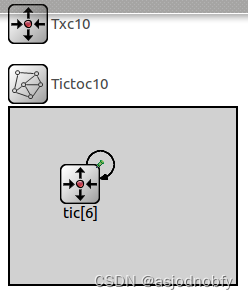
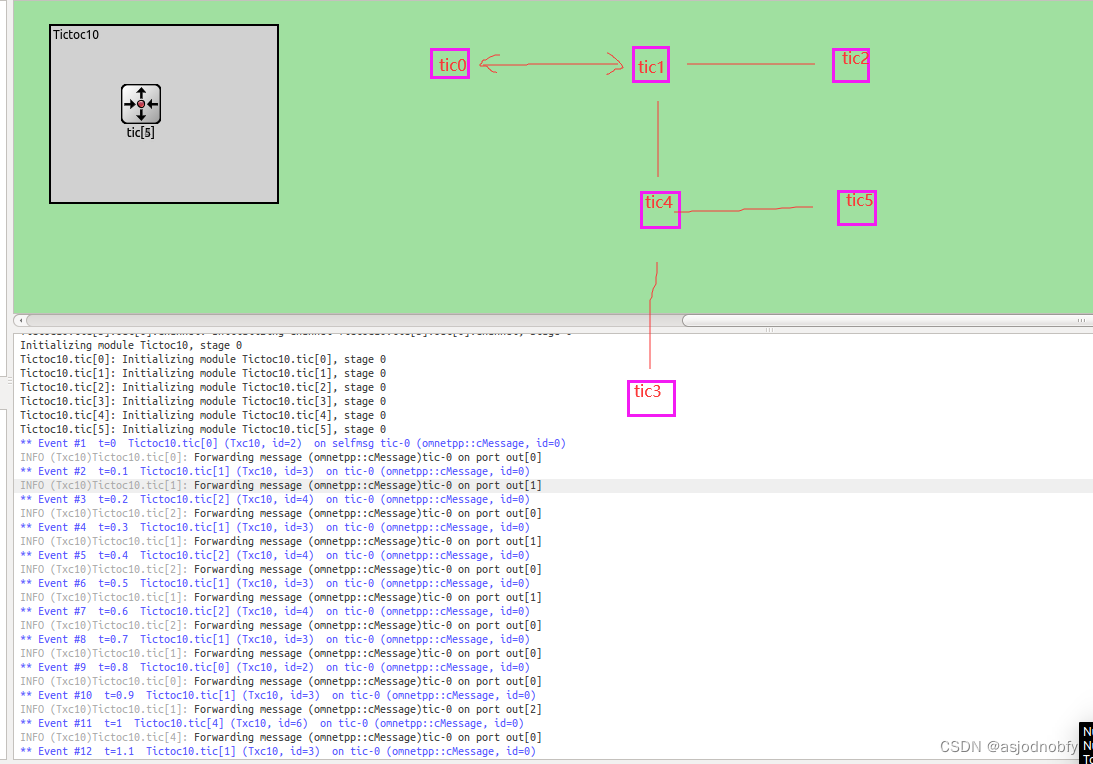
tictoc10-13
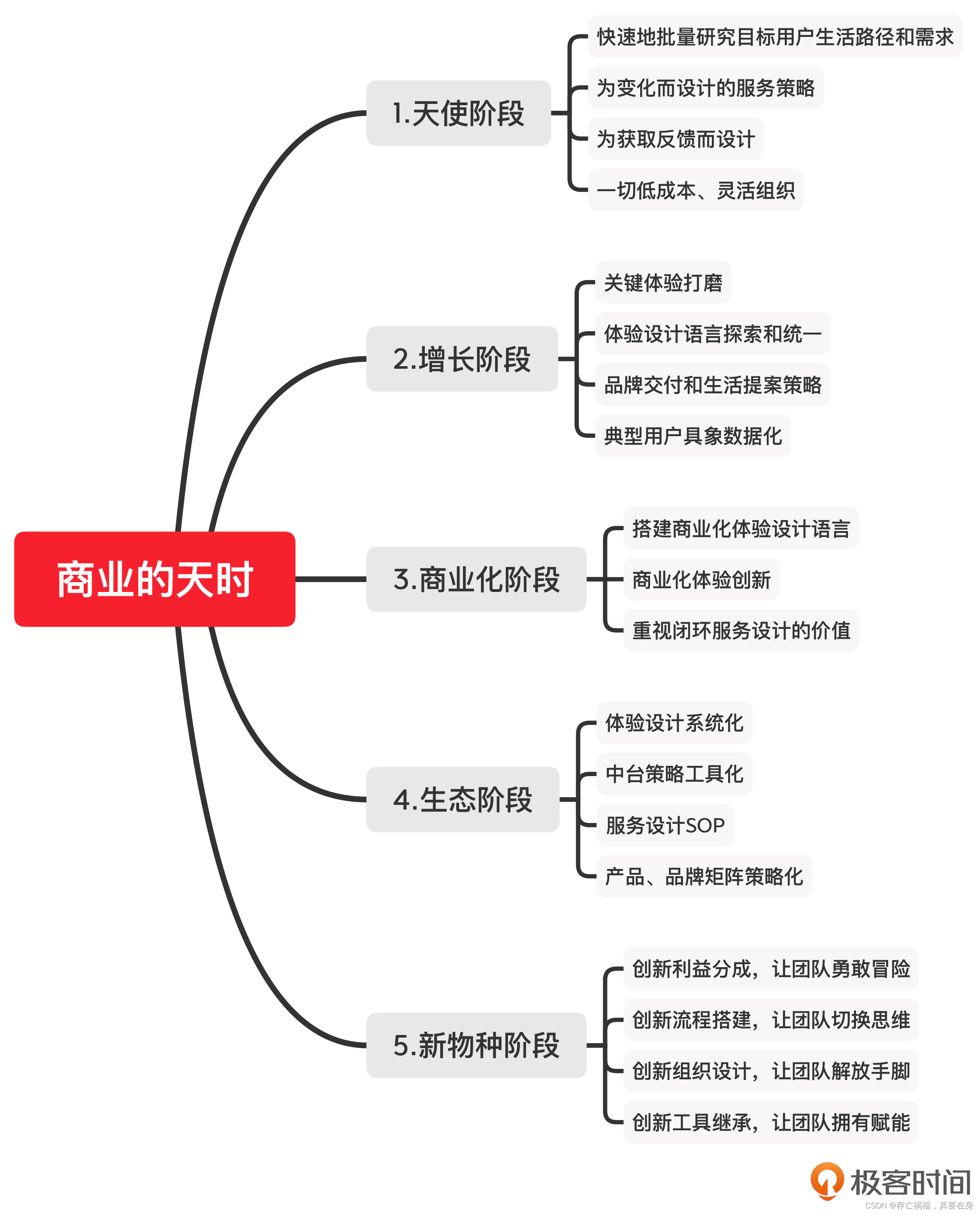
- tictoc 10 几个模块连接,发送消息直到模块3收到消息
- tictoc 11 新增信道定义
- tictoc 12 双向连接信息简化定义
tictoc 10 几个模块连接,发送消息直到模块3收到消息
- 让我们用几个(n)’ tic’模块让它更有趣,并将每个模块连接到其他模块。
- 把它们的工作简单化:模块0生成一条消息,其他模块继续向随机方向传递消息,直到它到达模块2。
ned
simple Txc10
{
parameters:
@display("i=block/routing");
gates:
input in[]; // declare in[] and out[] to be vector gates
output out[];
}
network Tictoc10
{
@display("bgb=226,176");
submodules:
tic[6]: Txc10 {
@display("p=70,76");
}
connections:
tic[0].out++ --> { delay = 100ms; } --> tic[1].in++;
tic[0].in++ <-- { delay = 100ms; } <-- tic[1].out++;
tic[1].out++ --> { delay = 100ms; } --> tic[2].in++;
tic[1].in++ <-- { delay = 100ms; } <-- tic[2].out++;
tic[1].out++ --> { delay = 100ms; } --> tic[4].in++;
tic[1].in++ <-- { delay = 100ms; } <-- tic[4].out++;
tic[3].out++ --> { delay = 100ms; } --> tic[4].in++;
tic[3].in++ <-- { delay = 100ms; } <-- tic[4].out++;
tic[4].out++ --> { delay = 100ms; } --> tic[5].in++;
tic[4].in++ <-- { delay = 100ms; } <-- tic[5].out++;
}
cc
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <omnetpp.h>
using namespace omnetpp;
/**
* Let's make it more interesting by using several (n) `tic' modules,
* and connecting every module to every other. For now, let's keep it
* simple what they do: module 0 generates a message, and the others
* keep tossing it around in random directions until it arrives at
* module 2.
