文章目录
- 一、迪杰斯特拉算法
- 1.1 算法介绍
- 1.2 算法步骤
- 1.3 应用场景
- 二、弗洛伊德算法
- 2.1 算法介绍
- 2.2 算法步骤
- 2.3 应用场景
一、迪杰斯特拉算法
1.1 算法介绍
从某顶点出发,沿图的边到达另一顶点所经过的路径中,各边上权值之和最小的一条路径叫做最短路径。 解决最短路径的问题有以下算法:Dijkstra
算法,Bellman-Ford 算法,Floyd 算法和 SPFA 算法等。
-
迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra 算法)是典型最短路径算法,用于计算一个节点到其它节点的最短路径,它的主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展(广度优先搜索思想),直到扩展到终点为止。
-
该算法的时间复杂度为 O(ElogV),其中 E 为边数,V 为节点数。
1.2 算法步骤
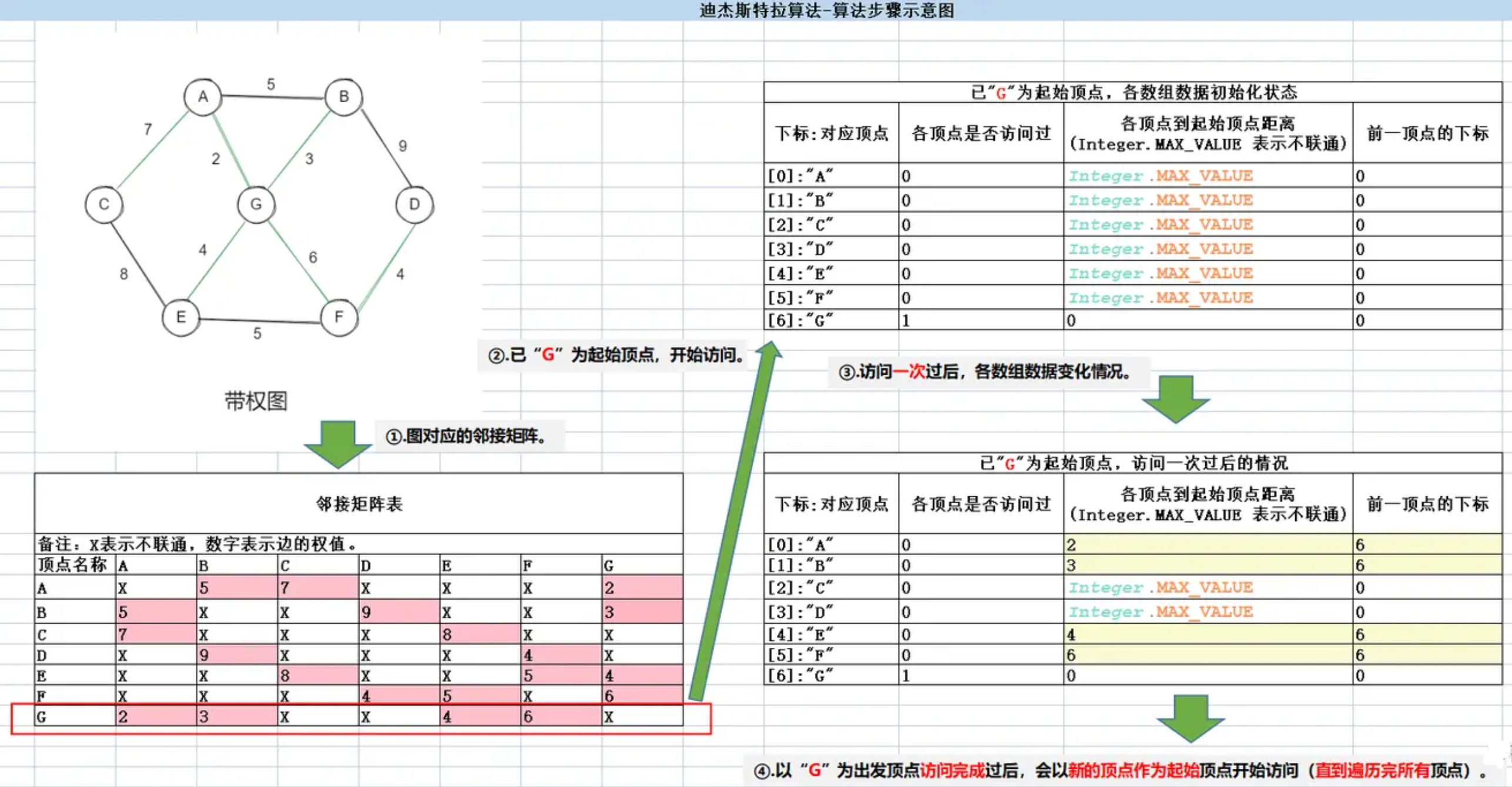
- 设置起始点,并有记录各顶点的数组A、记录各顶点到起始点距离的数组B(起始点到自身的距离记作0);
- 从距离数组中选取最小的值(即当前为最短路径),选好以后,将对应的顶点从数组A中移除,对应记录的距离从数组B中移除;
- 比较起始点与各顶点的距离值,更新前驱节点,并保留值较小的一个距离值,从而完成对各顶点到起始点距离的数组B的更新;
- 重复执行步骤2、步骤3,直到最短路径顶点为目标顶点时,算法结束。
1.3 应用场景
假设有 7 个村庄(A,B,C,D,E,F,G),各个村庄的距离用边线表示(权) ,比如 A<–>B 距离 5 公里。问:如何计算出 G
村庄到其它各个村庄的最短距离?如果从其它点出发到各个点的最短距离又是多少?(通过迪杰斯特拉算法求最短路径)
示意图:
代码示例:
public class DijkstraAlgorithmDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 顶点集合。
char[] vertexes = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G'};
// 邻接矩阵,`Integer.MAX_VALUE` 表示不联通。
final int x = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int[][] matrix = {
{x, 5, 7, x, x, x, 2},
{5, x, x, 9, x, x, 3},
{7, x, x, x, 8, x, x},
{x, 9, x, x, x, 4, x},
{x, x, 8, x, x, 5, 4},
{x, x, x, 4, 5, x, 6},
{2, 3, x, x, 4, 6, x}
};
// 创建图。
Graph graph = new Graph(vertexes, matrix);
// 查看矩阵创建。
