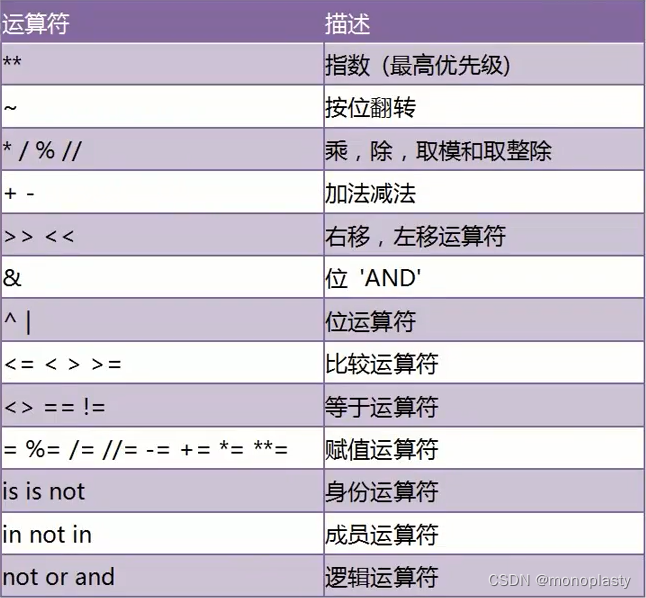
参考引用
- PCL Basic Usage
- PCL 点云库官网教程
1. pcl_viewer 基本使用
1.1 pcl_viewer 安装测试
- pcl_data 源码克隆
$ git clone https://github.com/PointCloudLibrary/data.git - 进入 /pcl_data/tutorials(如下图)
$ cd ~/pcl_data/tutorials # 此处为重命名后的文件夹 pcl_data

- 查看 .pcd 文件(以 ism_test_cat.pcd 为例)
$ pcl_viewer ism_test_cat.pcd

1.2 pcl_viewer 常用操作
-
基本使用
- 进入:pcl_viewer xxxxx.pcd
- 帮助:在界面中输入 h,可以在控制台看到帮助信息
- 退出:界面中输入 q
- 放大缩小:鼠标滚轮 或 Alt + [+/-]
- 平移:Shift + 鼠标拖拽
- 旋转:Ctrl + 鼠标拖拽
- 修改点颜色:数字 1,2,3,4,5…9,重复按 1 可切换不同颜色方便观察
- 修改点大小:放大 Ctrl + Shift + 加号,缩小 Ctrl + 减号
- 保存截图:j
- 显示颜色尺寸:u
- 显示比例尺寸:g
- 在控制列出所有几何和颜色信息:l
-
常用指令
# 1. 修改背景色或前景色 $ pcl_viewer ism_test_cat.pcd -bc 255,255,255 # 修改背景色为白色 $ pcl_viewer ism_test_cat.pcd -fc 0xff,0x0,0x0 # 修改前景色为红色 # 2. 设置点大小和不透明度 $ pcl_viewer ism_test_cat.pcd -ps 4 # 设置点大小为 4 $ pcl_viewer ism_test_cat.pcd -opaque 0.1 # 设置点透明度为 0.1 # 3. 设置坐标轴显示 $ pcl_viewer ism_test_cat.pcd -ax 64 # 显示大小为 64 的坐标轴 $ pcl_viewer ism_test_cat.pcd -ax 64 -ax_pos -64,-64,0 # 显示坐标轴并改变其位置(默认 0,0,0) # 4. 格式转换命令 $ pcl_pcd2ply input.pcd output.ply # 将 PCD 转为 ply 文件 $ pcl_mesh2pcd input.{ply,obj} output.pcd # 将 CAD 模型转为 PCD 文件 $ pcl_mesh2pcd input.{ply,obj} output.pcd -leaf_size 10 # -leaf_size :修改体素网格的 XYZ 大小,用于增减点的密度 # 5. Octrees 八叉树可视化(下图所示) $ pcl_octree_viewer ism_test_cat.pcd 0.2 # 0.2 代表分辨率

