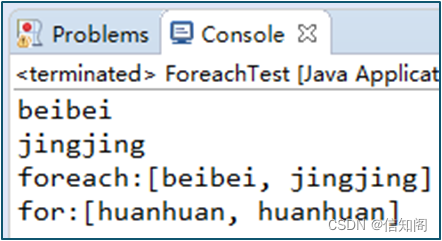
//检查容器是否无元素,即是否 begin() == end() 。
std::cout << "vector1 empty: " << vector1.empty() << std::endl;
//替换容器的内容。1) 以 count 份 value 的副本替换内容。
vector1.assign(6, generate());
//检查容器是否无元素,即是否 begin() == end() 。
std::cout << "vector1 empty: " << vector1.empty() << std::endl;
std::cout << "vector1: ";
std::copy(vector1.begin(), vector1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::vector<Cell> vector2;
for (size_t index = 0; index < 5; index++)
{
vector2.push_back(generate());
std::cout << "vector2 ";
//返回容器中的元素数,即 std::distance(begin(), end()) 。
std::cout << "size(): " << vector2.size() << " ";
std::copy(vector2.begin(), vector2.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
//返回根据系统或库实现限制的容器可保有的元素最大数量,即对于最大容器的 std::distance(begin(), end()) 。
std::vector<bool> vector_b;
std::cout << "vector<bool> max_size: " << vector_b.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<char> vector_c;
std::cout << "vector<char> max_size: " << vector_c.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<int> vector_i;
std::cout << "vector<int> max_size: " << vector_i.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<uint8_t> vector_ui8;
std::cout << "vector<uint8_t> max_size: " << vector_ui8.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<uint16_t> vector_ui16;
std::cout << "vector<uint16_t> max_size: " << vector_ui16.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<uint32_t> vector_ui32;
std::cout << "vector<uint32_t> max_size: " << vector_ui32.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<uint64_t> vector_ui64;
std::cout << "vector<uint64_t> max_size: " << vector_ui64.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<short> vector_s;
std::cout << "vector<short> max_size: " << vector_s.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<double> vector_d;
std::cout << "vector<double> max_size: " << vector_d.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<float> vector_f;
std::cout << "vector<float> max_size: " << vector_f.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<long> vector_l;
std::cout << "vector<long> max_size: " << vector_l.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<long long> vector_ll;
std::cout << "vector<long long> max_size: " << vector_ll.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<string> vector_str;
std::cout << "vector<string> max_size: " << vector_str.max_size() << std::endl;
std::vector<Cell> vector_Cell;
std::cout << "vector<Cell> max_size: " << vector_Cell.max_size() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
输出
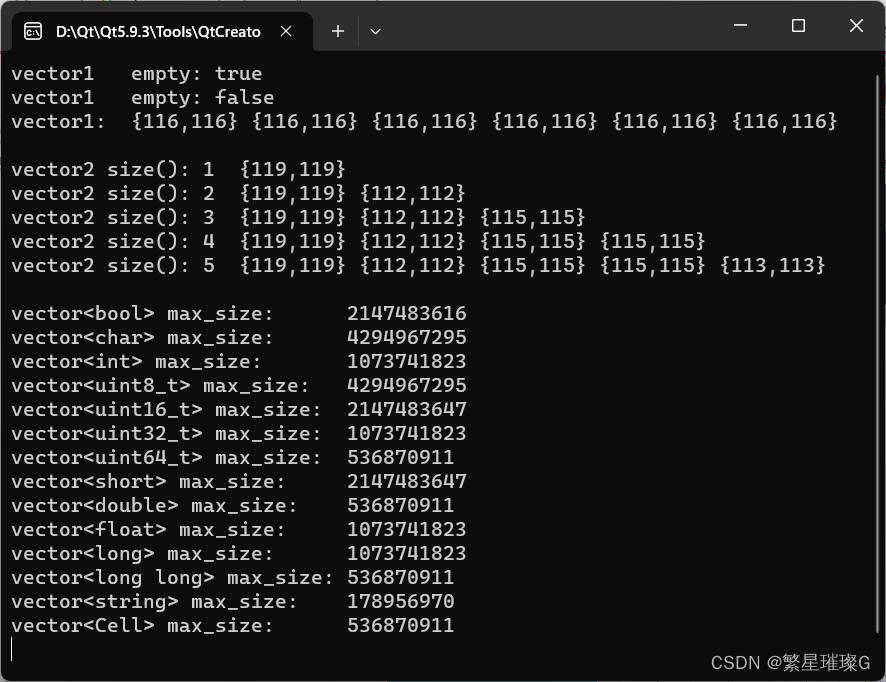




![[230508]托福听力真题TPO66|词汇总结| 精听|19:30~20:10 20:50~23:00 8:30~9:40](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2a9d0fb3fd8b4ad79a40717098fc0128.png)