graph.showGraph();
// [x, 5, 7, x, x, x, 2]
// [5, x, x, 9, x, x, 3]
// [7, x, x, x, 8, x, x]
// [x, 9, x, x, x, 4, x]
// [x, x, 8, x, x, 5, 4]
// [x, x, x, 4, 5, x, 6]
// [2, 3, x, x, 4, 6, x]
// 测试迪杰斯特拉算法
// [6]:"G"([下标]:对应顶点)。
int vertexIndex = 6;
graph.dijkstra(vertexIndex);
graph.dijkstraResult(vertexes, vertexIndex);
// 各顶点访问状态 (0:表示已访问 1:表示未访问): 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
// 前一顶点: 6 6 0 5 6 6 0
// 各顶点到起始顶点的距离: 2 3 9 10 4 6 0
// 具体详情如下:<G-A>:(2) <G-B>:(3) <G-C>:(9) <G-D>:(10) <G-E>:(4) <G-F>:(6) <G-G>:(0)
}
}
/**
* 图
*/
class Graph {
/**
* 顶点数组。
*/
private final char[] vertexes;
/**
* 邻接矩阵。
*/
private final int[][] matrix;
/**
* 已经访问的顶点的集合。
*/
private VisitedVertex visitedVertex;
/**
* 初始化构造。
*
* @param vertexes 顶点
* @param matrix 矩阵
*/
public Graph(char[] vertexes, int[][] matrix) {
this.vertexes = vertexes;
this.matrix = matrix;
}
/**
* 展示dijkstra算法结果。
*
* @param vertexes 顶点数组
* @param vertexIndex 顶点下标
*/
public void dijkstraResult(char[] vertexes, int vertexIndex) {
visitedVertex.show(vertexes, vertexIndex);
}
/**
* 展示图。
*/
public void showGraph() {
for (int[] link : matrix) {
// 将表示不联通的值替换输出(便于查看)。
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(link)
.replaceAll(Integer.MAX_VALUE + "", "x")
);
}
}
/**
* 迪杰斯特拉算法。
* 目的:根据起始顶点下标找到最短路径。
*
* @param index 顶点对应的下标(比如:0对应顶点A,1对应顶点B...)