* 让我们用几个(n)让它更有趣' tic'模块,并将每个模块连接到其他模块。现在,让我们把它们的工作简单化:模块0生成一条消息,其他模块继续向随机方向传递消息,直到它到达模块2。
*/
class Txc10 : public cSimpleModule
{
protected:
virtual void forwardMessage(cMessage *msg);
virtual void initialize() override;
virtual void handleMessage(cMessage *msg) override;
};
Define_Module(Txc10);
void Txc10::initialize()
{
if (getIndex() == 0) {
// Boot the process scheduling the initial message as a self-message.启动,将初始消息调度为自消息的进程。
char msgname[20];
sprintf(msgname, "tic-%d", getIndex());
cMessage *msg = new cMessage(msgname);
scheduleAt(0.0, msg);
}
}
void Txc10::handleMessage(cMessage *msg)
{
if (getIndex() == 3) {
// Message arrived.
EV << "Message " << msg << " arrived.\n";
delete msg;
}
else {
// We need to forward the message.
forwardMessage(msg);
}
}
void Txc10::forwardMessage(cMessage *msg)
{
// In this example, we just pick a random gate to send it on.
// We draw a random number between 0 and the size of gate `out[]'.
int n = gateSize("out");
int k = intuniform(0, n-1);
EV << "Forwarding message " << msg << " on port out[" << k << "]\n";
send(msg, "out", k);
}
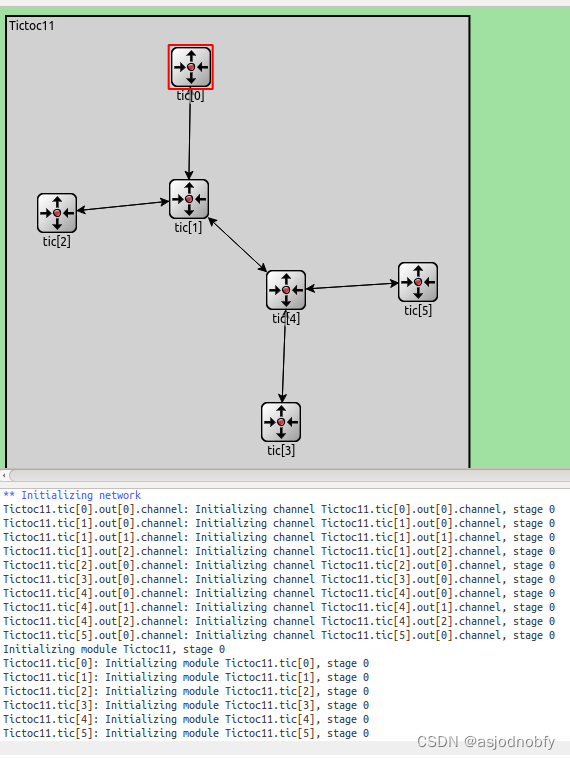
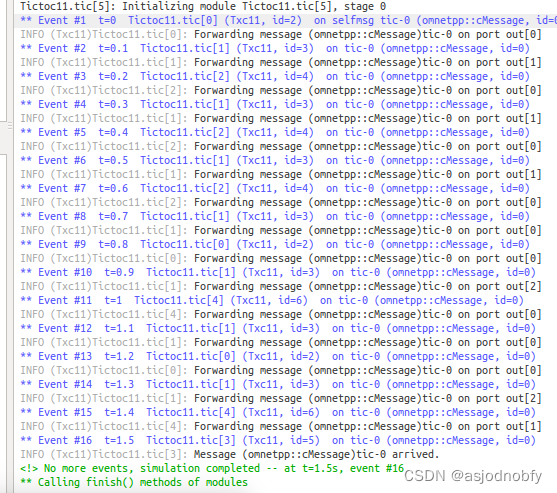
tictoc 11 新增信道定义
- (实现内容同上)让我们用几个(n)’ tic’模块让它更有趣,并将每个模块连接到其他模块。现在,让我们把它们的工作简单化:模块0生成一条消息,其他模块继续向随机方向传递消息,直到它到达模块2。
- 信道使用本地信道类型定义,减少连接冗余
types://定义信道
channel Channel extends ned.DelayChannel {
delay = 100ms;
}
ned
simple Txc11
{
parameters:
@display("i=block/routing");
gates:
input in[]; // declare in[] and out[] to be vector gates
output out[];
}
//
// Using local channel type definition to reduce the redundancy
// of connection definitions.