- 鼠标选点打印坐标
- 选点模式进入:pcl_viewer -use_point_picking bunny.pcd
- 选择指定点:shift + 鼠标左键
2. 在项目中使用 PCL
-
新建项目工作空间 pcl_demo_ws
$ mkdir pcl_demo_ws -
在工作空间新建 pcd_write.cpp 文件
// pcd_write.cpp // 随机生成了 5 个点,并将之以 ASCII 形式保存(序列化)在 test_pcd.pcd 文件中 #include <iostream> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/point_types.h> int main(int argc, char **argv) { pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud; // Fill in the cloud data cloud.width = 5; cloud.height = 1; cloud.is_dense = false; // 没有无穷值或 NaN 值 cloud.points.resize(cloud.width * cloud.height); std::cout << rand() << std::endl; std::cout << rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f) << std::endl; std::cout << 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f) << std::endl; // 随机生成5个点 for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud.points.size(); ++i) { cloud.points[i].x = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f); cloud.points[i].y = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f); cloud.points[i].z = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f); } pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("test_pcd.pcd", cloud); std::cerr << "Saved " << cloud.points.size() << " data points to test_pcd.pcd." << std::endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud.points.size(); ++i) std::cerr << " " << cloud.points[i].x << " " << cloud.points[i].y << " " << cloud.points[i].z << std::endl; return (0); } -
在工作空间新建 CMakeLists.txt 配置文件
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6 FATAL_ERROR) project(MY_GRAND_PROJECT) find_package(PCL 1.3 REQUIRED COMPONENTS common io) include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS}) link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS}) add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS}) add_executable(pcd_write_test pcd_write.cpp) target_link_libraries(pcd_write_test ${PCL_LIBRARIES}) -
编译与执行
# 编译 $ mkdir build $ cd build $ cmake .. $ make # 执行 $ ./pcd_write_test// 终端输出结果 1804289383 0.394383 -0.106395 Saved 5 data points to test_pcd.pcd. -0.397406 -0.473106 0.292602 -0.731898 0.667105 0.441304 -0.734766 0.854581 -0.0361733 -0.4607 -0.277468 -0.916762 0.183749 0.968809 0.512055 -
查看生成的 test_pcd.pcd 文件
$ pcl_viewer test_pcd.pcd- 查看 pcd 内容
$ cat test_pcd.pcd# .PCD v0.7 - Point Cloud Data file format VERSION 0.7 FIELDS x y z SIZE 4 4 4 TYPE F F F COUNT 1 1 1 WIDTH 5 HEIGHT 1 VIEWPOINT 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 POINTS 5 DATA ascii -0.3974061 -0.47310591 0.29260206 -0.73189831 0.66710472 0.44130373 -0.73476553 0.85458088 -0.036173344 -0.46070004 -0.2774682 -0.91676188 0.1837492 0.96880913 0.5120554
3. 使用矩阵变换点云
-
新建项目工作空间 pcl_demo_ws02
$ mkdir pcl_demo_ws02 -
在工作空间新建 matrix_transform.cpp 文件
#include <iostream> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/io/ply_io.h> #include <pcl/point_cloud.h> #include <pcl/console/parse.h> #include <pcl/common/transforms.h> #include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> int main(int argc, char **argv) { // Load file | Works with PCD and PLY files pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr source_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>()); if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile(argv[1], *source_cloud) < 0) { std::cout << "Error loading point cloud " << argv[1] << std::endl << std::endl; return -1; } /* Reminder: how transformation matrices work : |-------> This column is the translation | 1 0 0 x | \ | 0 1 0 y | }-> The identity 3x3 matrix (no rotation) on the left | 0 0 1 z | / | 0 0 0 1 | -> We do not use this row (and it has to stay 0,0,0,1) 方法一:使用 Matrix4f 这个方法容易理解但也容易出错 */ Eigen::Matrix4f transform_1 = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity(); float theta = M_PI / 4; // 旋转角(弧度) // 旋转矩阵:沿 z 轴旋转 45° transform_1(0, 0) = cos(theta); // transform_1(row, column) transform_1(0, 1) = -sin(theta); transform_1(1, 0) = sin(theta); transform_1(1, 1) = cos(theta); // 平移矩阵:沿 x 轴平移 2.5m transform_1(0, 3) = 2.5; /* | cos(θ) -sin(θ) 0.0 | R = | sin(θ) cos(θ) 0.0 | // 旋转矩阵:沿 z 轴旋转 45°(逆时针) | 0.0 0.0 1.0 | t = < 2.5, 0.0, 0.0 > // 平移矩阵:沿 x 轴平移 2.5m */ // 打印变换结果 printf("Method #1: using a Matrix4f\n"); std::cout << transform_1 << std::endl; /* 方法二: 使用 Affine3f 这个方法更容易且较少出错 */ // 创建仿射变换对象 Eigen::Affine3f transform_2 = Eigen::Affine3f::Identity(); // 在 z 轴平移 30m transform_2.translation() << 0.0, 0.0, 30.0; // 绕 Z 旋转 45 度(逆时针) transform_2.rotate(Eigen::AngleAxisf(theta, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ())); // 打印仿射变换矩阵 printf("\nMethod #2: using an Affine3f\n"); std::cout << transform_2.matrix() << std::endl; // 创建变换后的点云 pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr transformed_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>()); // 执行变换,source_cloud 为变换前的点云 pcl::transformPointCloud(*source_cloud, *transformed_cloud, transform_2); // 可视化操作 printf("\nPoint cloud colors : white = original point cloud\n" "red = transformed point cloud\n"); pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("Matrix transformation example"); // 定义点云的 RGB 值,并将点云添加到查看器中,并通过颜色处理程序 pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> source_cloud_color_handler(source_cloud, 255, 255, 255); viewer.addPointCloud(source_cloud, source_cloud_color_handler, "original_cloud"); pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> transformed_cloud_color_handler(transformed_cloud, 230, 20, 20); // Red viewer.addPointCloud(transformed_cloud, transformed_cloud_color_handler, "transformed_cloud"); // 设置坐标系系统 viewer.addCoordinateSystem(0.5, "cloud", 0); // 设置背景色为黑灰色 viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.05, 0.05, 0.05, 0); // 设置渲染属性(点大小) viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "original_cloud"); viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "transformed_cloud"); //viewer.setPosition(800, 400); // Setting visualiser window position // 当按下 q 之前不断循环可视化操作 while (!viewer.wasStopped()) { viewer.spinOnce(); } return 0; } -
在工作空间新建 CMakeLists.txt 配置文件
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5 FATAL_ERROR) project(pcl-matrix_transform) find_package(PCL 1.7 REQUIRED) include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS}) link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS}) add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS}) add_executable (matrix_transform matrix_transform.cpp) target_link_libraries (matrix_transform ${PCL_LIBRARIES}) -
编译与执行
# 编译 $ mkdir build $ cd build $ cmake .. $ make # 执行 $ ./matrix_transform ism_test_cat.pcd # 后面跟的 .pcd 或 .ply 文件为需要进行矩阵变换的文件// 终端输出结果 Method #1: using a Matrix4f 0.707107 -0.707107 0 2.5 0.707107 0.707107 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 Method #2: using an Affine3f 0.707107 -0.707107 0 0 0.707107 0.707107 0 0 0 0 1 30 0 0 0 1 Point cloud colors : white = original point cloud red = transformed point cloud