*/
public void dijkstra(int index) {
int vertexNum = this.vertexes.length;
this.visitedVertex = new VisitedVertex(vertexNum, index);
// 更新当前顶点到其它周围顶点的距离和前驱顶点。
update(index);
for (int i = 1; i < vertexNum; i++) {
// 选择并返回新的访问顶点。
index = this.visitedVertex.updateArray();
// 更新当前顶点到其它顶点的距离和前驱顶点。
update(index);
}
}
/**
* 更新下标顶点到周围顶点的距离及前驱顶点。
*
* @param index 对应下标
*/
private void update(int index) {
// 遍历邻接矩阵。
int len = this.matrix[index].length;
long distance = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
// `distance`表示:当前顶点到起始顶点的距离 + 从当前顶点到j顶点距离的和。
distance = this.visitedVertex.getDistance(index) + this.matrix[index][j];
// 如果j顶点没有被访问过,且求得的距离小于起始顶点到j顶点的距离,就需要进行更新。
if (!visitedVertex.in(j) && distance < this.visitedVertex.getDistance(j)) {
// 更新j顶点前驱顶点。
this.visitedVertex.updatePre(j, index);
// 更加起始顶点到j顶点的距离。
this.visitedVertex.updateDistance(j, distance);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 已访问的顶点集。
*/
class VisitedVertex {
/**
* 记录顶点是否被访问过。
* 0表示未访问,1表示访问过。
*/
private final int[] isVisited;
/**
* 记录前驱顶点。
*/
private final int[] preVisited;
/**
* 记录到起始顶点距离。
*/
private final long[] distances;
/**
* 使用 `Integer.MAX_VALUE` 表示无穷大,即不可联通。
*/
private static final int DISCONNECTED = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
/**
* 初始化构造。
*
* @param vertexNum 顶点个数
* @param index 顶点对应的下标(比如:0对应顶点A,1对应顶点B...)
*/
public VisitedVertex(int vertexNum, int index) {
this.isVisited = new int[vertexNum];
this.preVisited = new int[vertexNum];
this.distances = new long[vertexNum];
// 初始化距离数组数据。
Arrays.fill(distances, DISCONNECTED);
// 将起始顶点标记为已访问,并将访问距离设置为0。
this.isVisited[index] = 1;
this.distances[index] = 0;
}
/**
* 顶点是否被访问过。
*
* @param index 顶点下标
* @return boolean
*/
public boolean in(int index) {
return 1 == this.isVisited[index];
}
/**
* 更新距离。
*
* @param index 顶点下标
* @param distance 距离
*/
public void updateDistance(int index, long distance) {
this.distances[index] = distance;
}
/**
* 更新前驱顶点
*
* @param pre 前驱顶点下标
* @param index 当前顶点下标
*/
public void updatePre(int pre, int index) {
preVisited[pre] = index;
}
/**
* 得到到起始顶点距离。
*
* @param index 顶点下标
* @return long
*/
public long getDistance(int index) {
return this.distances[index];
}
/**