//
//使用本地通道类型定义来减少连接定义的冗余。
network Tictoc11
{
types://定义信道
channel Channel extends ned.DelayChannel {
delay = 100ms;
}
submodules:
tic[6]: Txc11;
connections:
tic[0].out++ --> Channel --> tic[1].in++;
tic[0].in++ <-- Channel <-- tic[1].out++;
tic[1].out++ --> Channel --> tic[2].in++;
tic[1].in++ <-- Channel <-- tic[2].out++;
tic[1].out++ --> Channel --> tic[4].in++;
tic[1].in++ <-- Channel <-- tic[4].out++;
tic[3].out++ --> Channel --> tic[4].in++;
tic[3].in++ <-- Channel <-- tic[4].out++;
tic[4].out++ --> Channel --> tic[5].in++;
tic[4].in++ <-- Channel <-- tic[5].out++;
}
cc
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <omnetpp.h>
using namespace omnetpp;
/**
* Let's make it more interesting by using several (n) `tic' modules,
* and connecting every module to every other. For now, let's keep it
* simple what they do: module 0 generates a message, and the others
* keep tossing it around in random directions until it arrives at
* module 2.
* 让我们用几个(n)让它更有趣' tic'模块,并将每个模块连接到其他模块。
* 现在,让我们把它们的工作简单化:
* 模块0生成一条消息,其他模块继续向随机方向传递消息,直到它到达模块2。
*/
class Txc11 : public cSimpleModule
{
protected:
virtual void forwardMessage(cMessage *msg);
virtual void initialize() override;
virtual void handleMessage(cMessage *msg) override;
};
Define_Module(Txc11);
void Txc11::initialize()
{
if (getIndex() == 0) {
// Boot the process scheduling the initial message as a self-message.
char msgname[20];
sprintf(msgname, "tic-%d", getIndex());
cMessage *msg = new cMessage(msgname);
scheduleAt(0.0, msg);
}
}
void Txc11::handleMessage(cMessage *msg)
{
if (getIndex() == 3) {
// Message arrived.
EV << "Message " << msg << " arrived.\n";
delete msg;
}
else {
// We need to forward the message.
forwardMessage(msg);
}
}
void Txc11::forwardMessage(cMessage *msg)
{
// In this example, we just pick a random gate to send it on.
// We draw a random number between 0 and the size of gate `out[]'.
int n = gateSize("out");
int k = intuniform(0, n-1);
EV << "Forwarding message " << msg << " on port out[" << k << "]\n";
send(msg, "out", k);
}
tictoc 12 双向连接信息简化定义
- 使用双向连接进一步简化网络定义
ned
simple Txc12
{
parameters:
@display("i=block/routing");
gates:
inout gate[]; // declare two way connections 声明双向连接
}
// using two way connections to further simplify the network definition
//使用双向连接进一步简化网络定义
network Tictoc12
{
types:
channel Channel extends ned.DelayChannel {
delay = 100ms;
}
submodules:
tic[6]: Txc12;
connections:
tic[0].gate++ <--> Channel <--> tic[1].gate++;
tic[1].gate++ <--> Channel <--> tic[2].gate++;
tic[1].gate++ <--> Channel <--> tic[4].gate++;
tic[3].gate++ <--> Channel <--> tic[4].gate++;
tic[4].gate++ <--> Channel <--> tic[5].gate++;
}
cc
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <omnetpp.h>
using namespace omnetpp;
/**
* Let's make it more interesting by using several (n) `tic' modules,
* and connecting every module to every other. For now, let's keep it
* simple what they do: module 0 generates a message, and the others
* keep tossing it around in random directions until it arrives at
* module 2.
*/
class Txc12 : public cSimpleModule
{
protected:
virtual void forwardMessage(cMessage *msg);
virtual void initialize() override;
virtual void handleMessage(cMessage *msg) override;
};
Define_Module(Txc12);
void Txc12::initialize()
{
if (getIndex() == 0) {
// Boot the process scheduling the initial message as a self-message.
char msgname[20];
sprintf(msgname, "tic-%d", getIndex());
cMessage *msg = new cMessage(msgname);
scheduleAt(0.0, msg);
}
}
void Txc12::handleMessage(cMessage *msg)
{
if (getIndex() == 3) {
// Message arrived.
EV << "Message " << msg << " arrived.\n";
delete msg;
}
else {
// We need to forward the message.
forwardMessage(msg);
}
}
void Txc12::forwardMessage(cMessage *msg)
{
// In this example, we just pick a random gate to send it on.
// We draw a random number between 0 and the size of gate `gate[]'.
int n = gateSize("gate");
int k = intuniform(0, n-1);
EV << "Forwarding message " << msg << " on gate[" << k << "]\n";
// $o and $i suffix is used to identify the input/output part of a two way gate
send(msg, "gate$o", k);
}





![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot课室预约系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2237d3eec6c243ea81843afe77282265.png)