* 继续选择并返回新的访问顶点,比如这里的G 完后,就是 A点作为新的访问顶点(注意不是起始顶点)。
*
* @return int
*/
public int updateArray() {
long minDis = DISCONNECTED;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < isVisited.length; i++) {
// 若没有被访问过且有权值,则进行更新。
if (0 == isVisited[i] && minDis > distances[i]) {
minDis = distances[i];
index = i;
}
}
// 设置已访问。
isVisited[index] = 1;
return index;
}
/**
* 将各数组数据情况进行输出并显示最终结果。
*
* @param vertexes 顶点数组
* @param vertexIndex 顶点下标
*/
public void show(char[] vertexes, int vertexIndex) {
System.out.println("==========================");
System.out.print("各顶点访问状态 (0:表示已访问 1:表示未访问): ");
for (int i : isVisited) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.print("前一顶点: ");
for (int i : preVisited) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.print("各顶点到起始顶点的距离: ");
for (long i : distances) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.print("具体详情如下:");
int counter = 0;
for (long i : distances) {
if (DISCONNECTED != i) {
System.out.print("<" + vertexes[vertexIndex] + "-" + vertexes[counter] + ">:(" + i + ") ");
} else {
System.out.println("N ");
}
counter++;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
二、弗洛伊德算法
2.1 算法介绍
弗洛伊德算法(Floyd 算法)又称为插点法,是一种利用动态规划的思想寻找给定的加权图中多源点之间最短路径的算法,与 Dijkstra
算法类似。
-
与迪杰斯特拉算法对比:
- 迪杰斯特拉算法通过选定的被访问顶点,求出从起始访问顶点到其它顶点的最短路径;
- 弗洛伊德算法中每一个顶点都是起始访问点,所以需要将每一个顶点看做被访问顶点,求出从每一个顶点到其它顶点的最短路径。
-
该算法的时间复杂度为 O(n³),其中 n 为节点数。
-
该算法可以处理有向图和无向图,但不能处理负权环,如果存在负权环,则最短路径不存在。
2.2 算法步骤
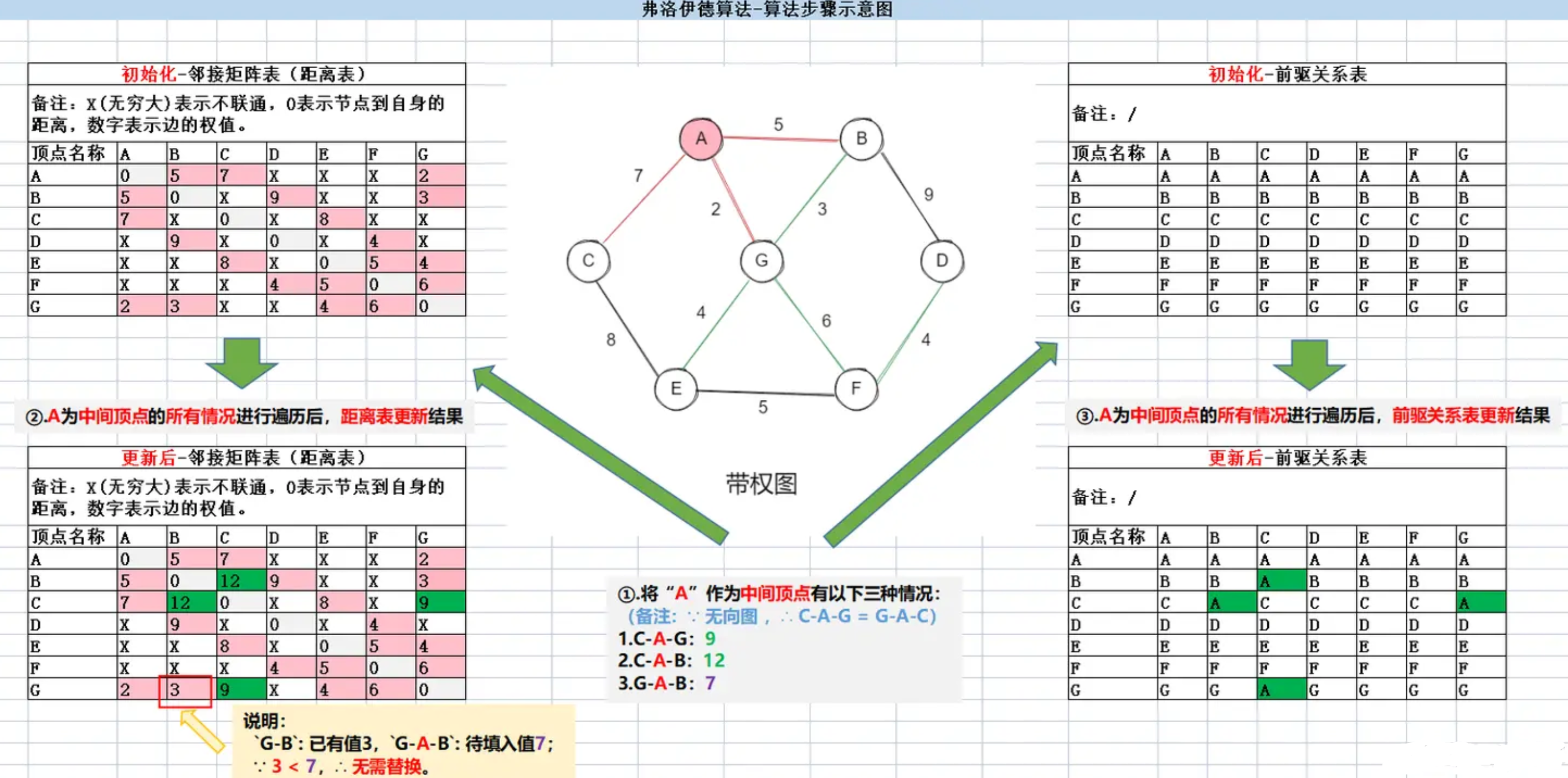
- 初始化距离矩阵:初始化一个 n*n 的矩阵D,其中 D[ i ][ j ] 表示从节点 i 到节点 j 的最短路径长度。如果 i 和 j 之间没有边相连,则 D[ i ][ j ] 为无穷大。
- 通过中间点更新距离矩阵:对于每个节点 k,依次更新矩阵D。具体地,对于每对节点 i 和 j,如果从 i 到 j 的路径经过节点 k 可以使得路径长度更短,则更新 D[ i ][ j ] 为 D[ i ][ k ]+D[ k ][ j ] 。
- 最终得到的矩阵D即为所有节点对之间的最短路径长度。
2.3 应用场景
假设有 7 个村庄(A,B,C,D,E,F,G),各个村庄的距离用边线表示(权),比如 A<–>B 距离 5
公里。问:如何计算出各村庄到其它各村庄的最短距离?(通过弗洛伊德算法求最短路径)
示意图:
代码示例:
public class FloydAlgorithmDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 顶点集合。
char[] vertexes = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G'};
// 邻接矩阵,`Integer.MAX_VALUE` 表示不联通。
final int x = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
long[][] matrix = {
{0, 5, 7, x, x, x, 2},
{5, 0, x, 9, x, x, 3},
{7, x, 0, x, 8, x, x},
{x, 9, x, 0, x, 4, x},
{x, x, 8, x, 0, 5, 4},
{x, x, x, 4, 5, 0, 6},
{2, 3, x, x, 4, 6, 0}
};
// 创建图。
Graph graph = new Graph(vertexes.length, vertexes, matrix);
// 测试弗洛伊德算法。
graph.floyd();
graph.show();
// <A-A>的最短路径是0; <A-B>的最短路径是5; <A-C>的最短路径是7; <A-D>的最短路径是12; <A-E>的最短路径是6; <A-F>的最短路径是8; <A-G>的最短路径是2;
// <B-A>的最短路径是5; <B-B>的最短路径是0; <B-C>的最短路径是12; <B-D>的最短路径是9; <B-E>的最短路径是7; <B-F>的最短路径是9; <B-G>的最短路径是3;
// <C-A>的最短路径是7; <C-B>的最短路径是12; <C-C>的最短路径是0; <C-D>的最短路径是17; <C-E>的最短路径是8; <C-F>的最短路径是13; <C-G>的最短路径是9;
// <D-A>的最短路径是12; <D-B>的最短路径是9; <D-C>的最短路径是17; <D-D>的最短路径是0; <D-E>的最短路径是9; <D-F>的最短路径是4; <D-G>的最短路径是10;
// <E-A>的最短路径是6; <E-B>的最短路径是7; <E-C>的最短路径是8; <E-D>的最短路径是9; <E-E>的最短路径是0; <E-F>的最短路径是5; <E-G>的最短路径是4;
// <F-A>的最短路径是8; <F-B>的最短路径是9; <F-C>的最短路径是13; <F-D>的最短路径是4; <F-E>的最短路径是5; <F-F>的最短路径是0; <F-G>的最短路径是6;
// <G-A>的最短路径是2; <G-B>的最短路径是3; <G-C>的最短路径是9; <G-D>的最短路径是10; <G-E>的最短路径是4; <G-F>的最短路径是6; <G-G>的最短路径是0;
}
}
/**
* 图。
*/
class Graph {
/**
* 顶点数组。
*/
private final char[] vertexes;
/**
* 记录各个顶点到其它顶点的距离。
*/
private final long[][] distances;
/**
* 到达目标顶点的前驱顶点。
*/
private final int[][] preVisited;
/**
* 初始化构造。
*
* @param size 数组大小
* @param vertexes 顶点集合
* @param distances 距离
*/
public Graph(int size, char[] vertexes, long[][] distances) {
this.vertexes = vertexes;
this.distances = distances;
this.preVisited = new int[size][size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// 对前驱节点数组进行初始化(存放前驱顶点下标)。
Arrays.fill(preVisited[i], i);
}
}
/**
* 展示前驱关系及距离信息。
*/
public void show() {
int length = this.distances.length;
for (int k = 0; k < length; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
System.out.print("<" + this.vertexes[k] + "-" + this.vertexes[i] + ">的最短路径是" + distances[k][i] + "; ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 弗洛伊德算法。
*/
public void floyd() {
// 距离变量。
long dist = 0;
int dLen = this.distances.length;
// 三层 `for`。
// k 就是中间顶点的下标。
for (int k = 0; k < dLen; k++) {
// i 作为起始顶点。
for (int i = 0; i < dLen; i++) {
// j 作为目标顶点。
for (int j = 0; j < dLen; j++) {
// 求出从 i 顶点出发,经过 k 中间顶点,到达 j 顶点距离。
dist = distances[i][k] + distances[k][j];
// 如果`算法得到的距离`小于`当前距离表中已有的距离`则进行更新。
if (dist < distances[i][j]) {
// 更新距离。
distances[i][j] = dist;
// 更新前驱顶点。
preVisited[i][j] = preVisited[k][j];
}
}
}
}
}
}